Wheezingaccording to TCM
Symptom family: Cough Related Symptoms
Sub-symptom(s): Persistent Wheezing
What is Wheezing?
Wheezing is a common respiratory symptom characterized by a high-pitched, whistling sound during breathing. It occurs when the airways are constricted or obstructed, often as a result of inflammation or a buildup of mucus.
Wheezing can range from mild to severe and is often associated with conditions like asthma, bronchitis, and allergies. Persistent wheezing is a notable sub-symptom that requires medical attention to determine and address the underlying cause.
How does TCM view Wheezing?
In Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), wheezing is viewed as a sign of disharmony within the body's energy pathways or Qi. TCM practitioners believe that wheezing is often a result of an imbalance in the Lung and Kidney systems, with factors such as Phlegm, external pathogens, and Yin or Yang Deficiencies playing crucial roles. Unlike Western medicine, which typically focuses on the symptom, TCM aims to restore the overall balance of the body to alleviate wheezing.
Root Causes of Wheezing in TCM
In Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), wheezing is considered a symptom arising from imbalances in the body's Qi (energy) flow, particularly within the Lung. One common cause identified in TCM is Damp-Phlegm in the Lungs, where the accumulation of Phlegm obstructs the flow of Qi, leading to wheezing, a feeling of chest heaviness, and difficulty in breathing.
Another pattern, Dry-Phlegm in the Lungs, is marked by a dry cough and the presence of scanty, sticky sputum. This indicates a Deficiency of Lung Yin, where the Dryness in the Lungs fails to nourish and moisten the airways.
Lung Yang Deficiency, characterized by symptoms like cold extremities, fatigue, and a pale complexion, suggests a diminished warming and Qi-moving function of the lungs, resulting in wheezing and shortness of breath.
Explore below more details about what might cause Wheezing according to TCM.
- By Syndrome
- By Organ
- Phlegm
- Heat
- Yin Deficiency
- Yang Deficiency
- Dampness
- Dryness
- View More Causes
- Lung
- Kidney
Phlegm
In TCM "Phlegm" as a pattern of disharmony is a complex concept that extends beyond the physical manifestation of mucus. It represents a pathological factor that can disrupt the flow of Qi (vital energy) and blood, leading to various health issues. Phlegm in TCM is seen as a sticky, turbid substance arising from the body's inability to metabolize fluids properly, often due to a dysfunction of the spleen. It's not only associated with respiratory problems like cough and congestion but also with systemic issues. Symptoms can include a feeling of heaviness, mental cloudiness, dizziness, and in some cases, the formation of lumps or masses. Phlegm can even be "invisible," contributing to emotional disturbances like depression or stress. ... see more
Phlegm Patterns That Can Lead to Wheezing
Common Symptoms: Stifling Sensation In The Chest Dizziness Coughing Sputum Shortness Of Breath Feeling Of Heaviness Asthma Pale Face
| Pattern Name | Relevant Symptoms | Relevant Formulas |
|---|---|---|
| Damp-Phlegm in the Lungs | Wheezing, Coughing, Pale face, Sputum, Stifling sensation in the chest, Shortness of breath, Discomfort when lying down, Nausea, Feeling of heaviness, Dizziness, Profuse white sputum, Asthma, Chest distension... see more | Er Chen Tang |
| Dry-Phlegm in the Lungs | Wheezing, Dry cough, Scanty sputum, Shortness of breath, Stifling sensation in the chest, Sputum, Feeling of heaviness, Dizziness, Dry throat, Pale face... see more | Bei Mu Gua Lou San |
| Phlegm-Heat in the Lungs | Wheezing, Coughing, Shortness of breath, Stifling sensation in the chest, Sputum, Feeling hot, Thirst, Head and body heaviness, Dizziness, Copious thick yellow sputum... see more | Er Chen Tang | Wen Dan Tang | Qing Qi Hua Tan Wan | Ma Xing Shi Gan Tang | Qing Xin Li Ge Tang | Ren Shen Ge Jie San | Pi Pa Qing Fei Yin |
| Phlegm-Fluids above the diaphragm | Wheezing, Coughing, Asthma, Edema, Feeling of oppression of the chest, Dizziness, Profuse white sputum... see more | Xiao Qing Long Tang |
Heat
In TCM "Heat" signifies an excess of Yang energy, leading to an imbalance where heat predominates over the body's cool Yin aspects. This condition is metaphorically akin to an internal over-heating. Symptoms indicative of Heat can include feelings of warmth, fever, sweating, irritability, red face, thirst with a preference for cold drinks, and a rapid pulse. The tongue may appear red with a yellow coating. Unlike the common interpretation of heat in terms of temperature, in TCM, it represents a state of hyperactivity or inflammation in the body.... see more
Heat Patterns That Can Lead to Wheezing
Common Symptoms: Asthma Coughing With Blood Streaked Sputum Dry Throat Hot Palms And Soles Night Sweats Chronic Bronchitis Chronic Pharyngitis Spontaneous Pneumothorax
| Pattern Name | Relevant Symptoms | Relevant Formulas |
|---|---|---|
| Phlegm-Heat in the Lungs | Wheezing, Coughing, Shortness of breath, Stifling sensation in the chest, Sputum, Feeling hot, Thirst, Head and body heaviness, Dizziness, Copious thick yellow sputum... see more | Er Chen Tang | Wen Dan Tang | Qing Qi Hua Tan Wan | Ma Xing Shi Gan Tang | Qing Xin Li Ge Tang | Ren Shen Ge Jie San | Pi Pa Qing Fei Yin |
| Lung and Kidney Yin Deficiency with Empty Fire | Wheezing, Coughing with blood streaked sputum, Dry throat, Hot palms and soles, Night sweats, Chronic bronchitis, Chronic pharyngitis, Spontaneous pneumothorax, Cor pulmonale, Silicosis, Pulmonary tuberculosis... see more | Bai He Gu Jin Tang |
Yin Deficiency
Yin deficiency in TCM is a pattern of disharmony characterized by a depletion of the body's Yin energy, which represents the cooling, moistening, and nurturing aspects of our physiology. This condition often arises from factors like chronic stress, overwork, insufficient rest, or prolonged illness. Symptoms of Yin deficiency can include a sensation of heat, especially in the afternoon or evening, night sweats, insomnia, a dry mouth or throat, and a red tongue with little coating. There might also be a general feeling of restlessness or irritability. Since Yin is essential for balancing the body's active and warm Yang energy, its deficiency leads to a relative excess of Yang, manifesting as heat or dryness symptoms.... see more
Yin Deficiency Patterns That Can Lead to Wheezing
| Pattern Name | Relevant Symptoms | Relevant Formulas |
|---|---|---|
| Lung and Kidney Yin Deficiency with Empty Fire | Wheezing, Coughing with blood streaked sputum, Dry throat, Hot palms and soles, Night sweats, Chronic bronchitis, Chronic pharyngitis, Spontaneous pneumothorax, Cor pulmonale, Silicosis, Pulmonary tuberculosis... see more | Bai He Gu Jin Tang |
Yang Deficiency
Yang deficiency in TCM refers to a state where the body's Yang energy, which is responsible for warmth, activity, and function, is weakened or diminished. This pattern of disharmony often arises from chronic illness, aging, or inherent constitutional weakness. Symptoms of Yang deficiency are typically associated with cold and sluggishness, such as a feeling of coldness, cold extremities, pale complexion, low energy or fatigue, and a desire for warmth. Digestive issues like poor appetite, loose stools, and water retention can also be indicative of Yang deficiency.... see more
Yang Deficiency Patterns That Can Lead to Wheezing
| Pattern Name | Relevant Symptoms | Relevant Formulas |
|---|---|---|
| Lung Yang Deficiency | Wheezing, Coughing and wheezing with copious sputum, Cold extremities, Spontaneous sweat, Frequent colds or flu, Pale face, Generalized fatigue, Shortness of breath, Absence of thirst, Weak voice... see more | Gan Cao Gan Jiang Tang | Si Jun Zi Tang | Sheng Mai San |
Dampness
"Dampness" in TCM is a concept that describes a pattern of disharmony where the body accumulates excess moisture. Imagine the heavy, sticky feeling you get on a very humid day; that's similar to what dampness feels like internally. It can manifest as a sense of heaviness, bloating, sluggishness, or even a foggy mind. This condition is often thought to arise from environmental factors like living in a damp place, dietary habits that promote moisture in the body, or internal imbalances that hinder the body's ability to process fluids properly. In TCM, dampness can obstruct the normal flow of energy and fluids in the body, leading to various symptoms.... see more
Dampness Patterns That Can Lead to Wheezing
| Pattern Name | Relevant Symptoms | Relevant Formulas |
|---|---|---|
| Damp-Phlegm in the Lungs | Wheezing, Coughing, Pale face, Sputum, Stifling sensation in the chest, Shortness of breath, Discomfort when lying down, Nausea, Feeling of heaviness, Dizziness, Profuse white sputum, Asthma, Chest distension... see more | Er Chen Tang |
Dryness
"Dryness" in TCM refers to a state where there is a lack of moisture in the body, much like how the land feels during a drought. It's a pattern of disharmony that can arise from external factors like dry weather or internal issues, such as insufficient fluid intake or certain lifestyle habits. When your body experiences this dryness, you might notice symptoms like dry skin, a scratchy throat, dry eyes, or even constipation. It's similar to the feeling of being parched or having dry, chapped lips in a very dry climate. TCM views this as an imbalance where the body's yin - often associated with moisture and cooling - is depleted.... see more
Dryness Patterns That Can Lead to Wheezing
| Pattern Name | Relevant Symptoms | Relevant Formulas |
|---|---|---|
| Dry-Phlegm in the Lungs | Wheezing, Dry cough, Scanty sputum, Shortness of breath, Stifling sensation in the chest, Sputum, Feeling of heaviness, Dizziness, Dry throat, Pale face... see more | Bei Mu Gua Lou San |
Lung
In TCM the Lungs are seen as the organ responsible for controlling Qi and respiration, as well as being a key part of the body's defensive system. They are thought to maintain the balance and flow of air and moisture, and are closely linked to the skin and hair. When the Lungs are imbalanced or malfunctioning in TCM, it can lead to respiratory issues like coughing or asthma, a weakened immune system, dry skin, and emotional disturbances such as sadness or grief. These symptoms are believed to arise from disruptions in the Lungs' ability to regulate Qi and protect the body, highlighting their central role in maintaining overall health and well-being.... see more
Lung Patterns That Can Lead to Wheezing
Common Symptoms: Shortness Of Breath Asthma Pale Face Sputum Stifling Sensation In The Chest Dizziness Dry Throat Coughing
| Pattern Name | Relevant Symptoms | Relevant Formulas |
|---|---|---|
| Damp-Phlegm in the Lungs | Wheezing, Coughing, Pale face, Sputum, Stifling sensation in the chest, Shortness of breath, Discomfort when lying down, Nausea, Feeling of heaviness, Dizziness, Profuse white sputum, Asthma, Chest distension... see more | Er Chen Tang |
| Dry-Phlegm in the Lungs | Wheezing, Dry cough, Scanty sputum, Shortness of breath, Stifling sensation in the chest, Sputum, Feeling of heaviness, Dizziness, Dry throat, Pale face... see more | Bei Mu Gua Lou San |
| Lung Yang Deficiency | Wheezing, Coughing and wheezing with copious sputum, Cold extremities, Spontaneous sweat, Frequent colds or flu, Pale face, Generalized fatigue, Shortness of breath, Absence of thirst, Weak voice... see more | Gan Cao Gan Jiang Tang | Si Jun Zi Tang | Sheng Mai San |
| Phlegm-Heat in the Lungs | Wheezing, Coughing, Shortness of breath, Stifling sensation in the chest, Sputum, Feeling hot, Thirst, Head and body heaviness, Dizziness, Copious thick yellow sputum... see more | Er Chen Tang | Wen Dan Tang | Qing Qi Hua Tan Wan | Ma Xing Shi Gan Tang | Qing Xin Li Ge Tang | Ren Shen Ge Jie San | Pi Pa Qing Fei Yin |
| Lung and Kidney Yin Deficiency with Empty Fire | Wheezing, Coughing with blood streaked sputum, Dry throat, Hot palms and soles, Night sweats, Chronic bronchitis, Chronic pharyngitis, Spontaneous pneumothorax, Cor pulmonale, Silicosis, Pulmonary tuberculosis... see more | Bai He Gu Jin Tang |
Kidney
In TCM the Kidneys are regarded as the body's most fundamental reservoir of Essence, known as Jing, which influences growth, reproduction, and aging. They are not just organs for filtering blood, but a holistic system governing vital life forces. When the Kidneys malfunction in TCM, it can manifest as a variety of health issues, such as chronic fatigue, reproductive problems, imbalances in fluid metabolism leading to edema or dryness, lower back pain, and a sense of fear or insecurity.... see more
Kidney Patterns That Can Lead to Wheezing
| Pattern Name | Relevant Symptoms | Relevant Formulas |
|---|---|---|
| Lung and Kidney Yin Deficiency with Empty Fire | Wheezing, Coughing with blood streaked sputum, Dry throat, Hot palms and soles, Night sweats, Chronic bronchitis, Chronic pharyngitis, Spontaneous pneumothorax, Cor pulmonale, Silicosis, Pulmonary tuberculosis... see more | Bai He Gu Jin Tang |
TCM Herbal Formulas for Wheezing
In Traditional Chinese Medicine, wheezing is often treated with specific formulas and herbs that target the underlying patterns. For the pattern of Damp-Phlegm in the Lungs, characterized by chest heaviness and difficulty in breathing, the formula Er Chen Tang is frequently used. This formula incorporates Crow-Dipper Rhizomes (Ban Xia) and Tangerine peel (Chen Pi), which are effective in transforming Phlegm and drying Dampness.
In the case of Dry-Phlegm in the Lungs, where patients experience a dry cough and scanty, sticky sputum, Bei Mu Gua Lou San is commonly recommended. This formula contains Fritillary Bulbs (Chuan Bei Mu), which is known for its ability to dispel phlegm and moisten the lungs, providing relief from dry cough.
Additionally, for Lung Yang Deficiency, which manifests as wheezing with cold extremities and fatigue, Gan Cao Gan Jiang Tang is often prescribed. This formula typically includes Dried ginger (Gan Jiang), recognized for its warming properties and ability to expel cold from the interior. These formulas and herbs are carefully selected based on the patient's specific TCM diagnosis to effectively alleviate wheezing symptoms.
Explore below some TCM herbal formulas used to address wheezing, organized by cause and by formula type.
- By Cause
- By Formula Type
- Phlegm
- Heat
- Yin Deficiency
- Yang Deficiency
- Dampness
- Dryness
- View More Causes
- Formulas that tonify qi
- Formulas that dry dampness and transform phlegm
- Formulas that clear wind-Cold
- Formulas that nourish yin and tonify
- Formulas that dispel phlegm
- Formulas that warm yang and tonify
- Formulas that warm interior cold
- Formulas that clear heat and transform phlegm
- Formulas that clear heat from the organs
- Formulas that clear internal abscesses and sores
- Formulas that clear lung-Heat
Top Formula for Phlegm:
Er Chen Tang
Suitable for Phlegm patterns that may cause wheezing, such as Damp-Phlegm in the Lungs or Phlegm-Heat in the Lungs
Learn moreAll Formulas Recommended for Wheezing Caused by Phlegm
| Formula | Patterns Suitable For |
|---|---|
| Er Chen Tang | Damp-Phlegm in the Lungs, Phlegm-Heat in the Lungs |
| Bei Mu Gua Lou San | Dry-Phlegm in the Lungs |
| Wen Dan Tang | Phlegm-Heat in the Lungs |
| Qing Qi Hua Tan Wan | Phlegm-Heat in the Lungs |
| Ma Xing Shi Gan Tang | Phlegm-Heat in the Lungs |
| Qing Xin Li Ge Tang | Phlegm-Heat in the Lungs |
| Ren Shen Ge Jie San | Phlegm-Heat in the Lungs |
| Pi Pa Qing Fei Yin | Phlegm-Heat in the Lungs |
| Xiao Qing Long Tang | Phlegm-Fluids above the diaphragm |
Top Formula for Heat:
Er Chen Tang
Suitable for Heat patterns that may cause wheezing, such as Phlegm-Heat in the Lungs
Learn moreAll Formulas Recommended for Wheezing Caused by Heat
| Formula | Patterns Suitable For |
|---|---|
| Er Chen Tang | Phlegm-Heat in the Lungs |
| Bai He Gu Jin Tang | Lung and Kidney Yin Deficiency with Empty Fire |
| Wen Dan Tang | Phlegm-Heat in the Lungs |
| Qing Qi Hua Tan Wan | Phlegm-Heat in the Lungs |
| Ma Xing Shi Gan Tang | Phlegm-Heat in the Lungs |
| Qing Xin Li Ge Tang | Phlegm-Heat in the Lungs |
| Ren Shen Ge Jie San | Phlegm-Heat in the Lungs |
| Pi Pa Qing Fei Yin | Phlegm-Heat in the Lungs |
Top Formula for Yin Deficiency:
Bai He Gu Jin Tang
Suitable for Yin Deficiency patterns that may cause wheezing, such as Lung and Kidney Yin Deficiency with Empty Fire
Learn moreTop Formula for Yang Deficiency:
Gan Cao Gan Jiang Tang
Suitable for Yang Deficiency patterns that may cause wheezing, such as Lung Yang Deficiency
Learn moreAll Formulas Recommended for Wheezing Caused by Yang Deficiency
| Formula | Patterns Suitable For |
|---|---|
| Gan Cao Gan Jiang Tang | Lung Yang Deficiency |
| Si Jun Zi Tang | Lung Yang Deficiency |
| Sheng Mai San | Lung Yang Deficiency |
Top Formula for Dampness:
Er Chen Tang
Suitable for Dampness patterns that may cause wheezing, such as Damp-Phlegm in the Lungs
Learn moreTop Formula for Dryness:
Bei Mu Gua Lou San
Suitable for Dryness patterns that may cause wheezing, such as Dry-Phlegm in the Lungs
Learn moreFormulas that tonify Qi
These formulas are suitable for some wheezing-causing patterns like Lung Yang Deficiency.
One such formula is Si Jun Zi Tang, with ginseng as a key herb.
Other formulas of this category are listed in the table below.
All "formulas that tonify qi" recommended for wheezing
| Formula | Patterns Suitable For (if applicable) |
|---|---|
| Si Jun Zi Tang | Lung Yang Deficiency |
| Sheng Mai San | Lung Yang Deficiency |
| Ren Shen Ge Jie San | Phlegm-Heat in the Lungs |
Formulas that dry Dampness and transform Phlegm
These formulas are suitable for some wheezing-causing patterns like Damp-Phlegm in the Lungs or Phlegm-Heat in the Lungs.
One such formula is Er Chen Tang, with crow-dipper rhizome as a key herb.
Other formulas of this category are listed in the table below.
All "formulas that dry dampness and transform phlegm" recommended for wheezing
| Formula | Patterns Suitable For (if applicable) |
|---|---|
| Er Chen Tang | Damp-Phlegm in the Lungs, Phlegm-Heat in the Lungs |
| Wen Dan Tang | Phlegm-Heat in the Lungs |
Formulas that clear Wind-Cold
These formulas are suitable for some wheezing-causing patterns like Phlegm-Fluids above the diaphragm.
One such formula is Xiao Qing Long Tang, with ephedra as a key herb.
Other formulas of this category are listed in the table below.
All "formulas that clear wind-Cold" recommended for wheezing
| Formula | Patterns Suitable For (if applicable) |
|---|---|
| Xiao Qing Long Tang | Phlegm-Fluids above the diaphragm |
| Jin Fei Cao San | Not applicable |
Formulas that nourish Yin and tonify
These formulas are suitable for some wheezing-causing patterns like Lung and Kidney Yin Deficiency with Empty Fire.
One such formula is Bai He Gu Jin Tang, with lily bulb as a key herb.
Formulas that dispel Phlegm
These formulas are suitable for some wheezing-causing patterns like Dry-Phlegm in the Lungs.
One such formula is Bei Mu Gua Lou San, with fritillary bulb as a key herb.
Formulas that warm Interior Cold
These formulas are suitable for some wheezing-causing patterns like Lung Yang Deficiency.
One such formula is Gan Cao Gan Jiang Tang, with dried ginger as a key herb.
Formulas that clear Heat and transform Phlegm
These formulas are suitable for some wheezing-causing patterns like Phlegm-Heat in the Lungs.
One such formula is Qing Qi Hua Tan Wan, with arisaema with bile as a key herb.
Formulas that clear Heat from the Organs
These formulas are suitable for some wheezing-causing patterns like Phlegm-Heat in the Lungs.
One such formula is Ma Xing Shi Gan Tang, with ephedra as a key herb.
Formulas that clear internal abscesses and sores
These formulas are suitable for some wheezing-causing patterns like Phlegm-Heat in the Lungs.
One such formula is Qing Xin Li Ge Tang, with saposhnikovia root as a key herb.
Formulas that clear Lung-Heat
These formulas are suitable for some wheezing-causing patterns like Phlegm-Heat in the Lungs.
One such formula is Pi Pa Qing Fei Yin, with loquat leaves as a key herb.
Formulas that warm Yang and tonify
Wheezing can be treated by these formulas if it stems from a depletion of Yang energy, requiring actions that warm and strengthen Yang.
One such formula is Ji Sheng Shen Qi Wan, with prepared aconite as a key herb.
Acupoints for Wheezing
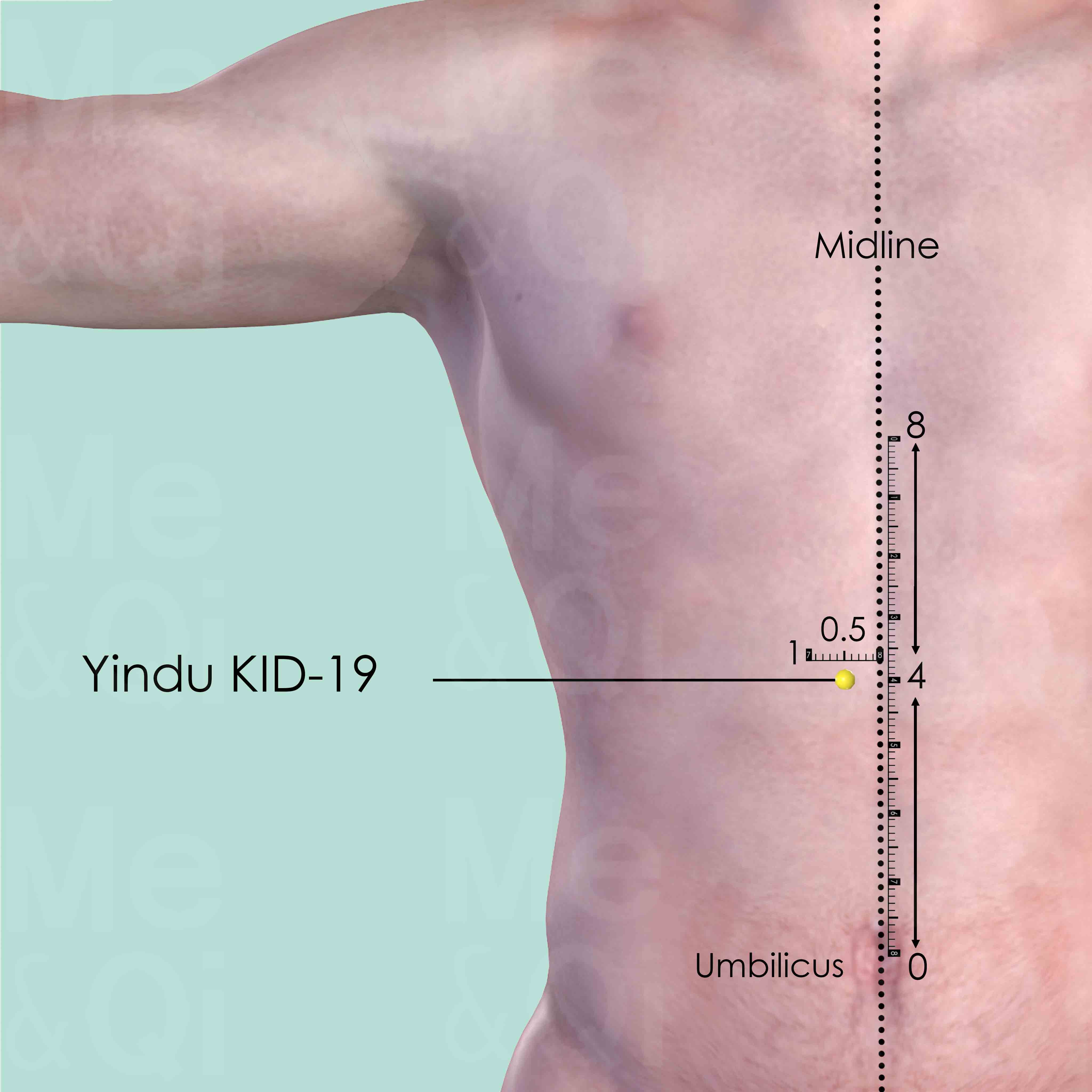
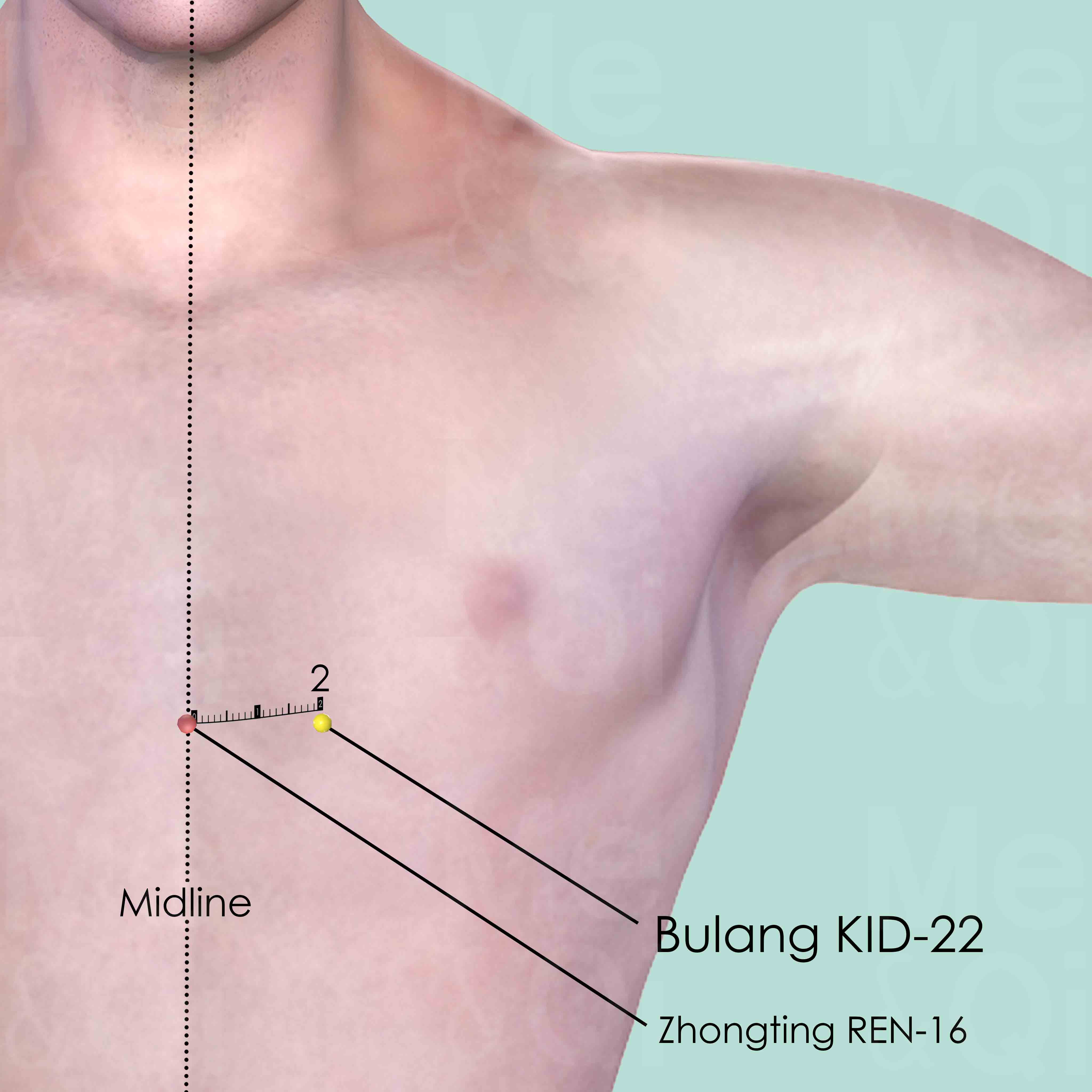
TCM also incorporates acupuncture as part of its holistic approach. Effective acupoints for wheezing include Bulang KID-22 and Dazhong KID-4 in the Kidney Channel, which help in subduing rebellious Qi and strengthening the kidney's Qi reception. In the Lung Channel, points like Chize LU-5 and Jingqu LU-8 are used to clear lung heat and regulate Qi. These acupoints are selected based on their ability to directly influence the lung and kidney systems, which are crucial in the treatment of wheezing.
Explore below some acupoints used to address wheezing, organized by meridian.
- By Meridian
- Kidney Channel
- Lung Channel
- Directing Vessel
- Bladder Channel
- Stomach Channel
- Extra Points: Back (EX-B)
- Large Intestine Channel
- Small Intestine Channel
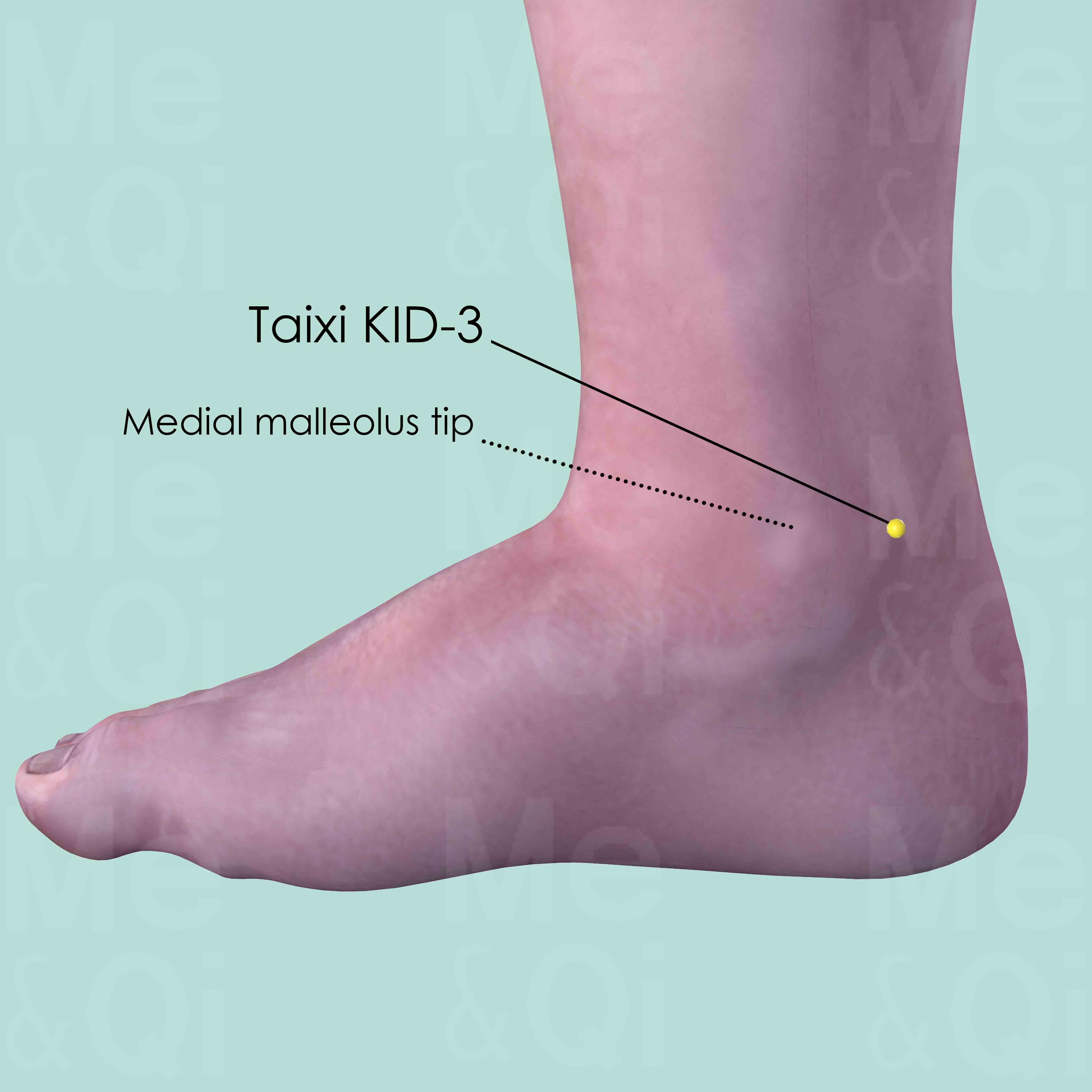
Taixi KID-3
In the depression between the medial malleolus tip and Achilles tendon (Calcaneal tendon), level with the tip of the medial malleolus.
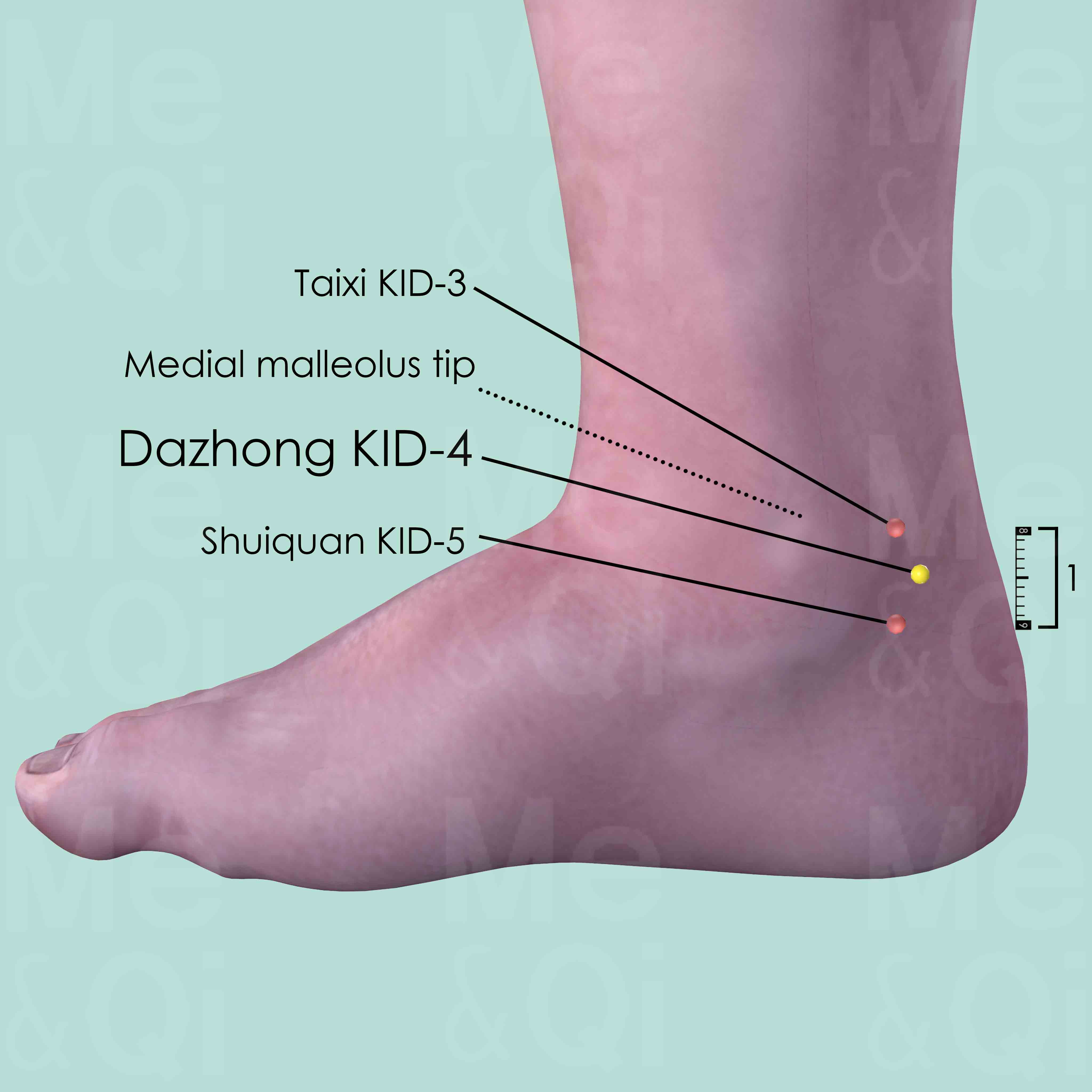
Dazhong KID-4
Posterior and inferior to the medial malleolus, in the depression medial to the Achilles tendon, superior to its insertion at the calcaneus.
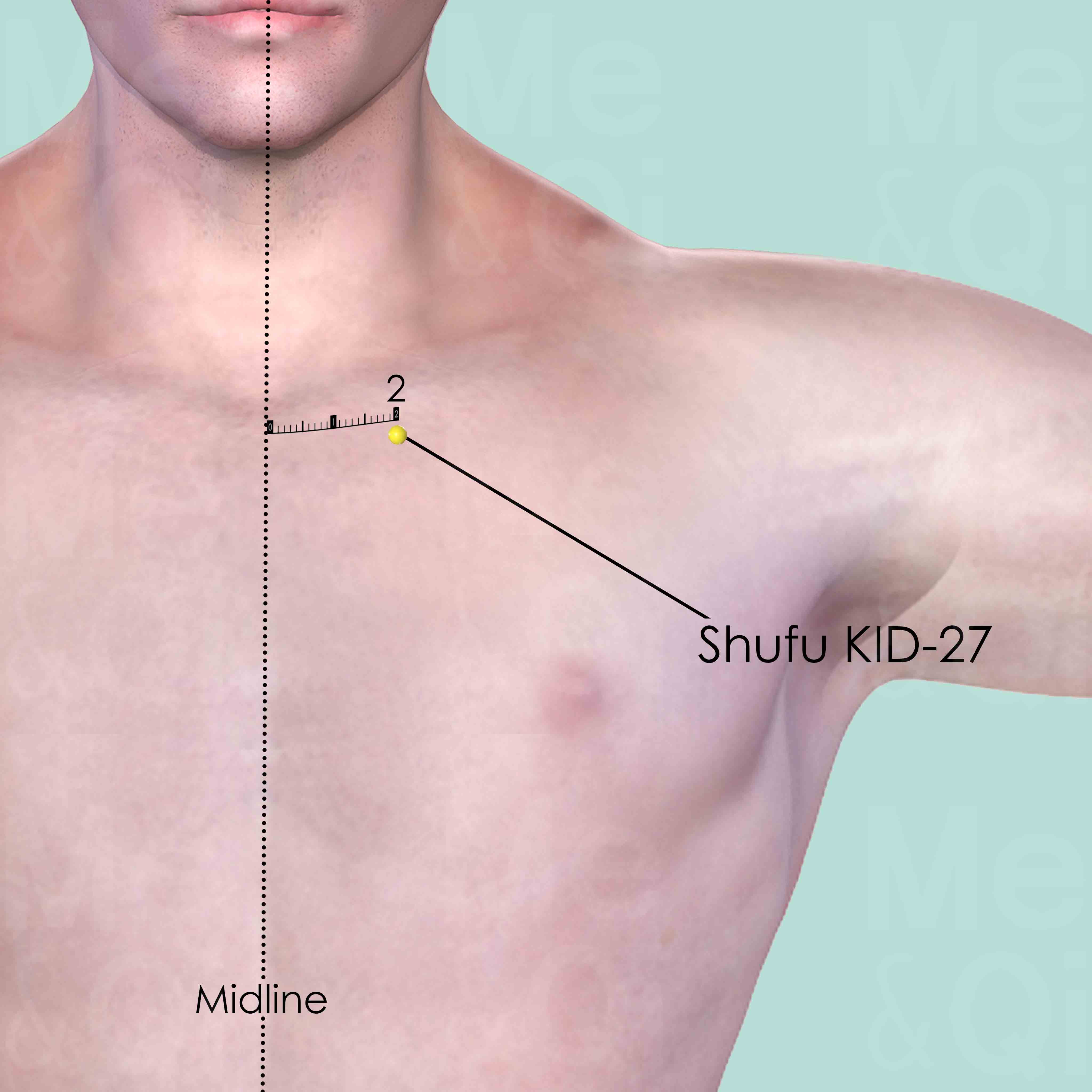
Shufu KID-27
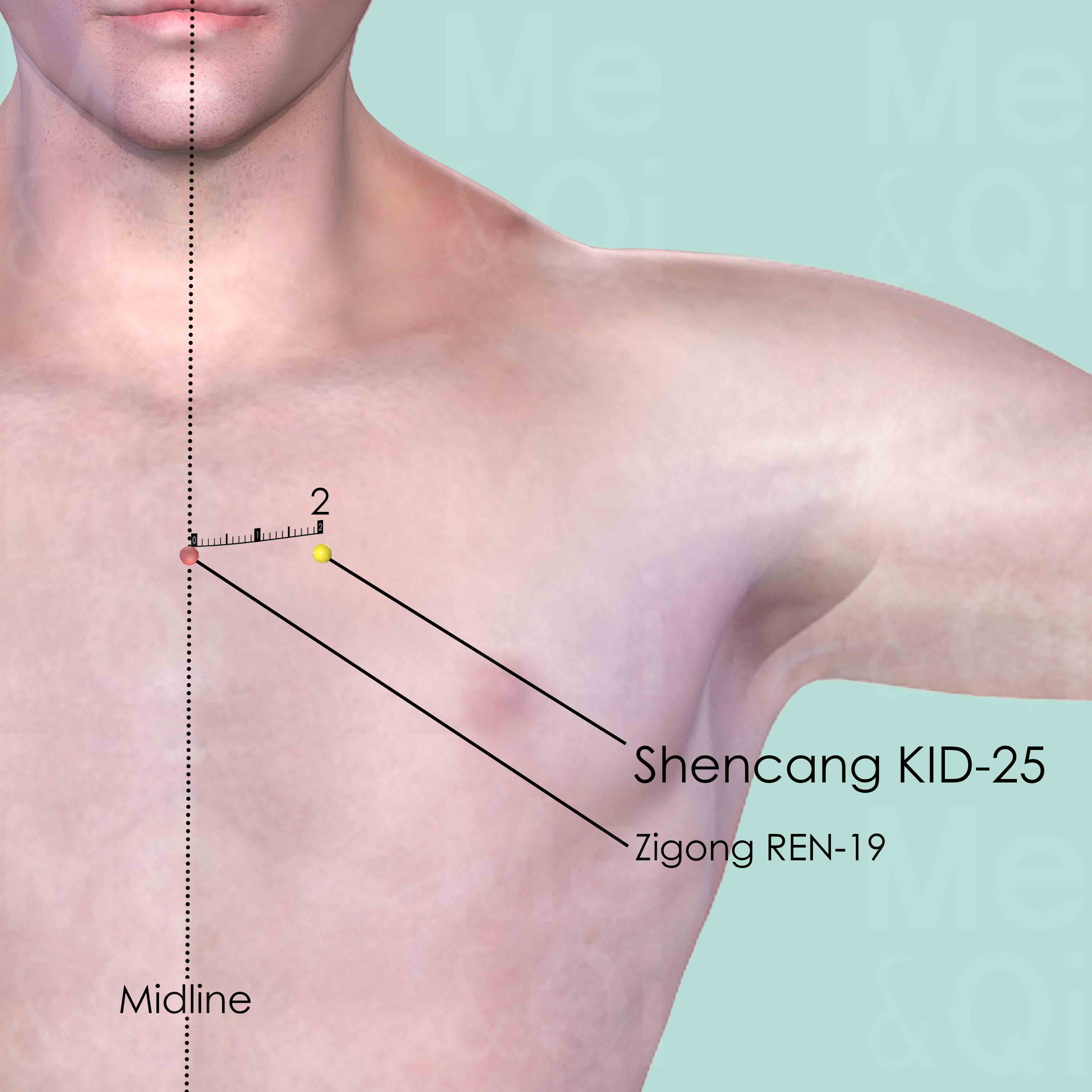
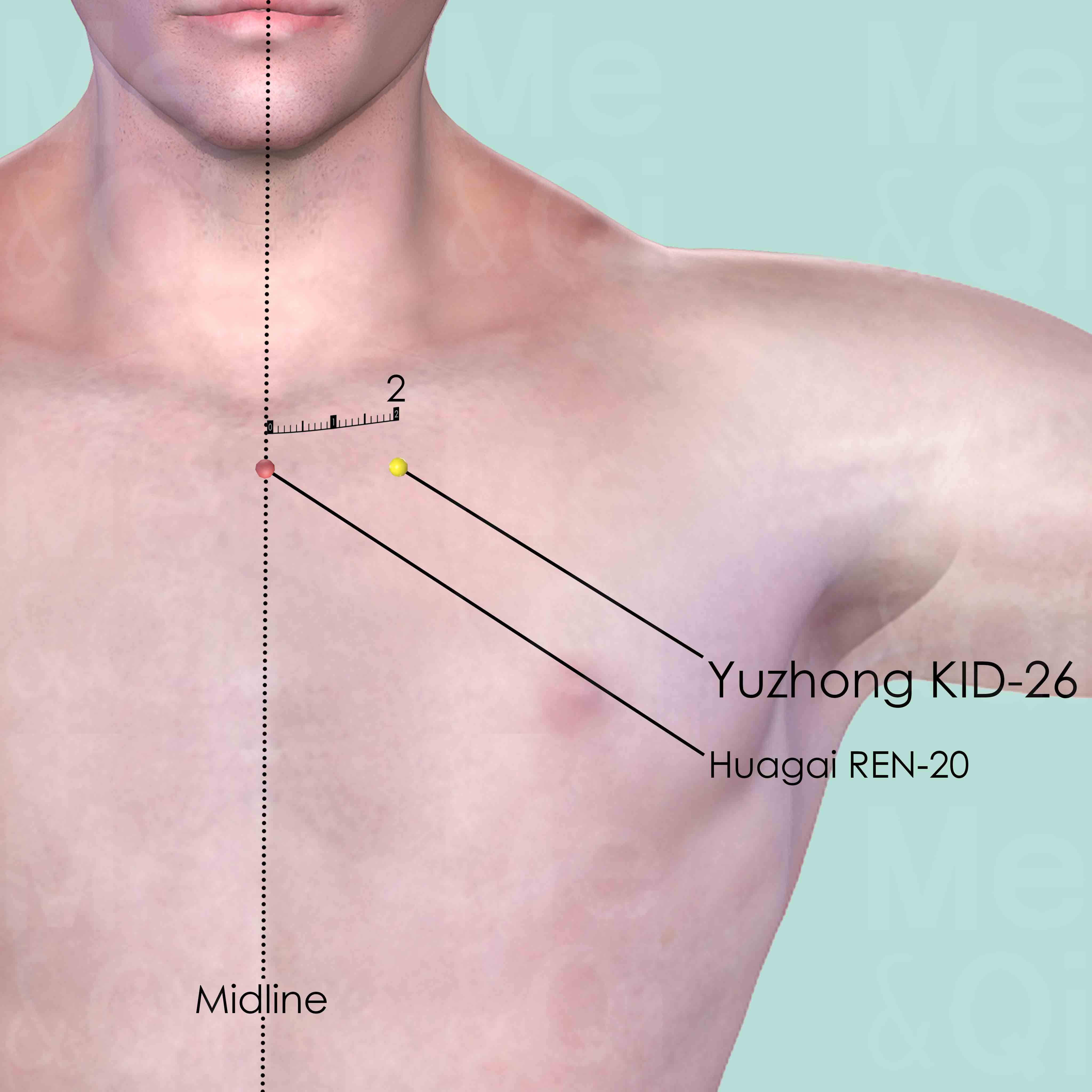
In the depression on the lower border of the clavicle, 2 cun lateral to the anterior midline.
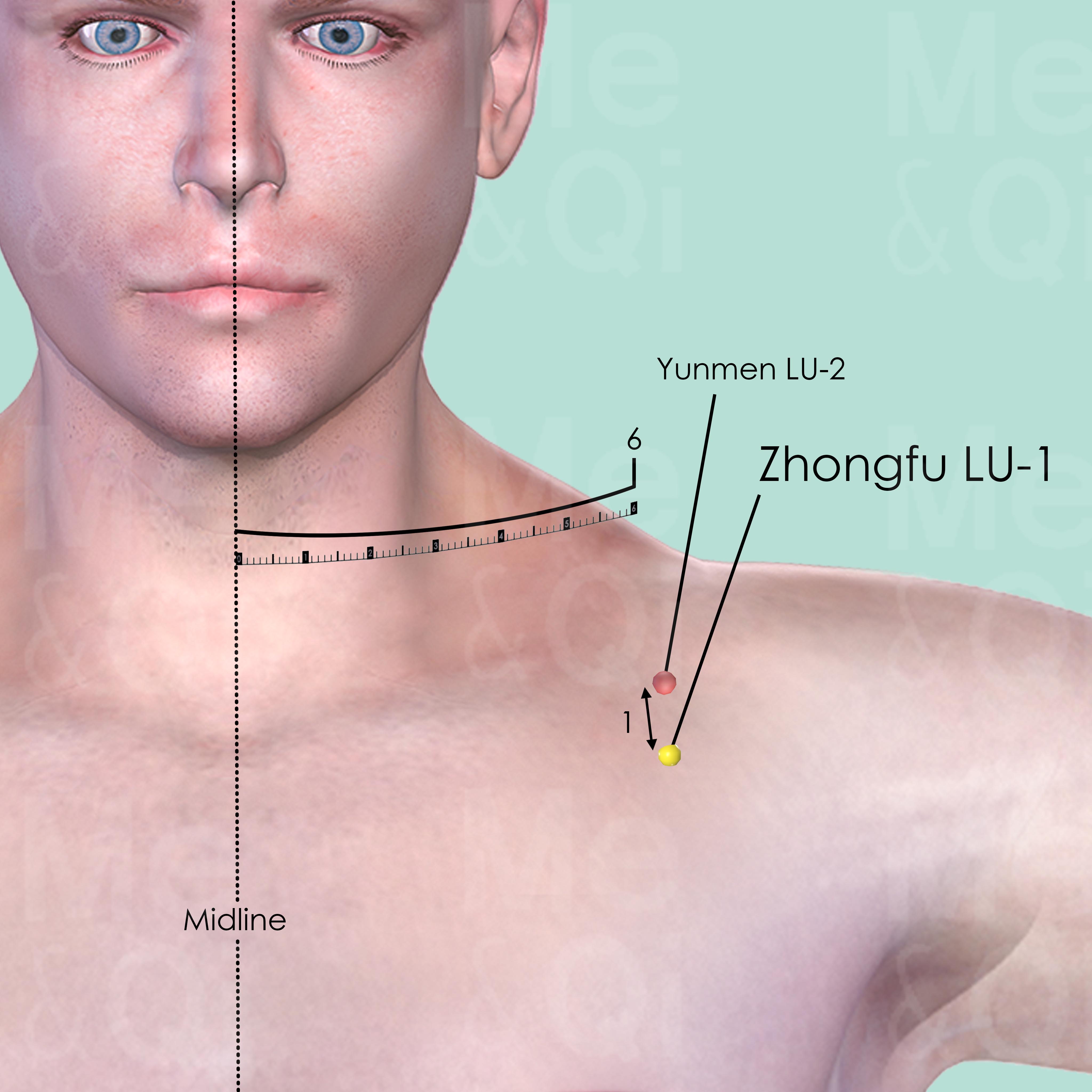
Zhongfu LU-1
On the lateral aspect of the chest, in the 1st intercostal space, 6 cun lateral to the midline, 1 cun inferior to Yunmen LU-2. Below the acromial extremity of the clavicle, slightly medial to the lower border of the coracoid process.
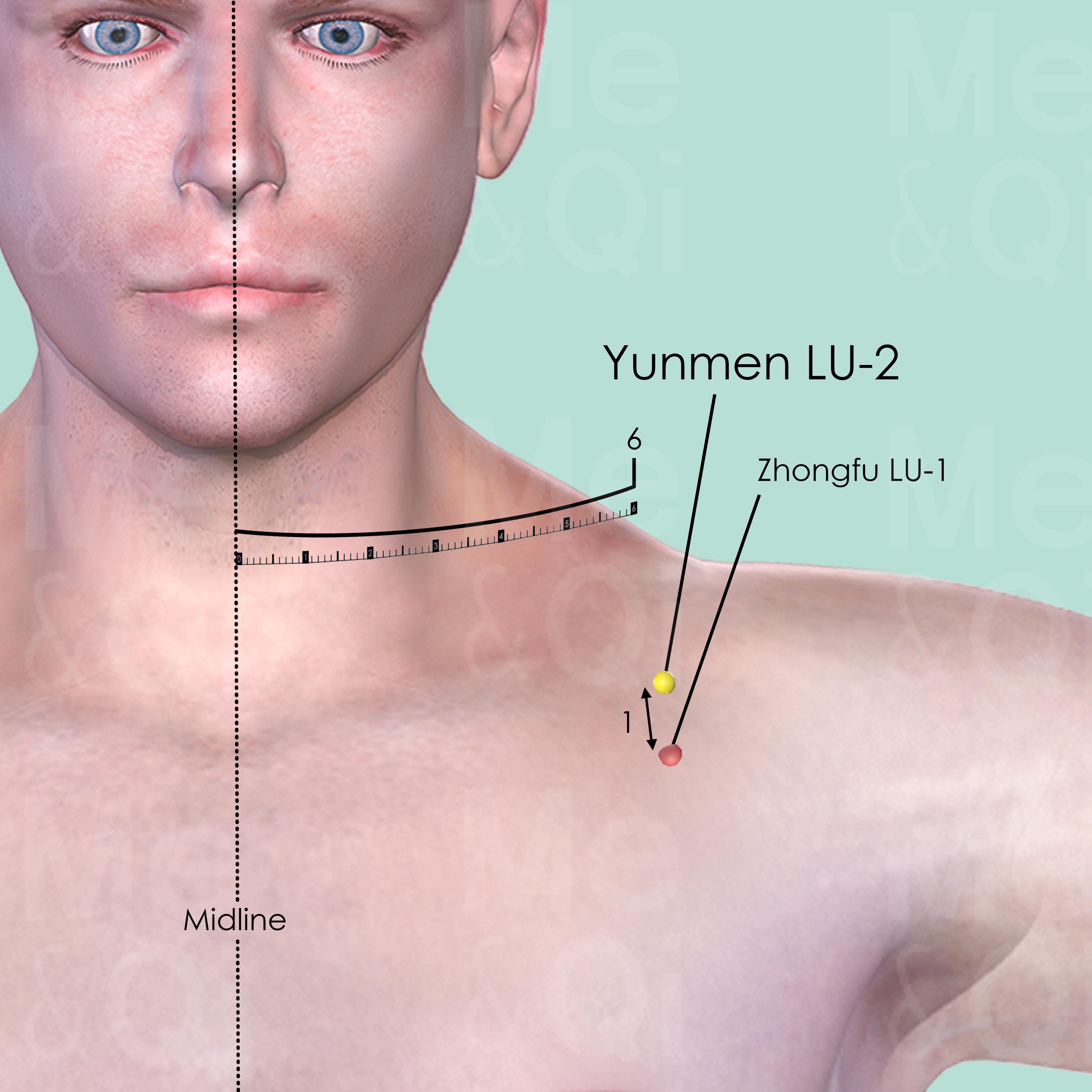
Yunmen LU-2
On the antero-lateral aspect of the chest, below the lateral extremity of the clavicle, about 6 cun lateral to the anterior midline in the centre of the deltopectoral triangle.
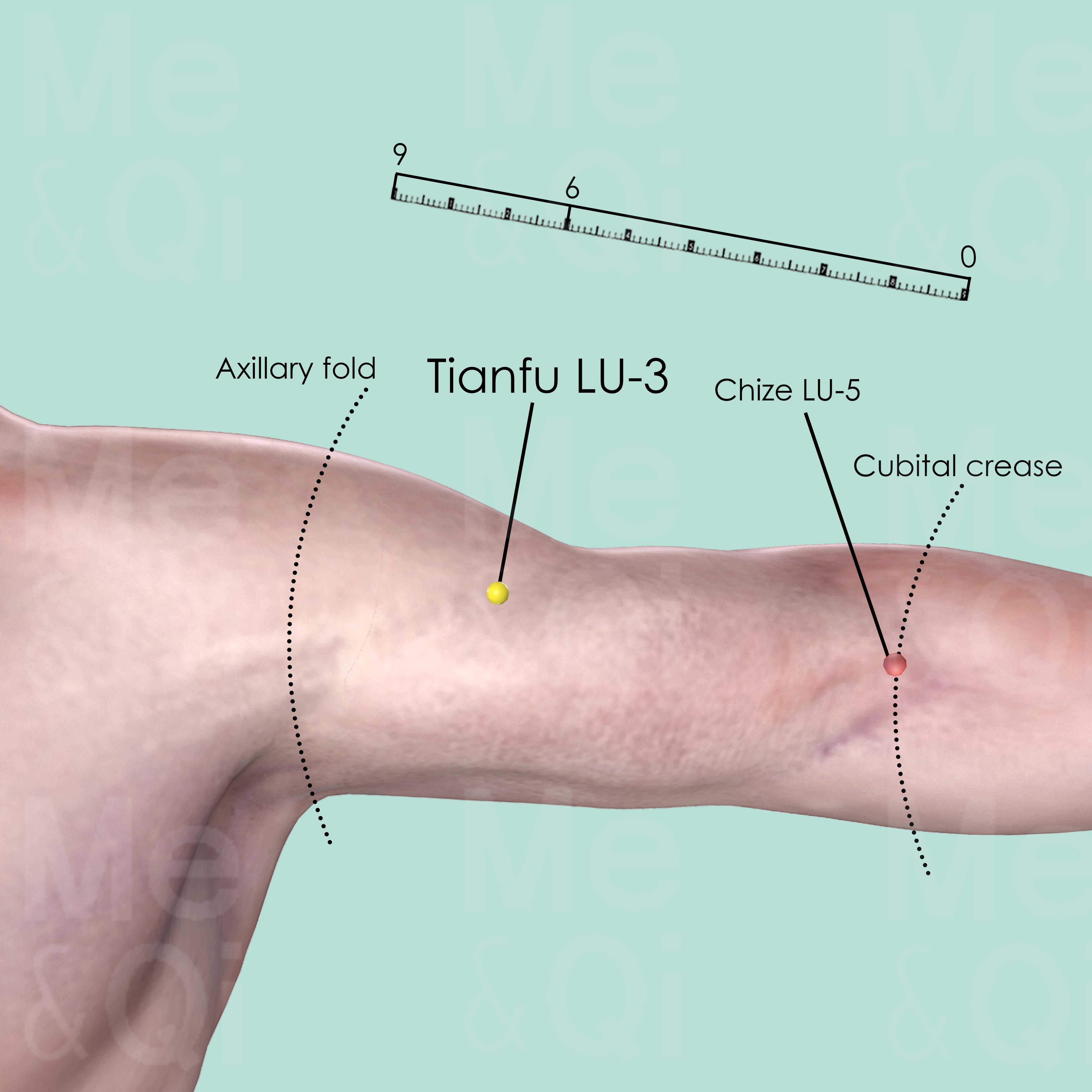
Tianfu LU-3
On the medial aspect of the upper arm, 3 cun below the end of the axillary fold and 6 cun above Chize LU-5, in the depression on the lateral border of biceps muscle.
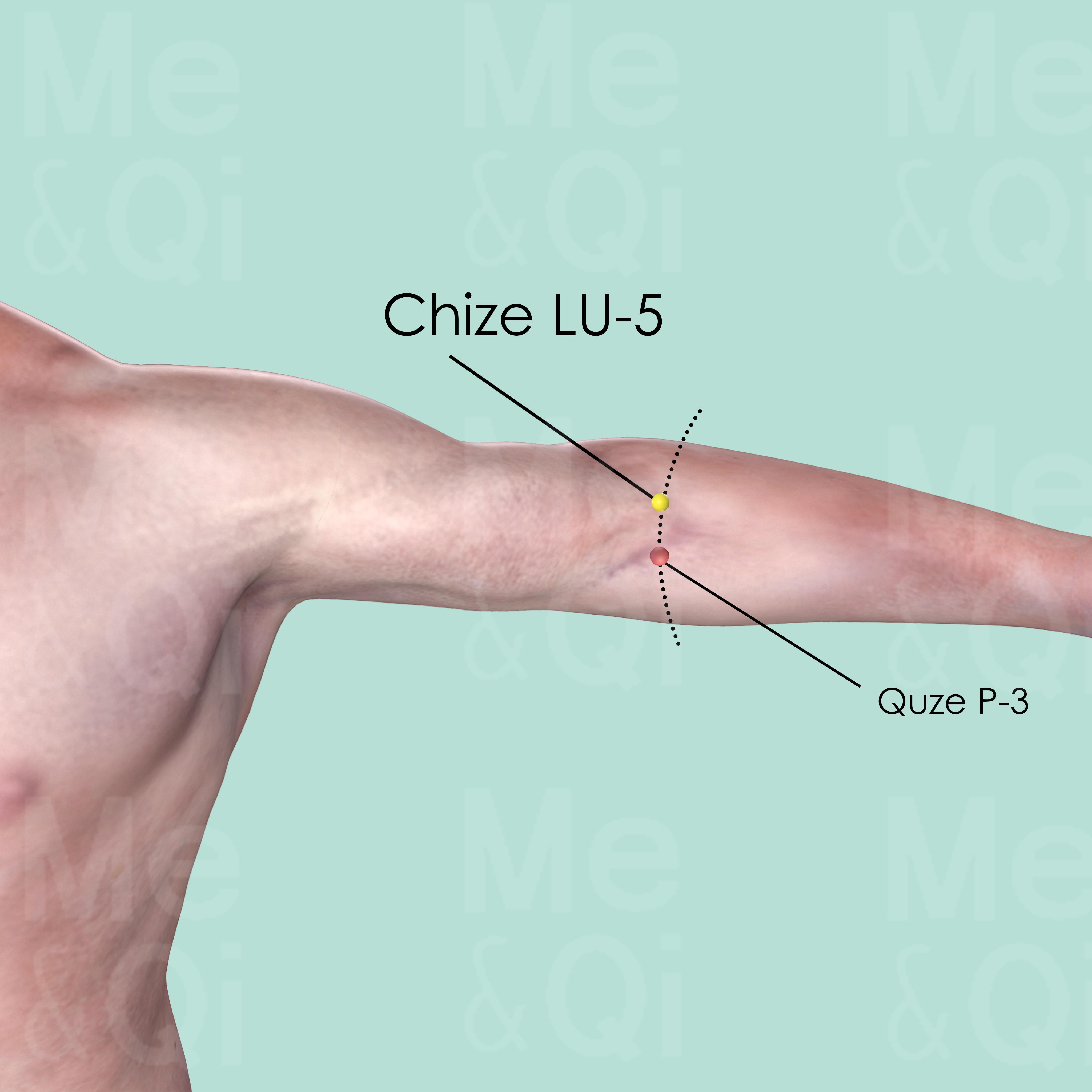
Chize LU-5
On the cubital crease, on the redial aspect of the biceps tendon. It can be easily identified when the elbow is slightly flexed.
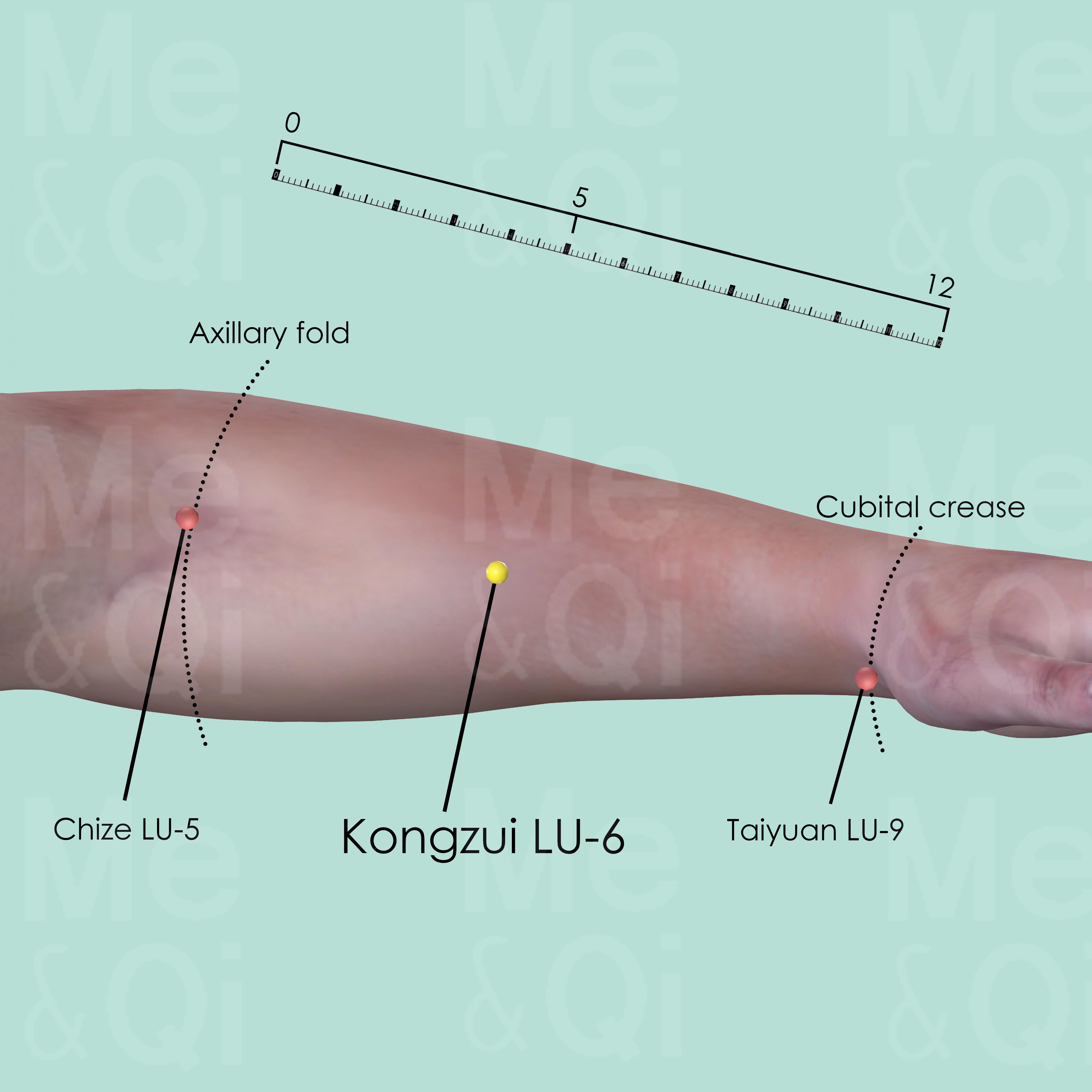
Kongzui LU-6
On the palmar aspect of the forearm, on the line joining Taiyuan LU-9 and Chize LU-5, 7 cun above Taiyuan LU-9.
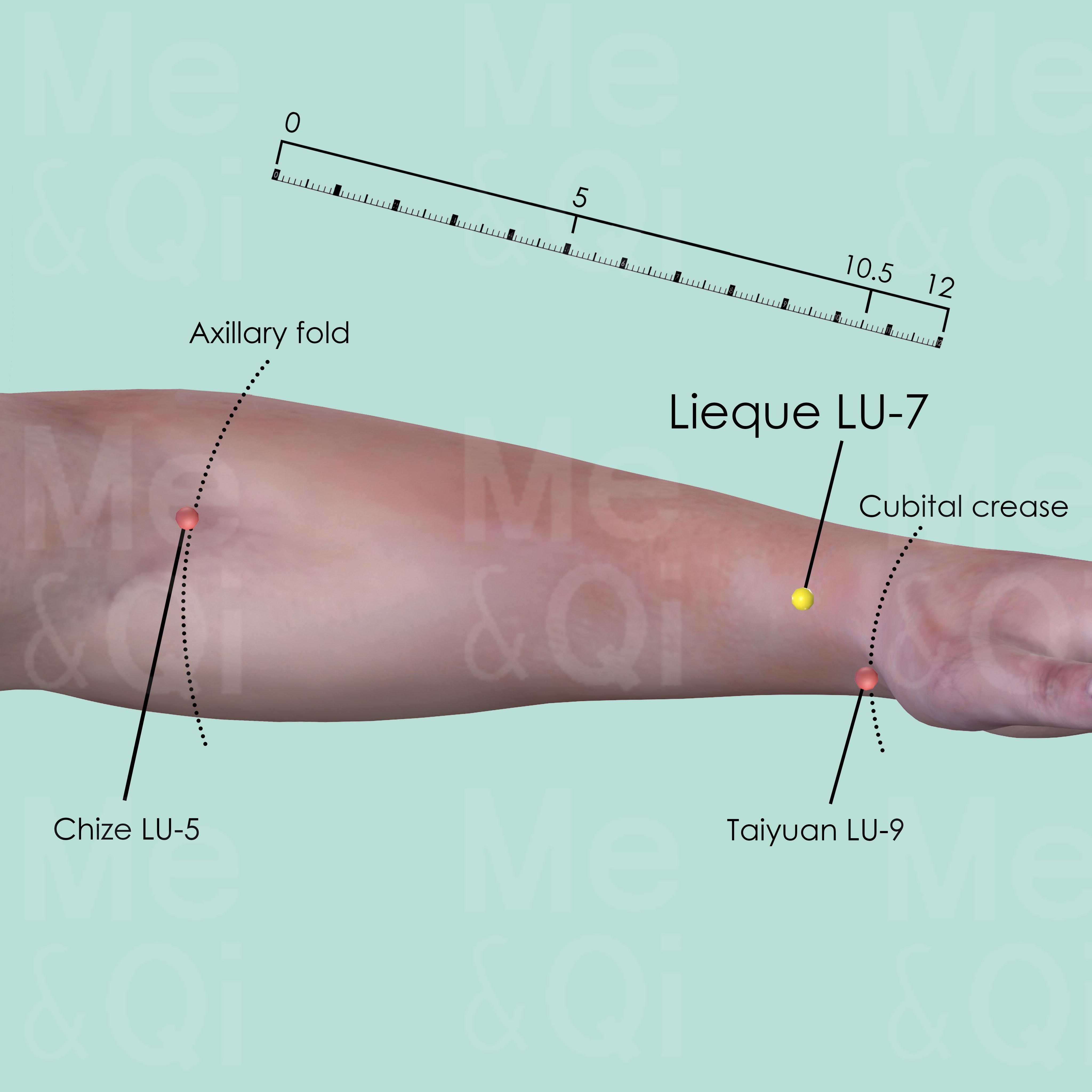
Lieque LU-7
Above the styloid process of the radius, about 1.5 cun proximal to the wrist crease (wrist joint space) in a V-shaped depression.
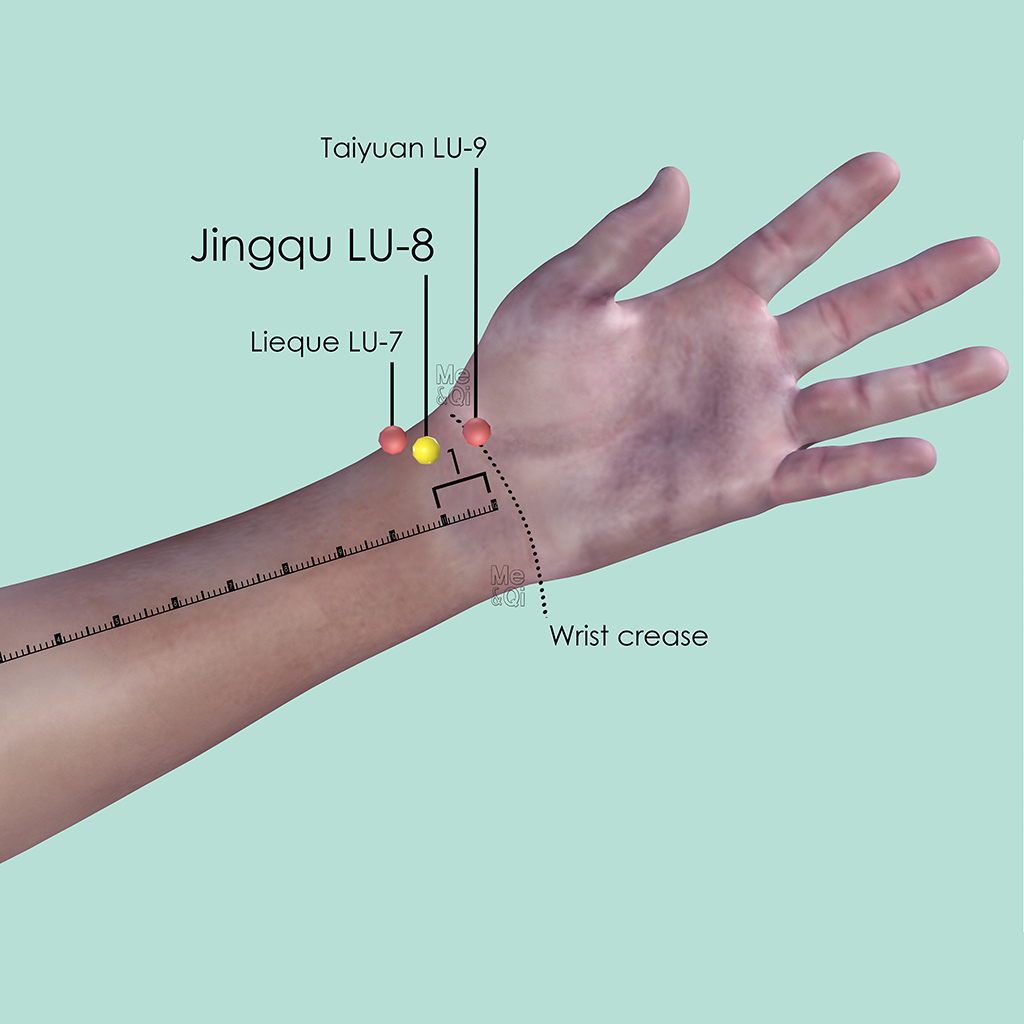
Jingqu LU-8
1 cun proximal to the wrist crease (wrist joint space), in the depression on the radial side of the radial artery.
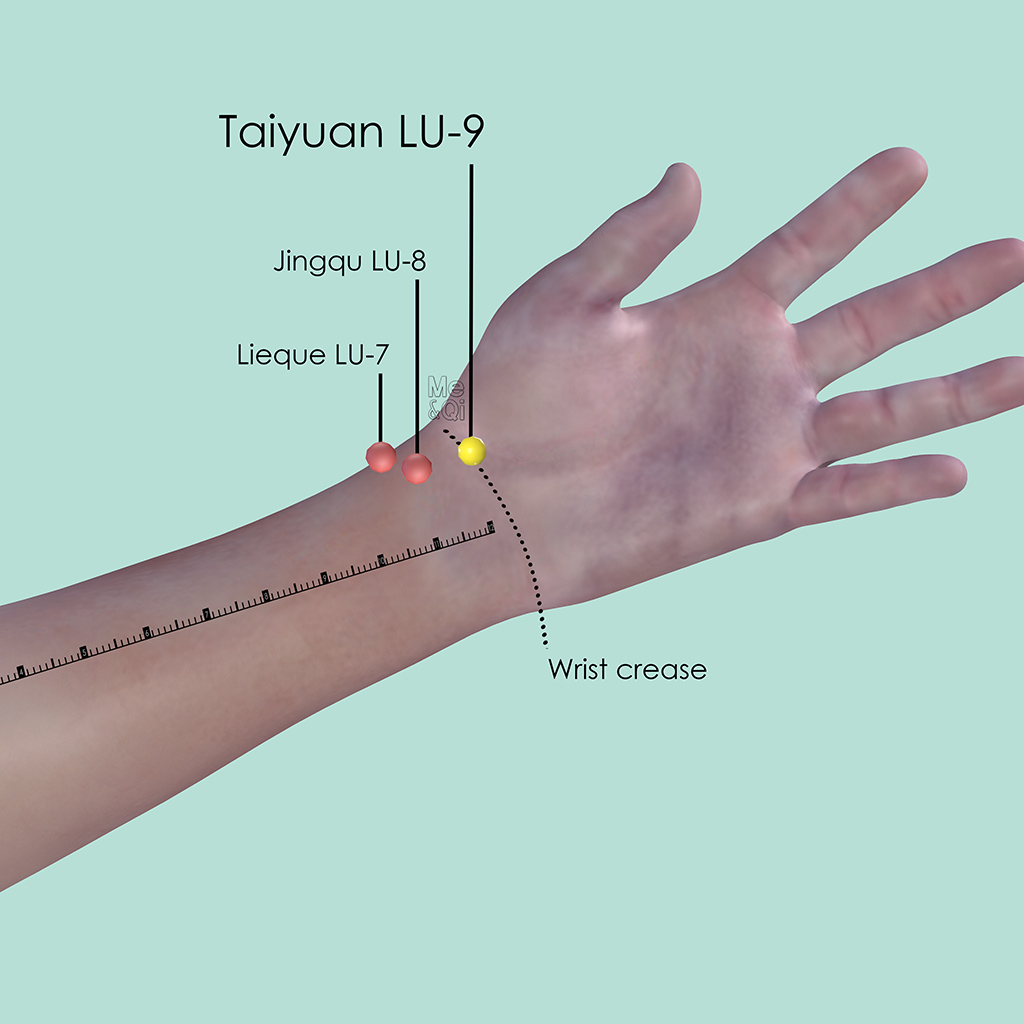
Taiyuan LU-9
At the wrist crease (wrist joint space), in the depression on the radial aspect of the radial artery and ulnar to the tendon of the abductor pollicis longus muscle.
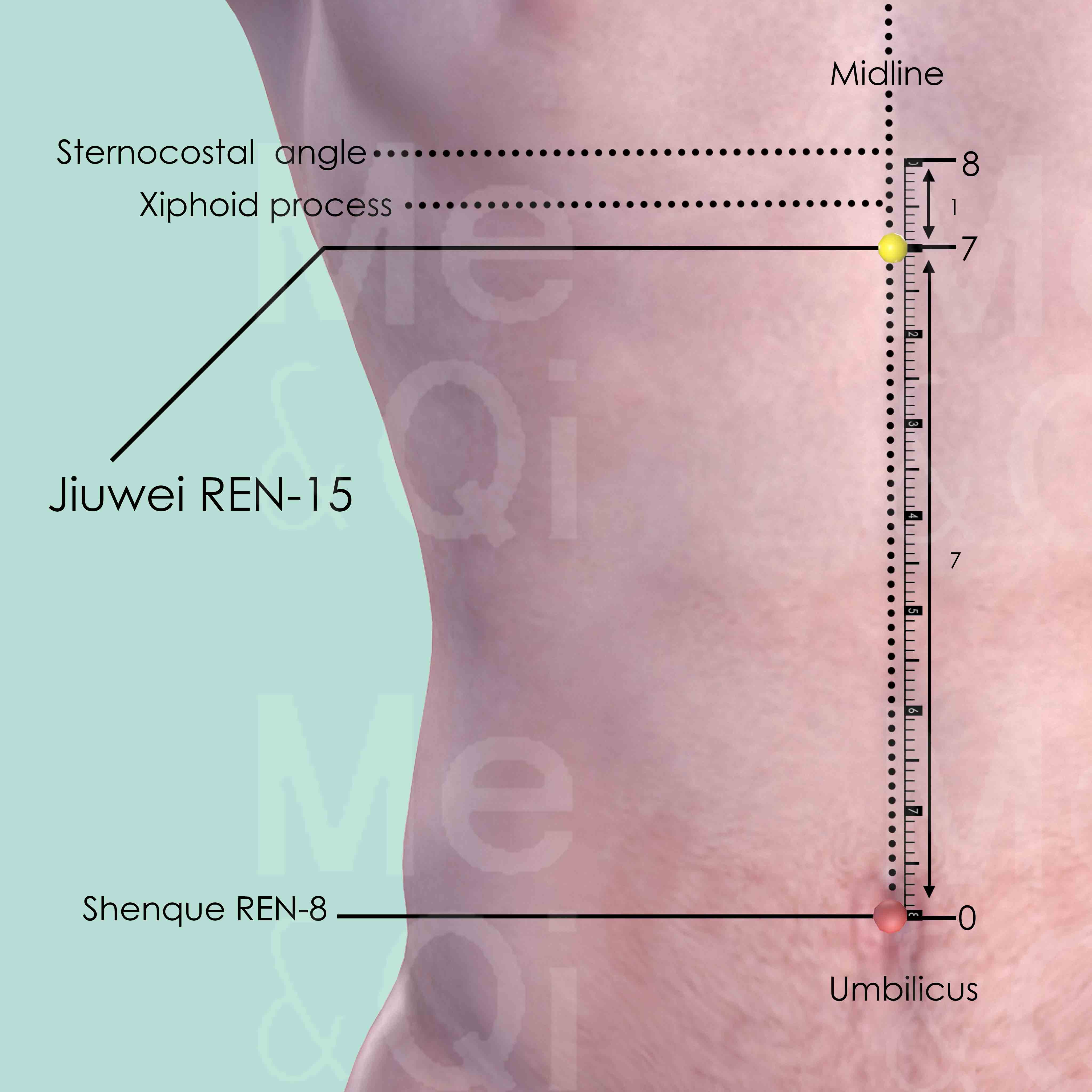
Jiuwei REN-15
On the midline of the abdomen, 7 cun above the umbilicus and 1 cun below the sternocostal angle. This point is located at the tip of the xiphoid process, which is commonly known as ‘dove-tail’ in China, hence the name of the point.
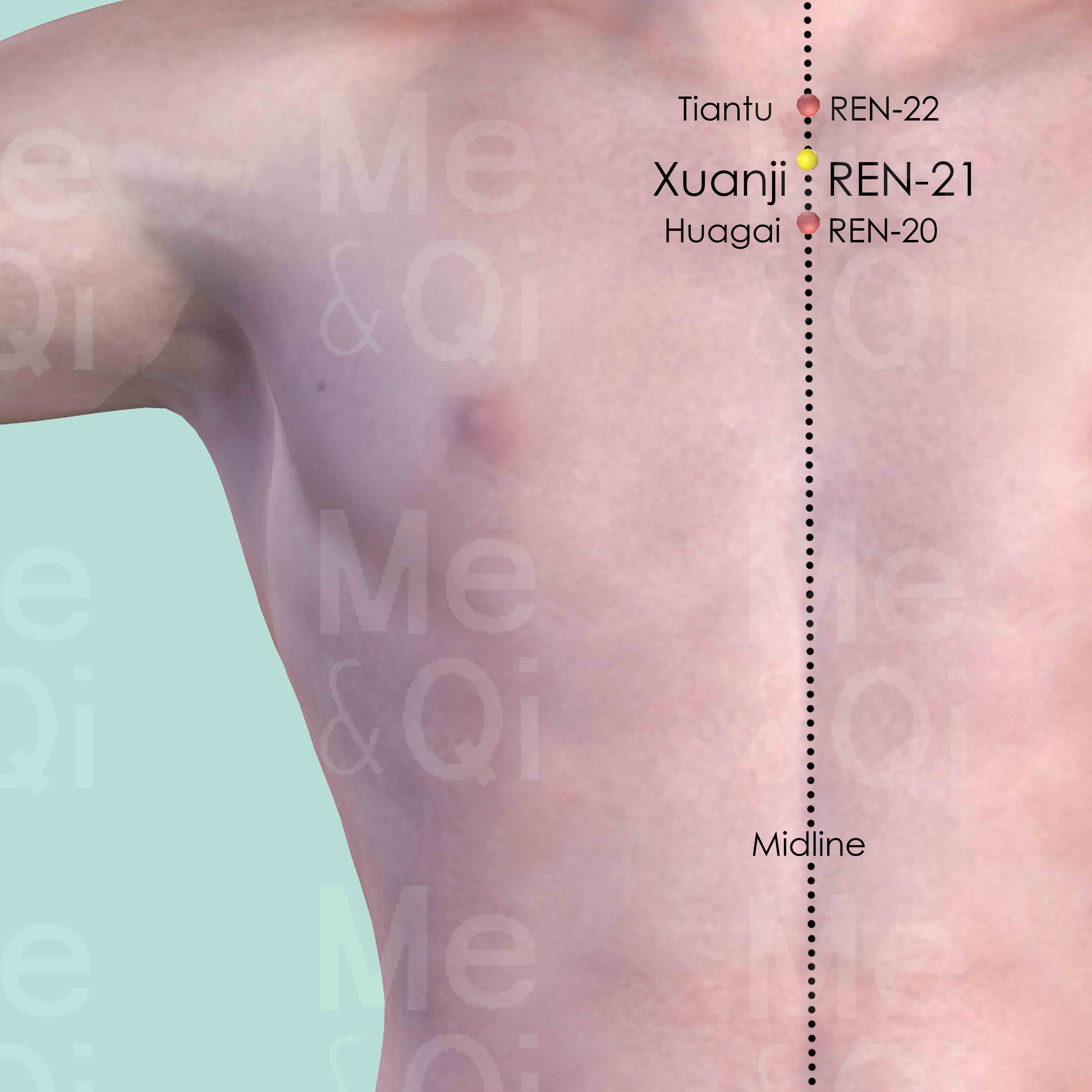
Xuanji REN-21
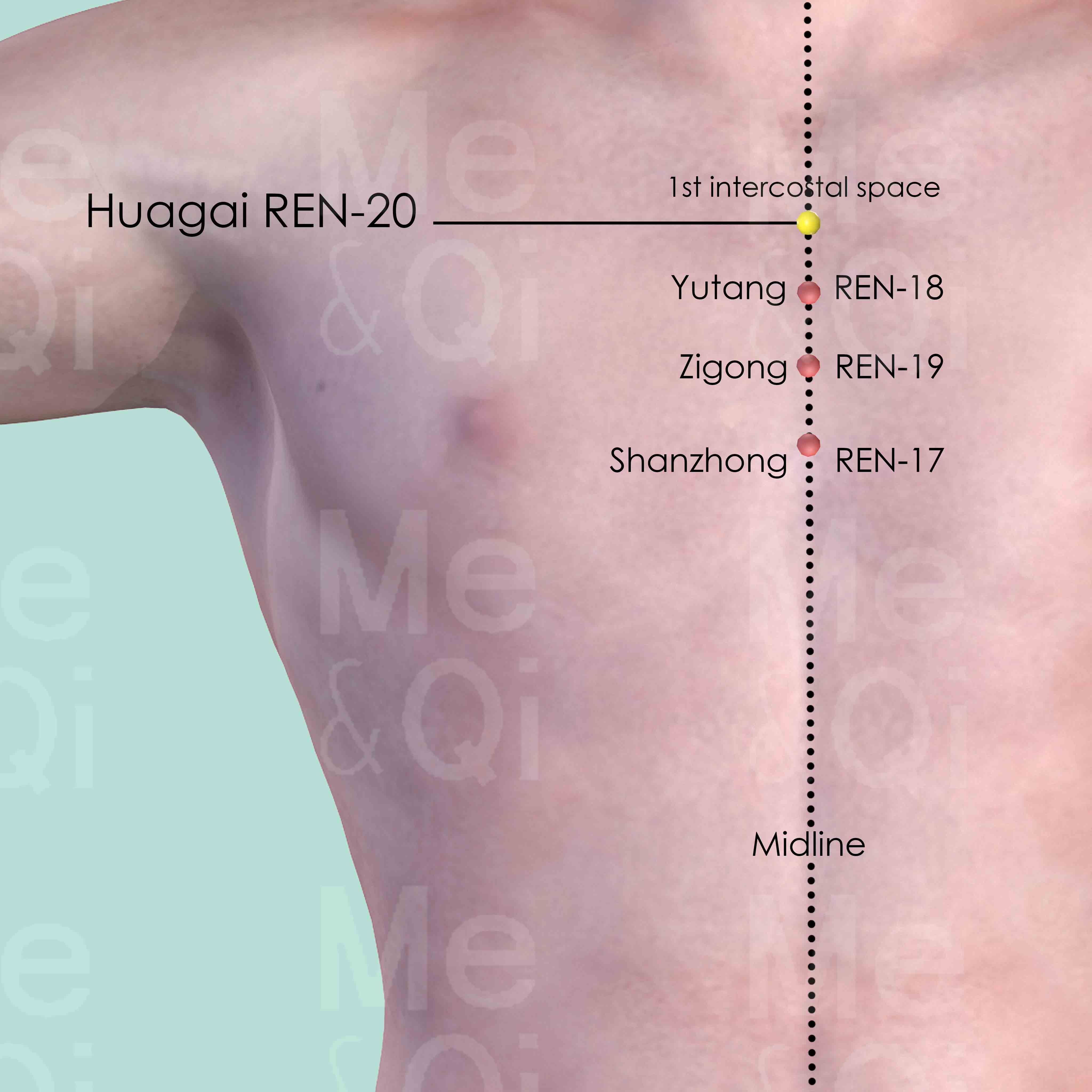
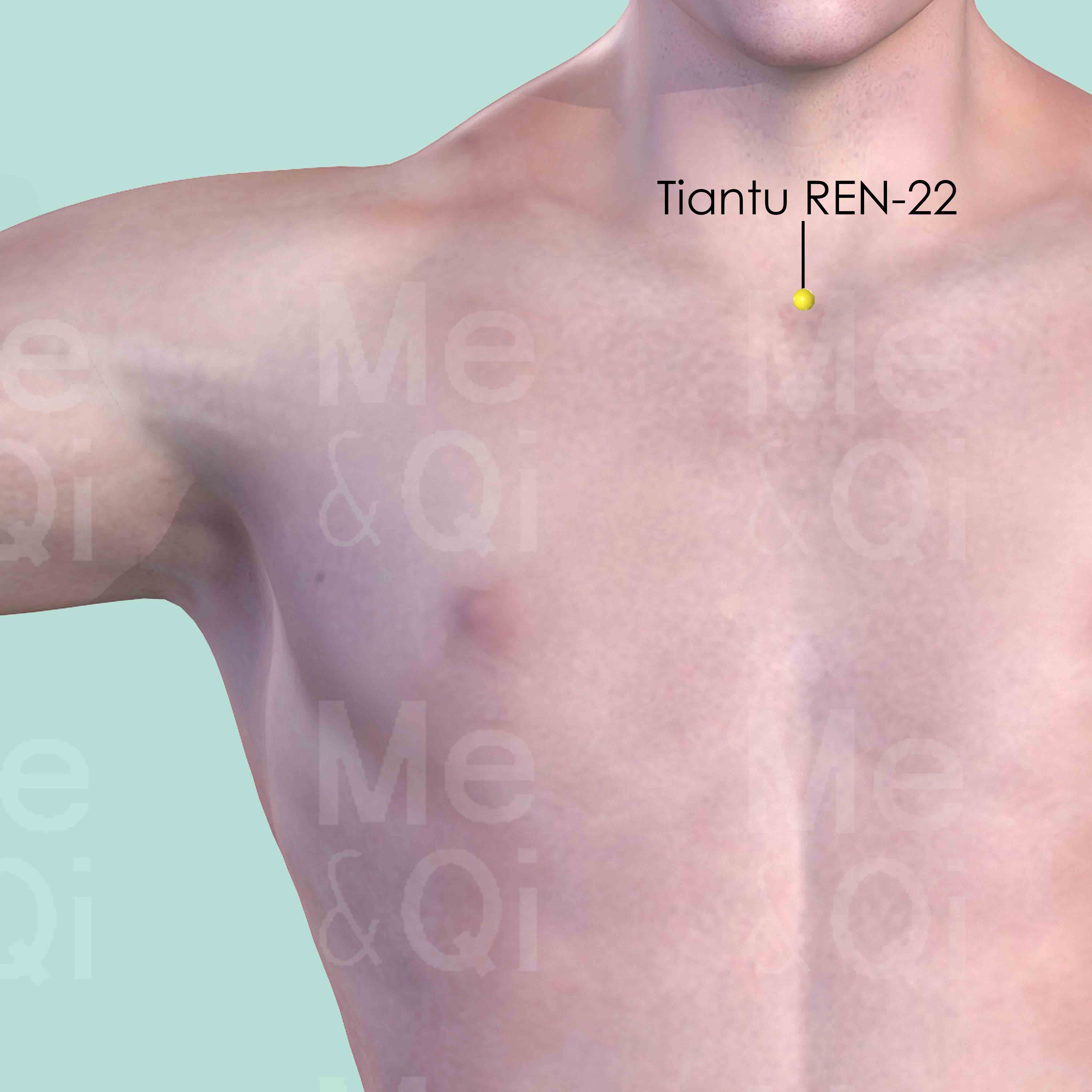
On the midline of the sternum, below the upper border of the manubrium sterni and midway between Huagai REN-20 and Tiantu REN-22.
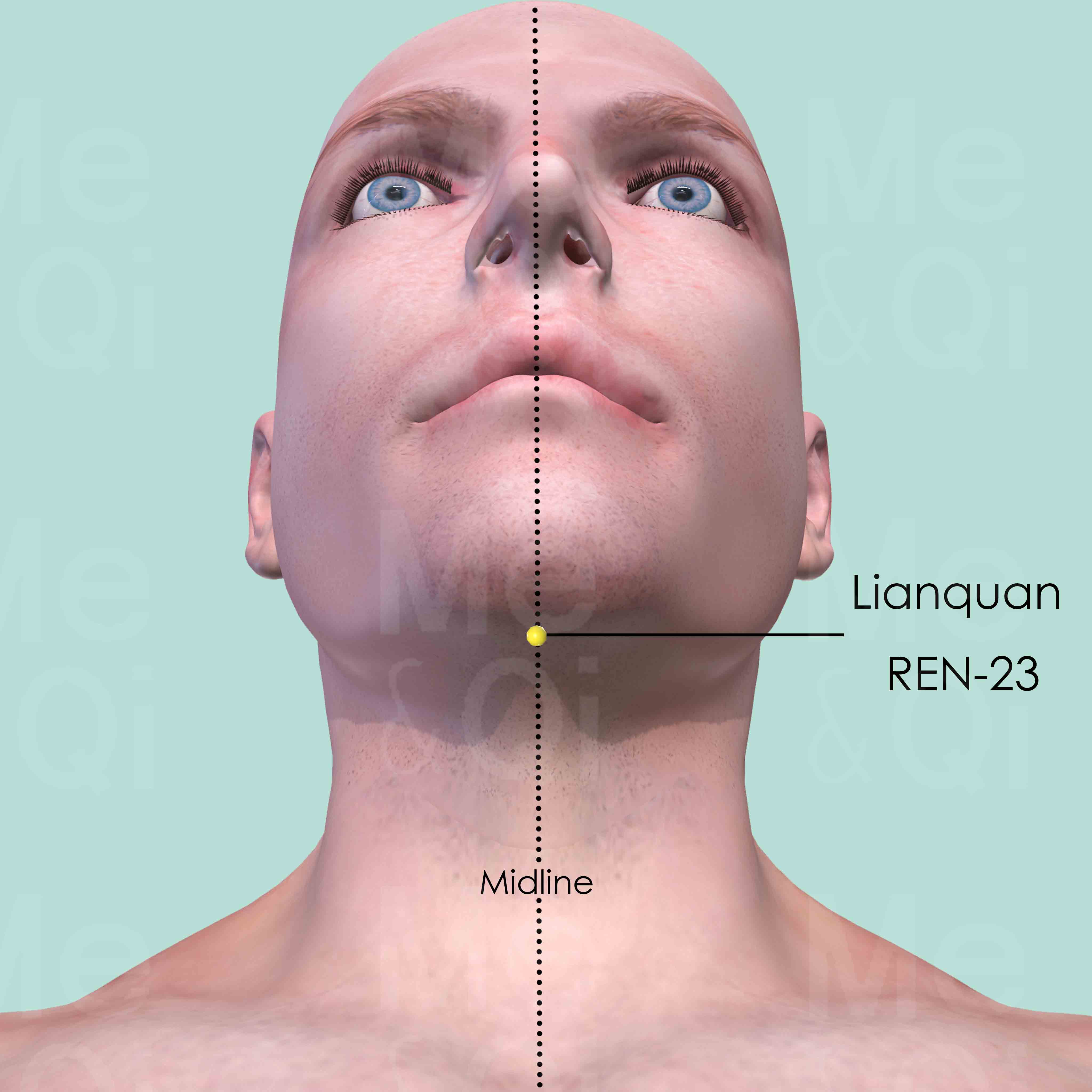
Lianquan REN-23
On the anterior midline of the neck, above the Adm's apple, in the depression at the upper border of the hyoid bone.
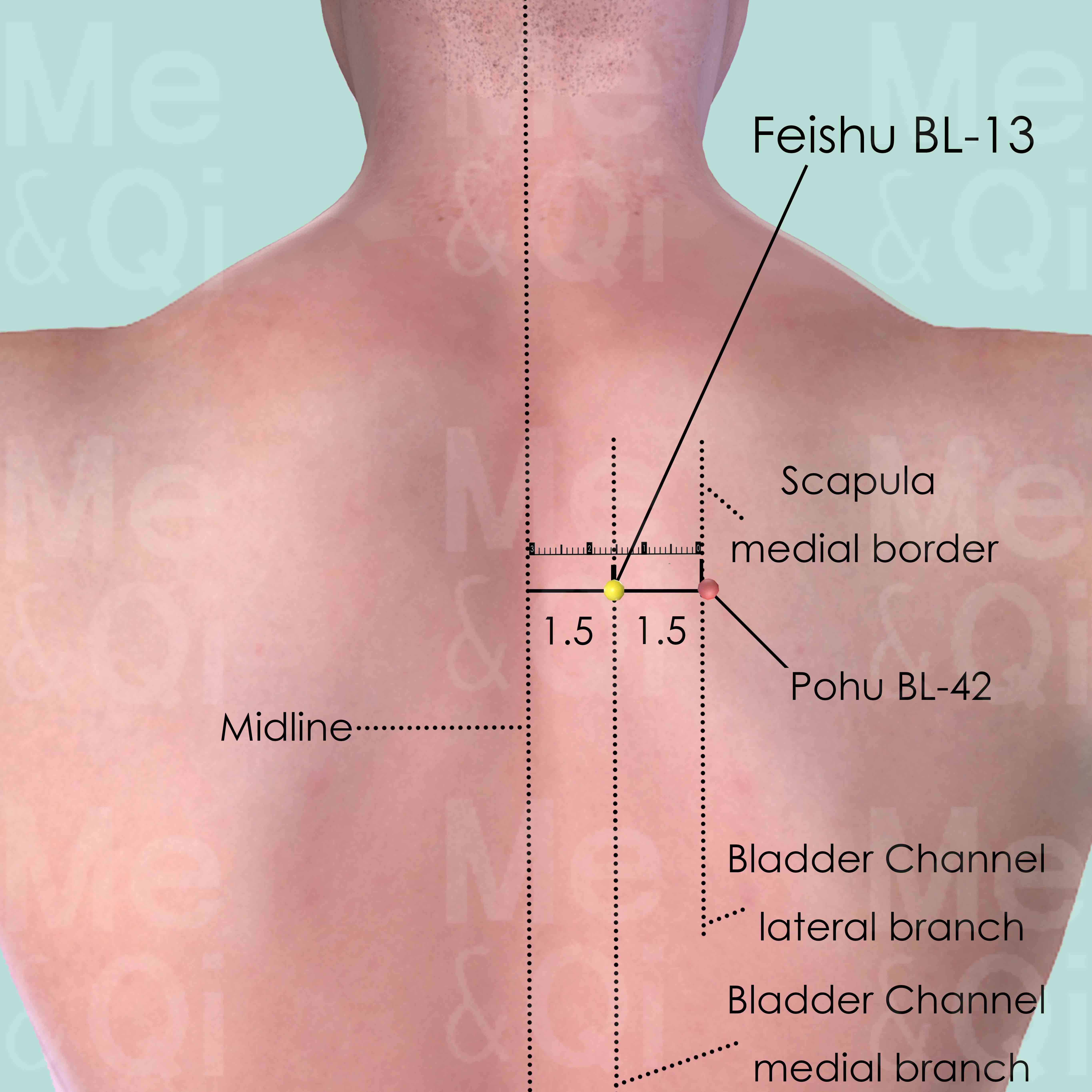
Feishu BL-13
1.5 cun lateral to the lower border of the spinous process of the 3rd thoracic vertebra (T3).
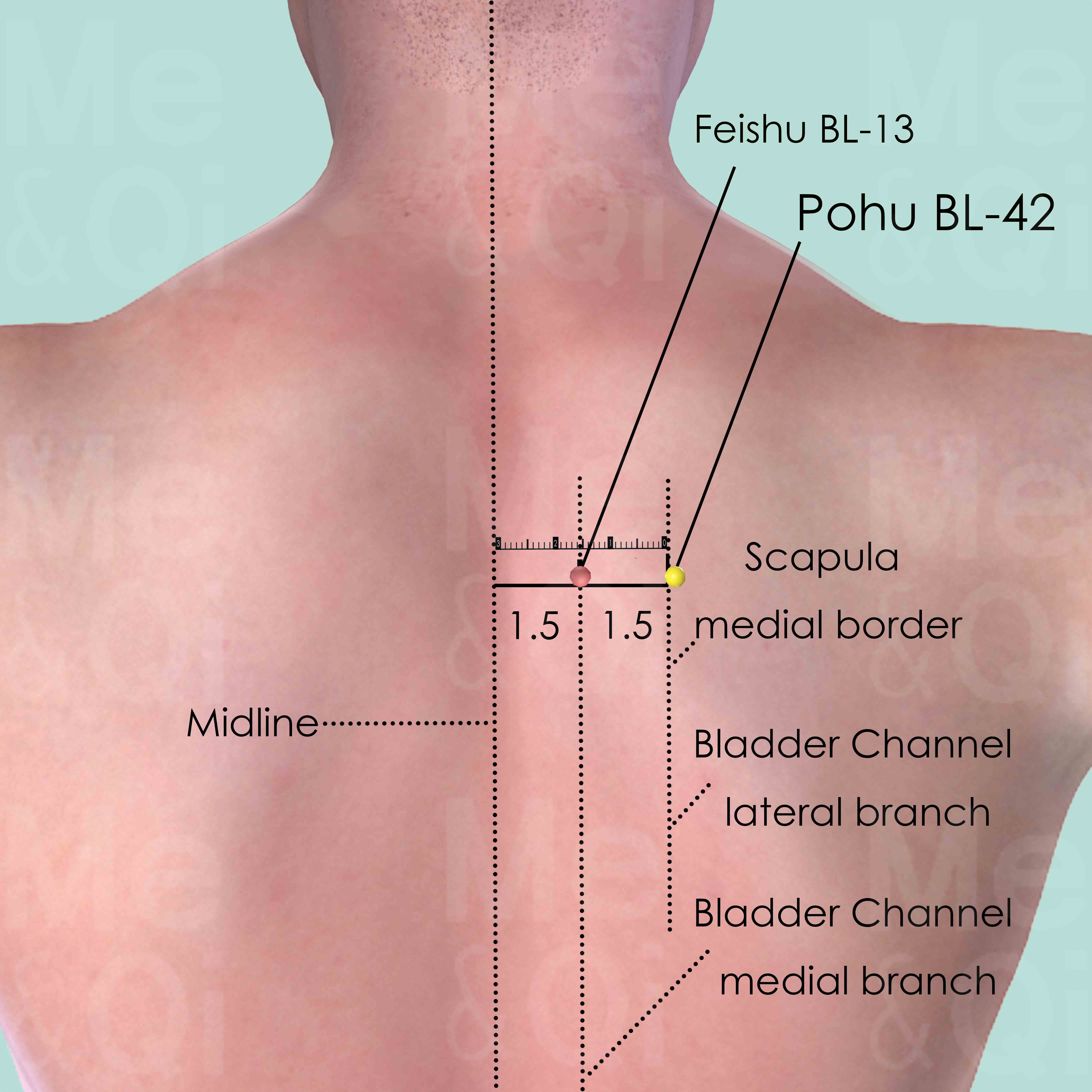
Pohu BL-42
3 cun (about 4 finger-breadths) lateral to the lower border of the spinous process of the 3rd thoracic vertebra (T3).
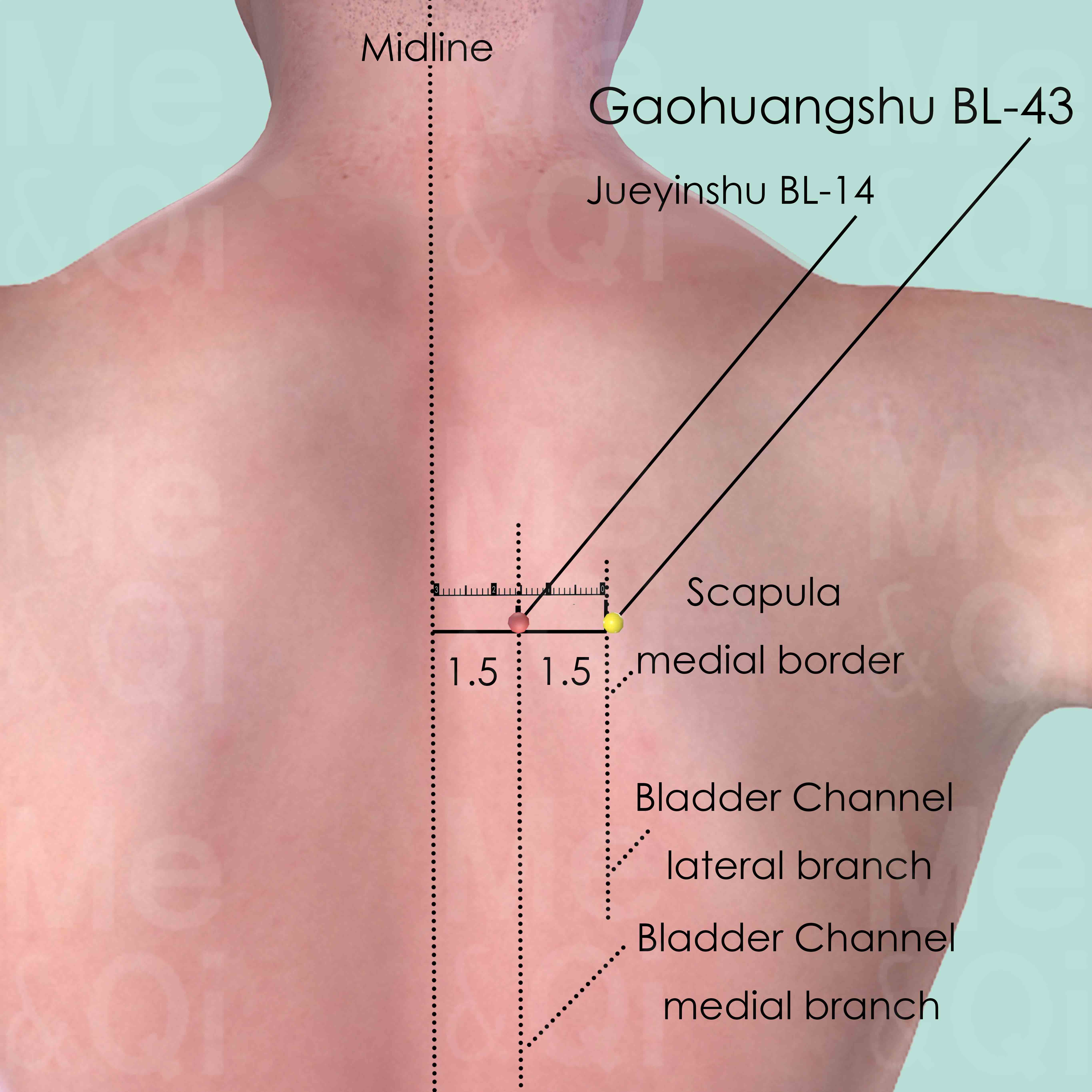
Gaohuangshu BL-43
3 cun (about 4 finger-breadths) lateral to the lower border of the spinous process of the 4th thoracic vertebra (T4).
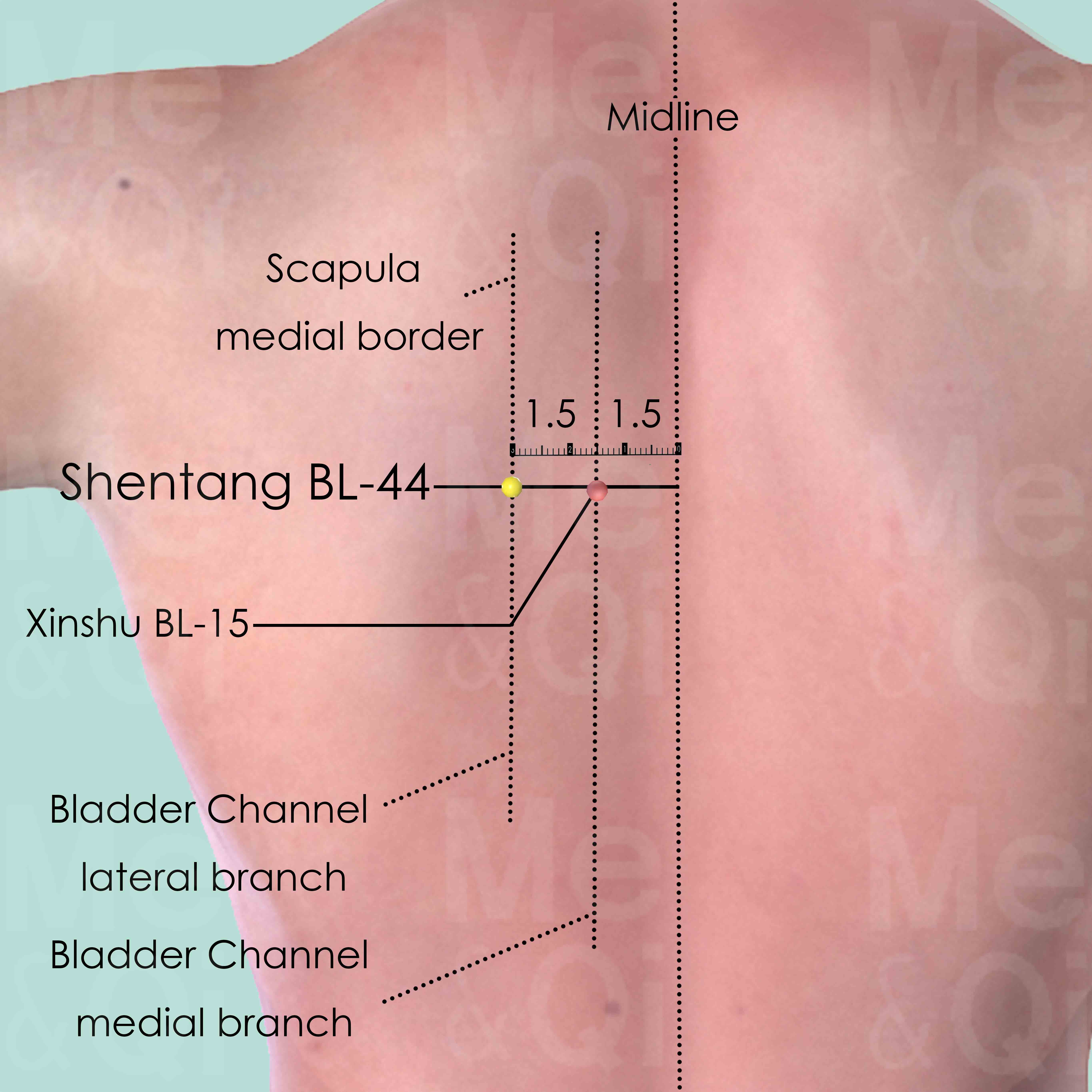
Shentang BL-44
3 cun (about 4 finger-breadths) lateral to the lower border of the spinous process of the 5th thoracic vertebra (T5).
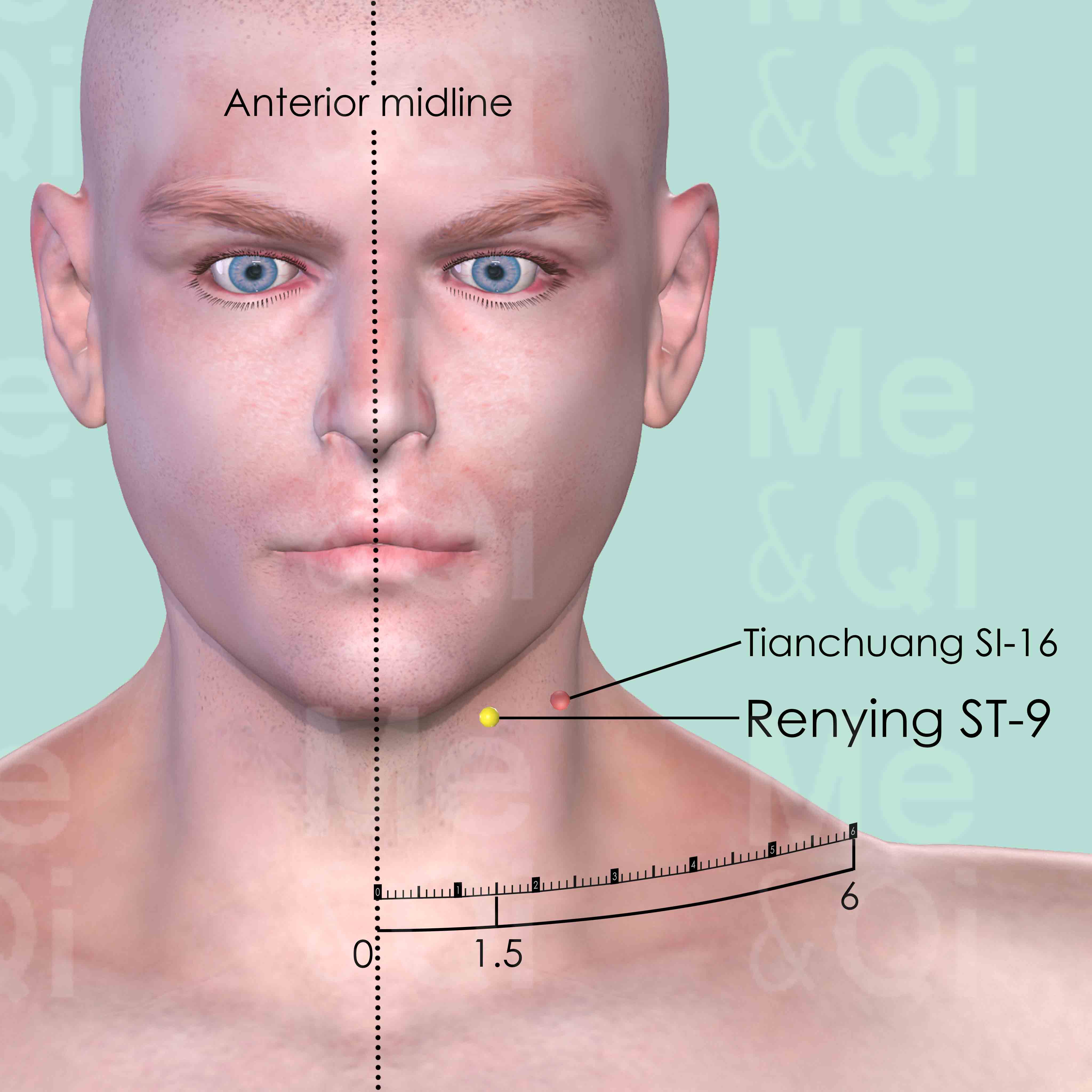
Renying ST-9
Level with the tip of Adam's apple, 1.5 cun lateral to the anterior midline, on the anterior border of the sternocleidomastoid muscle.
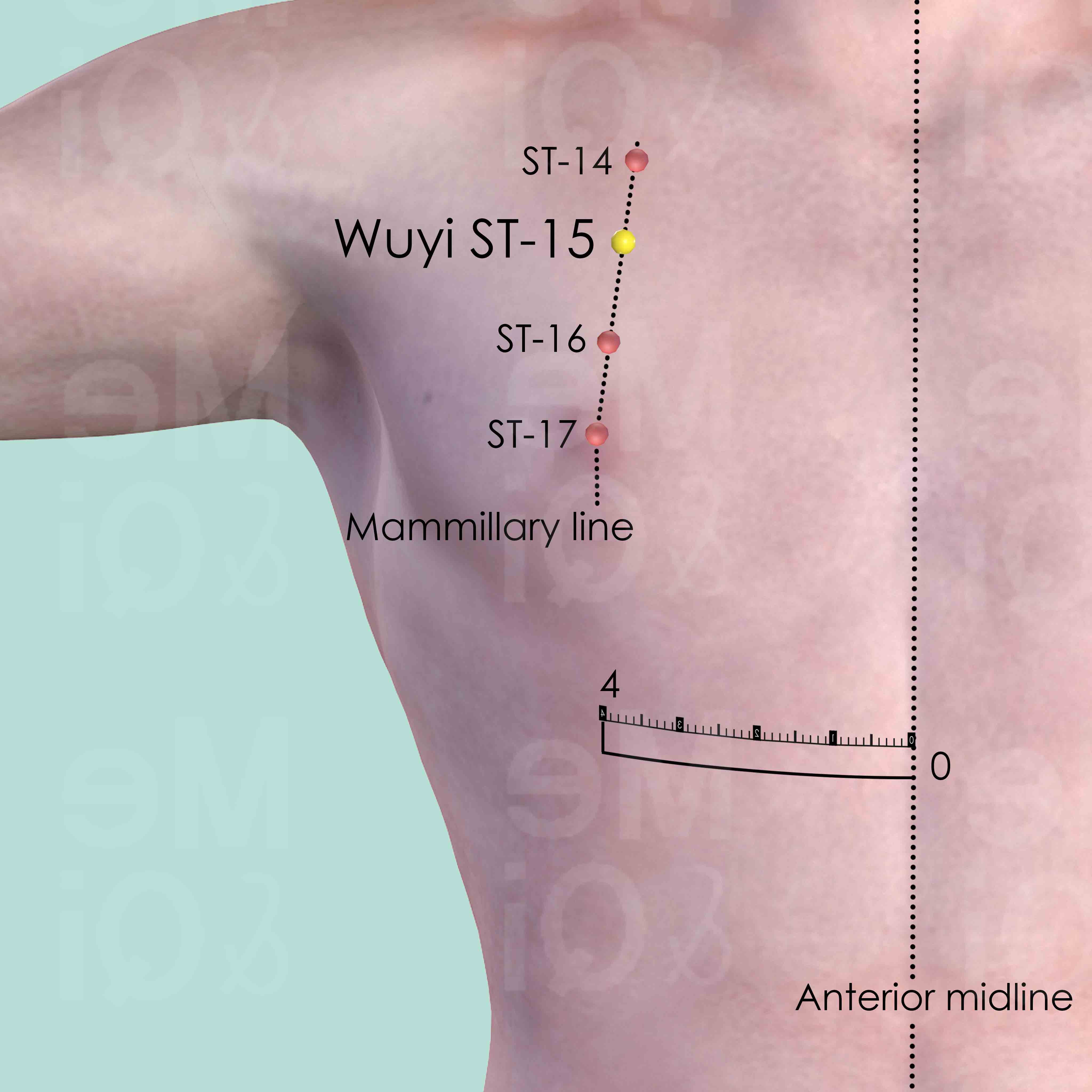
Wuyi ST-15
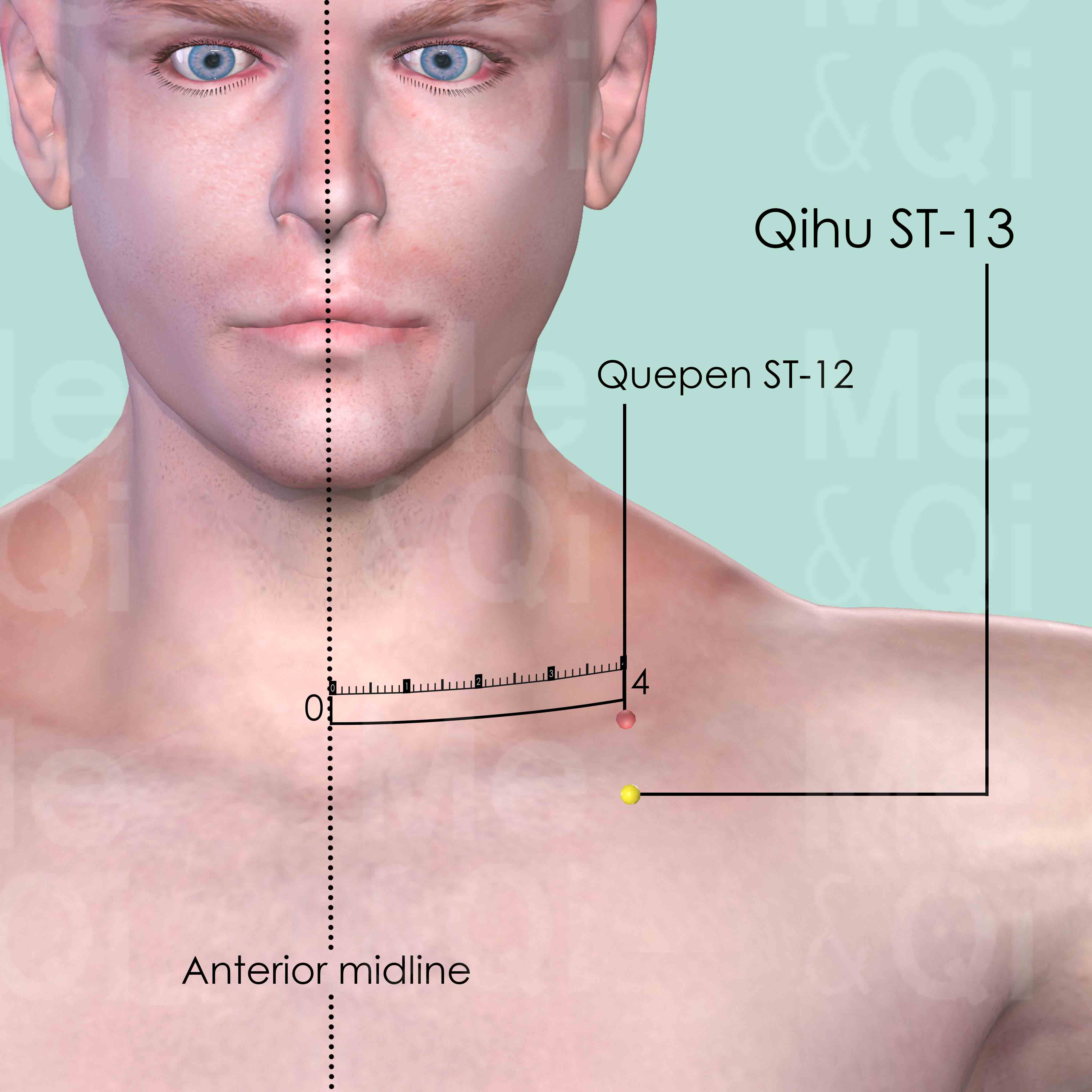
In the 2nd intercostal space, on the mammillary line, 4 cun lateral to the anterior midline.
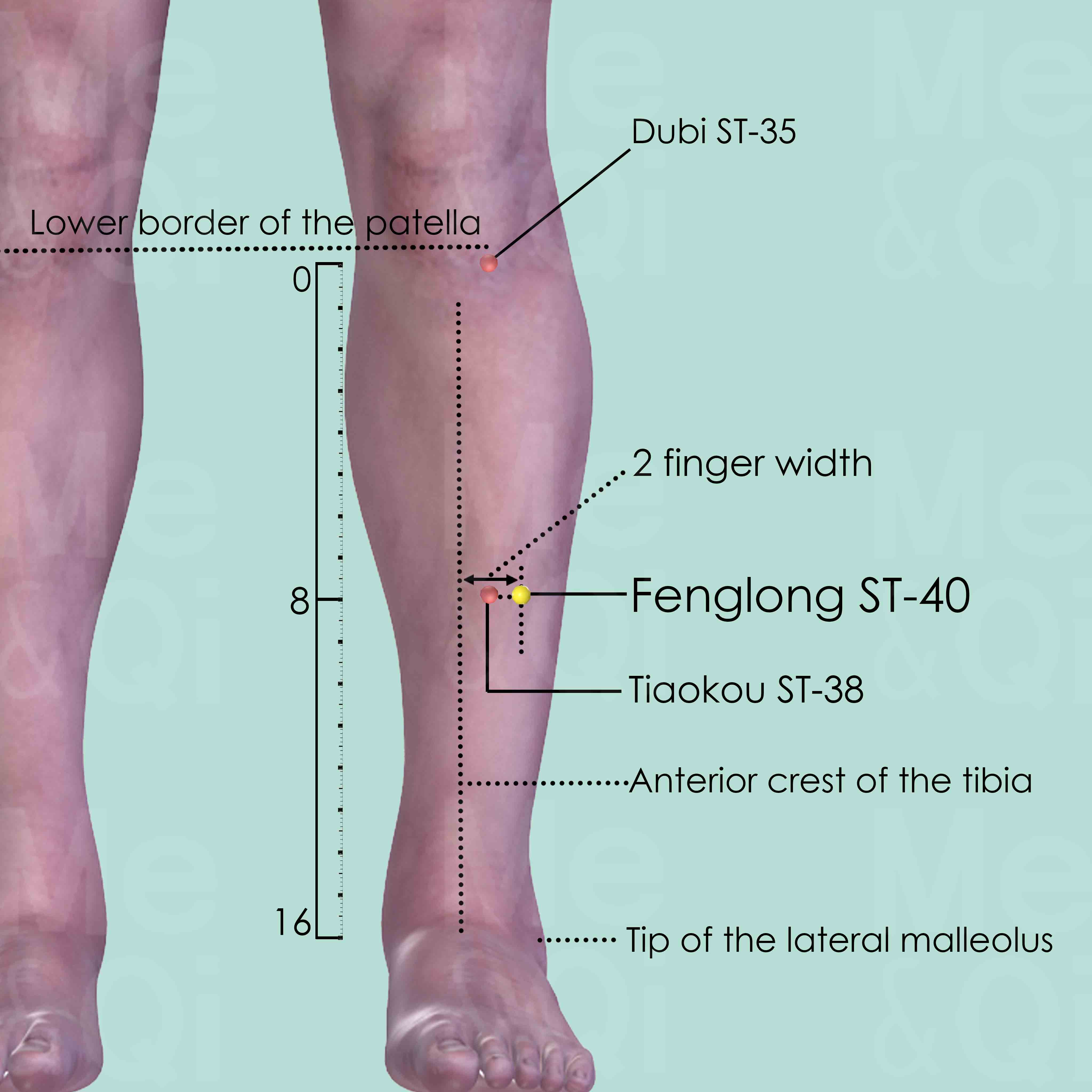
Fenglong ST-40
Midway between Dubi ST-35 and Jiexi ST-41, two middle finger-width from the anterior crest of the tibia, or one middle finger-width from Tiaokou ST-38.
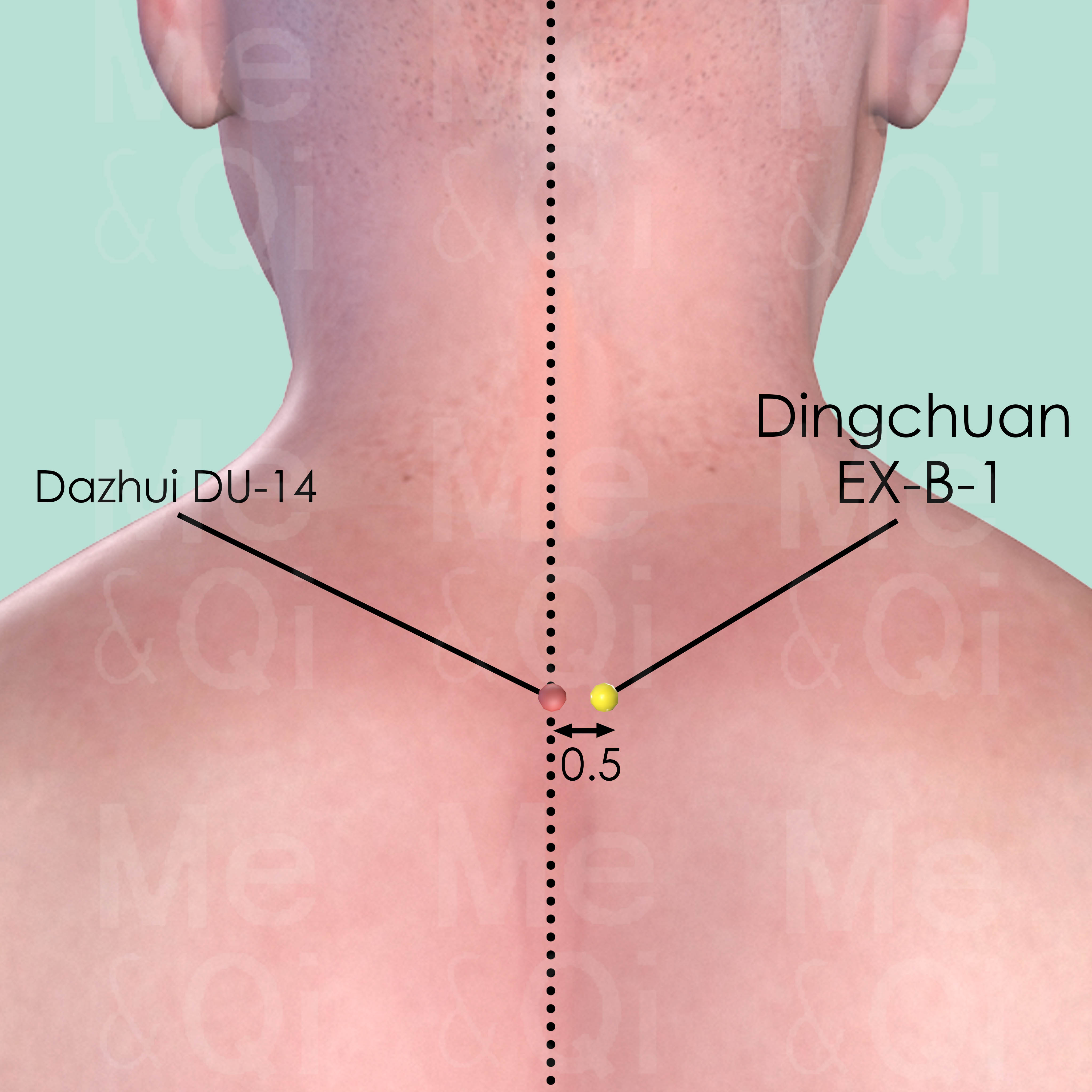
Dingchuan EX-B-1
0.5 cun lateral to the lower border of the spinous process of the 7th cervical vertebra (C7).
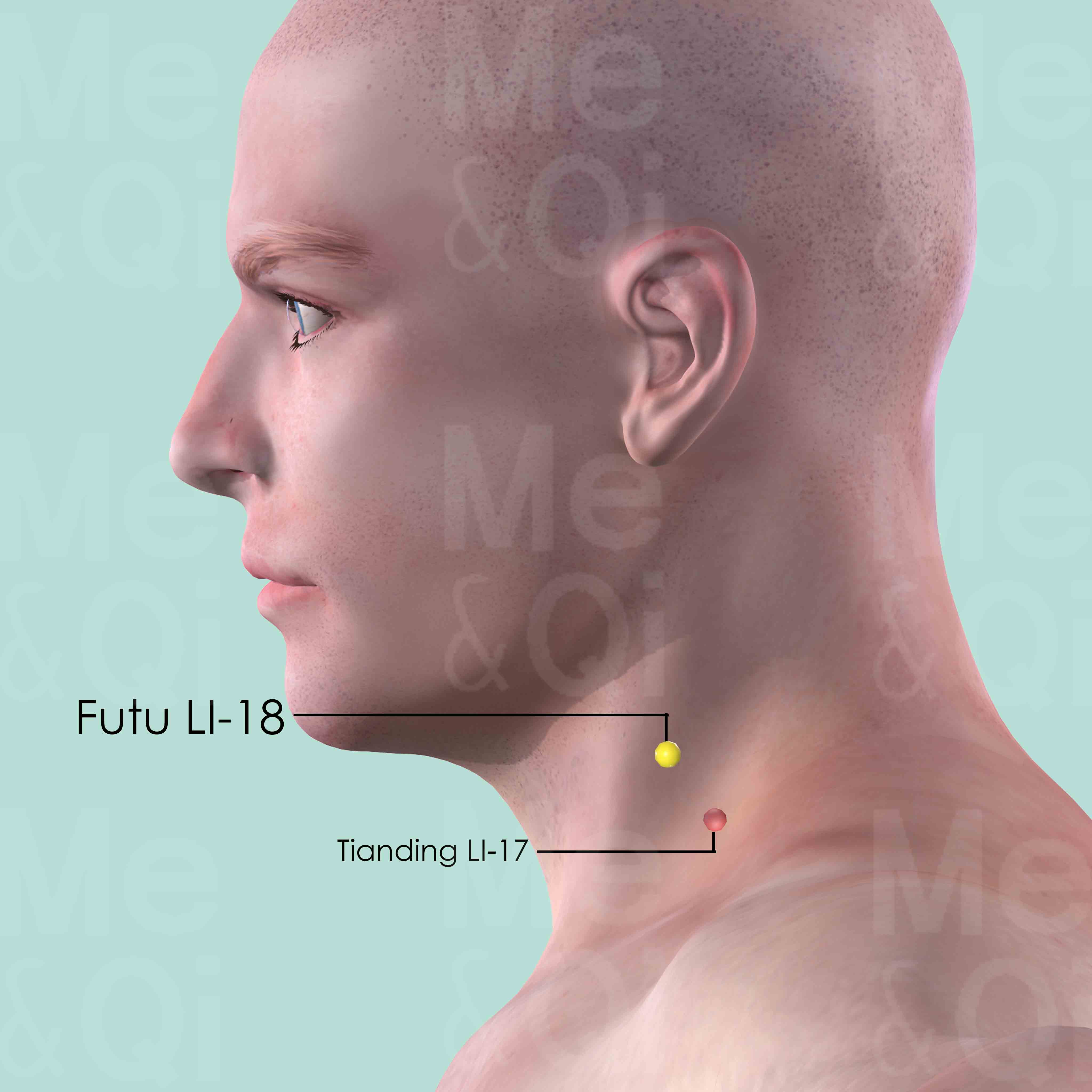
Futu LI-18
On the lateral side of the neck, level with the tip of Adam's apple, between the sternal head and clavicular head of sternocleidomastoid muscle.
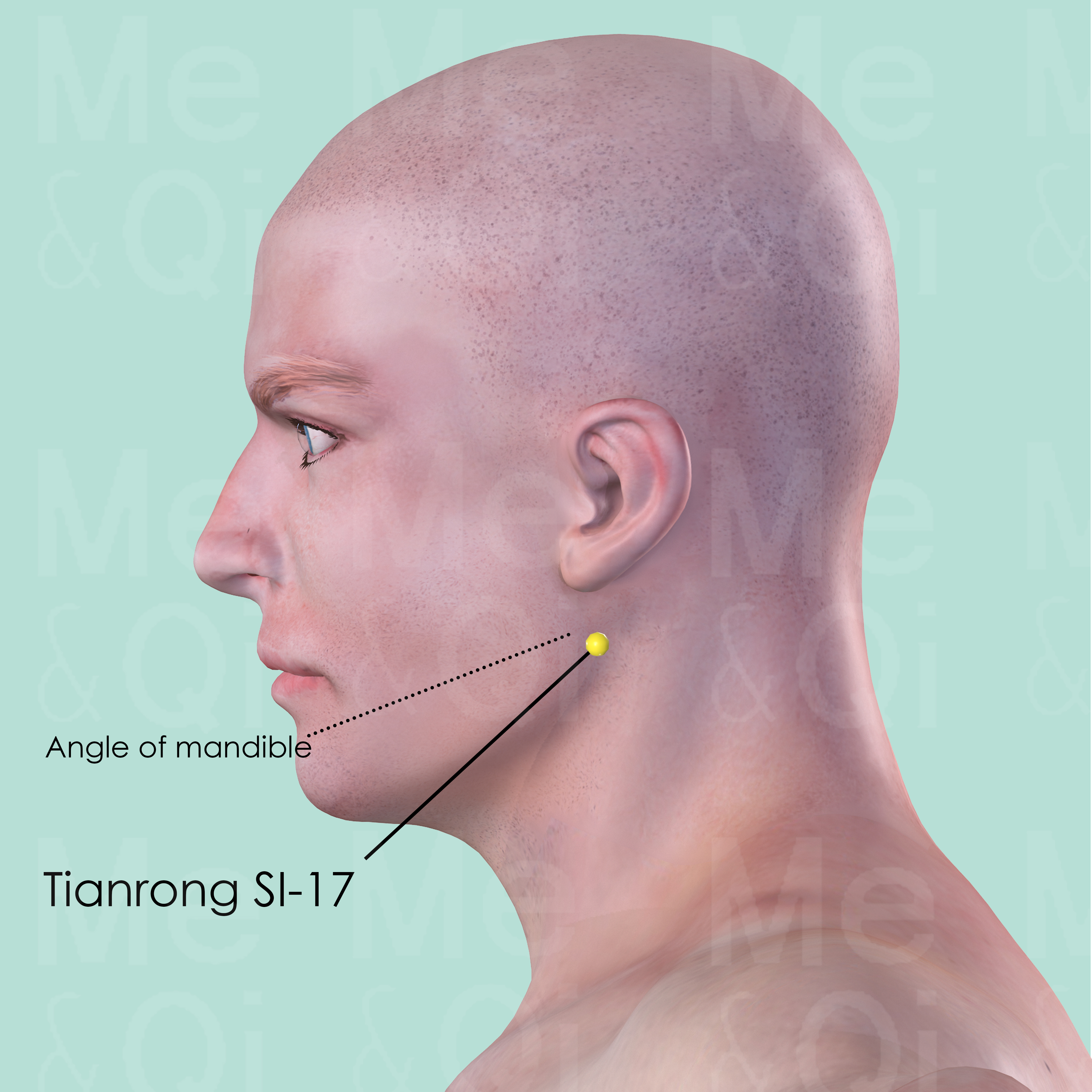
Tianrong SI-17
Posterior to the angle of mandible, in the depression on the anterior border of sternocleidomastoid muscle.