Epilepsyaccording to TCM
Symptom family: Seizure and Epileptic Disorders
Sub-symptom(s): Infantile Epilepsy
Did you mean? Seizures
What is Epilepsy?
Epilepsy is a neurological disorder characterized by a tendency for recurrent seizures. These seizures are episodes of disturbed brain activity that can cause changes in attention or behavior.
The condition spans a spectrum, with seizures varying from brief and nearly undetectable to long periods of vigorous shaking. The specific type of seizure may depend on the part of the brain involved and the cause of epilepsy.
How Does TCM View Epilepsy?
Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) perceives epilepsy as a manifestation of internal disharmony, often relating to a disturbance in the body's energetic system. It identifies a 'pattern' — a complex framework of signs and symptoms that indicate an imbalance.
Recognizing these patterns is essential because TCM treatments, including acupuncture and herbal medicine, are tailored to correct the specific imbalances, rather than just treating the symptoms.
Causes of Epilepsy According to TCM
TCM attributes epilepsy to multiple internal disharmonies, predominantly disturbances in the liver. A common cause is seen as Liver Wind, which arises from extreme Heat or Yin Deficiency, leading to internal movement akin to Wind.
Another cause might be Phlegm misting the mind, where metabolic byproducts obstruct the flow of Qi, or vital energy. Understanding these causes (patterns) helps TCM practitioners choose the most effective treatments to harmonize the body's Qi and Blood, calm the Liver, or clear Phlegm or Heat.
TCM Herbal Formulas for Epilepsy
For epilepsy characterized by Liver Wind or Yin Deficiency, formulas like Tian Ma Gou Teng Yin, with gastrodia as a key herb, are recommended to subdue the Wind and nourish the Liver.
When Phlegm Heat is implicated, Zhi Bao Dan with buffalo horn might be used to clear Heat and dissolve Phlegm. The choice of formula is crucial as each person's pattern of disharmony can differ, necessitating a personalized treatment approach.
Explore below some TCM herbal formulas used to address epilepsy, organized by formula type.
- By Formula Type
- Formulas that sedate and calm the mind
- Formulas that clear heat and open sensory orifices
- Formulas that harmonize lesser yang-warp disorders
- Formulas that invigorate blood and dispel blood stagnation
- Formulas that pacify and extinguish internal wind
- Formulas that regulate blood
- Formulas that clear heat from the organs
- Formulas that dredge and disperse external wind
- Formulas that nourish the heart and calm the mind
- Formulas that clear heat and transform phlegm
- Formulas that clear heat and resolve toxicity
- Formulas that warm and open sensory orifices
- Formulas that purge heat accumulation
- Formulas that clear wind-Cold
- Formulas that promote qi movement
- Formulas that dispel phlegm
Formulas that sedate and calm the Mind
Epilepsy can be treated by these formulas when it stems from an agitated or disturbed mental state, requiring calming and mind-stabilizing actions.
One such formula is Ci Zhu Wan, with magnetite as a key herb.
Other formulas of this category are listed in the table below.
All "formulas that sedate and calm the mind" recommended for epilepsy
| Formula | Key herbs |
|---|---|
| Ci Zhu Wan | Magnetite (Ci Shi) |
| Sheng Tie Luo Yin | Oxidized Iron Filings (Sheng Tie Luo), Cinnabar (Zhu Sha) |
| Zhen Zhu Mu Wan | Mother Of Pearl (Zhen Zhu Mu), Dragon Bones (Long Gu) |
Formulas that clear Heat and open sensory orifices
Epilepsy can be treated by formulas that clear Heat and open sensory orifices if it is due to heat causing disturbances in sensory functions.
One such formula is Zi Xue Dan, with water buffalo horn as a key herb.
Other formulas of this category are listed in the table below.
All "formulas that clear heat and open sensory orifices" recommended for epilepsy
Formulas that harmonize lesser Yang-warp disorders
Epilepsy can be treated by these formulas in cases of imbalances in the lesser Yang (Shao Yang) phase, which often involve alternating hot and cold sensations.
One such formula is Chai Hu Jia Long Gu Mu Li Tang, with bupleurum root as a key herb.
Other formulas of this category are listed in the table below.
All "formulas that harmonize lesser yang-warp disorders" recommended for epilepsy
| Formula | Key herbs |
|---|---|
| Chai Hu Jia Long Gu Mu Li Tang | Bupleurum Roots (Chai Hu), Baikal Skullcap Roots (Huang Qin), Cinnamon Twigs (Gui Zhi), Rhubarb (Da Huang) |
| Xiao Chai Hu Tang | Bupleurum Roots (Chai Hu) |
Formulas that invigorate Blood and dispel Blood Stagnation
Epilepsy can be treated by these formulas if it arises from poor blood circulation or stagnation of blood, which often manifests in pain or swelling.
One such formula is Di Dang Tang, with leech as a key herb.
Other formulas of this category are listed in the table below.
All "formulas that invigorate blood and dispel blood stagnation" recommended for epilepsy
| Formula | Key herbs |
|---|---|
| Di Dang Tang | Leeches (Shui Zhi), Tabanus Horseflies (Meng Chong) |
| Tao He Cheng Qi Tang | Peach Kernels (Tao Ren), Rhubarb (Da Huang) |
Formulas that pacify and extinguish Internal Wind
Epilepsy can be treated by these formulas when it is due to internal wind, which is often associated with spasms, tremors, or dizziness.
One such formula is Tian Ma Gou Teng Yin, with gastrodia rhizome as a key herb.
Other formulas of this category are listed in the table below.
All "formulas that pacify and extinguish internal wind" recommended for epilepsy
| Formula | Key herbs |
|---|---|
| Tian Ma Gou Teng Yin | Gastrodia Rhizomes (Tian Ma), Gambir Stems And Thorns (Gou Teng) |
| Zhen Gan Xi Feng Tang | Achyranthes Roots (Niu Xi) |
Formulas that regulate Blood
Epilepsy can be treated by these formulas when it stems from irregularities or imbalances in the blood, which may affect circulation or cause other blood-related issues.
One such formula is Bu Yang Huang Wu Tang, with milkvetch root as a key herb.
Formulas that clear Heat from the Organs
Epilepsy can be treated by these formulas if it stems from an excess heat condition in specific organs, leading to internal disharmony.
One such formula is Dang Gui Long Hui Wan, with dong quai as a key herb.
Formulas that dredge and disperse External Wind
Epilepsy can be treated by these formulas when it results from external wind invasion disrupting the body's surface and normal function, requiring wind-dispersing actions.
One such formula is Feng Yin Tang, with dragon bones as a key herb.
Formulas that nourish the Heart and calm the Mind
Epilepsy can be treated by these formulas when it stems from a disharmony between the heart and the mind, often manifesting as emotional disturbances or sleep issues.
One such formula is Gan Mai Da Zao Tang, with light wheat as a key herb.
Formulas that clear Heat and transform Phlegm
Epilepsy can be treated by formulas that clear Heat and transform Phlegm if it is linked to heat leading to phlegm accumulation.
One such formula is Gun Tan Wan, with chlorite schist as a key herb.
Formulas that clear Heat and resolve toxicity
Epilepsy can be treated by formulas that clear Heat and resolve toxicity if it arises from heat toxins affecting the body.
One such formula is Liang Ge San, with forsythia fruit as a key herb.
Formulas that warm and open sensory orifices
Epilepsy can be treated by these formulas when it is due to cold affecting the sensory orifices, requiring warming and opening actions.
One such formula is Su He Xiang Wan, with styrax resin as a key herb.
Formulas that purge Heat accumulation
Epilepsy can be treated by these formulas if it arises from an excess of internal heat, needing actions that clear heat and reduce its intensity.
One such formula is Xiao Cheng Qi Tang
Formulas that clear Wind-Cold
Epilepsy can be treated by these formulas when it stems from external pathogenic influences characterized by cold and wind symptoms.
One such formula is Xiao Qing Long Tang, with ephedra as a key herb.
Formulas that promote Qi movement
Epilepsy can be treated by these formulas if it stems from stagnation or imbalance in the flow of Qi, the vital life energy, within the body.
One such formula is Yue Ju Wan, with atractylodes rhizome as a key herb.
Formulas that dispel Phlegm
Epilepsy can be treated by these formulas when it is linked to phlegm accumulation, affecting respiratory and other body functions.
One such formula is Di Tan Tang, with arisaema as a key herb.
Acupoints for Epilepsy
In managing epilepsy, TCM also employs acupuncture, targeting points that harmonize the Liver, extinguish Wind, and clear Phlegm. Points such as Baihui (DU-20) on the top of the head are used for their powerful effect on calming the Liver and subduing Wind, which are critical in the treatment of seizures.
Other points like Fengchi (GB-20) at the base of the skull, Taichong (LIV-3) on the foot, and Yintang (EX-HN-3) between the eyebrows are chosen for their reputed ability to clear internal Heat, settle the Liver, and restore a sense of balance.
Explore below some acupoints used to address epilepsy, organized by meridian.
- By Meridian
- Governing Vessel
- Bladder Channel
- Gall Bladder Channel
- Extra Points: Head and Neck (EX-HN)
- Liver Channel
- Kidney Channel
- Triple Burner Channel
- Directing Vessel
- Small Intestine Channel
- Pericardium Channel
- Extra Points: Upper Extremities (EX-UE)
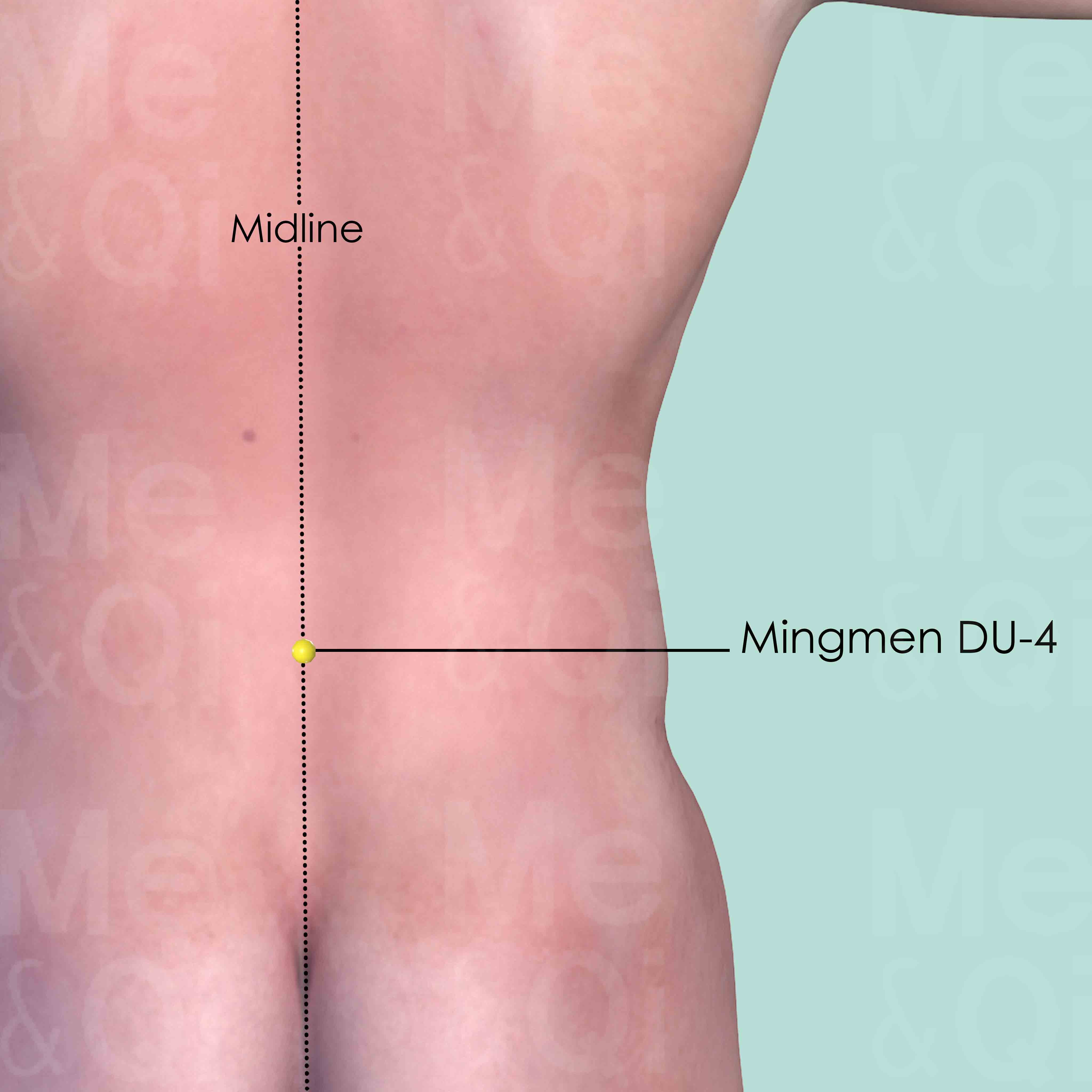
Mingmen DU-4
On the lower back midline, in the depression below the spinous process of the 2nd lumber vertebra (L2).
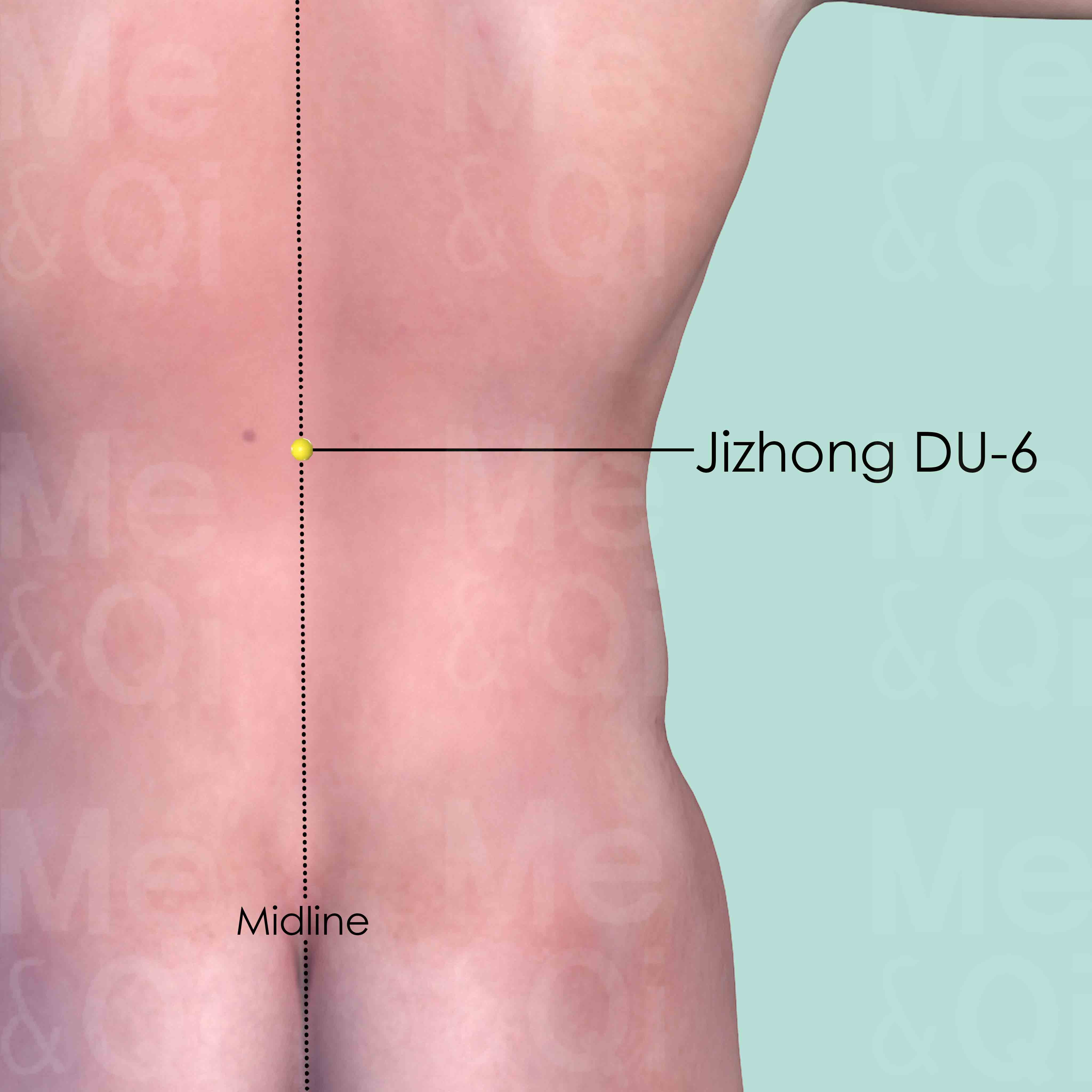
Jizhong DU-6
On the back midline, in the depression below the spinous process of the 11th thoracic vertebra (T11).
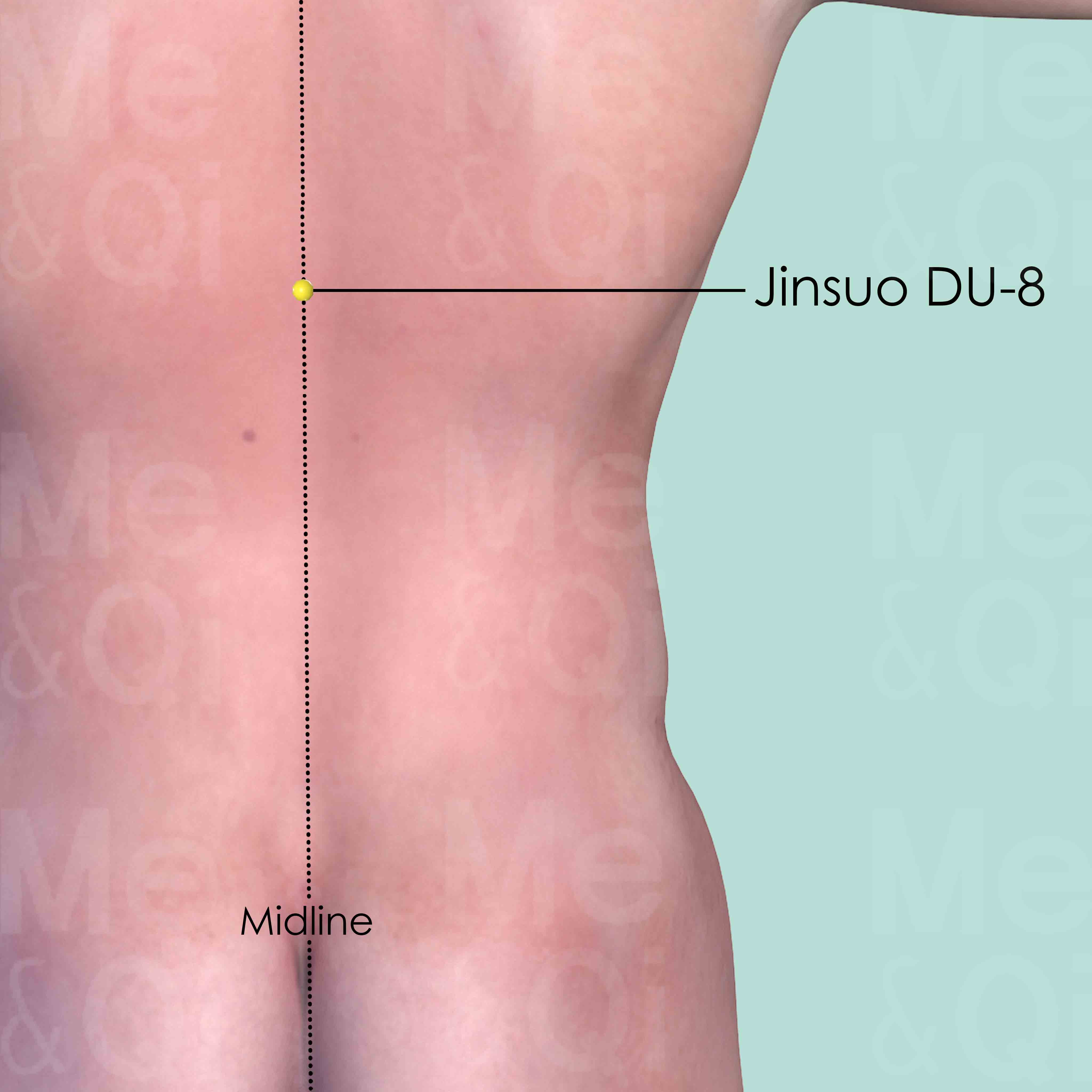
Jinsuo DU-8
On the back midline, in the depression below the spinous process of the 9th thoracic vertebra (T9).
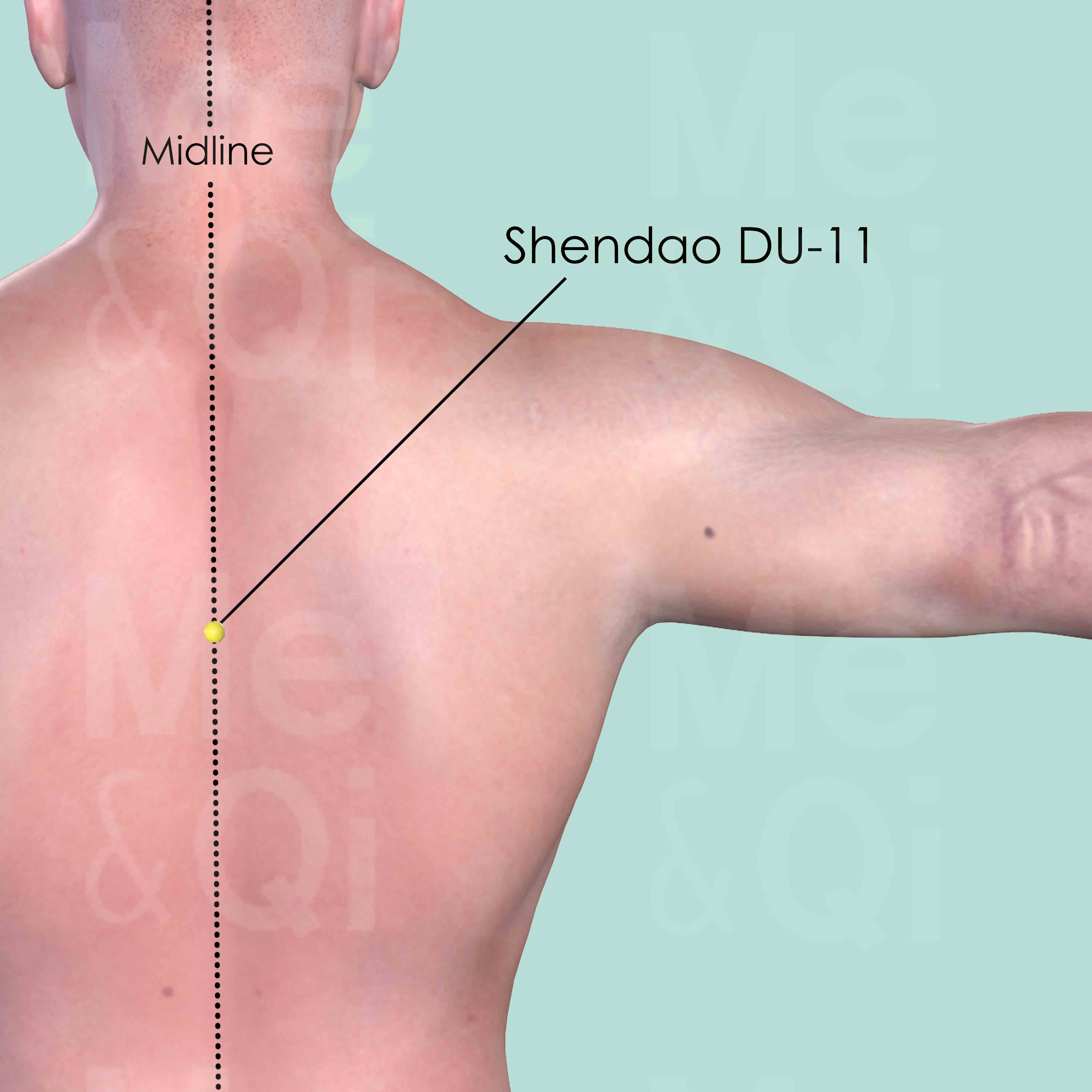
Shendao DU-11
On the back midline, in the depression below the spinous process of the 5th thoracic vertebra (T5).
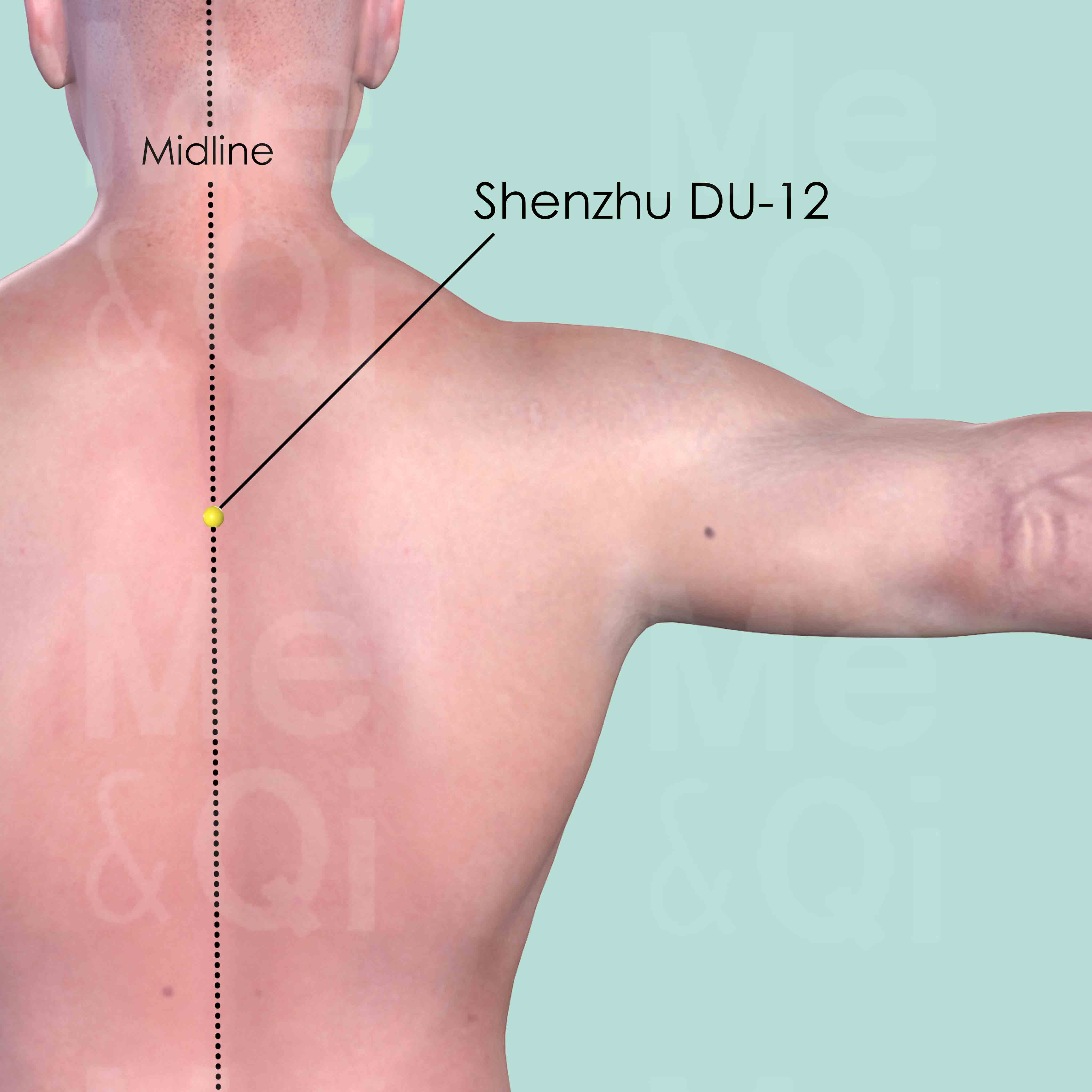
Shenzhu DU-12
On the back midline, in the depression below the spinous process of the 3th thoracic vertebra (T3).
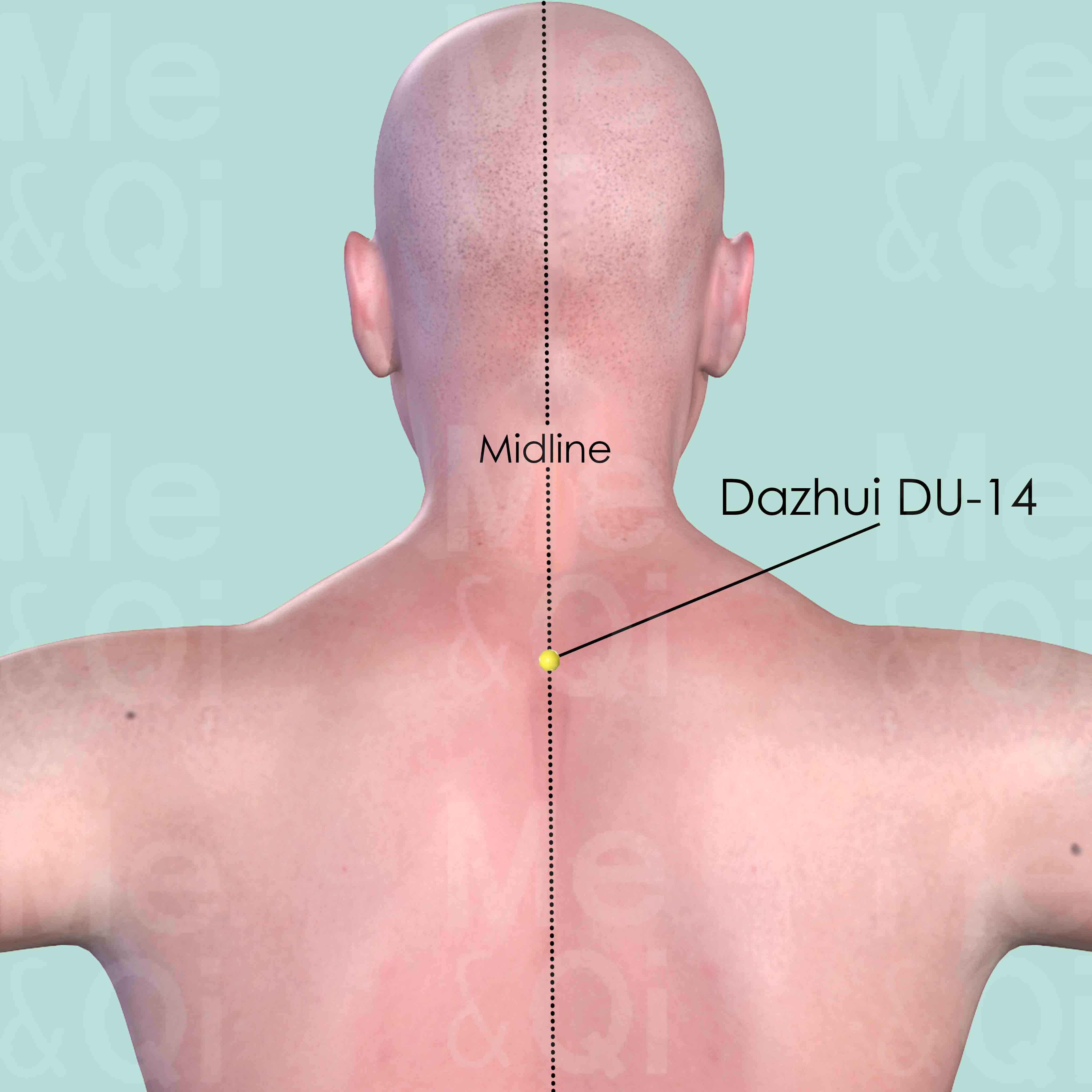
Dazhui DU-14
On the midline at the base of the neck, in the depression below the spinous process of the seventh cervical vertebra (C7).
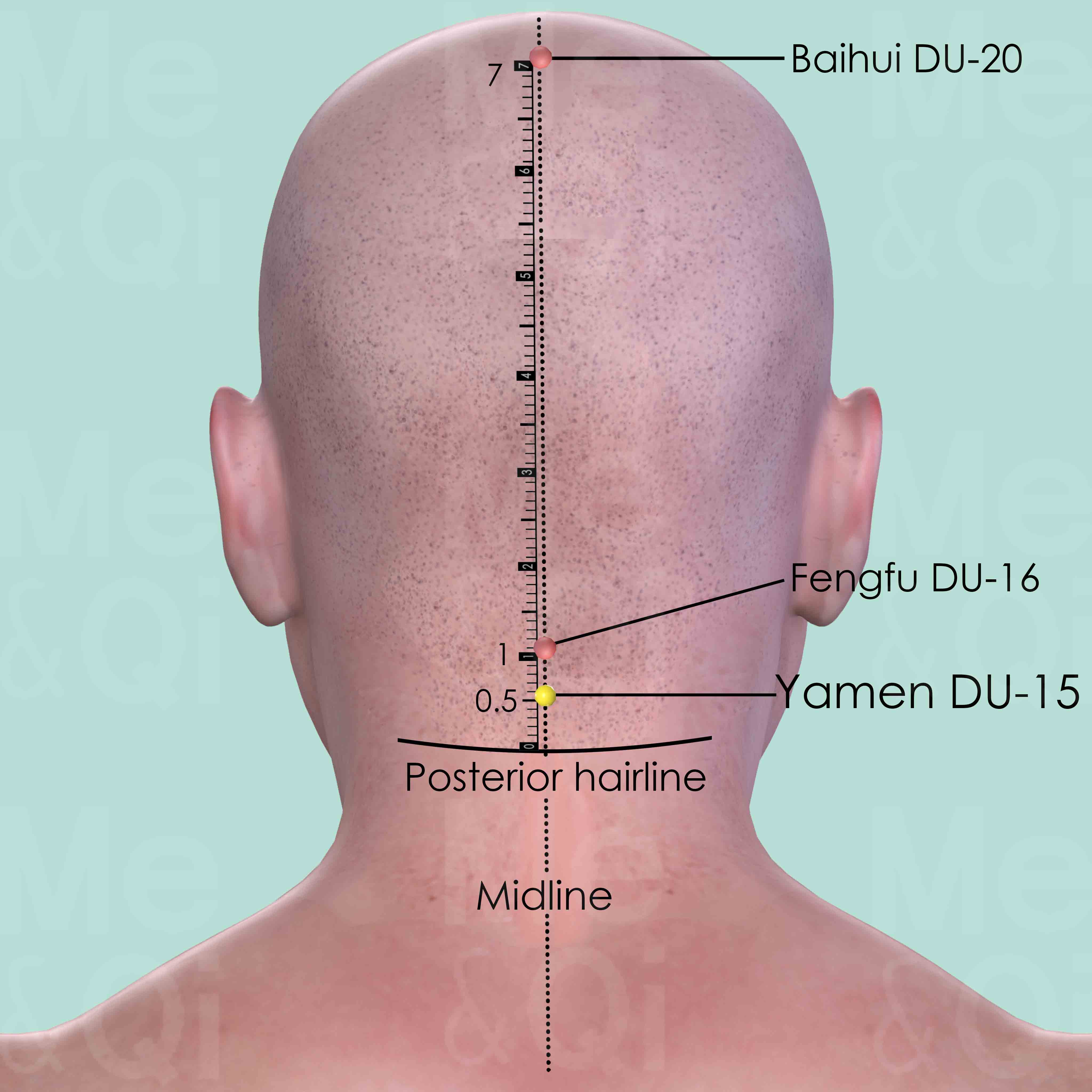
Yamen DU-15
On the back of the neck, 0.5 cun directly above the midpoint of the posterior hairline, below the spinous process of 1st cervical vertebra (C1).
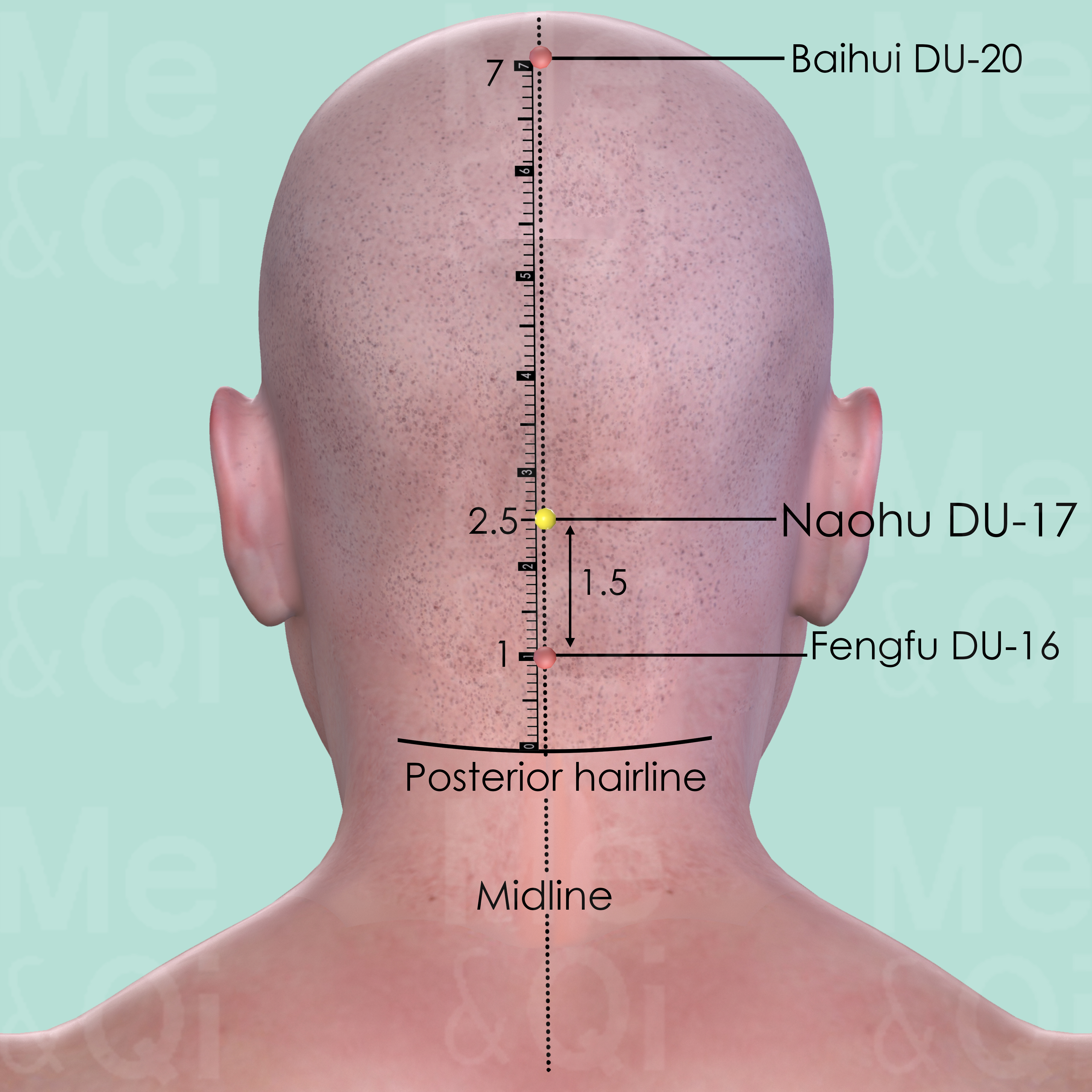
Naohu DU-17
1.5 cun above Fengfu DU-16 or 2.5 cun above the posterior hairline, in a depression superior to the external occipital protuberance.
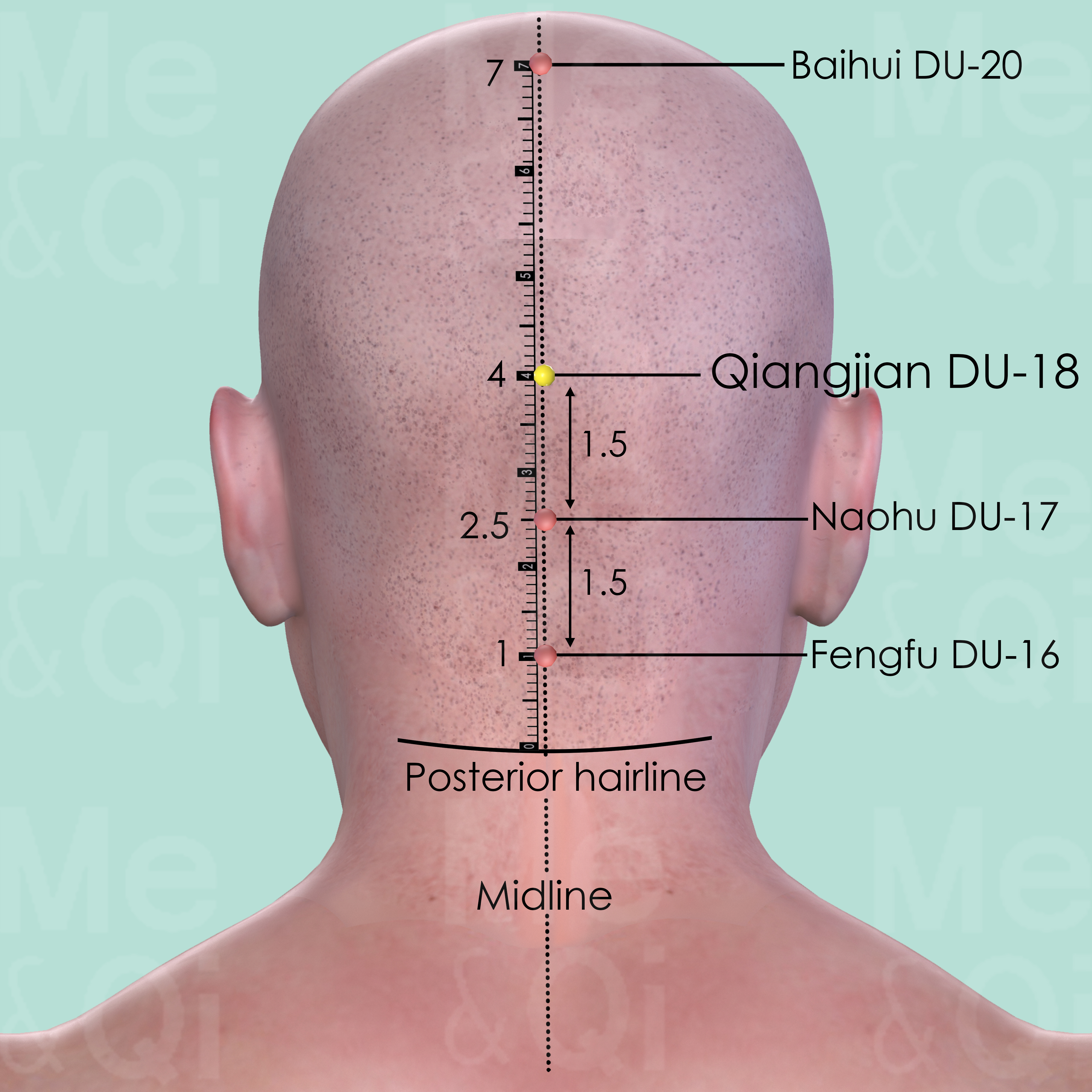
Qiangjian DU-18
On the posterior midline, 1.5 cun above Naohu DU-17, midway between Fengfu DU-16 and Baihui DU-20.
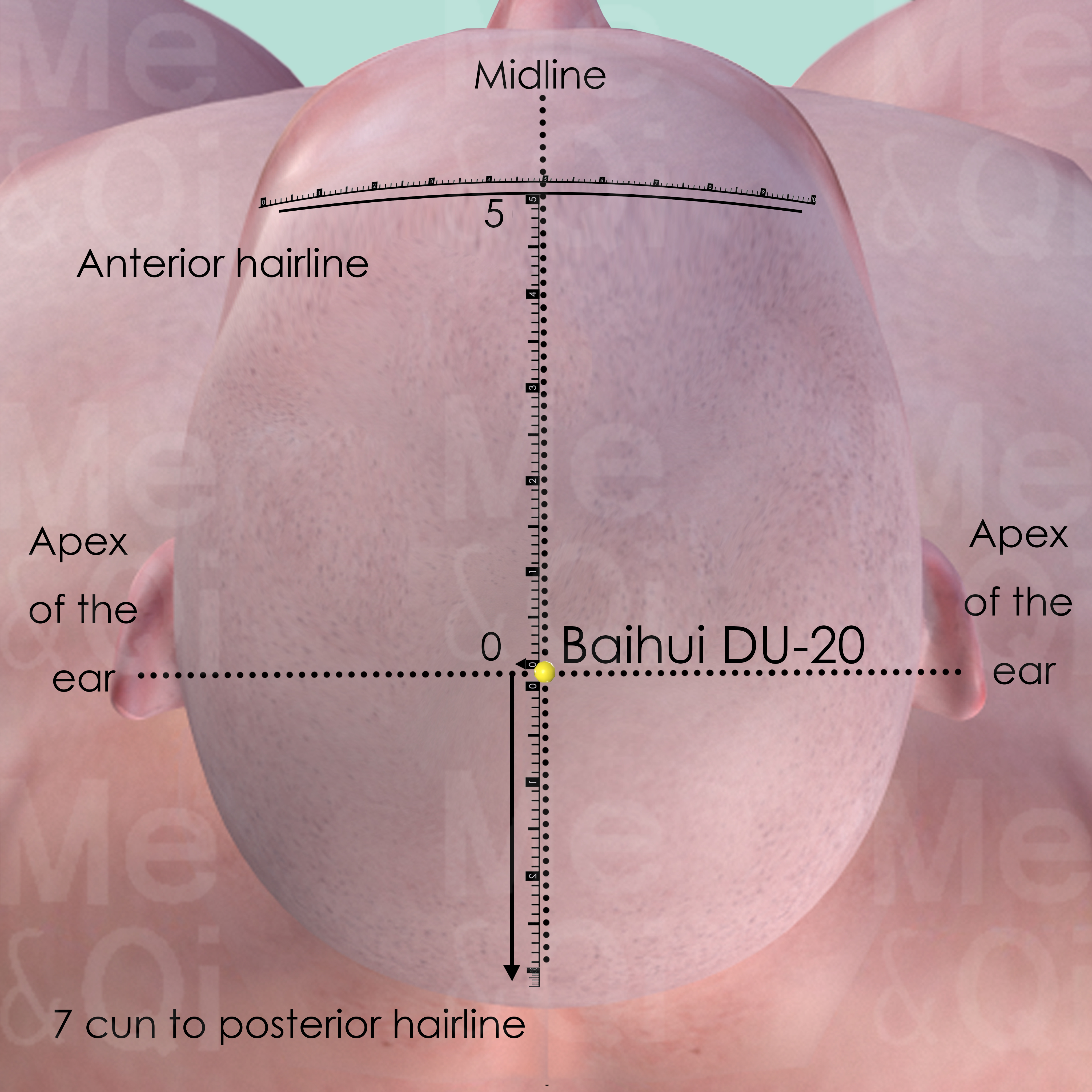
Baihui DU-20
At the vertex, at the junction of a line connecting the apex of the ears and the midline, in the depression 7 cun above the posterior hairline and 5 cun behind the anterior hairline.
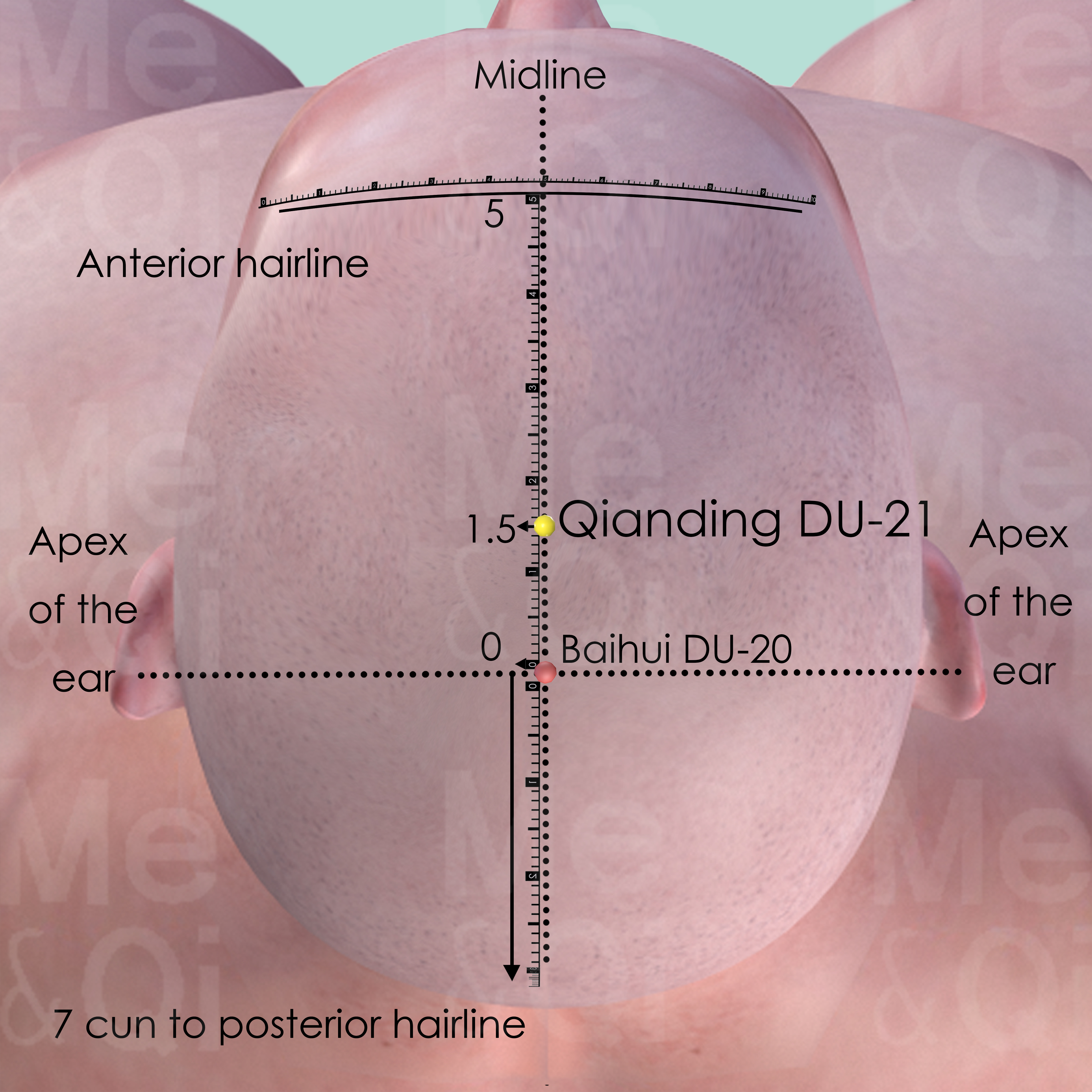
Qianding DU-21
On the midline, 1.5 cun anterior to Baihui DU-20 or 3.5 cun posterior to the anterior hairline.
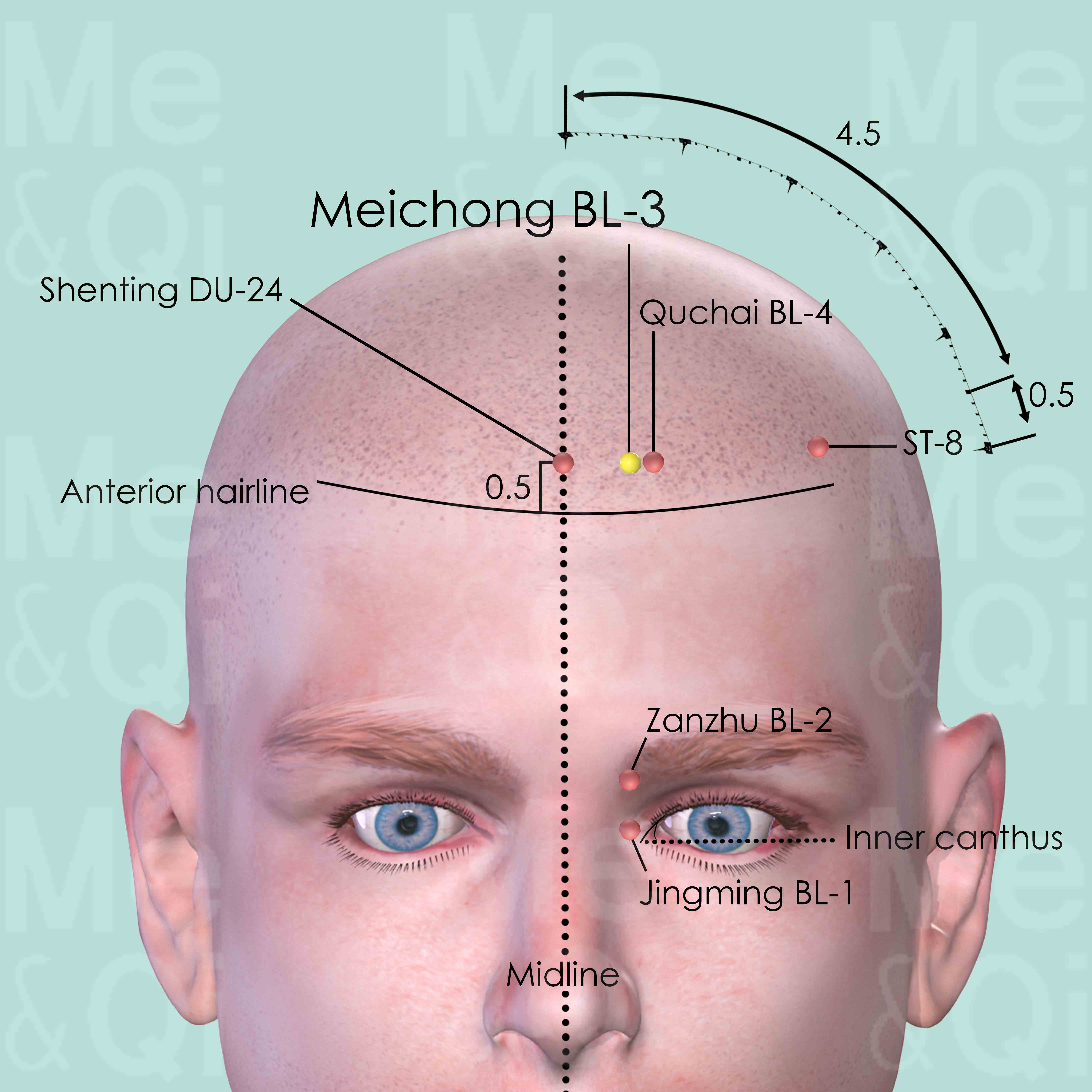
Meichong BL-3
Vertically above the medial extremity of the eyebrow and medial canthus of the eye, 0.5 cun within the anterior hairline, between Shenting DU-24 and Quchai BL-4.
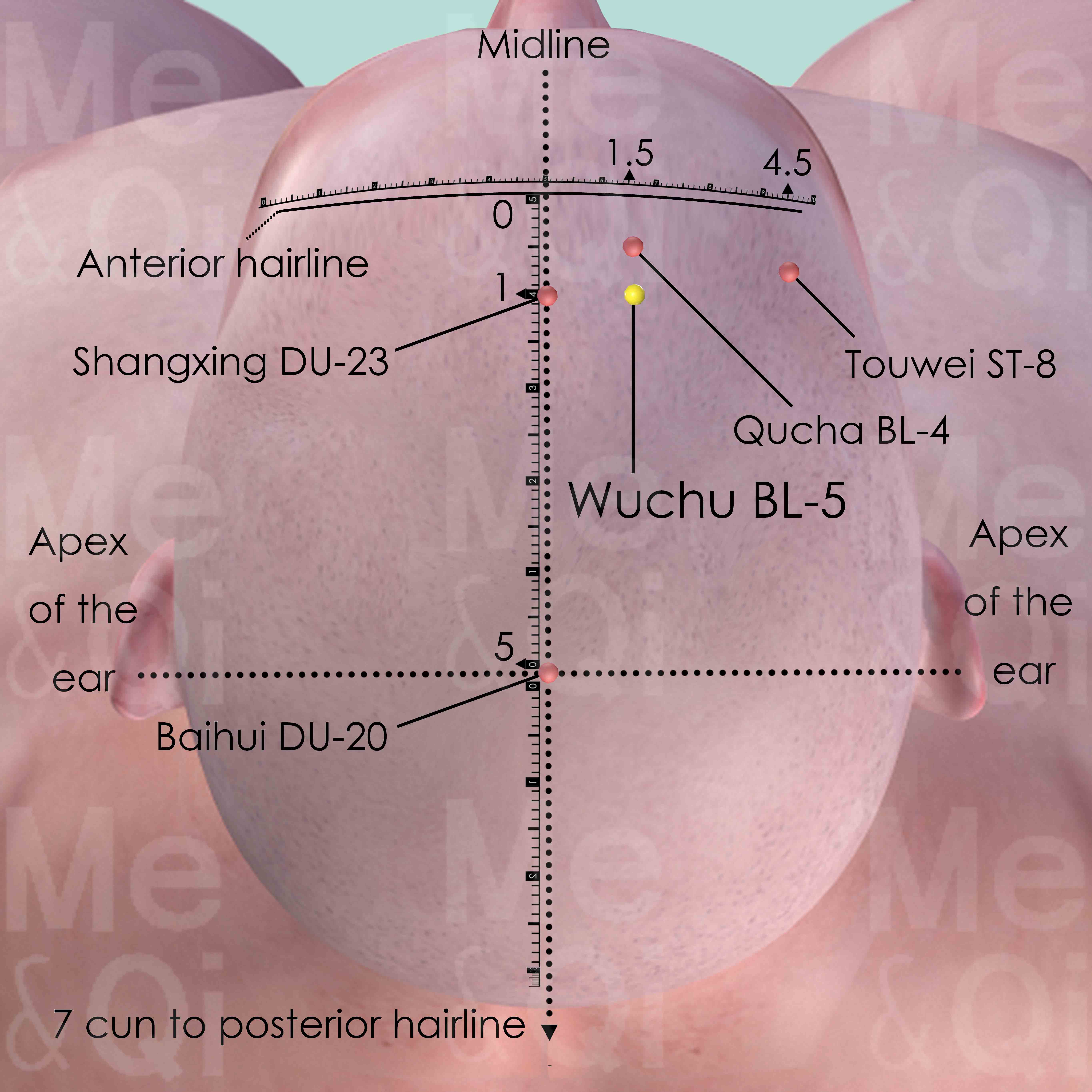
Wuchu BL-5
1 cun within the anterior hairline and 1.5 cun lateral to the anterior midline. It is also 0.5 cun posterior to Quchai BL-4.
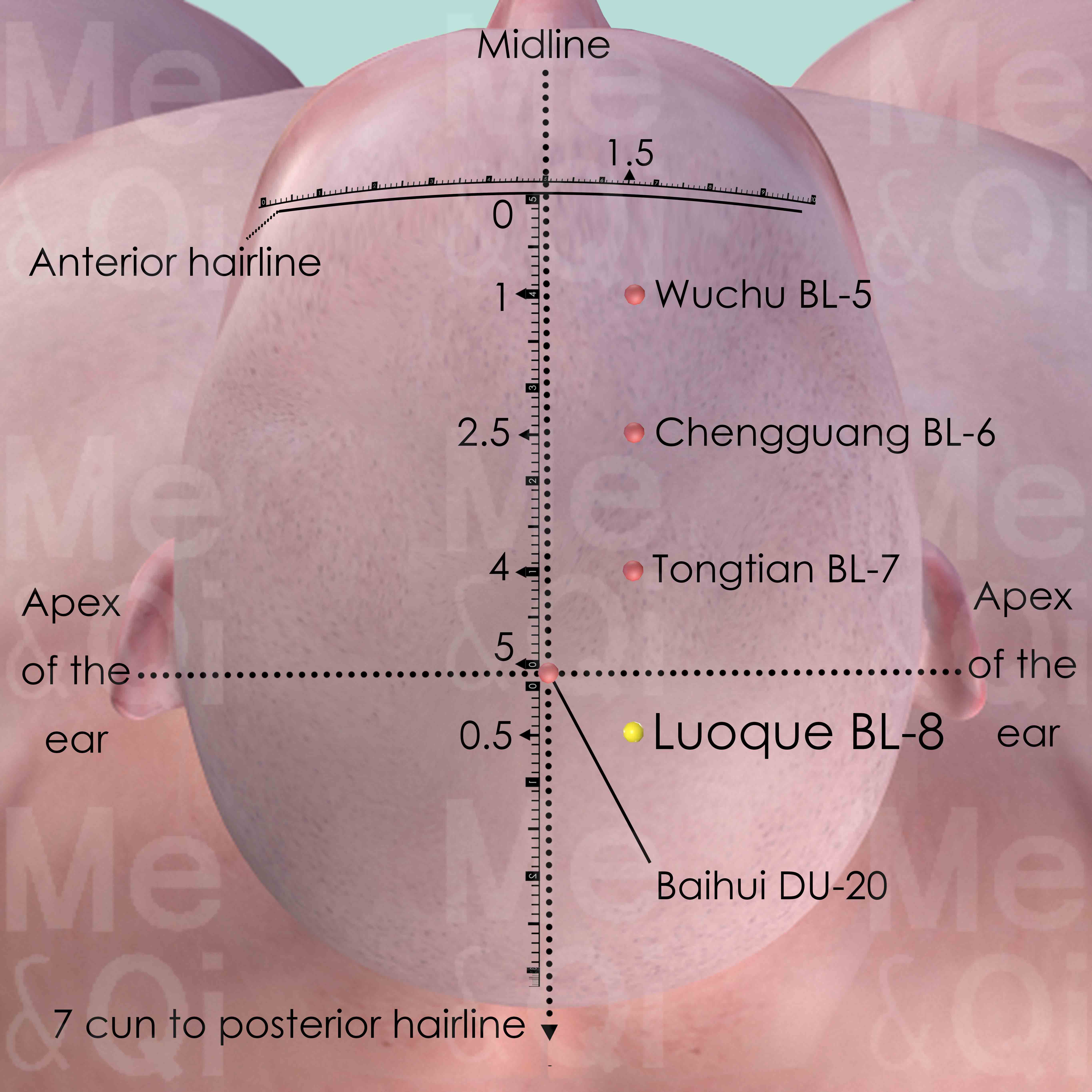
Luoque BL-8
1.5 cun lateral to the anterior midline and 5.5 cun superior to the anterior hairline. Or 0.5 cun posterior to Baihui Du-20 at the vertex.
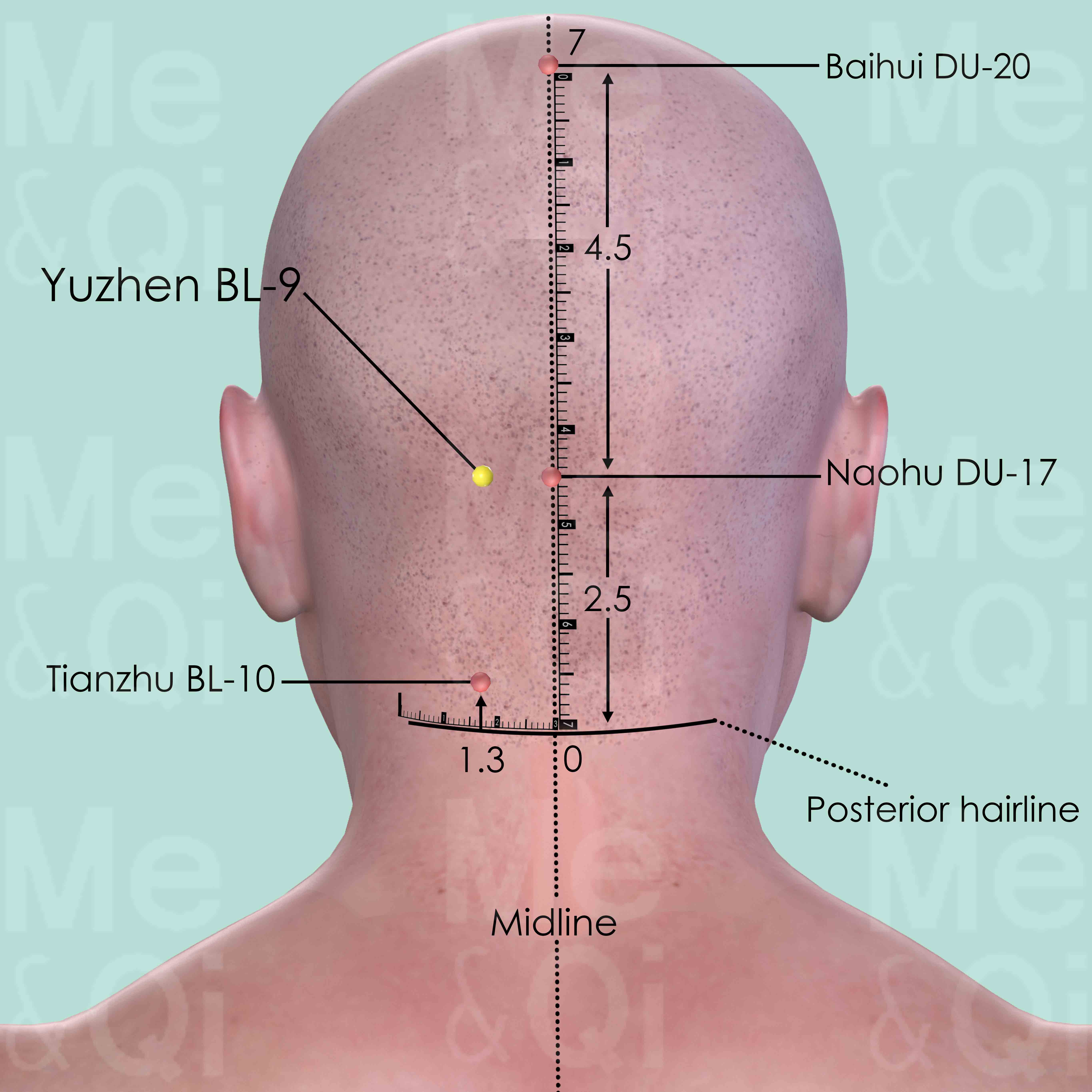
Yuzhen BL-9
First identify Naohu DU-17 which is on the superior border of the external occipital protuberance. Yuzhen BL-9 is 1.3 cun lateral to Naohu DU-17.
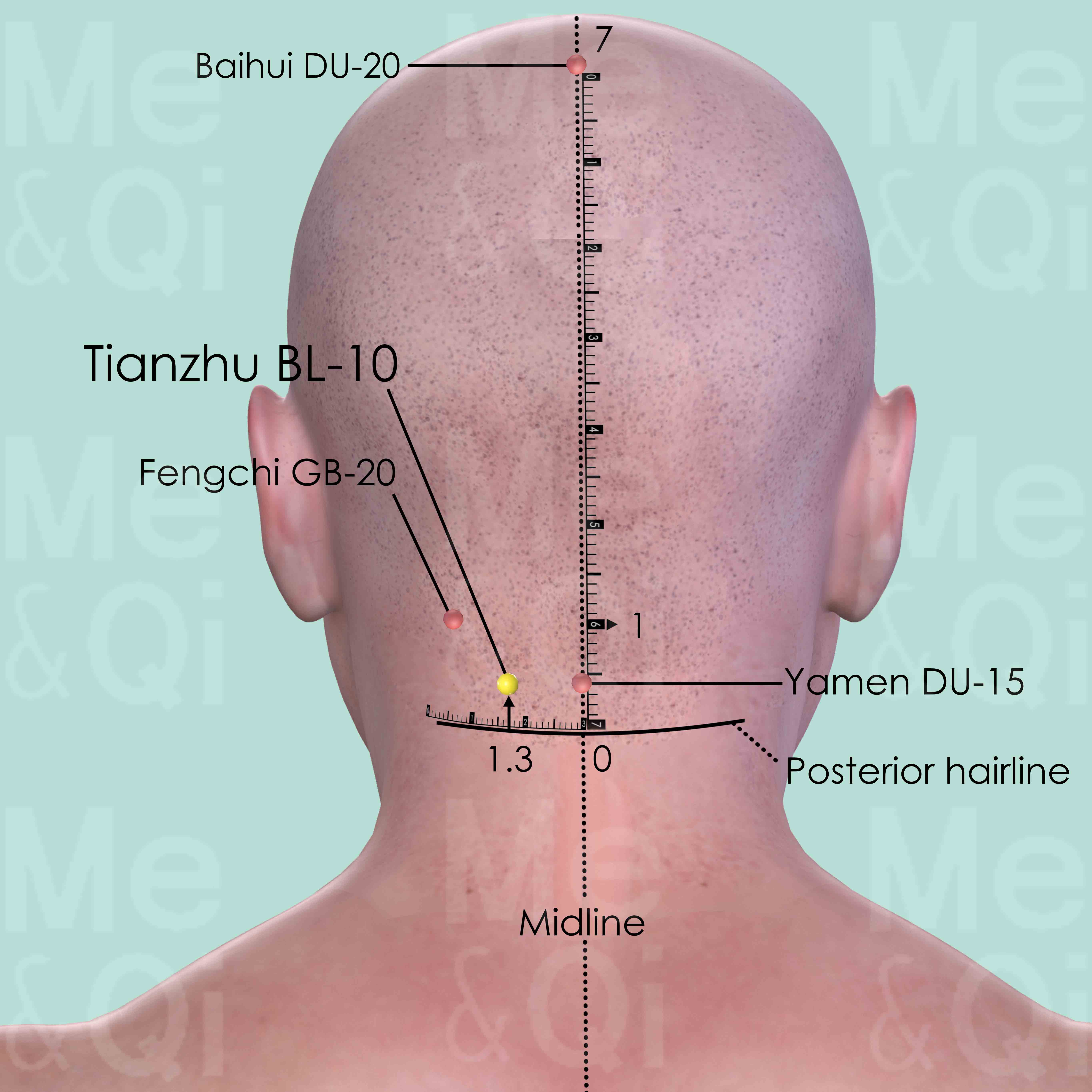
Tianzhu BL-10
1.3 cun lateral to Yamen DU-15 on the posterior midline, 0.5 cun above the posterior hairline, on the lateral side of trapezius muscle.
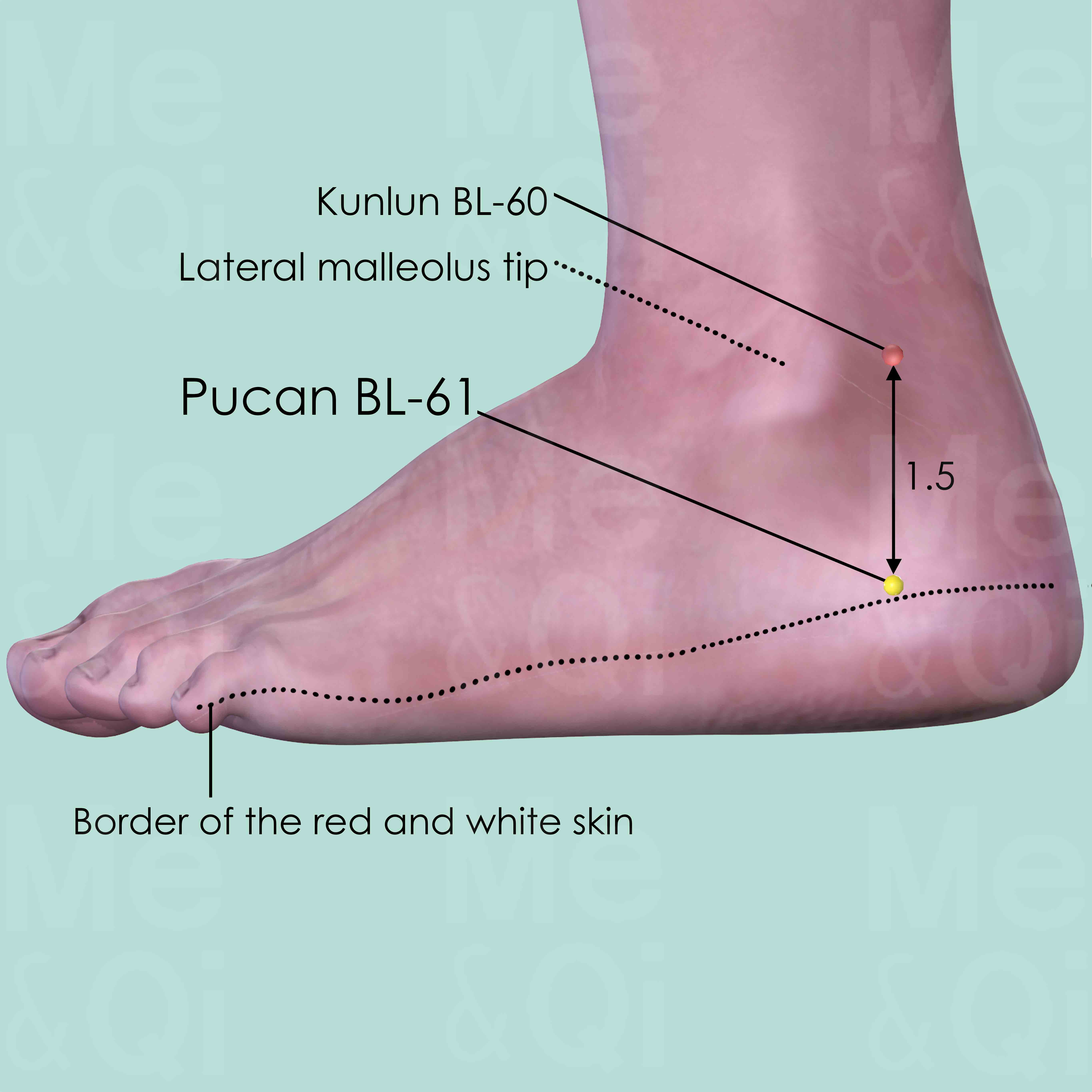
Pucan BL-61
Posterior and inferior to the external malleolus, directly below Kunlun BL-60, in the depression of the calcaneum at the junction of the red and white skin.
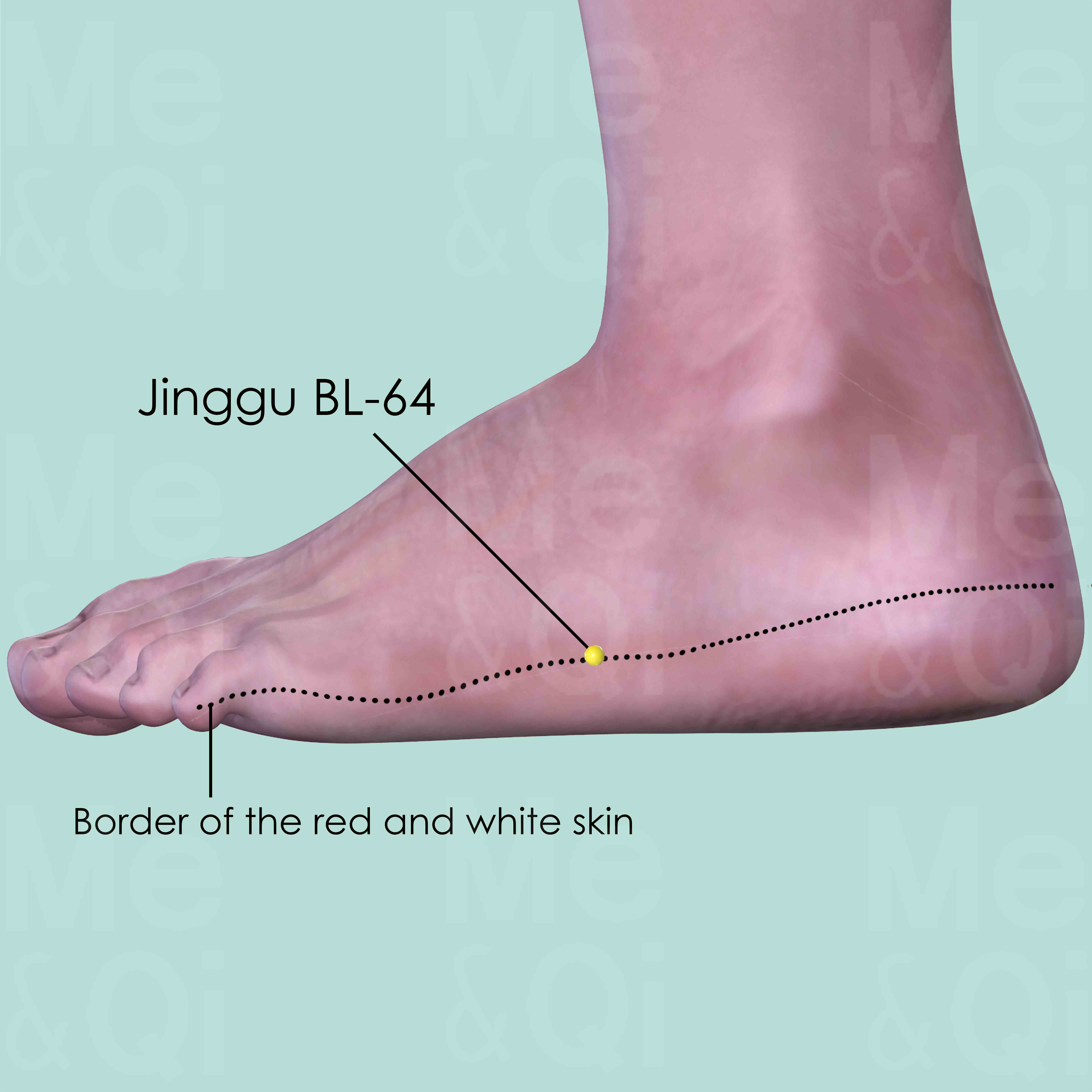
Jinggu BL-64
On the lateral side of the foot dorsum, below the tuberosity of the 5th metatarsal bone, at the border of the red and white skin.
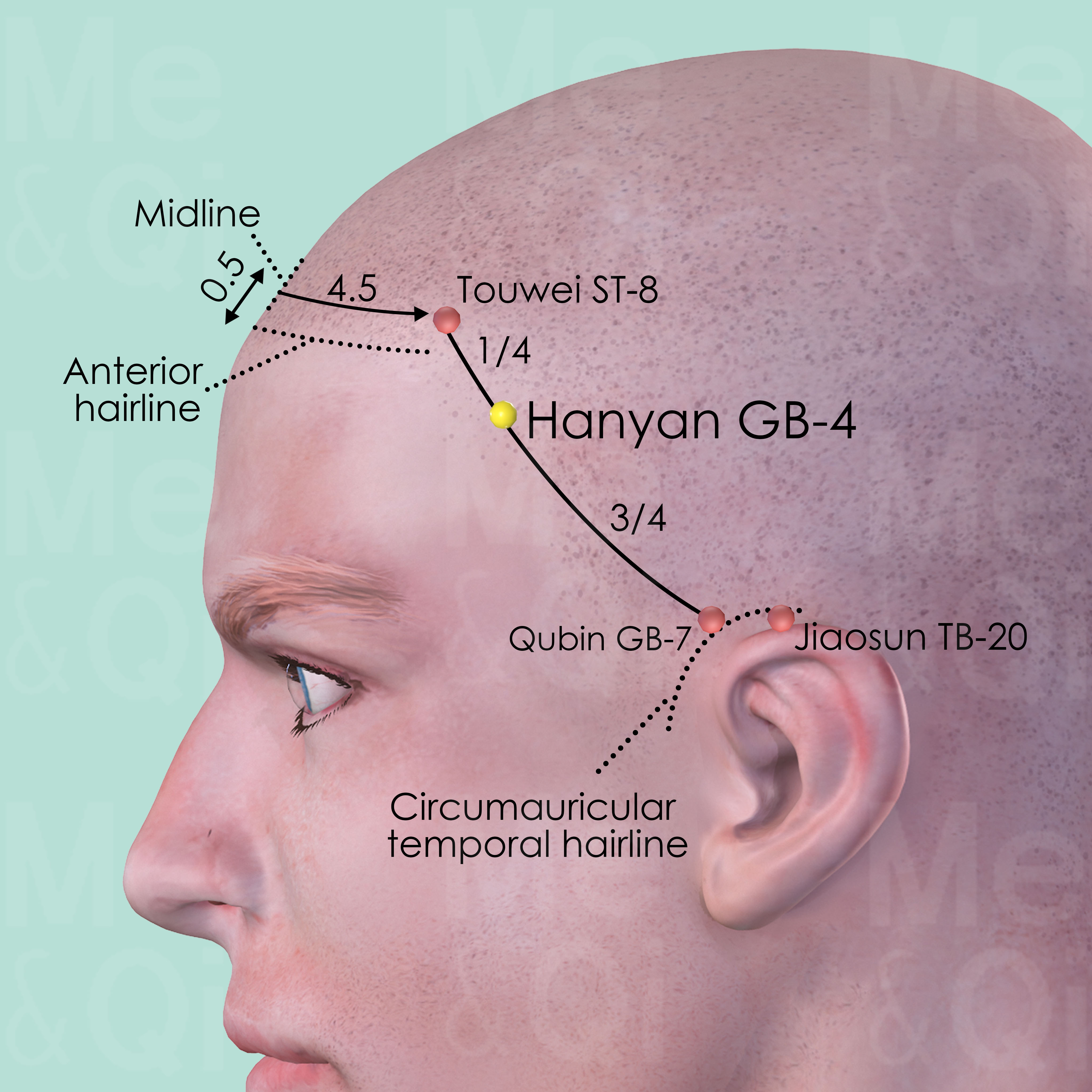
Hanyan GB-4
Within the hairline of the temporal region, midway of the upper half of the distance between Touwei ST-8 and Qubin GB-7.
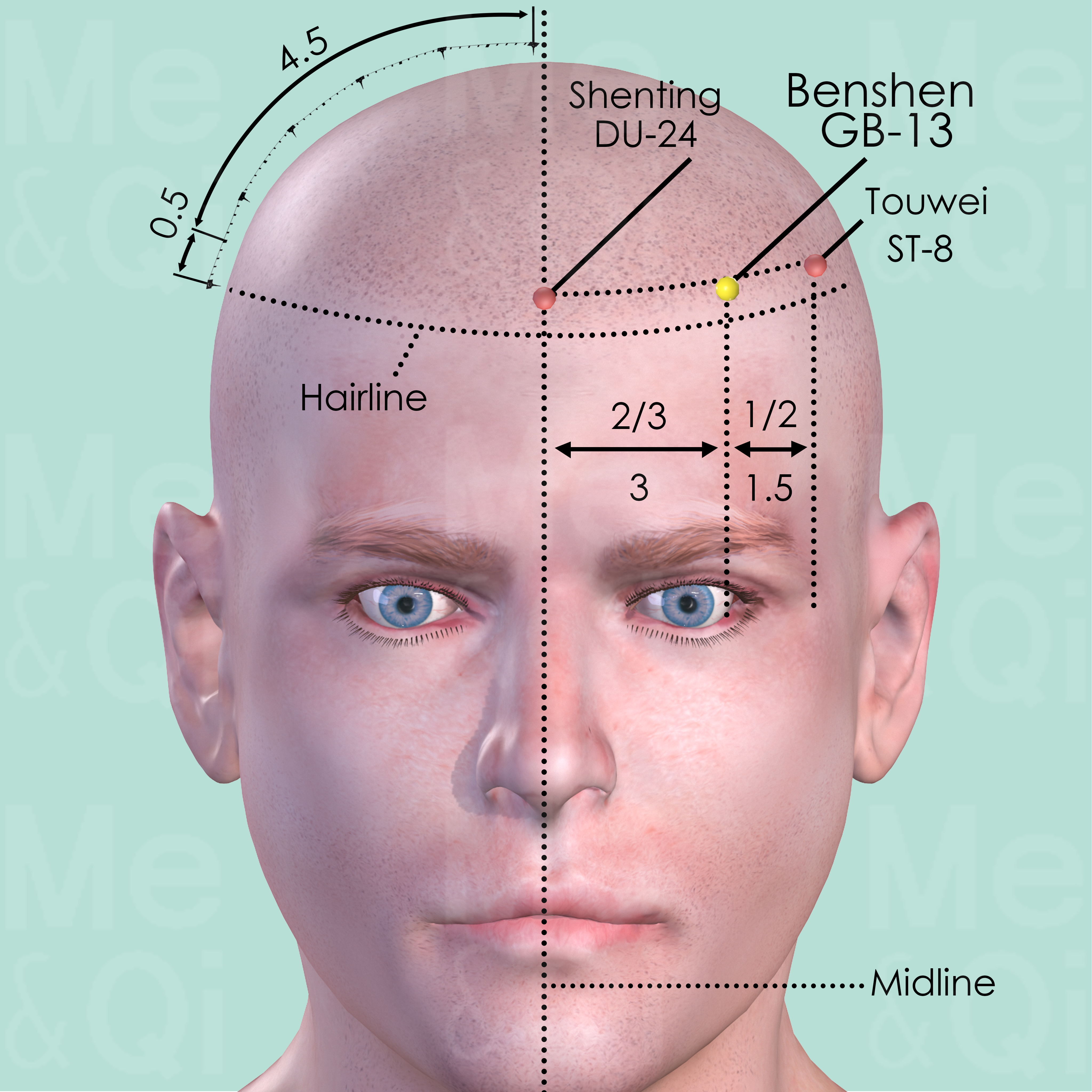
Benshen GB-13
0.5 cun within the hairline of the forehead, at the junction of the medial two-third and lateral third of the distance from Shenting DU-24 to Touwei ST-8.
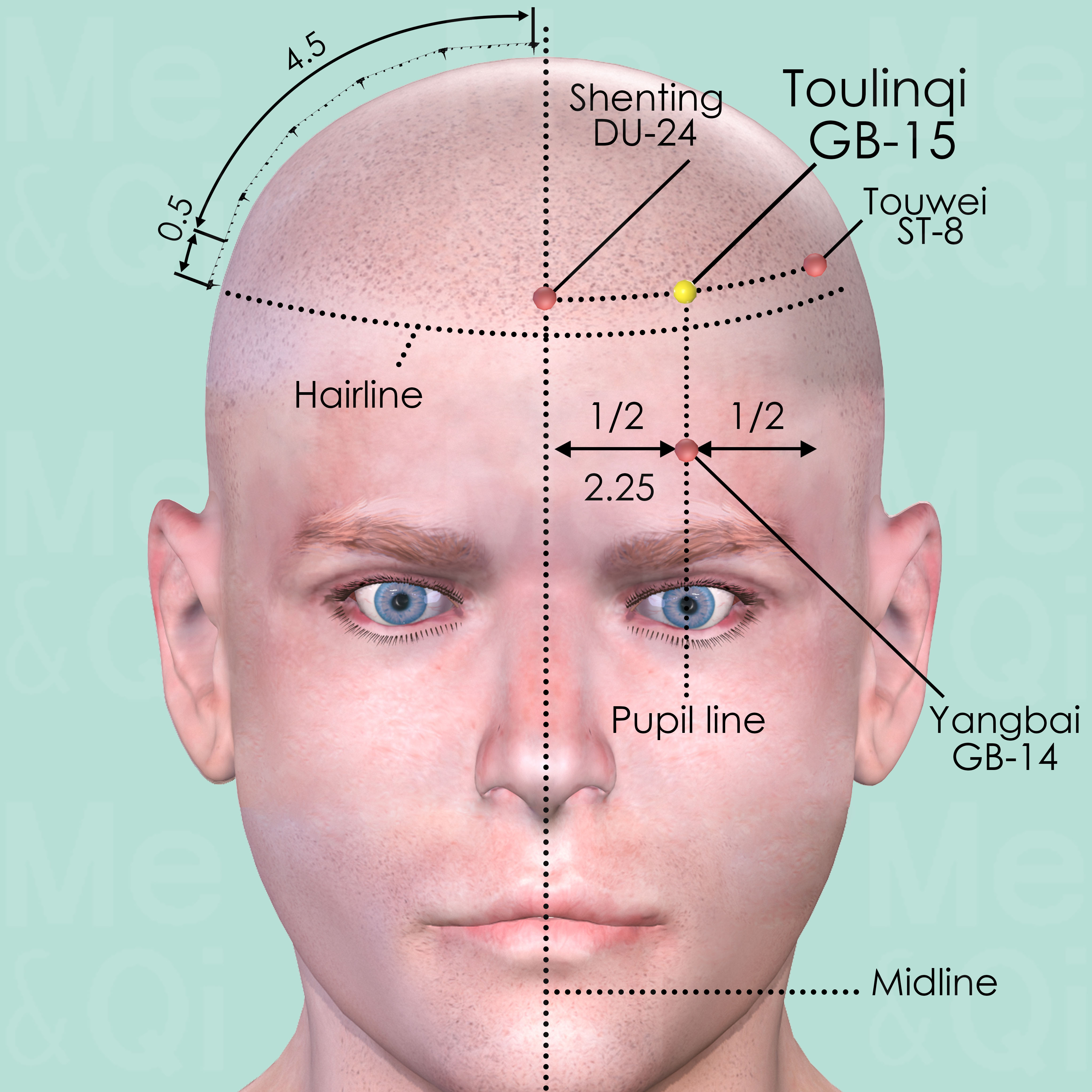
Toulinqi GB-15
Directly above Yangbai GB-14, on the pupil line, 0.5 cun within the hairline, midway between Shenting DU-24 and Touwei ST-8.
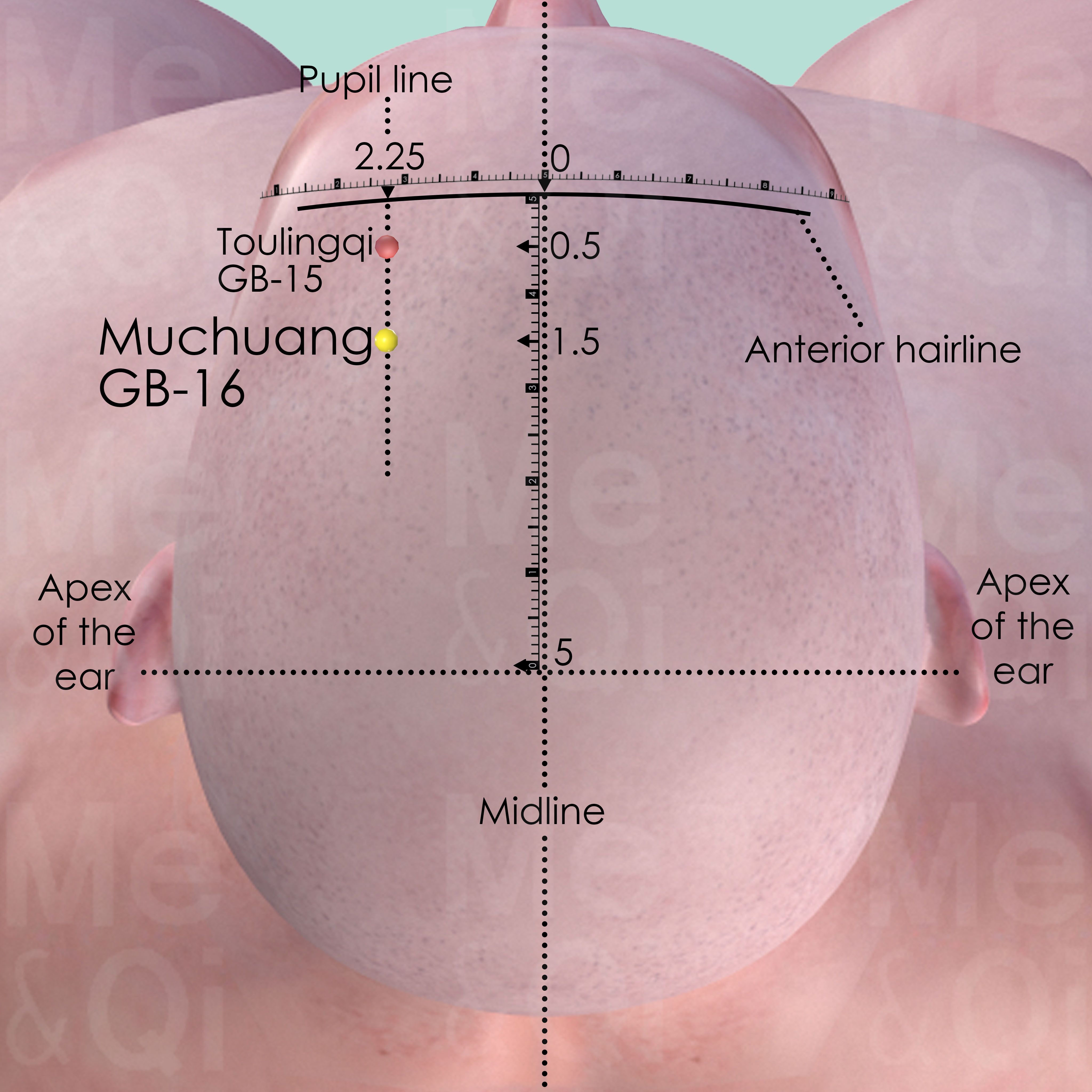
Muchuang GB-16
1 cun posterior to the Toulingqi GB-15 or 1.5 cun posterior to the anterior hairline, on the pupil line which is 2.25 cun lateral to the midline.
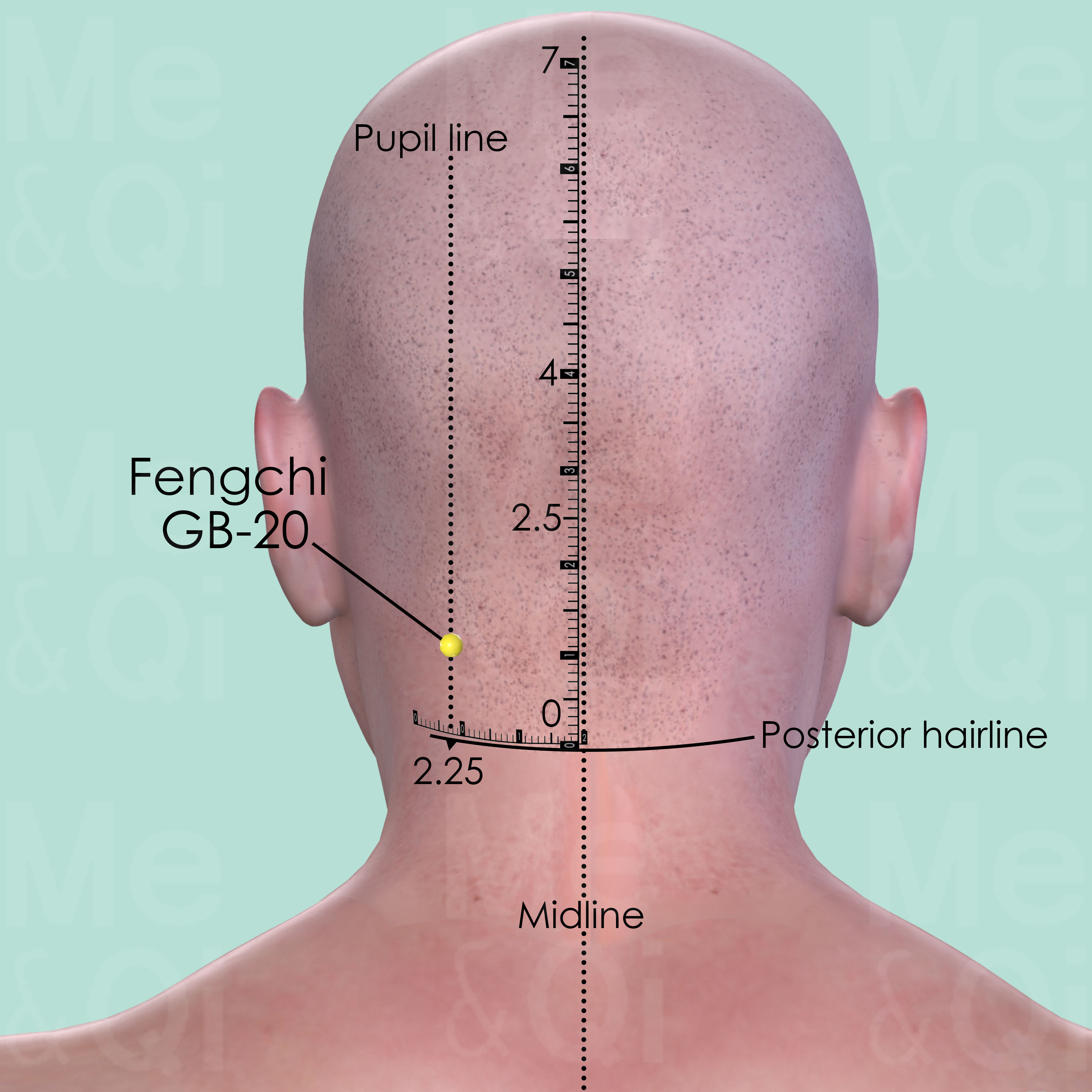
Fengchi GB-20
In the posterior aspect of the neck, below the occipital bone, in the depression between the upper portion of sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscle.
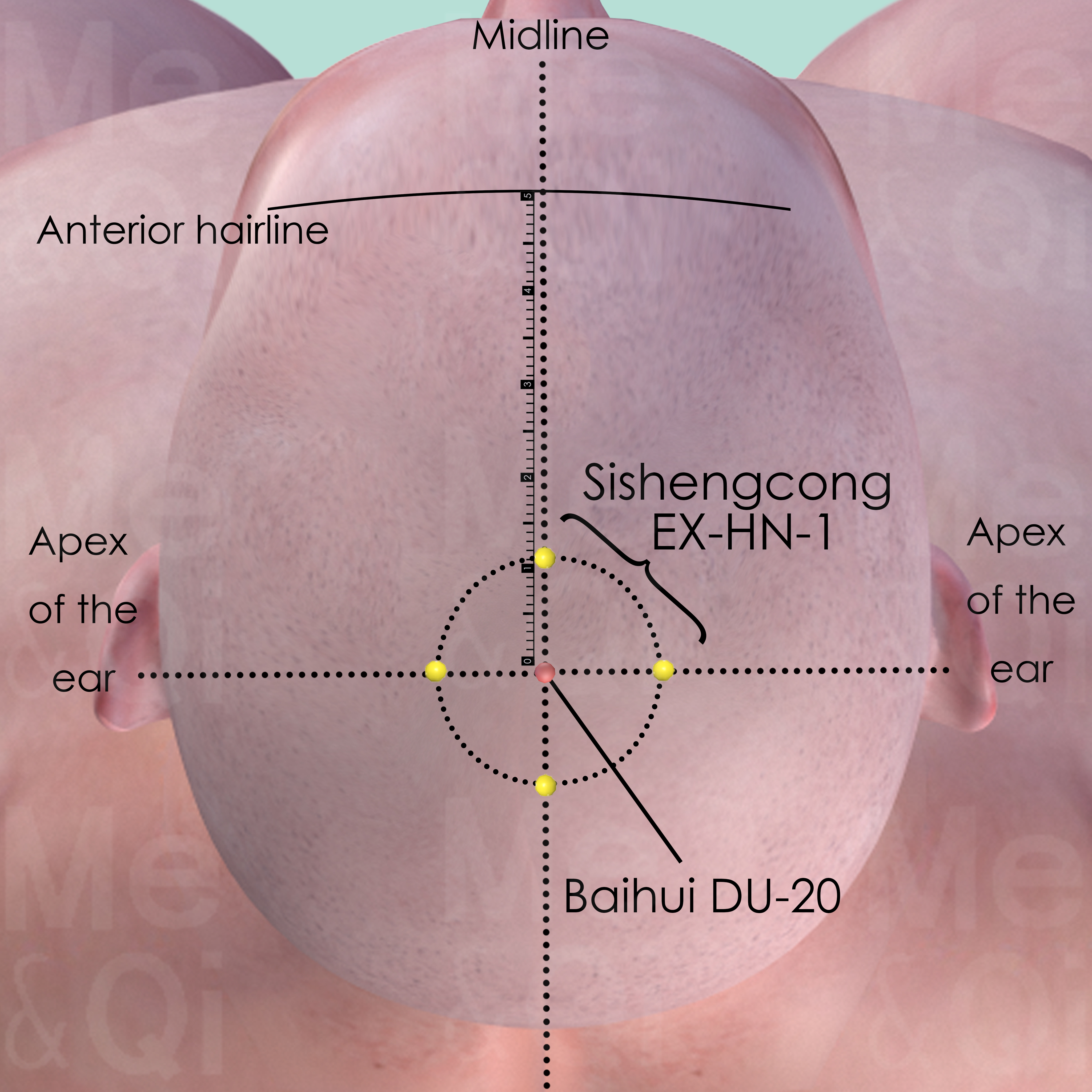
Sishengcong EX-HN-1
This is a group of 4 points and each located 1 cun from Baihui DU-20 in the anterior, posterior and lateral direction.
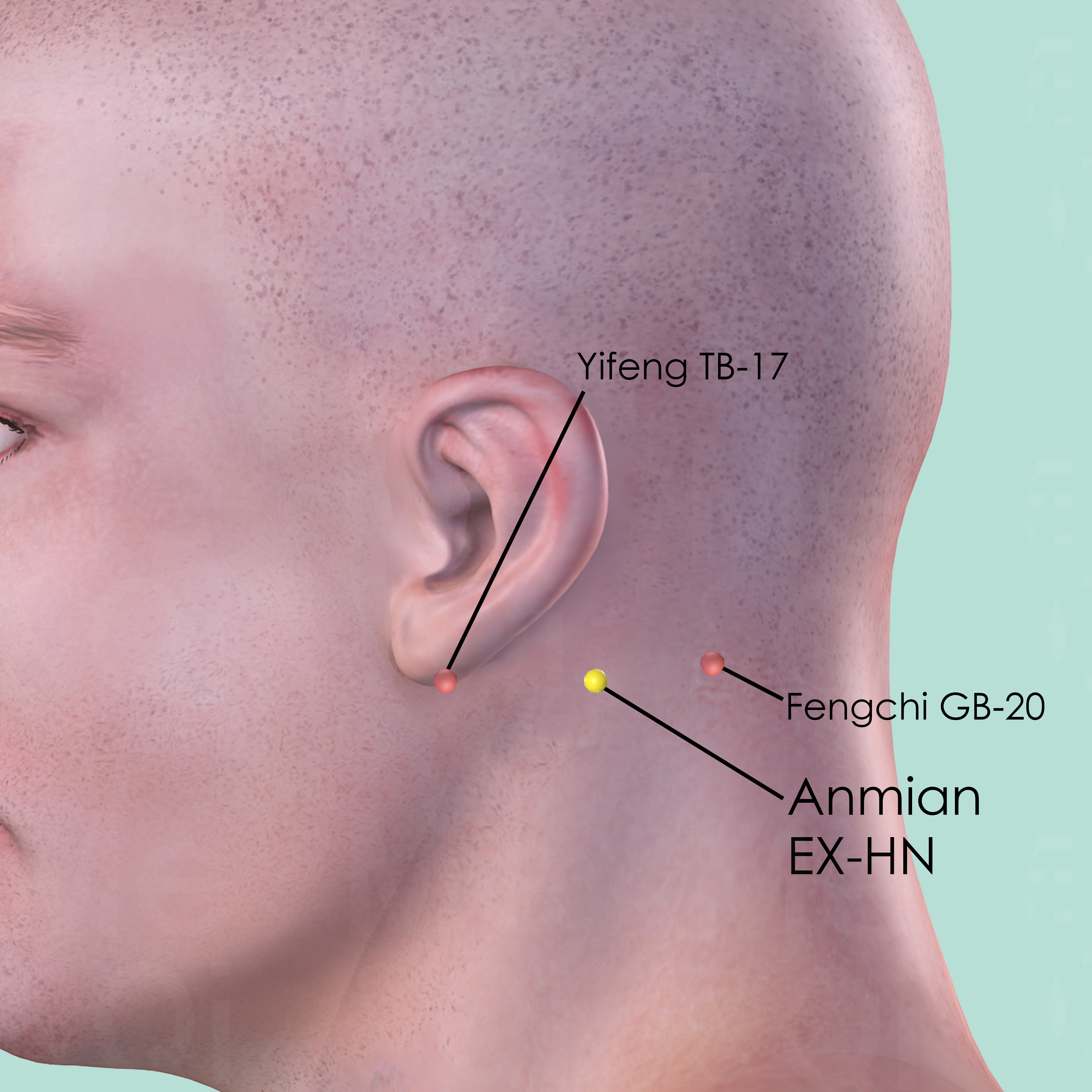
Anmian EX-HN
Posterior to the ear and to the mastoid process, between Yifeng TB-17 and Fengchi GB-20.
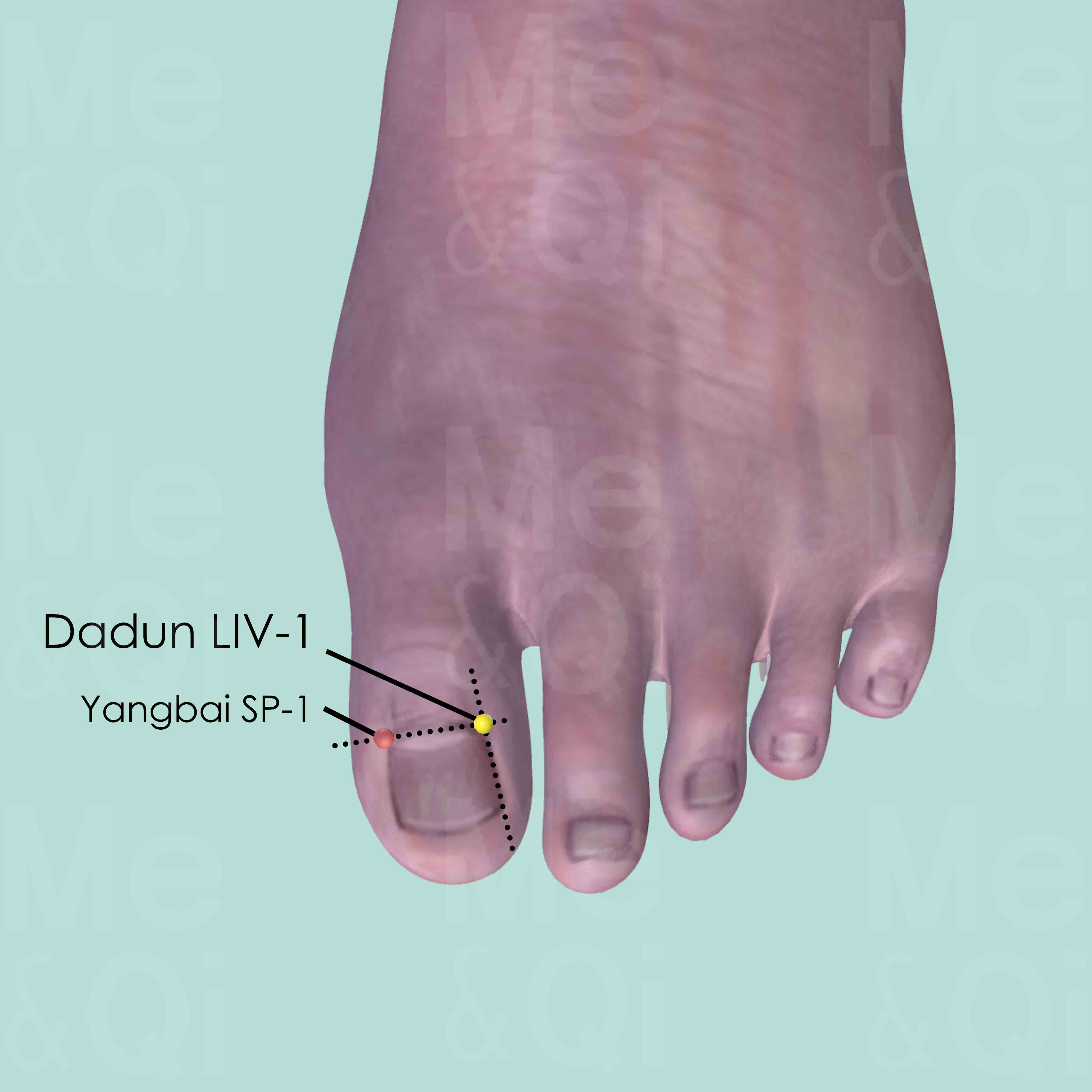
Dadun LIV-1
On the lateral side of the dorsum of the great toe terminal phalanx, between the lateral corner of the nail and interphalangeal joint.
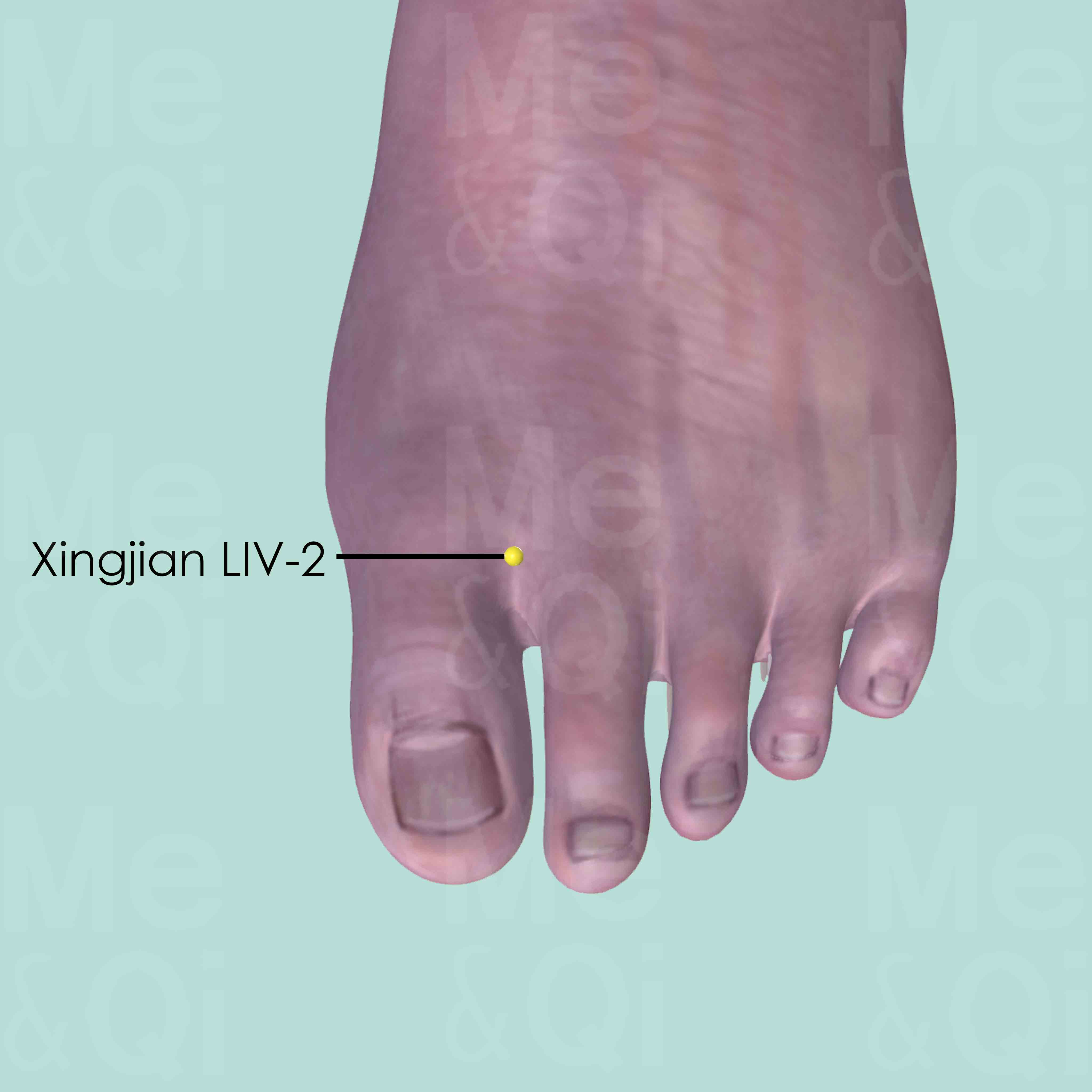
Xingjian LIV-2
Between the first and second toe, on the dorsum of the foot, 0.5 cun proximal to the interdigital fold.
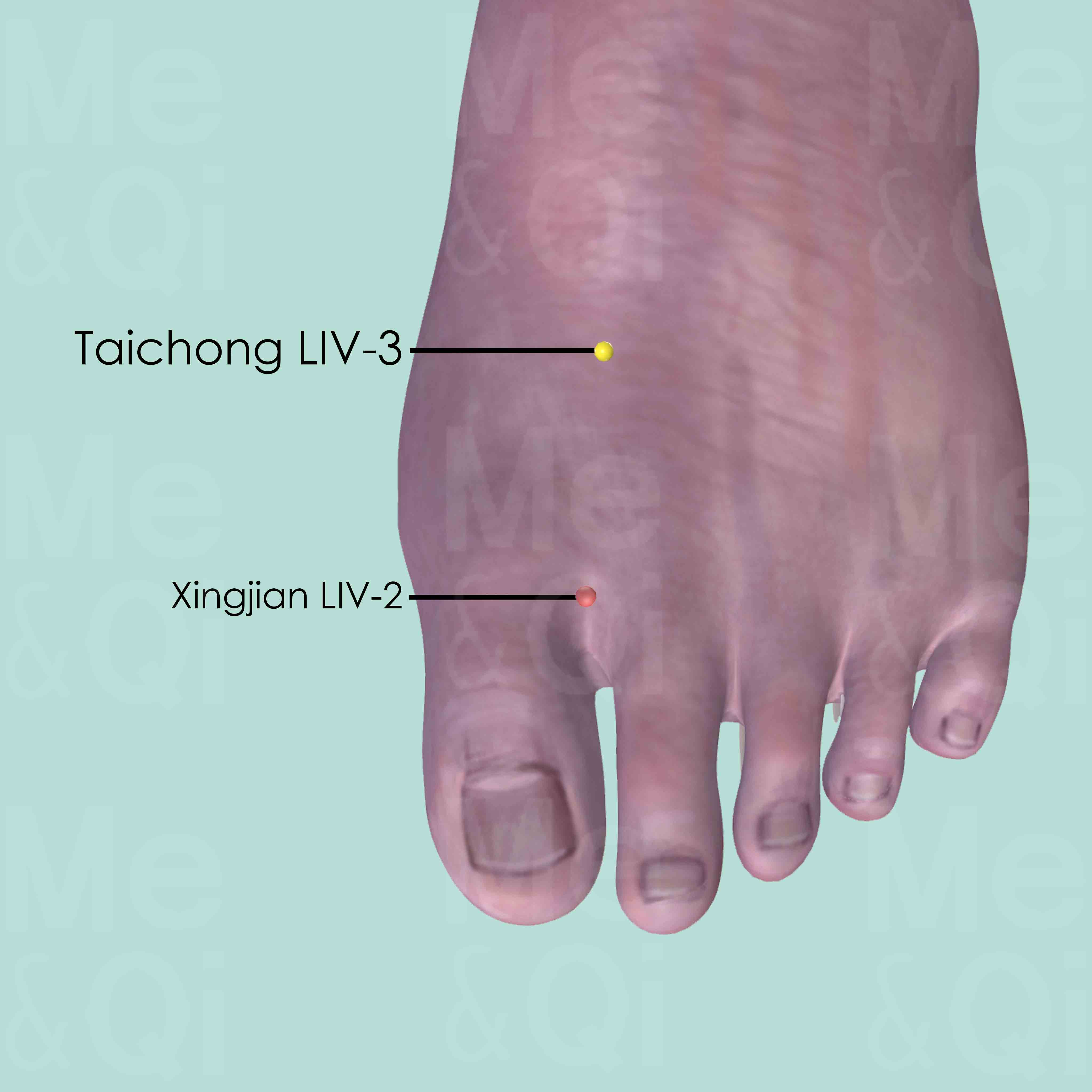
Taichong LIV-3
On the dorsum of the foot, between the 1st and 2nd metatarsal bones, in the depression proximal to the metatarsophalangeal joints and the proximal angle between the two bones.
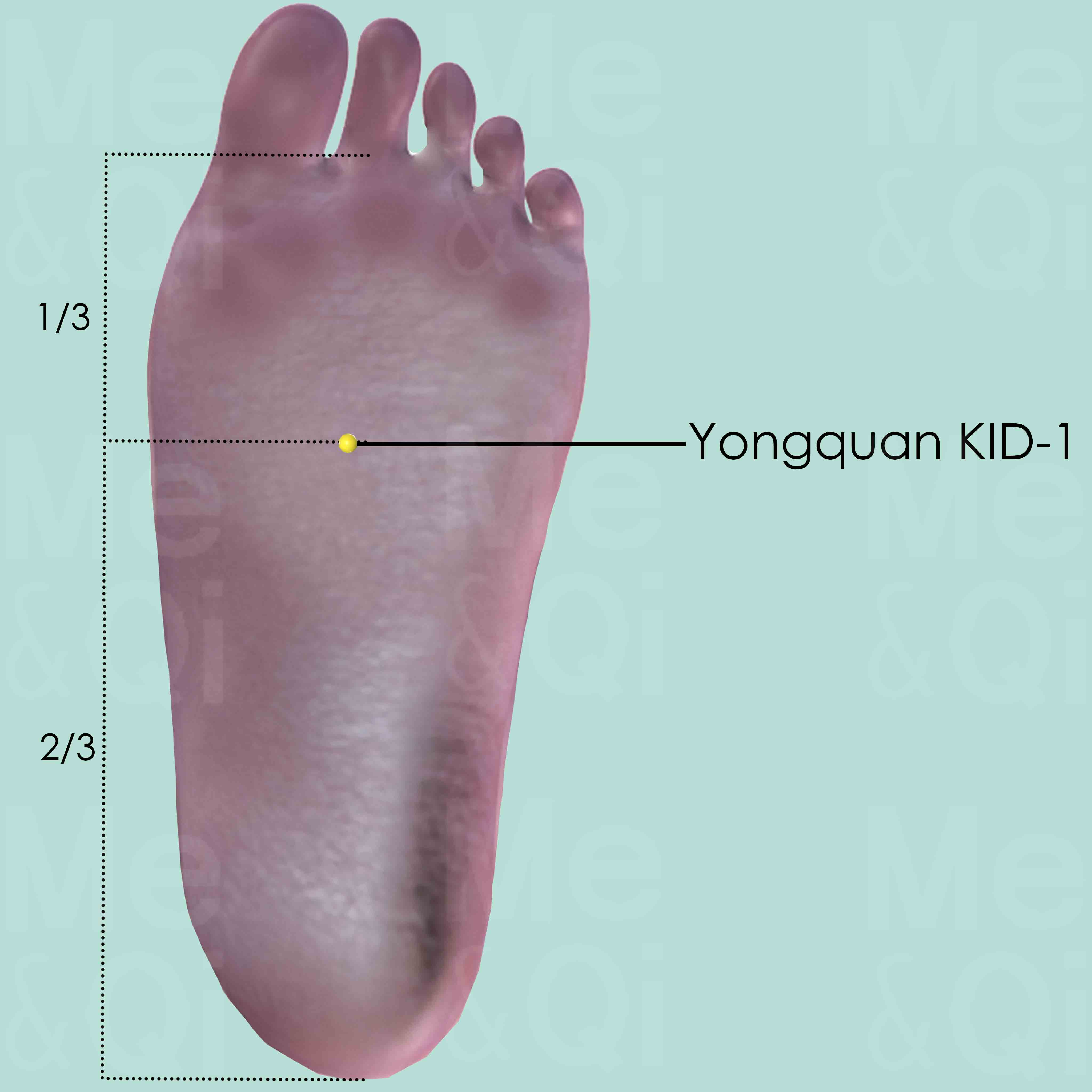
Yongquan KID-1
In the depression between the 2nd and 3rd metatarsal bones on the sole when the foot is in plantar flexion, approximately at the junction of the anterior and middle third of the sole.
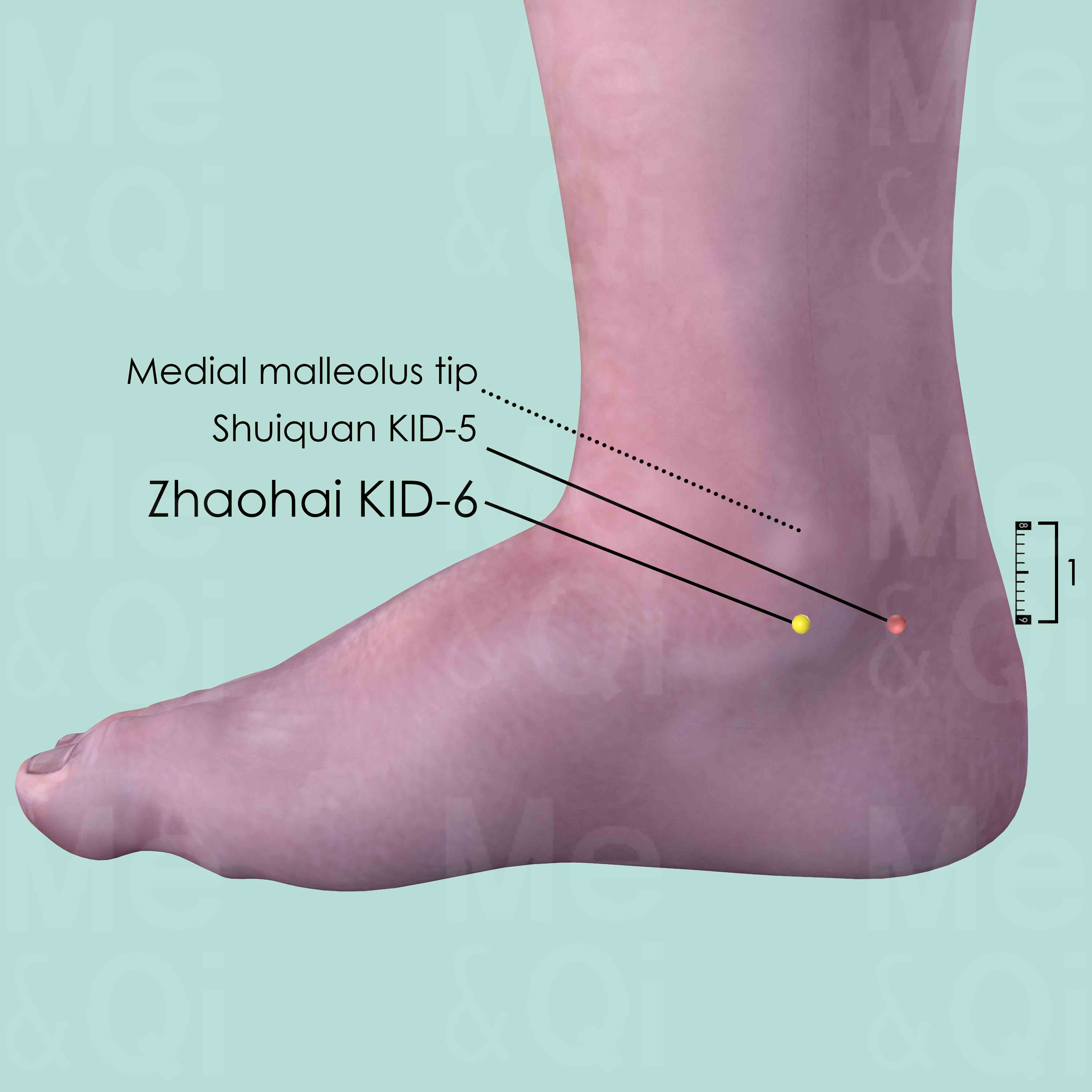
Zhaohai KID-6
Approximately 1 cun below the medial malleolus tip, over the joint space between the talus and the calcaneus.
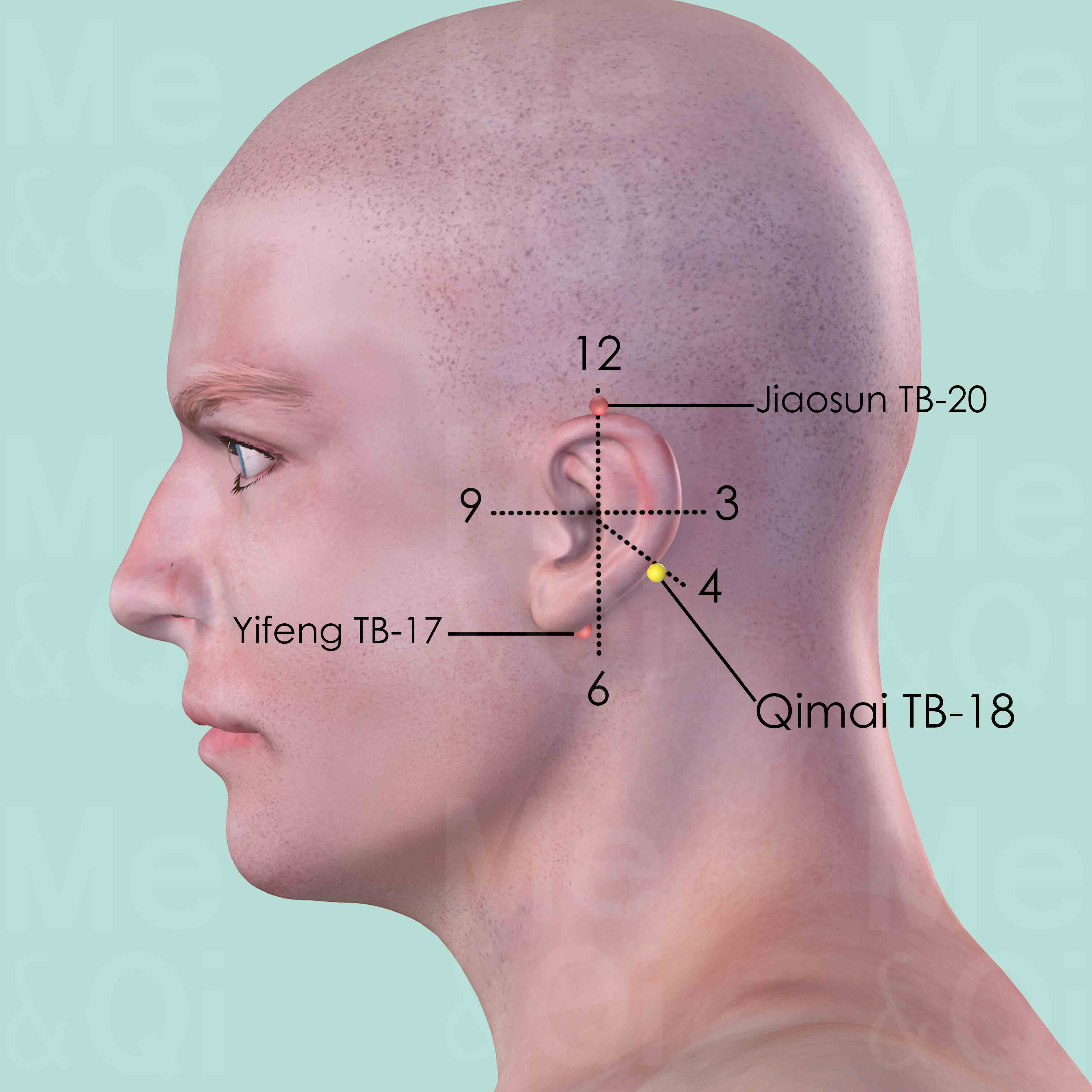
Qimai TB-18
In the center of the mastoid process, at the junction of the middle and lower third of the curve formed by Yifeng TB-17 and Jiaosun TB-20 posterior to the helix.
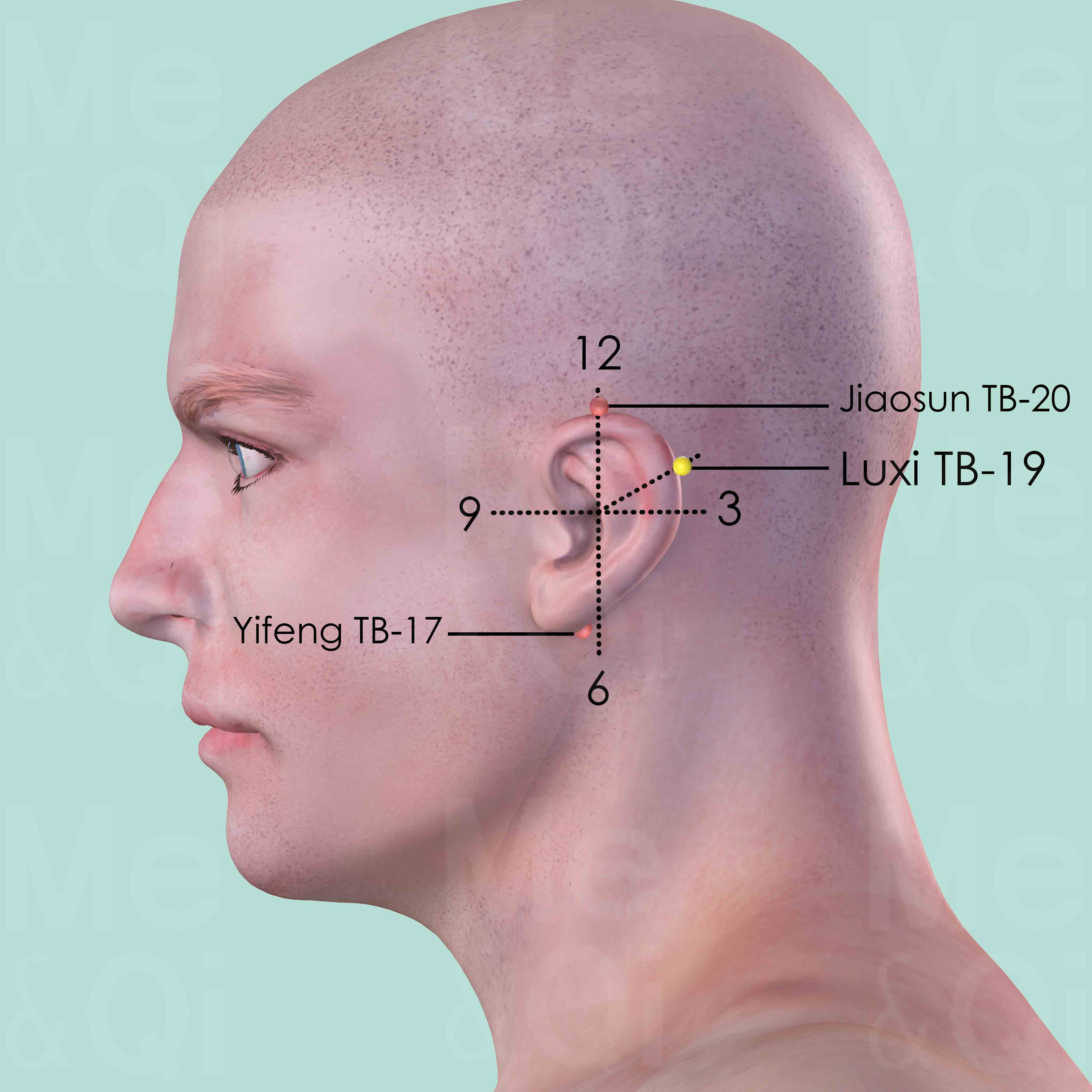
Luxi TB-19
Posterior to the ear, at the junction of the upper and middle third of the curve formed by Yifeng ST-17 and Jiaosun ST-20 behind the helix.
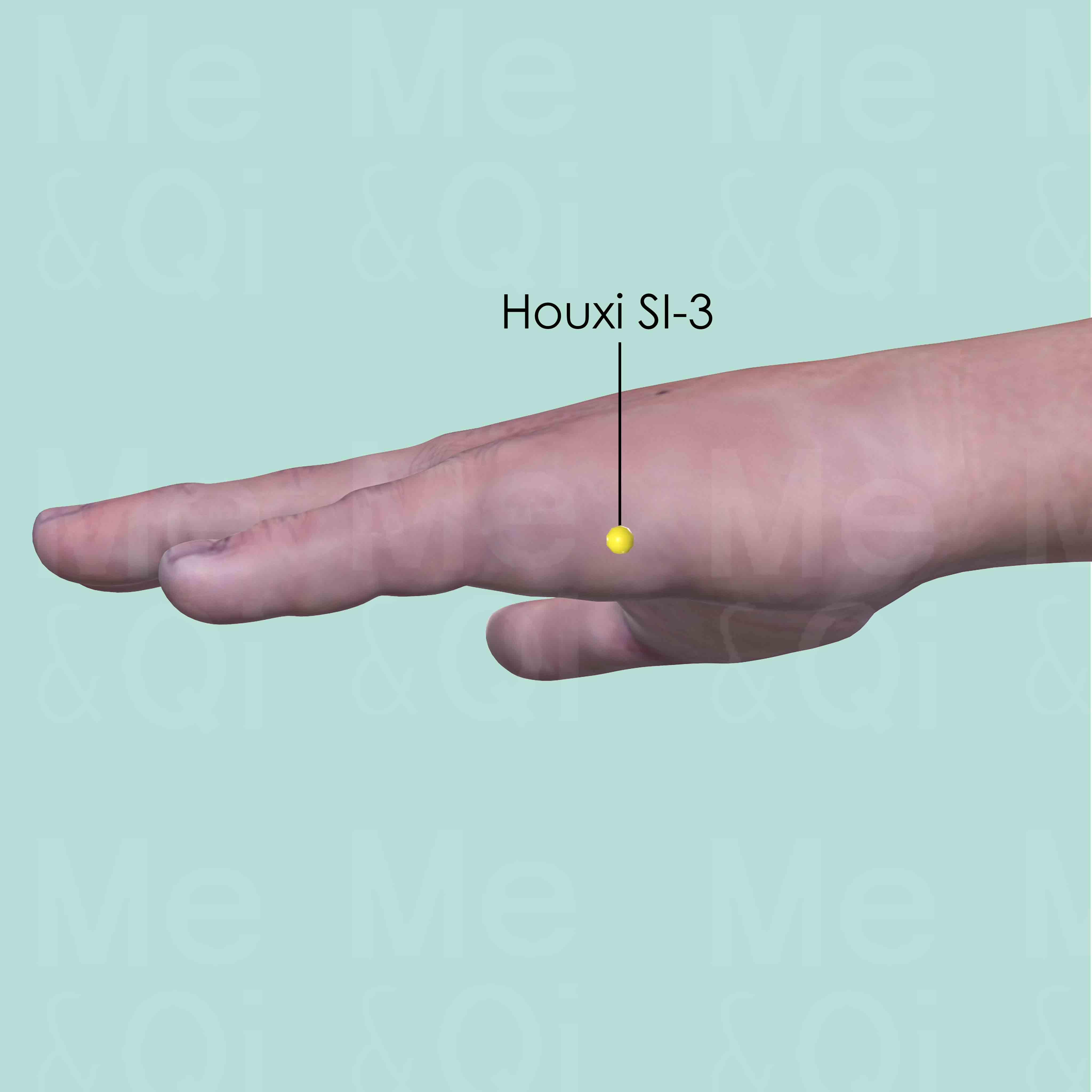
Houxi SI-3
Proximal to the head of the 5th metacarpal bone on the ulnar side, in the depression at the junction of the red and white skin.
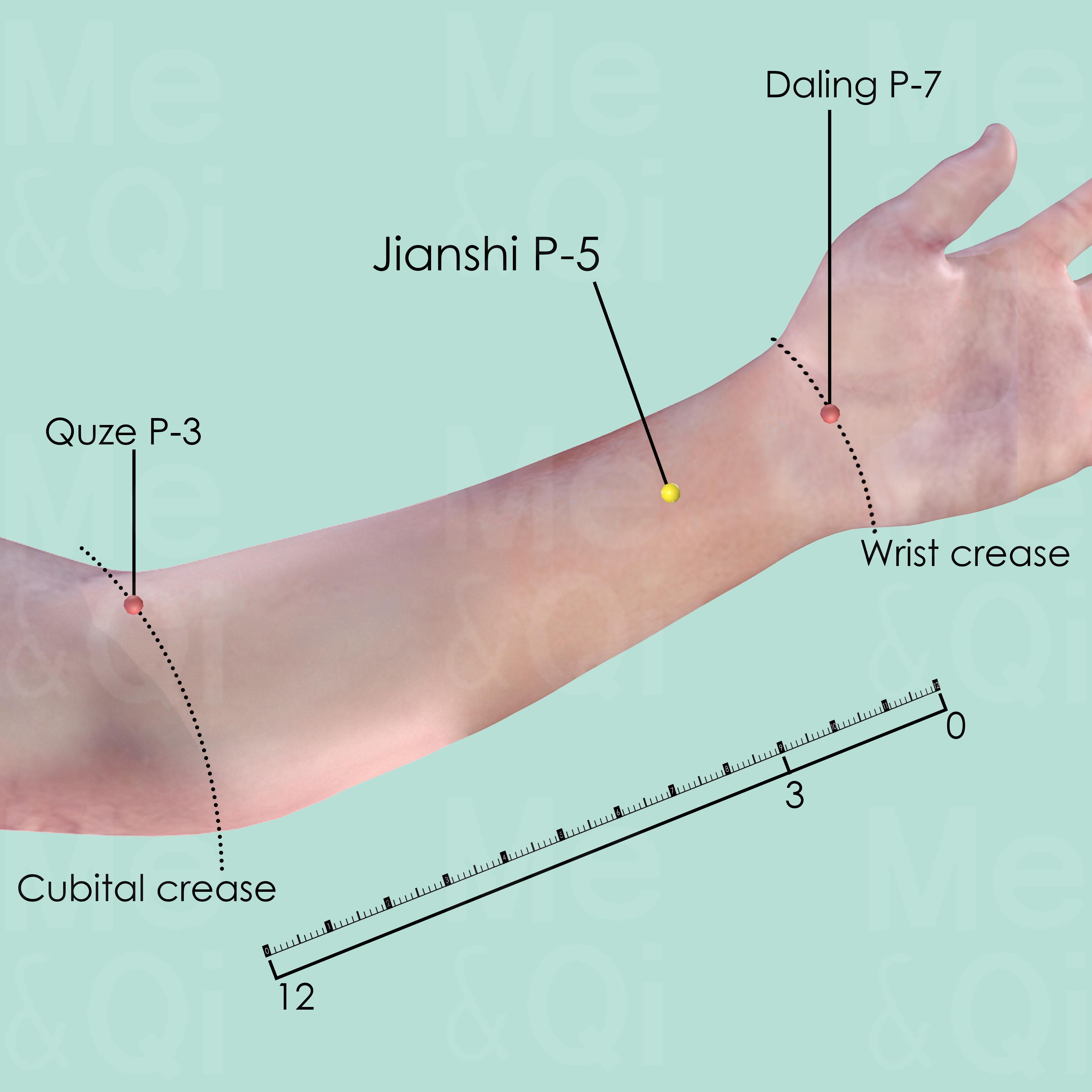
Jianshi P-5
3 cun above the transverse crease of the wrist, between the tendons of palmaris longus and flexor carpi radialis muscle.
TCM Herbs for Epilepsy
Explore below some TCM herbs used to address epilepsy, organized by herb category.
- By Herb Category
- Herbs that anchor and calm the spirit
- Herbs that invigorate the blood
- Herbs that pacify internal liver wind and stop tremors
- Herbs that open the orifices
- Warm herbs that transform phlegm and stop cough
- Tonic herbs for qi deficiency
- Herbs that clear heat and dry dampness
- Warm/Acrid herbs that release the exterior
- Herbs that cool the blood
- Herbs that warm the interior and/or expel cold
- Herbs that nourish the heart and calm the spirit
- Cool/Acrid herbs that release the exterior
- Purgative herbs that drain downward
- Tonic herbs for blood deficiency
- Herbs that stabilize and bind
- Cool herbs that transform phlegm and stop cough
- Herbs that clear heat and relieve toxicity
- Herbs that regulate qi
Herbs that anchor and calm the Spirit
Epilepsy can be treated by these herbs if it stems from disturbances in the Shen (spirit), often due to instability in the heart and kidney energies.
One such herb is Dragon Bones (Long Gu), a key herb in some formulas recommended for epilepsy, like Feng Yin Tang.
Other herbs of this category are listed in the table below.
"Herbs that anchor and calm the Spirit" recommended for epilepsy
Herbs that invigorate the Blood
Epilepsy can be treated by these herbs when it stems from stagnation or poor circulation of blood, helping to improve blood flow and alleviate related discomfort.
One such herb is Leeches (Shui Zhi), a key herb in some formulas recommended for epilepsy, like Di Dang Tang.
Other herbs of this category are listed in the table below.
"Herbs that invigorate the Blood" recommended for epilepsy
| Herb | Formulas they belong to (if applicable) |
|---|---|
| Leeches (Shui Zhi) | Di Dang Tang |
| Tabanus Horseflies (Meng Chong) | Di Dang Tang |
| Peach Kernels (Tao Ren) | Tao He Cheng Qi Tang |
| Szechuan Lovage Roots (Chuan Xiong) | Yue Ju Wan |
| Achyranthes Roots (Niu Xi) | Zhen Gan Xi Feng Tang |
| Turmeric Tubers (Yu Jin) | Not applicable |
Herbs that pacify Internal Liver Wind and stop Tremors
Epilepsy can be treated by these herbs when caused by internal wind from Liver disharmony, often manifesting in symptoms like spasms or tremors.
One such herb is Gastrodia Rhizomes (Tian Ma), a key herb in some formulas recommended for epilepsy, like Tian Ma Gou Teng Yin.
Other herbs of this category are listed in the table below.
"Herbs that pacify Internal Liver Wind and stop Tremors" recommended for epilepsy
| Herb | Formulas they belong to (if applicable) |
|---|---|
| Gastrodia Rhizomes (Tian Ma) | Tian Ma Gou Teng Yin |
| Gambir Stems And Thorns (Gou Teng) | Tian Ma Gou Teng Yin |
| Saiga Antelope's Horns (Ling Yang Jiao) | Zi Xue Dan |
| Centipedes (Wu Gong) | Not applicable |
| Silkworms (Jiang Can) | Not applicable |
Herbs that open the Orifices
Epilepsy can be treated by these herbs if it's a result of blockages in the body's sensory orifices, aiding in restoring clarity and consciousness.
One such herb is Musk (She Xiang), a key herb in some formulas recommended for epilepsy, like Su He Xiang Wan.
Other herbs of this category are listed in the table below.
"Herbs that open the Orifices" recommended for epilepsy
| Herb | Formulas they belong to (if applicable) |
|---|---|
| Musk (She Xiang) | Su He Xiang Wan | Zi Xue Dan | Hui Chun Dan | Zhi Bao Dan |
| Styrax (Su He Xiang) | Su He Xiang Wan |
| Borneol (Bing Pian) | Su He Xiang Wan |
| Benzoin (An Xi Xiang) | Su He Xiang Wan |
| Sweetflag Rhizomes (Shi Chang Pu) | Not applicable |
Warm herbs that transform Phlegm and stop Cough
Epilepsy can be treated by these herbs when it results from phlegm due to cold deficiency, aiming to warm the lungs and dissolve phlegm accumulation.
One such herb is Arisaema (Tian Nan Xing), a key herb in some formulas recommended for epilepsy, like Di Tan Tang.
Other herbs of this category are listed in the table below.
"Warm herbs that transform Phlegm and stop Cough" recommended for epilepsy
| Herb | Formulas they belong to (if applicable) |
|---|---|
| Arisaema (Tian Nan Xing) | Di Tan Tang |
| Chinese Honeylocust Abnormal Fruits (Zhu Ya Zao) | Not applicable |
| Giant Typhonium Rhizomes (Bai Fu Zi) | Not applicable |
Tonic herbs for Qi Deficiency
Epilepsy can be treated by these herbs when stemming from a lack of vital energy or Qi, helping to boost energy and overall vitality.
One such herb is Milkvetch Roots (Huang Qi), a key herb in some formulas recommended for epilepsy, like Bu Yang Huang Wu Tang.
Other herbs of this category are listed in the table below.
"Tonic herbs for Qi Deficiency" recommended for epilepsy
| Herb | Formulas they belong to (if applicable) |
|---|---|
| Milkvetch Roots (Huang Qi) | Bu Yang Huang Wu Tang |
| Liquorice (Gan Cao) | Feng Yin Tang |
| Atractylodes Rhizomes (Bai Zhu) | Yue Ju Wan |
Herbs that clear Heat and dry Dampness
Epilepsy can be treated by these herbs when caused by excessive dampness and heat within the body, aiming to restore balance by drying dampness and clearing heat.
One such herb is Baikal Skullcap Roots (Huang Qin), a key herb in some formulas recommended for epilepsy, like Chai Hu Jia Long Gu Mu Li Tang.
Other herbs of this category are listed in the table below.
"Herbs that clear Heat and dry Dampness" recommended for epilepsy
| Herb | Formulas they belong to (if applicable) |
|---|---|
| Baikal Skullcap Roots (Huang Qin) | Chai Hu Jia Long Gu Mu Li Tang |
| Chinese Gentian (Long Dan Cao) | Dang Gui Long Hui Wan |
Warm/Acrid herbs that release the Exterior
Epilepsy can be treated by these herbs when there is a need to dispel external cold and warm the body, especially in cases where there is insufficient Yang energy internally.
One such herb is Cinnamon Twigs (Gui Zhi), a key herb in some formulas recommended for epilepsy, like Chai Hu Jia Long Gu Mu Li Tang.
Other herbs of this category are listed in the table below.
"Warm/Acrid herbs that release the Exterior" recommended for epilepsy
| Herb | Formulas they belong to (if applicable) |
|---|---|
| Cinnamon Twigs (Gui Zhi) | Chai Hu Jia Long Gu Mu Li Tang | Feng Yin Tang | Xiao Qing Long Tang |
| Ephedra (Ma Huang) | Xiao Qing Long Tang |
Herbs that cool the Blood
Epilepsy can be treated by these herbs when it is a consequence of excess heat in the blood, helping to cool and detoxify the blood.
One such herb is Water Buffalo Horns (Shui Niu Jiao), a key herb in some formulas recommended for epilepsy, like Zi Xue Dan.
Other herbs of this category are listed in the table below.
"Herbs that cool the Blood" recommended for epilepsy
| Herb | Formulas they belong to (if applicable) |
|---|---|
| Water Buffalo Horns (Shui Niu Jiao) | Zi Xue Dan | Zhi Bao Dan |
| Ox Gallstones (Niu Huang) | Hui Chun Dan |
Herbs that warm the Interior and/or expel Cold
Epilepsy can be treated by these herbs if it is due to internal coldness or deficient Yang energy, working to warm the body and dispel cold.
One such herb is Black Pepper (Hu Jiao), which is directly recommended for epilepsy.
Herbs that nourish the Heart and calm the Spirit
Epilepsy can be treated by these herbs when it is linked to deficiencies in heart nourishment, addressing both physical and emotional imbalances.
One such herb is Gold Leaves (Jin Bo), which is directly recommended for epilepsy.
Cool/Acrid herbs that release the Exterior
Epilepsy can be treated by these herbs when the body needs to harmonize with external environmental changes, particularly when there's a need to expel pathogenic factors like wind or cold without overly cooling the body.
One such herb is Bupleurum Roots (Chai Hu), a key herb in some formulas recommended for epilepsy, like Chai Hu Jia Long Gu Mu Li Tang.
Purgative herbs that drain downward
Epilepsy can be treated by these herbs in cases of severe constipation or internal heat, using strong downward movement to purge accumulation.
One such herb is Rhubarb (Da Huang), a key herb in some formulas recommended for epilepsy, like Chai Hu Jia Long Gu Mu Li Tang.
Tonic herbs for Blood Deficiency
Epilepsy can be treated by these herbs in cases of blood deficiency, working to nourish and replenish the body's blood supply.
One such herb is Dong Quai (Dang Gui), a key herb in some formulas recommended for epilepsy, like Dang Gui Long Hui Wan.
Herbs that stabilize and bind
Epilepsy can be treated by these herbs if it is caused by a leakage of bodily fluids or energies, helping to consolidate and preserve the body's essential substances.
One such herb is Light Wheats (Fu Xiao Mai), a key herb in some formulas recommended for epilepsy, like Gan Mai Da Zao Tang.
Cool herbs that transform Phlegm and stop Cough
Epilepsy can be treated by these herbs when it is related to heat-phlegm accumulation, aiding in dissolving phlegm and soothing the respiratory system.
One such herb is Chlorite Schist (Meng Shi), a key herb in some formulas recommended for epilepsy, like Gun Tan Wan.
Herbs that clear Heat and relieve Toxicity
Epilepsy can be treated by these herbs if it arises from internal heat and toxic accumulations, aiding in detoxification and cooling the body.
One such herb is Forsythia Fruits (Lian Qiao), a key herb in some formulas recommended for epilepsy, like Liang Ge San.
Herbs that regulate Qi
Epilepsy can be treated by these herbs when resulting from Qi stagnation or imbalance, helping to promote the smooth flow of Qi in the body.
One such herb is Red Tangerine Peel (Ju Hong), a key herb in some formulas recommended for epilepsy, like Di Tan Tang.