Peripheral Edemaaccording to TCM
Symptom families: Edema-associated Concerns, Limbs disorders and Symptoms
Parent symptom: Edema
Did you mean? Edema
What is Peripheral Edema?
Peripheral edema is a condition characterized by the accumulation of fluid in the tissues, particularly in the extremities, leading to swelling. This can affect any body part but is most commonly seen in the legs, ankles, and feet due to gravity's effect on fluid in the body.
Synonyms for this condition include edema of limbs, limb swelling, and fluid retention in the limbs. Understanding peripheral edema is crucial for identifying the underlying causes and determining the appropriate treatment approach.
How does TCM view Peripheral Edema?
In Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), peripheral edema is seen through a lens that differs significantly from Western medical perspectives. TCM interprets this condition as a manifestation of imbalance within the body's fundamental systems, particularly involving the Qi, the Spleen, Kidneys, and the concept of Dampness and Phlegm.
The approach to treatment in TCM is holistic, aiming to restore balance and harmony by addressing the root cause of the edema rather than just the symptoms.
Root Causes of Peripheral Edema in TCM
TCM identifies several patterns that may lead to peripheral edema, with Phlegm and Yang Deficiency among the common culprits. Phlegm accumulation can cause fluid retention manifesting as superficial edema, marked by a feeling of heaviness and swollen limbs.
On the other hand, Yang Deficiency, particularly of the Spleen and Kidneys, can lead to a lack of warmth and energy needed to transform and transport body fluids, resulting in edema. Treatment strategies in TCM focus on dispelling Phlegm, strengthening Yang, and promoting the proper movement of fluids throughout the body.
Explore below more details about what might cause Peripheral edema according to TCM.
- By Syndrome
- By Organ
- Phlegm
- Yang Deficiency
- Dampness
- Spleen
- Kidney
Phlegm
In TCM "Phlegm" as a pattern of disharmony is a complex concept that extends beyond the physical manifestation of mucus. It represents a pathological factor that can disrupt the flow of Qi (vital energy) and blood, leading to various health issues. Phlegm in TCM is seen as a sticky, turbid substance arising from the body's inability to metabolize fluids properly, often due to a dysfunction of the spleen. It's not only associated with respiratory problems like cough and congestion but also with systemic issues. Symptoms can include a feeling of heaviness, mental cloudiness, dizziness, and in some cases, the formation of lumps or masses. Phlegm can even be "invisible," contributing to emotional disturbances like depression or stress. ... see more
Phlegm Patterns That Can Lead to Peripheral Edema
Common Symptoms: Absence Of Thirst Profuse White Sputum Feeling Of Heaviness Muscle Pain Lack Of Sweating Urinary Dysfunction Irritability Restlessness
| Pattern Name | Relevant Symptoms | Relevant Formulas |
|---|---|---|
| Phlegm-Fluids in the limbs | Superficial edema in the extremities, Swollen limbs, Feeling of heaviness, Muscle pain, Lack of sweating, Absence of thirst, Profuse white sputum, Urinary dysfunction... see more | Da Qing Long Tang | Xiao Qing Long Tang |
| Damp-Phlegm | Swollen limbs, Profuse white sputum, Focal distention of the chest, Upper abdominal focal distention, Nausea, Sticky taste in the mouth, Absence of thirst, Obesity, Abdominal fat... see more | Er Chen Tang | Xiang Sha Liu Jun Zi Tang | Shen Qi Wan |
Yang Deficiency
Yang deficiency in TCM refers to a state where the body's Yang energy, which is responsible for warmth, activity, and function, is weakened or diminished. This pattern of disharmony often arises from chronic illness, aging, or inherent constitutional weakness. Symptoms of Yang deficiency are typically associated with cold and sluggishness, such as a feeling of coldness, cold extremities, pale complexion, low energy or fatigue, and a desire for warmth. Digestive issues like poor appetite, loose stools, and water retention can also be indicative of Yang deficiency.... see more
Yang Deficiency Patterns That Can Lead to Peripheral Edema
| Pattern Name | Relevant Symptoms | Relevant Formulas |
|---|---|---|
| Spleen and Kidney Yang Deficiency | Oedema of limbs, Pale face, Facial edema, Abdominal distention, Cold extremities, Shortness of breath, Diarrhea, Frequent urination, Lupus... see more | Wu Ling San |
Dampness
"Dampness" in TCM is a concept that describes a pattern of disharmony where the body accumulates excess moisture. Imagine the heavy, sticky feeling you get on a very humid day; that's similar to what dampness feels like internally. It can manifest as a sense of heaviness, bloating, sluggishness, or even a foggy mind. This condition is often thought to arise from environmental factors like living in a damp place, dietary habits that promote moisture in the body, or internal imbalances that hinder the body's ability to process fluids properly. In TCM, dampness can obstruct the normal flow of energy and fluids in the body, leading to various symptoms.... see more
Dampness Patterns That Can Lead to Peripheral Edema
| Pattern Name | Relevant Symptoms | Relevant Formulas |
|---|---|---|
| Damp-Phlegm | Swollen limbs, Profuse white sputum, Focal distention of the chest, Upper abdominal focal distention, Nausea, Sticky taste in the mouth, Absence of thirst, Obesity, Abdominal fat... see more | Er Chen Tang | Xiang Sha Liu Jun Zi Tang | Shen Qi Wan |
Spleen
In TCM the Spleen plays a vital role in digestion and transformation, converting food into energy and nutrients, and overseeing the distribution of Qi and Blood. It's also crucial in maintaining the health of muscles and limbs and ensuring the blood remains within the vessels. When the Spleen malfunctions in TCM, it can lead to a variety of issues such as digestive disorders, fatigue, weak muscles, bloating, and a feeling of heaviness. It can also cause a pale complexion, poor appetite, and a tendency to bruise easily. Emotionally, a Spleen imbalance is often associated with excessive worry or overthinking, reflecting its role in the interplay between physical and mental health.... see more
Spleen Patterns That Can Lead to Peripheral Edema
| Pattern Name | Relevant Symptoms | Relevant Formulas |
|---|---|---|
| Spleen and Kidney Yang Deficiency | Oedema of limbs, Pale face, Facial edema, Abdominal distention, Cold extremities, Shortness of breath, Diarrhea, Frequent urination, Lupus... see more | Wu Ling San |
Kidney
In TCM the Kidneys are regarded as the body's most fundamental reservoir of Essence, known as Jing, which influences growth, reproduction, and aging. They are not just organs for filtering blood, but a holistic system governing vital life forces. When the Kidneys malfunction in TCM, it can manifest as a variety of health issues, such as chronic fatigue, reproductive problems, imbalances in fluid metabolism leading to edema or dryness, lower back pain, and a sense of fear or insecurity.... see more
Kidney Patterns That Can Lead to Peripheral Edema
| Pattern Name | Relevant Symptoms | Relevant Formulas |
|---|---|---|
| Spleen and Kidney Yang Deficiency | Oedema of limbs, Pale face, Facial edema, Abdominal distention, Cold extremities, Shortness of breath, Diarrhea, Frequent urination, Lupus... see more | Wu Ling San |
TCM Herbal Formulas for Peripheral Edema
For managing peripheral edema, TCM relies on a variety of formulas and herbs tailored to the individual's specific pattern of disharmony. For example, Da Qing Long Tang and Er Chen Tang are used to clear Wind-Cold and transform Phlegm, respectively, addressing the Dampness that can lead to fluid accumulation.
Wu Ling San is recommended for Spleen and Kidney Yang Deficiency, promoting urination and leaching out Dampness to alleviate edema. These formulas exemplify TCM's nuanced approach to treating peripheral edema by focusing on the underlying patterns of imbalance.
Explore below some TCM herbal formulas used to address peripheral edema, organized by cause and by formula type.
- By Cause
- By Formula Type
- Phlegm
- Yang Deficiency
- Dampness
- Formulas that clear wind-Cold
- Formulas that promote urination and leach out dampness
- Formulas that dry dampness and transform phlegm
- Formulas that dispel phlegm
- Formulas that warm yang and tonify
Top Formula for Phlegm:
Da Qing Long Tang
Suitable for Phlegm patterns that may cause peripheral edema, such as Phlegm-Fluids in the limbs
Learn moreAll Formulas Recommended for Peripheral Edema Caused by Phlegm
| Formula | Patterns Suitable For |
|---|---|
| Da Qing Long Tang | Phlegm-Fluids in the limbs |
| Xiao Qing Long Tang | Phlegm-Fluids in the limbs |
| Er Chen Tang | Damp-Phlegm |
| Xiang Sha Liu Jun Zi Tang | Damp-Phlegm |
| Shen Qi Wan | Damp-Phlegm |
Top Formula for Yang Deficiency:
Wu Ling San
Suitable for Yang Deficiency patterns that may cause peripheral edema, such as Spleen and Kidney Yang Deficiency
Learn moreTop Formula for Dampness:
Er Chen Tang
Suitable for Dampness patterns that may cause peripheral edema, such as Damp-Phlegm
Learn moreAll Formulas Recommended for Peripheral Edema Caused by Dampness
| Formula | Patterns Suitable For |
|---|---|
| Er Chen Tang | Damp-Phlegm |
| Xiang Sha Liu Jun Zi Tang | Damp-Phlegm |
| Shen Qi Wan | Damp-Phlegm |
Formulas that clear Wind-Cold
These formulas are suitable for some peripheral edema-causing patterns like Phlegm-Fluids in the limbs.
One such formula is Da Qing Long Tang, with ephedra as a key herb.
Other formulas of this category are listed in the table below.
All "formulas that clear wind-Cold" recommended for peripheral edema
| Formula | Patterns Suitable For (if applicable) |
|---|---|
| Da Qing Long Tang | Phlegm-Fluids in the limbs |
| Xiao Qing Long Tang | Phlegm-Fluids in the limbs |
Formulas that promote urination and leach out Dampness
These formulas are suitable for some peripheral edema-causing patterns like Spleen and Kidney Yang Deficiency.
One such formula is Wu Ling San, with water plantain as a key herb.
Formulas that dry Dampness and transform Phlegm
These formulas are suitable for some peripheral edema-causing patterns like Damp-Phlegm.
One such formula is Er Chen Tang, with crow-dipper rhizome as a key herb.
Formulas that dispel Phlegm
These formulas are suitable for some peripheral edema-causing patterns like Damp-Phlegm.
One such formula is Xiang Sha Liu Jun Zi Tang, with ginseng as a key herb.
Formulas that warm Yang and tonify
These formulas are suitable for some peripheral edema-causing patterns like Damp-Phlegm.
One such formula is Shen Qi Wan, with prepared aconite as a key herb.
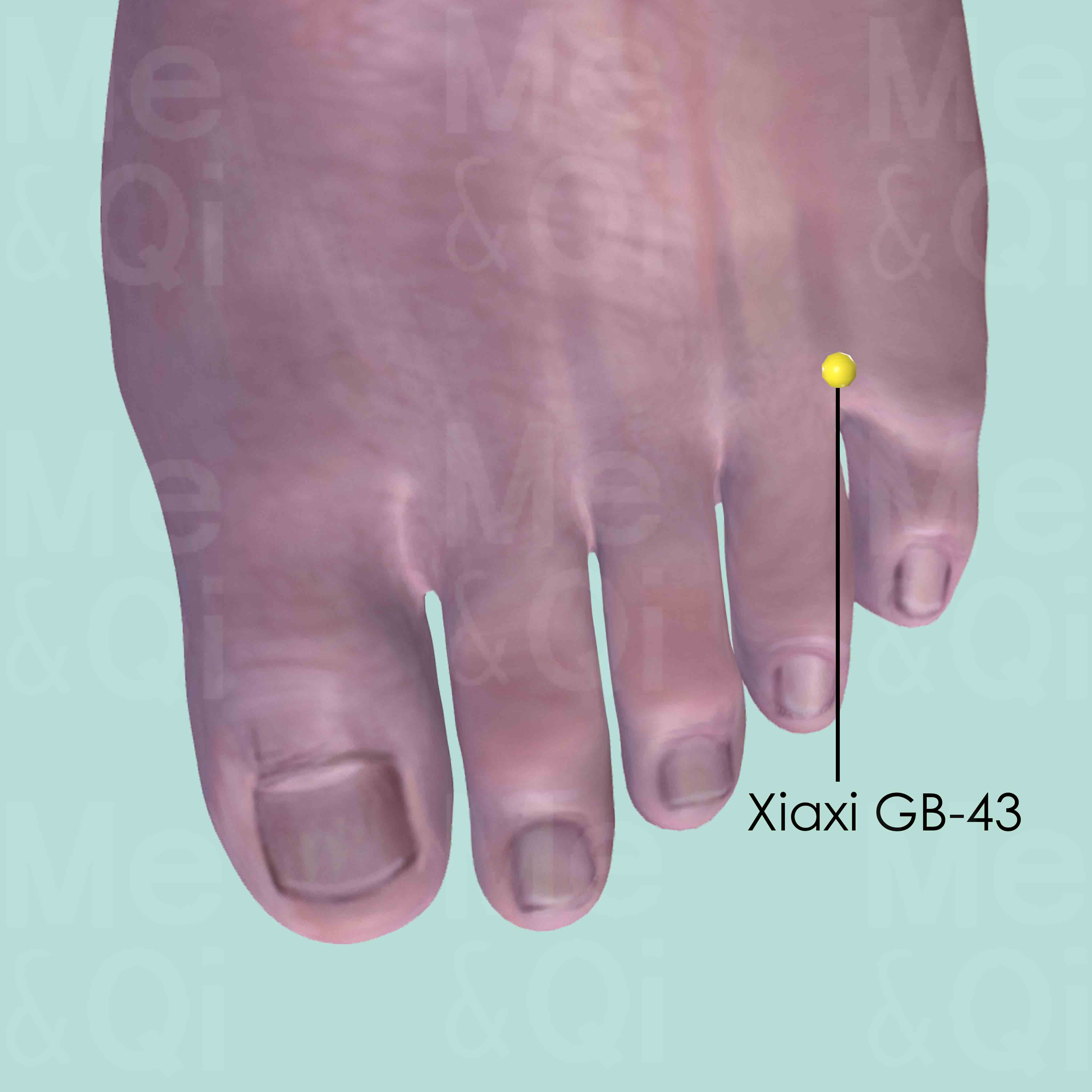
Acupoints for Peripheral Edema
TCM also utilizes acupuncture as a method to treat peripheral edema, targeting specific acupoints that correspond to the underlying imbalances contributing to the condition. Acupoints like Chize LU-5 and Xiaxi GB-43 are selected for their properties in clearing Lung Heat, descending Lung Qi, and expelling Damp-Heat, respectively.
By stimulating these points, TCM practitioners aim to restore the free flow of Qi and fluids, reduce swelling, and address the root causes of peripheral edema.
Explore below some acupoints used to address peripheral edema, organized by meridian.
- By Meridian
- Lung Channel
- Gall Bladder Channel
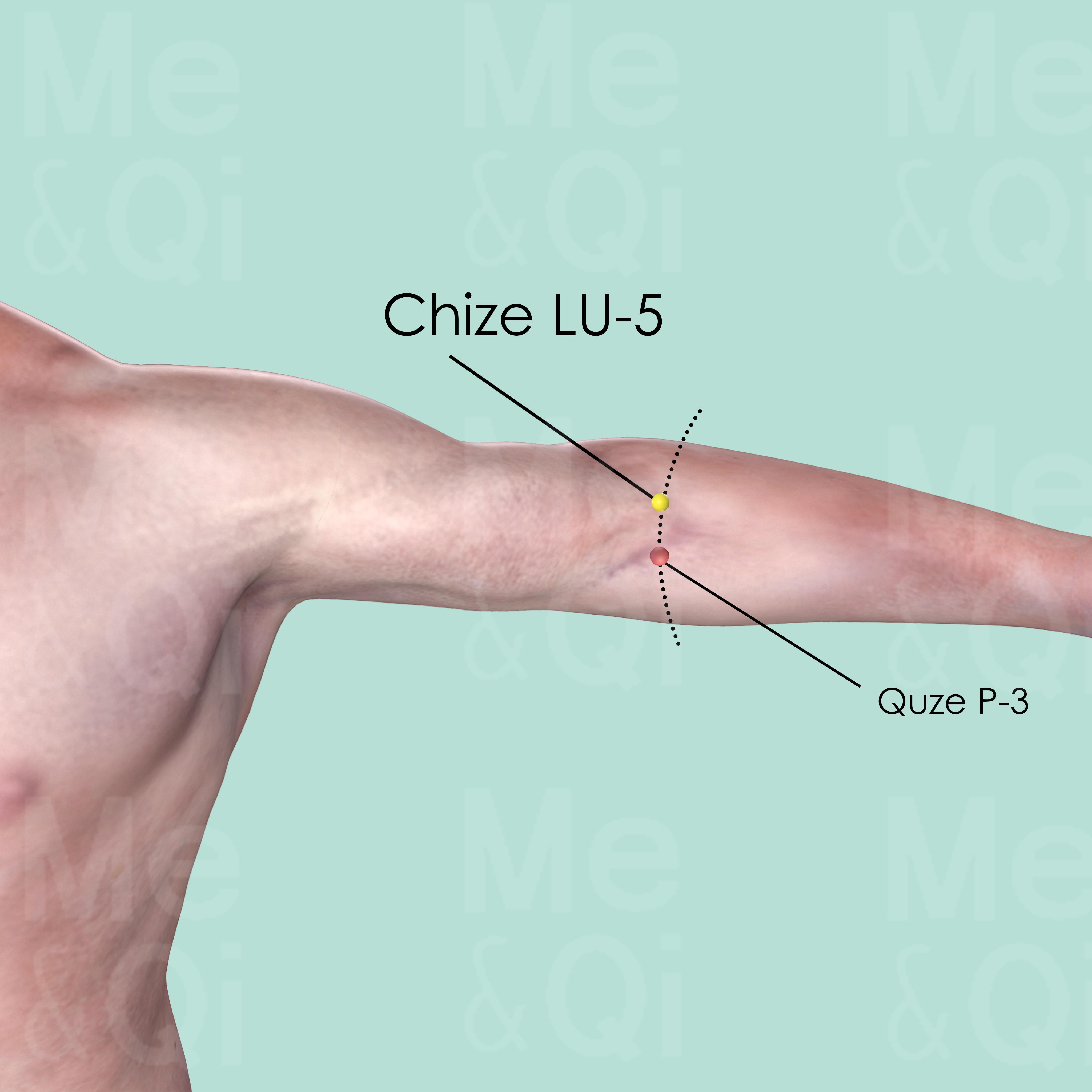
Chize LU-5
On the cubital crease, on the redial aspect of the biceps tendon. It can be easily identified when the elbow is slightly flexed.