Upper Arm Muscle Atrophyaccording to TCM
Symptom families: Muscle Pain, Disorders and Symptoms, Arms disorders and Symptoms
Parent symptom: Arm Atrophy
What is Upper Arm Muscle Atrophy?
Upper arm muscle atrophy refers to the degeneration or loss of muscle mass specifically in the upper arms. This condition, also known as muscle wasting in the upper arms, can result in a visible thinning of the upper arm muscles and a reduction in strength and function. Individuals experiencing upper arm muscle atrophy may notice a decrease in arm size or increased prominence of bones and tendons in the affected area.
How Does TCM View Upper Arm Muscle Atrophy?
In Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), upper arm muscle atrophy is seen as a manifestation of underlying imbalances in the body's energy systems. TCM views health as a state of balance between opposing forces such as Yin and Yang, Qi and Blood.
Muscle atrophy is often attributed to deficiencies in these vital substances or blockages in the flow of Qi and Blood. TCM emphasizes the importance of identifying the specific pattern of disharmony causing the symptoms before initiating treatment, as different patterns may require different approaches to restore balance and promote healing.
Acupoints for Upper Arm Muscle Atrophy
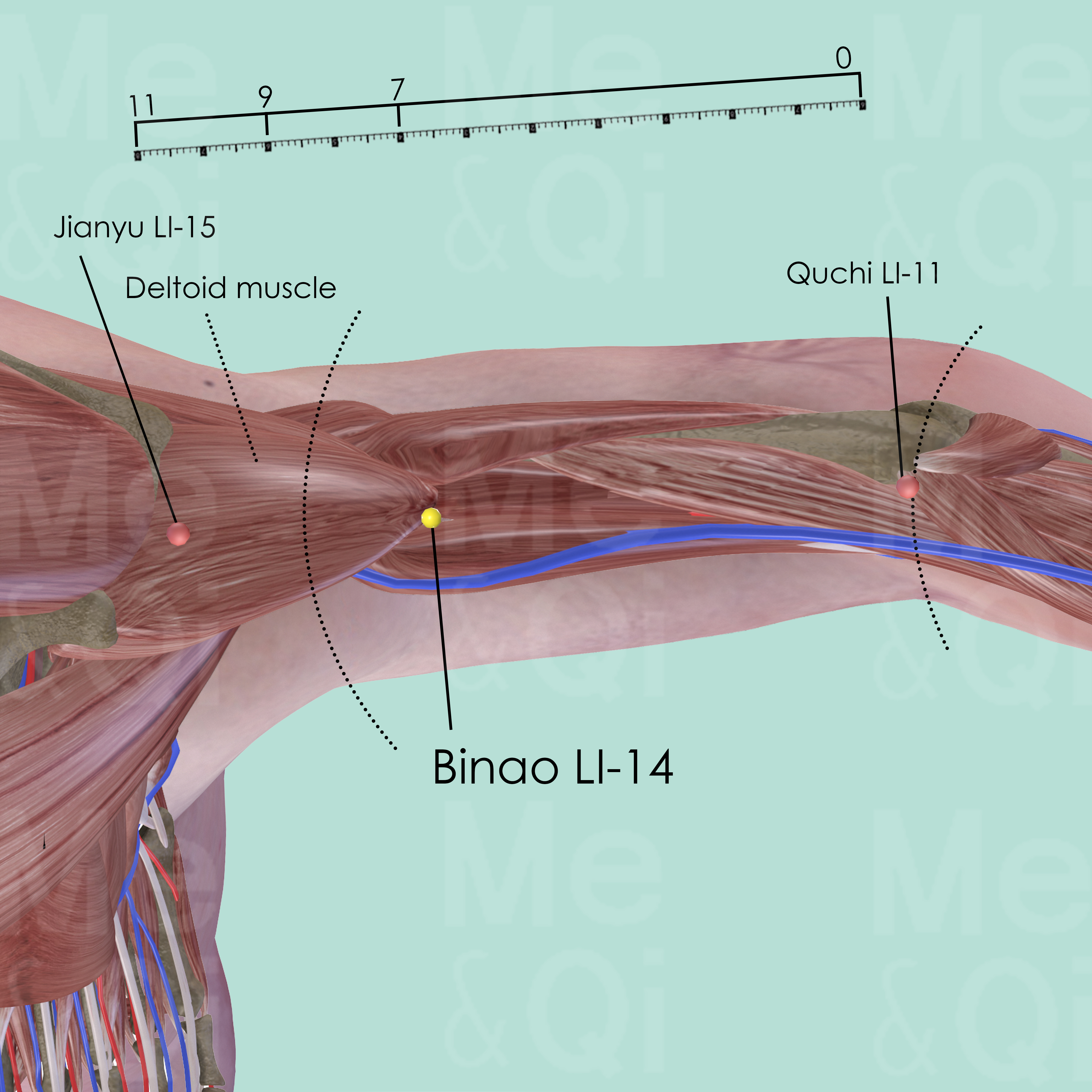
In TCM, acupoints play a crucial role in restoring balance and promoting the flow of Qi and Blood to alleviate symptoms such as muscle atrophy. Recommended acupoints for upper arm muscle atrophy include Binao LI-14 along the Large Intestine Channel.
Located on the radial side of the humerus, this acupoint helps remove obstructions from the channel, benefit the eyes, and resolve Phlegm, addressing underlying imbalances that contribute to muscle atrophy in the upper arms. Acupuncture at these points, along with other TCM interventions, aims to support the body's natural healing processes and restore optimal function to the affected area.
See more details below about Binao LI-14, an acupoint used to address upper arm muscle atrophy.
- By Meridian
- Large Intestine Channel
Binao LI-14
On the radial side of the humerus, superior to the lower end of deltoid muscle, on the line connecting Quchi LI-11 and Jianyu LI-15, 7 cun proximal to Quchi LI-11.
