Swollen Complexionaccording to TCM
Symptom family: Skin Inflammation & Swelling
What is Swollen Complexion?
Swollen complexion refers to visible puffiness or edema, predominantly in the facial region, often indicative of underlying health issues. This condition can manifest as a general swelling across the face or be localized to specific areas such as around the eyes or cheeks. Common in a variety of medical contexts, a swollen complexion can result from fluid retention, inflammation, or more systemic health conditions. It's a symptom that not only affects one's appearance but can also be a sign of the body's response to physiological imbalances or distress.
How does TCM view Swollen Complexion?
In Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), the concept of a "pattern" is fundamental to understanding and treating health conditions, including a swollen complexion. A pattern describes the underlying disharmony or imbalance within the body's energy systems that leads to symptoms.
Identifying the specific pattern is crucial because it guides the practitioner in tailoring treatments directly to the root cause of the issue, rather than just addressing superficial symptoms. This approach ensures a more effective and holistic path to healing by restoring the body's natural balance and harmony.
Root Causes of Swollen Complexion in TCM
Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) interprets a swollen complexion as a manifestation of internal imbalances, primarily involving Spleen Qi Deficiency. TCM principles suggest that when the body's vital energy, or Qi, is weak—especially within the Spleen, which is responsible for the transformation and transportation of fluids—edema can occur, leading to visible swelling.
This perspective underscores the significance of identifying and treating the underlying pattern of disharmony, emphasizing a holistic approach that aims to restore equilibrium and the proper flow of Qi throughout the body.
Explore below more details about what might cause Swollen complexion according to TCM.
- By Syndrome
- By Organ
- Qi Deficiency
- Spleen
Qi Deficiency
Qi Deficiency in TCM is like running low on battery power. Qi is the vital energy that powers every function in your body. When there's a Qi Deficiency, it means your body doesn't have enough of this essential energy. This can make you feel tired all the time, weak, or even cause shortness of breath. It's similar to how you feel when you haven't had enough sleep or nutritious food. Your body just doesn't have the energy it needs to perform at its best. Unlike modern medicine, which often focuses on specific physical causes for fatigue and weakness, TCM views Qi Deficiency as an overall energy depletion that affects your entire well-being, and it seeks to replenish and balance this vital energy.... see more
Qi Deficiency Patterns That Can Lead to Swollen Complexion
| Pattern Name | Relevant Symptoms | Relevant Formulas |
|---|---|---|
| Spleen Qi Deficiency | Swollen complexion, Slight abdominal distension after eating, General weakness, Desire to lie down, Slight abdominal pain, Excessive gas and flatulence, Bloated abdomen, Dyspepsia, Obesity... see more | Si Jun Zi Tang | Liu Jun Zi Tang | Fei Er Wan |
Spleen
In TCM the Spleen plays a vital role in digestion and transformation, converting food into energy and nutrients, and overseeing the distribution of Qi and Blood. It's also crucial in maintaining the health of muscles and limbs and ensuring the blood remains within the vessels. When the Spleen malfunctions in TCM, it can lead to a variety of issues such as digestive disorders, fatigue, weak muscles, bloating, and a feeling of heaviness. It can also cause a pale complexion, poor appetite, and a tendency to bruise easily. Emotionally, a Spleen imbalance is often associated with excessive worry or overthinking, reflecting its role in the interplay between physical and mental health.... see more
Spleen Patterns That Can Lead to Swollen Complexion
| Pattern Name | Relevant Symptoms | Relevant Formulas |
|---|---|---|
| Spleen Qi Deficiency | Swollen complexion, Slight abdominal distension after eating, General weakness, Desire to lie down, Slight abdominal pain, Excessive gas and flatulence, Bloated abdomen, Dyspepsia, Obesity... see more | Si Jun Zi Tang | Liu Jun Zi Tang | Fei Er Wan |
TCM Herbal Formulas for Swollen Complexion
For treating a swollen complexion rooted in Spleen Qi Deficiency, TCM recommends specific herbal formulas that tonify Qi and strengthen the Spleen. Si Jun Zi Tang is a classic formula utilized in such cases, featuring key herbs like Ginseng (Ren Shen), known for its potent Qi-tonifying properties.
This formula aims to enhance the Spleen's ability to manage fluids effectively, thereby reducing facial puffiness and restoring a balanced, healthy complexion. Through such targeted herbal therapy, TCM seeks to address the root cause of the swollen complexion, offering a path to long-term well-being.
Explore below some TCM herbal formulas used to address swollen complexion, organized by cause and by formula type.
- By Cause
- By Formula Type
- Qi Deficiency
- Formulas that tonify qi
- Formulas that reduce food accumulation and transform stagnation
Top Formula for Qi Deficiency:
Si Jun Zi Tang
Suitable for Qi Deficiency patterns that may cause swollen complexion, such as Spleen Qi Deficiency
Learn moreAll Formulas Recommended for Swollen Complexion Caused by Qi Deficiency
| Formula | Patterns Suitable For |
|---|---|
| Si Jun Zi Tang | Spleen Qi Deficiency |
| Liu Jun Zi Tang | Spleen Qi Deficiency |
| Fei Er Wan | Spleen Qi Deficiency |
Formulas that tonify Qi
These formulas are suitable for some swollen complexion-causing patterns like Spleen Qi Deficiency.
One such formula is Si Jun Zi Tang, with ginseng as a key herb.
Other formulas of this category are listed in the table below.
All "formulas that tonify qi" recommended for swollen complexion
| Formula | Patterns Suitable For (if applicable) |
|---|---|
| Si Jun Zi Tang | Spleen Qi Deficiency |
| Liu Jun Zi Tang | Spleen Qi Deficiency |
Formulas that reduce food accumulation and transform Stagnation
These formulas are suitable for some swollen complexion-causing patterns like Spleen Qi Deficiency.
One such formula is Fei Er Wan, with quisqualis fruit as a key herb.
Acupoints for Swollen Complexion
Acupuncture is another cornerstone of TCM treatment for a swollen complexion, with specific acupoints selected to harmonize Qi flow, tonify the Spleen, and eliminate fluid retention. Points like Chongyang ST-42 and Jiexi ST-41 on the Stomach Channel are targeted for their ability to strengthen the digestive system and clear obstructions from the Channel, directly addressing the underlying causes of facial swelling.
Additionally, acupoints such as Tianyou TB-16 in the Triple Burner Channel are utilized to regulate Qi ascending and descending to the head, further alleviating symptoms of puffiness. This comprehensive approach underscores TCM's integrative strategy in treating swollen complexion, emphasizing the importance of restoring internal harmony to achieve external healing.
Explore below some acupoints used to address swollen complexion, organized by meridian.
- By Meridian
- Stomach Channel
- Triple Burner Channel
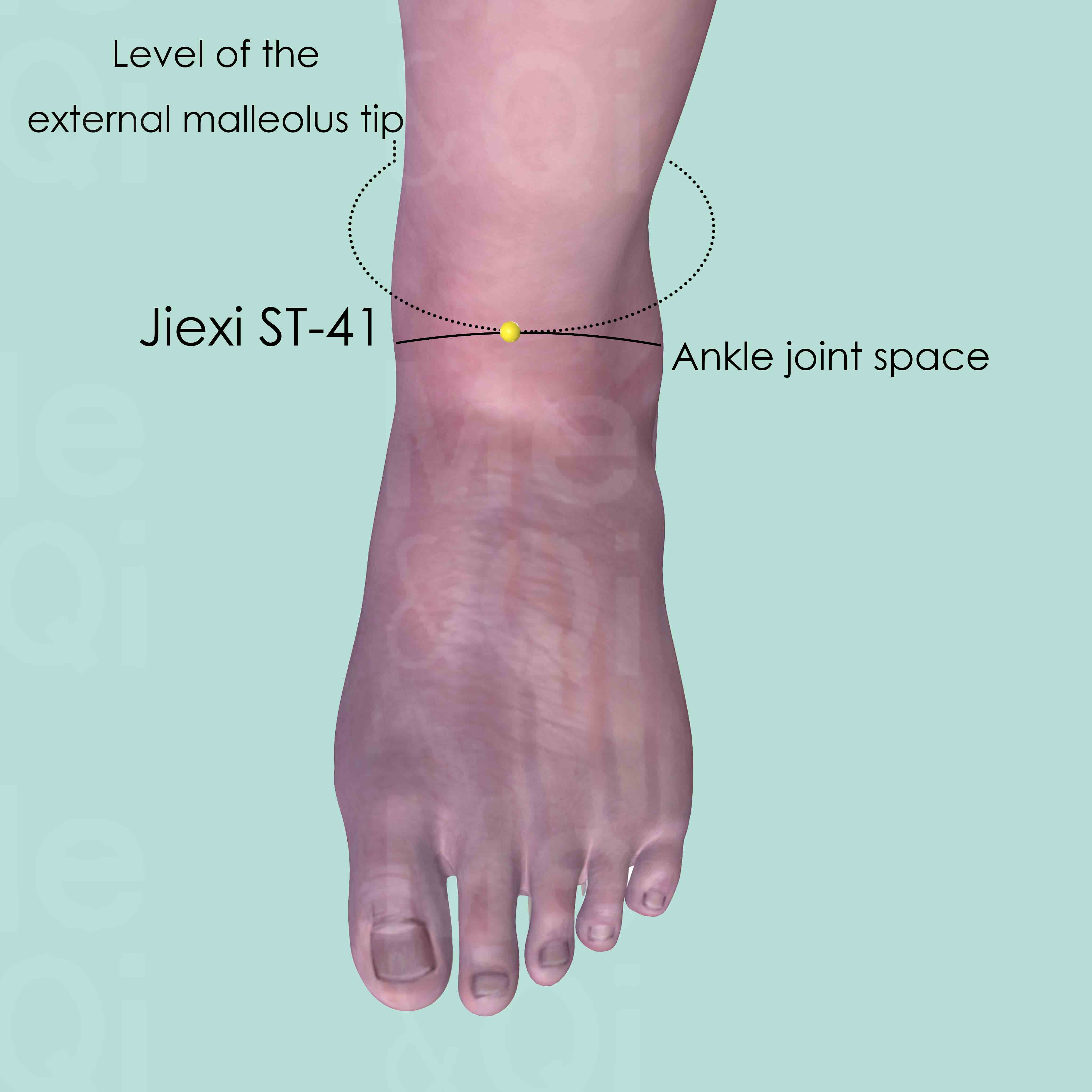
Jiexi ST-41
At the junction of the dorsum of the foot and leg, between the tendons of extensor digitorum and the extensor hallucis longus muscle. Approximately at the level of the tip of the external malleolus.
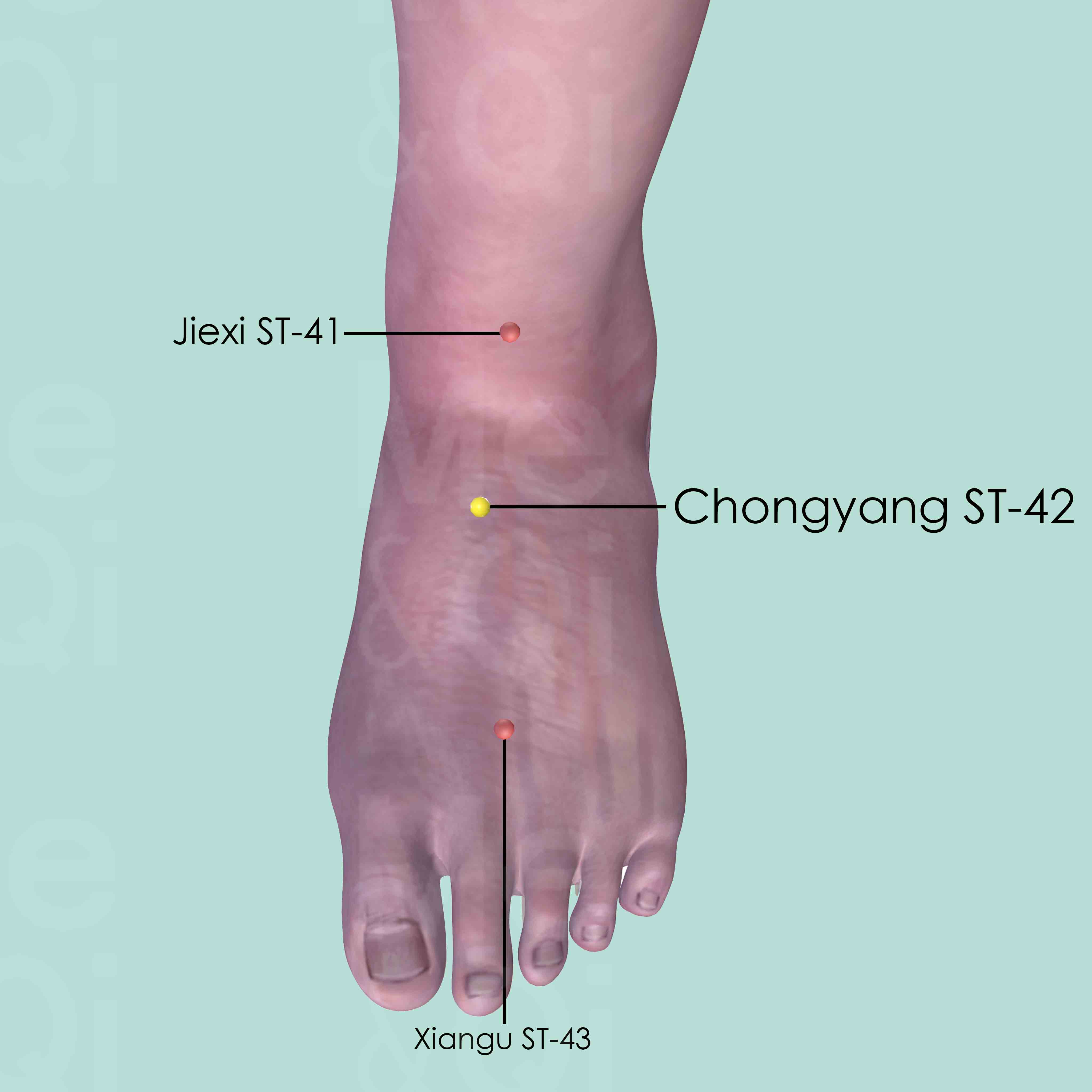
Chongyang ST-42
Distal to Jiexi ST-41, at the highest point of the dorsum of foot, between the tendons of the extensor hallucis longus and the extensor digitorum longus, directly lateral to the point where the dorsalis pedis artery may be palpated. The point is bordered proximally by the 2nd and 3rd metatarsal bones and distally by the 2nd and 3rd cuneiform bones.
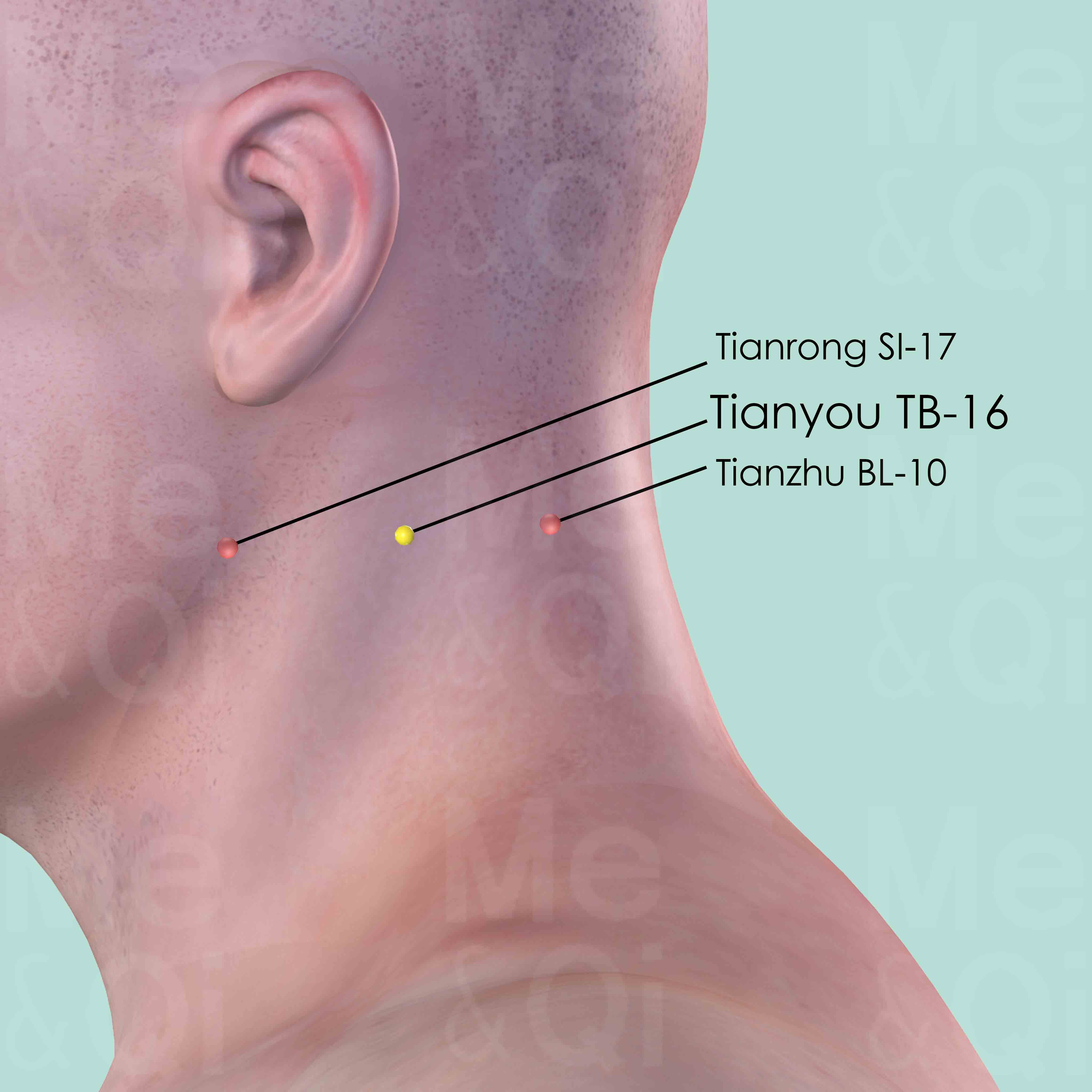
Tianyou TB-16
Posterior and inferior to the mastoid process, on the posterior border of sternocleidomastoid muscle, level with Tianrong SI-17 and Tianzhu BL-10.
