Painful Eyesaccording to TCM
Symptom family: Eye Disorders and Symptoms
Sub-symptom(s): Eye Upper Orbit Pain
What is Painful Eyes?
Painful eyes, medically referred to as ocular pain or ophthalmalgia, encompass various discomforts or pains within the eye region. This symptom can range from a dull ache to sharp pain and may be accompanied by other eye-related issues like redness, itching, or visual disturbances.
Pain in the eyes can be a result of several causes, including eye strain, infections, or more serious conditions like glaucoma. In some cases, the pain may be localized to specific areas, such as the upper orbit of the eye.
How does TCM view Painful Eyes?
Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) offers a unique perspective on painful eyes, distinct from the typical Western medical view. In TCM, eye pain is often seen as a symptom of imbalances within the body's internal systems, particularly related to the Liver, Kidney, and Spleen.
TCM suggests that the health of our eyes is closely linked to the state of our internal organs and Qi (vital energy). Consequently, TCM practitioners focus on identifying the underlying disharmony causing the eye pain, rather than treating the symptom in isolation.
Causes of Painful Eyes According to TCM
TCM identifies several patterns that can lead to painful eyes. One common cause is Liver Yang Rising, which can cause symptoms like headache and eye pain. This condition is often associated with stress and emotional tension affecting the Liver's function.
Another pattern is Liver Yin Deficiency, where a lack of nourishing Yin results in symptoms like dry eyes and blurred vision. These patterns highlight TCM's understanding of eye pain as a reflection of broader systemic issues, emphasizing the need for a holistic treatment approach.
TCM Herbal Formulas for Painful Eyes
In addressing painful eyes, TCM relies on specific formulas and herbs, tailored to the individual's pattern of imbalance. For patterns such as Liver Yang Rising and Liver Yin Deficiency, a formula like Qi Ju Di Huang Wan, containing Prepared rehmannia (Shu Di Huang), is often recommended. This formula works to nourish yin and subdue rising yang, helping to alleviate eye pain and associated symptoms. TCM treatments are highly personalized, focusing on restoring balance to the affected organ systems and the overall flow of Qi.
See more details below about Qi Ju Di Huang Wan, a herbal formula used to address painful eyes.
- By Formula Type
- Formulas that nourish yin and tonify
Formulas that nourish Yin and tonify
Painful eyes can be treated by these formulas when it arises from a deficiency in Yin energy, needing nourishment and strengthening of the body's vital essence.
One such formula is Qi Ju Di Huang Wan, with prepared rehmannia as a key herb.
Acupoints for Painful Eyes
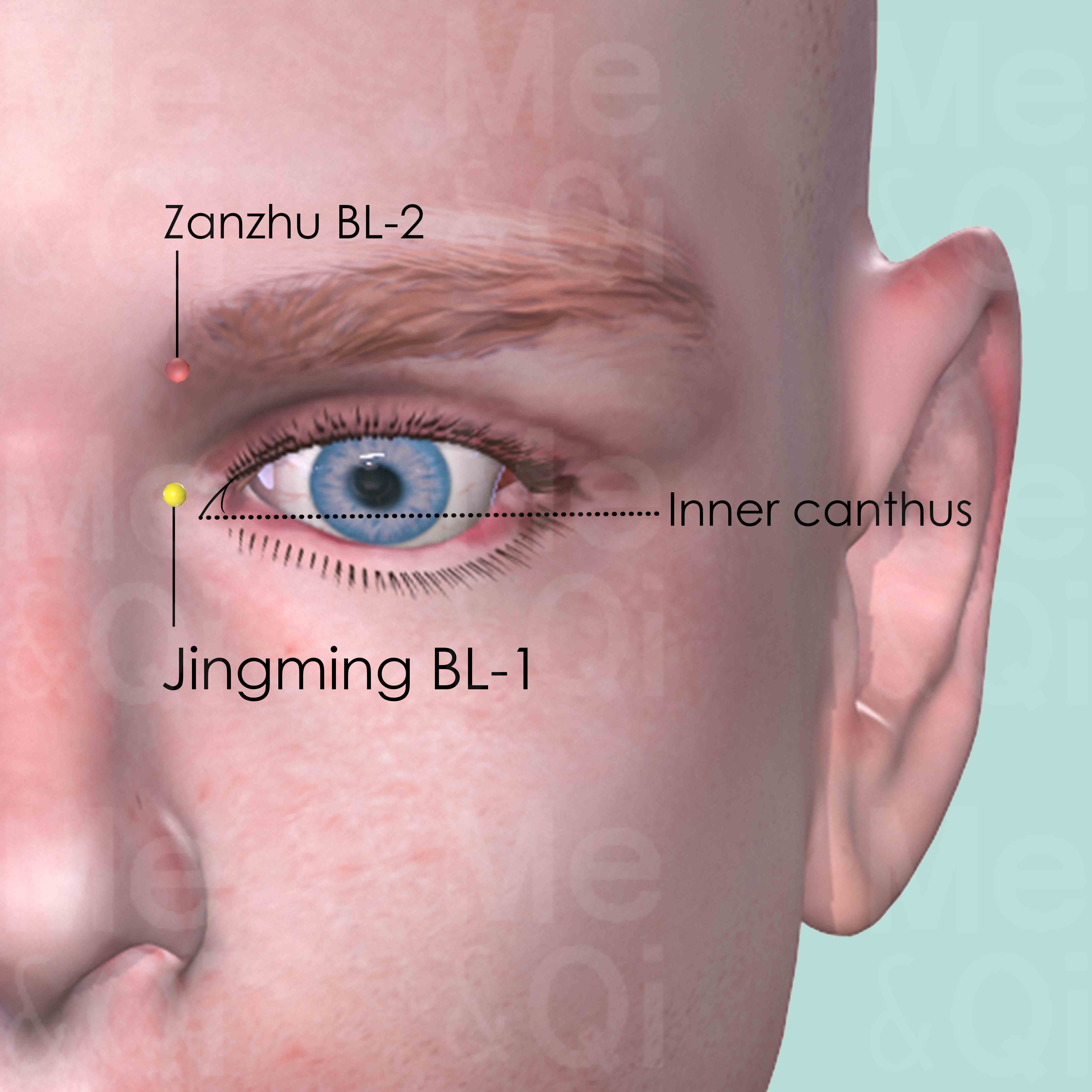
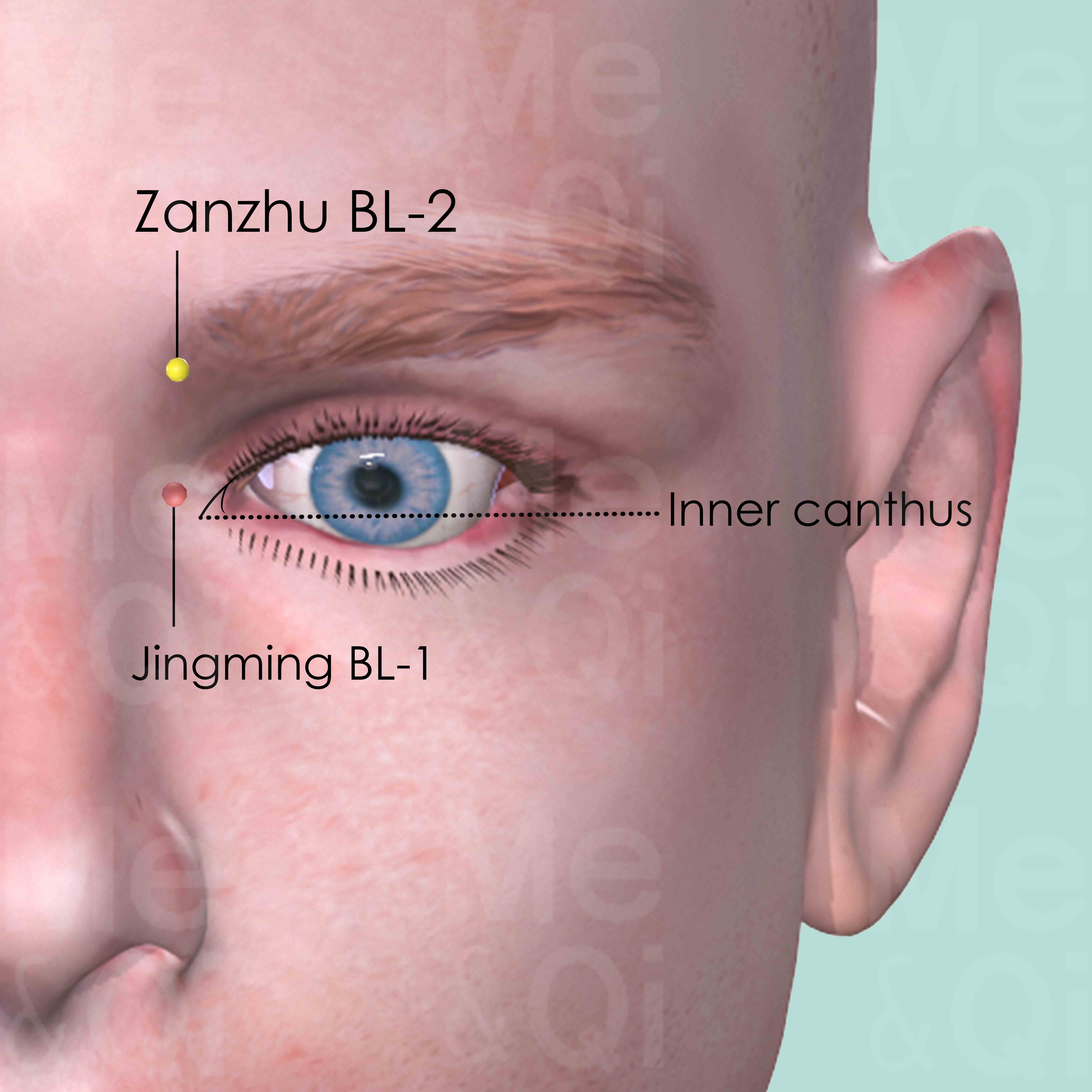
TCM also incorporates acupuncture as a treatment for painful eyes, targeting specific acupoints to alleviate symptoms. Points such as Ganshu BL-18 and Jingming BL-1 in the Bladder Channel are utilized for their efficacy in nourishing liver blood and clearing heat, respectively.
Other points like Fengchi GB-20 in the Gall Bladder Channel and Hegu LI-4 in the Large Intestine Channel are used for their actions in subduing Liver Yang and expelling wind, which are beneficial for eye health. These acupoints are selected based on the individual's specific TCM diagnosis, aiming to enhance the body’s natural healing processes and restore balance.
Explore below some acupoints used to address painful eyes, organized by meridian.
- By Meridian
- Bladder Channel
- Gall Bladder Channel
- Large Intestine Channel
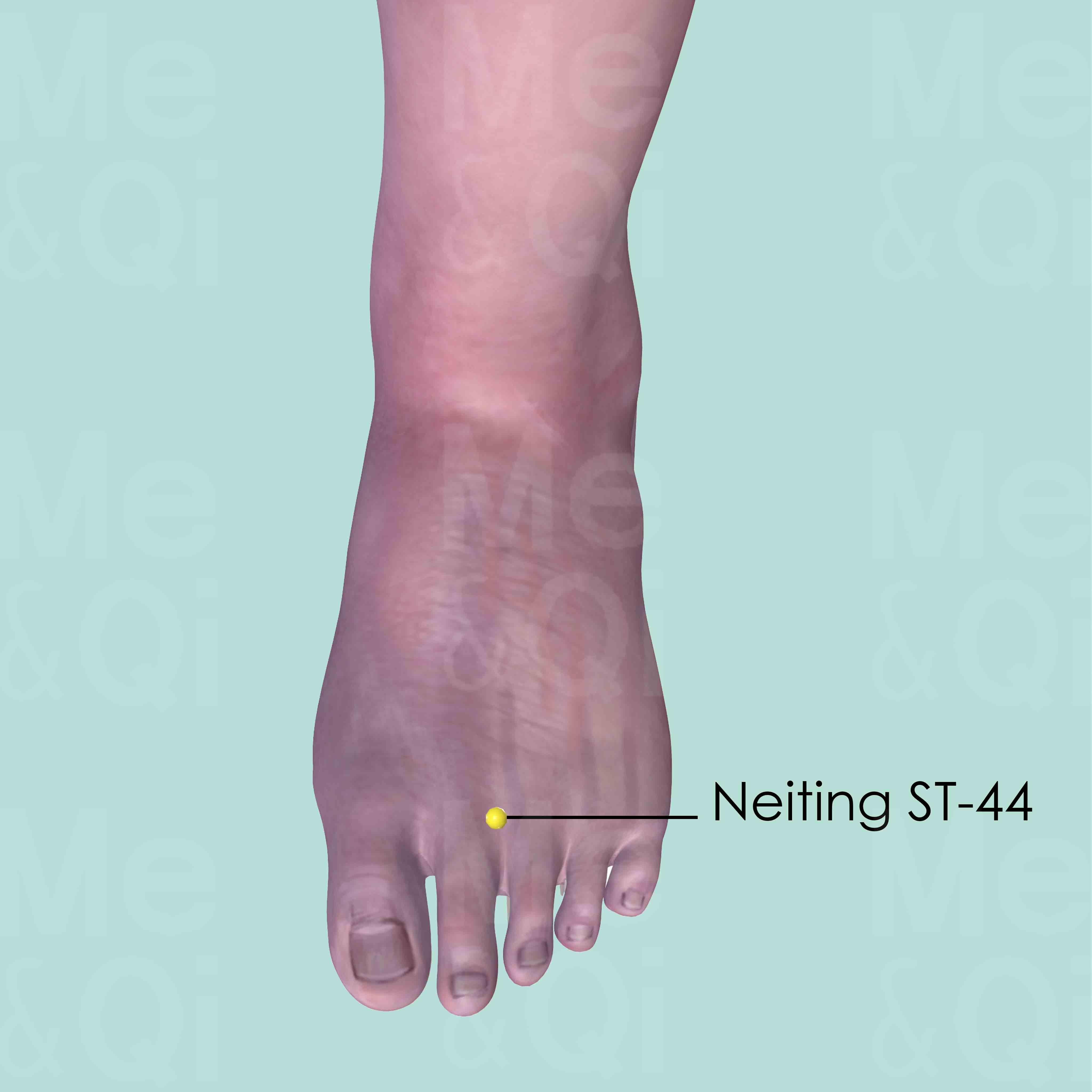
- Stomach Channel
- Kidney Channel
- Small Intestine Channel
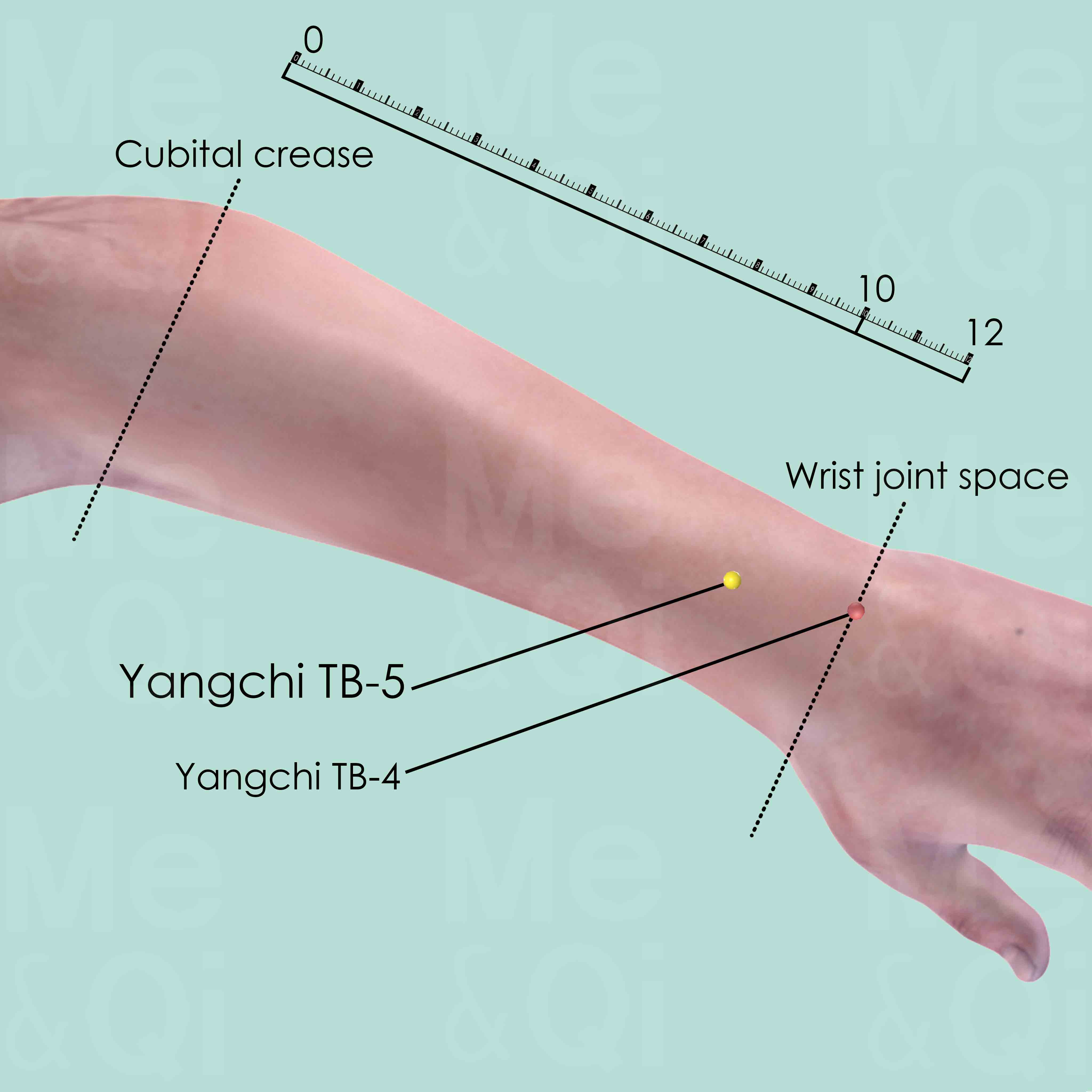
- Triple Burner Channel
- Extra Points: Head and Neck (EX-HN)
- Governing Vessel
- Heart Channel
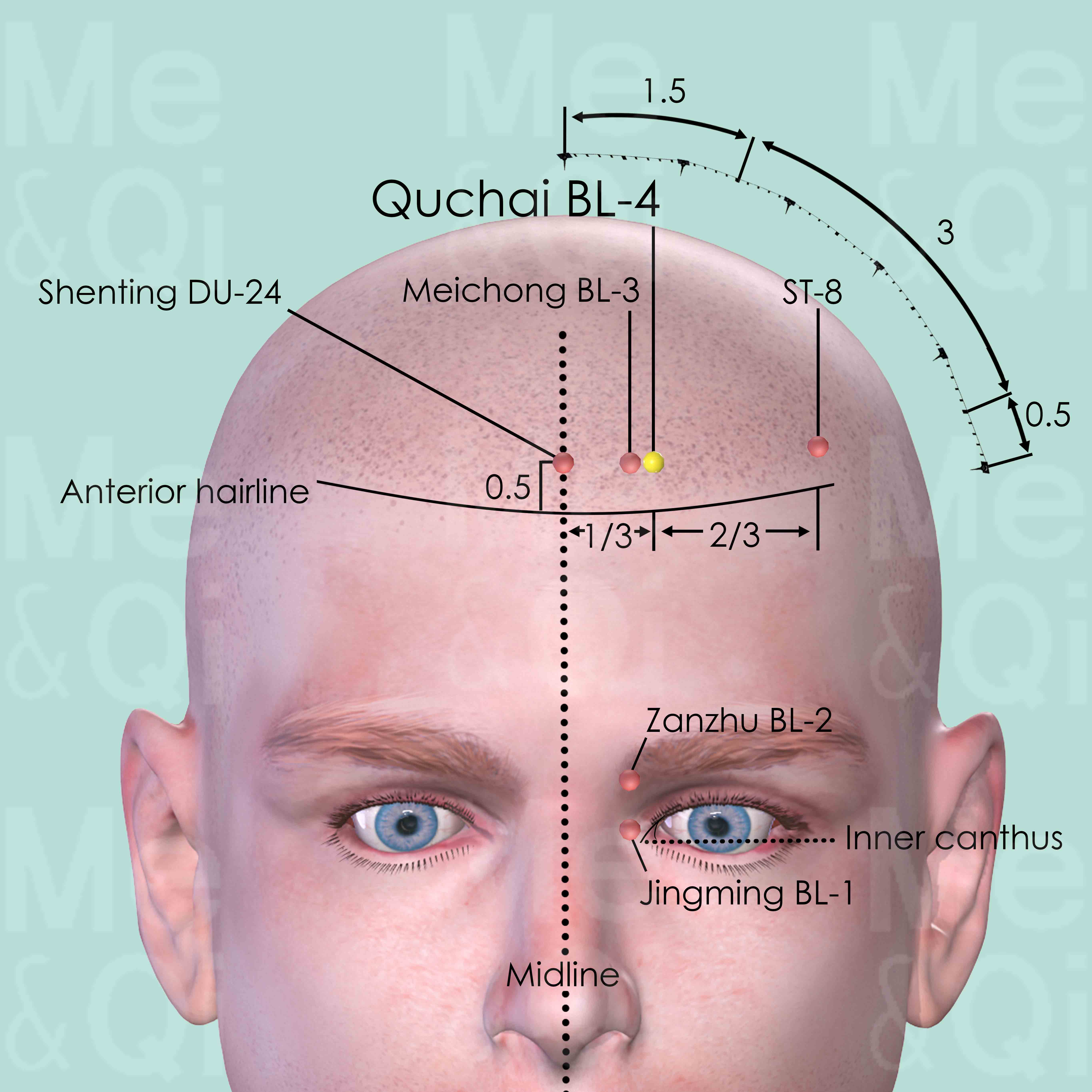
Qucha BL-4
0.5 cun superior to the anterior hairline and 1.5 cun lateral to the anterior midline, at the junction of the medial third and lateral two-thirds of the distance from anterior midline to Touwei ST-8.
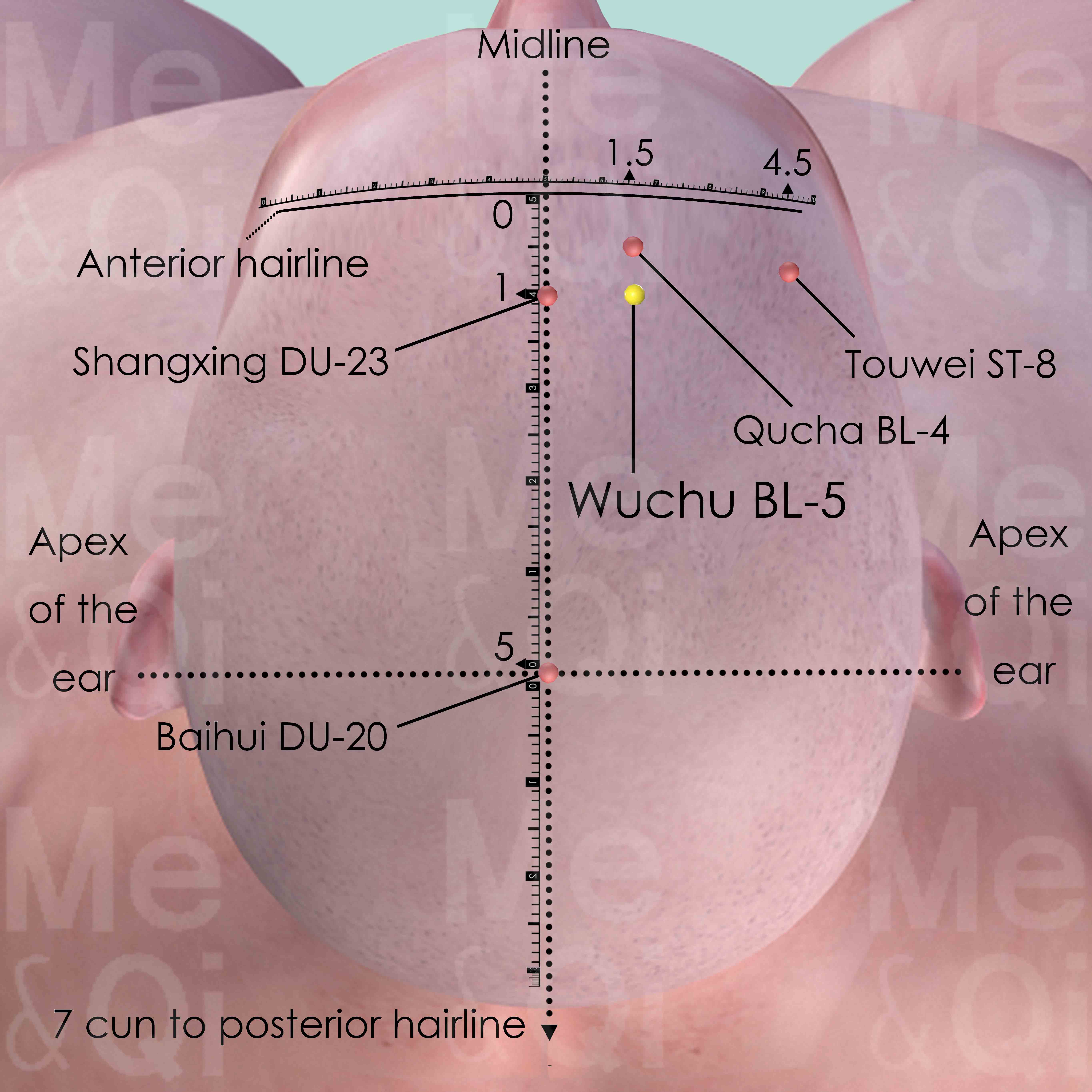
Wuchu BL-5
1 cun within the anterior hairline and 1.5 cun lateral to the anterior midline. It is also 0.5 cun posterior to Quchai BL-4.
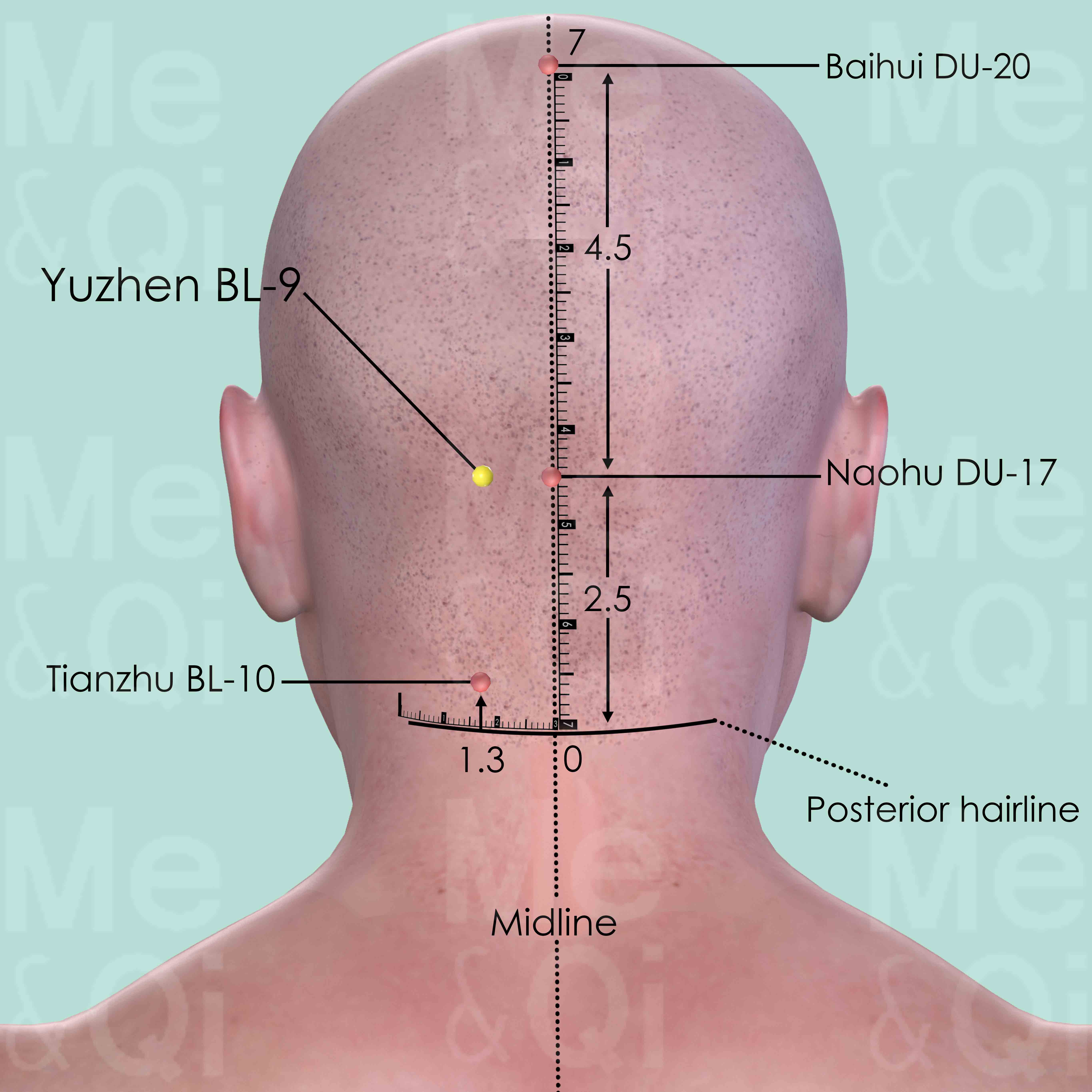
Yuzhen BL-9
First identify Naohu DU-17 which is on the superior border of the external occipital protuberance. Yuzhen BL-9 is 1.3 cun lateral to Naohu DU-17.
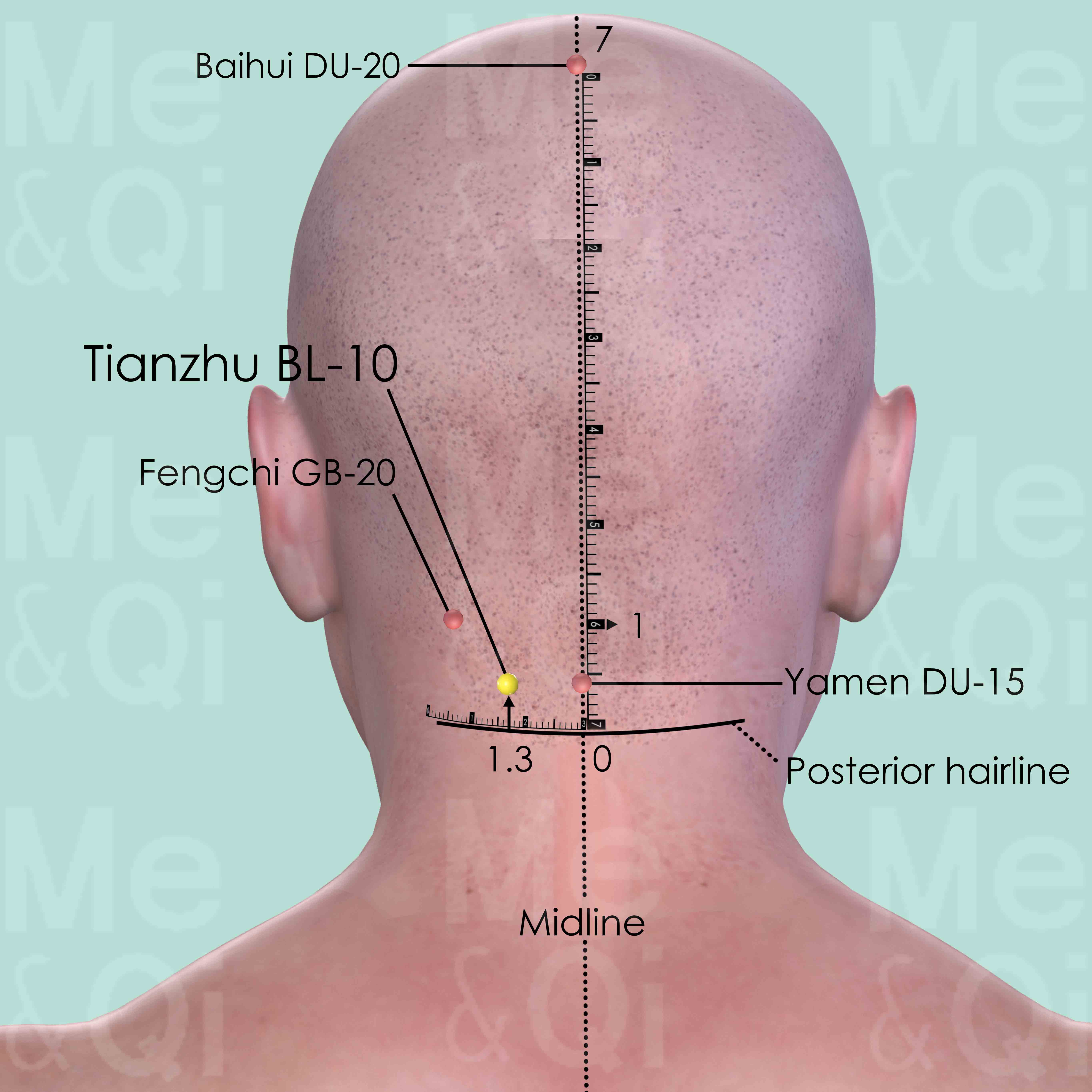
Tianzhu BL-10
1.3 cun lateral to Yamen DU-15 on the posterior midline, 0.5 cun above the posterior hairline, on the lateral side of trapezius muscle.
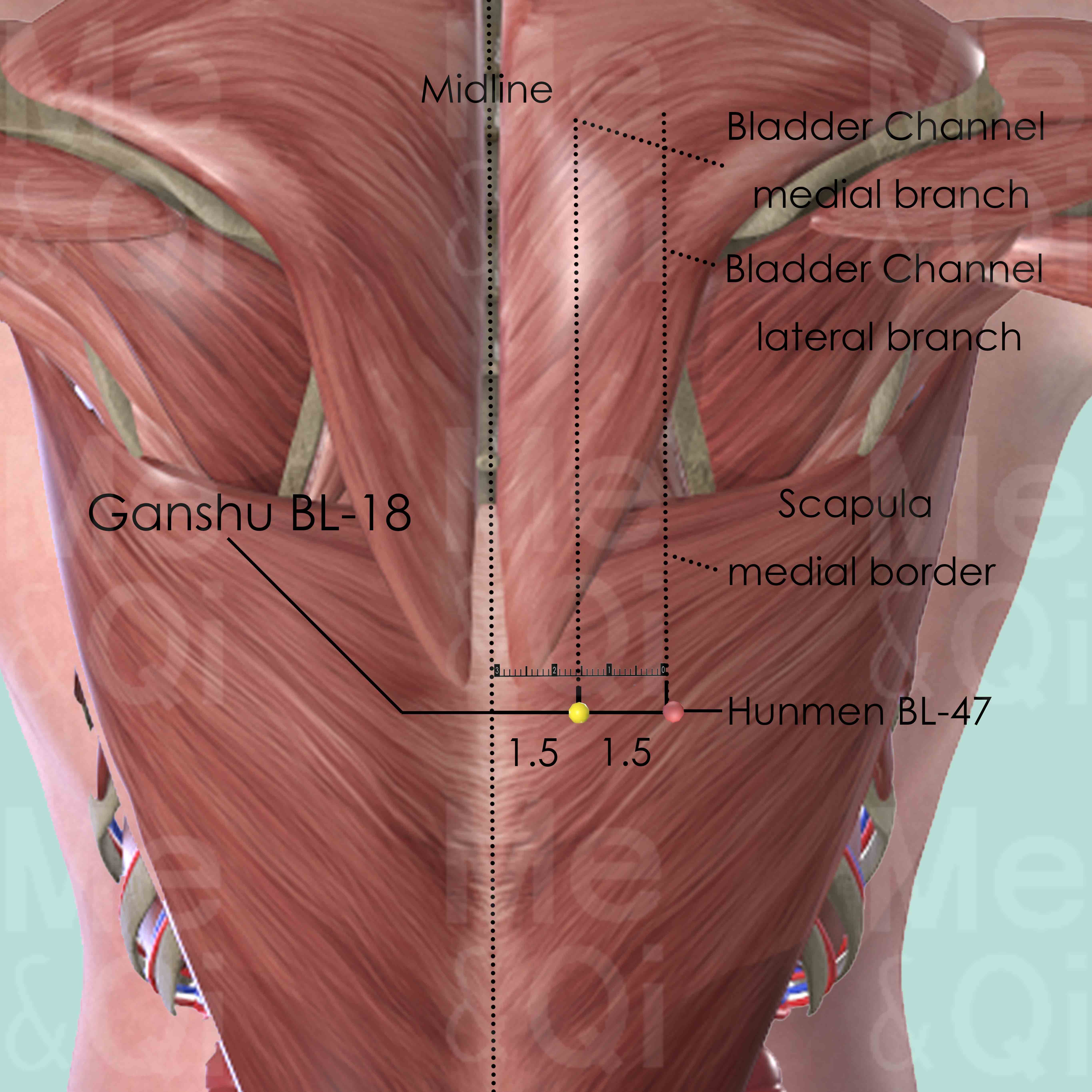
Ganshu BL-18
1.5 cun lateral to the lower border of the spinous process of the 9th thoracic vertebra (T9).
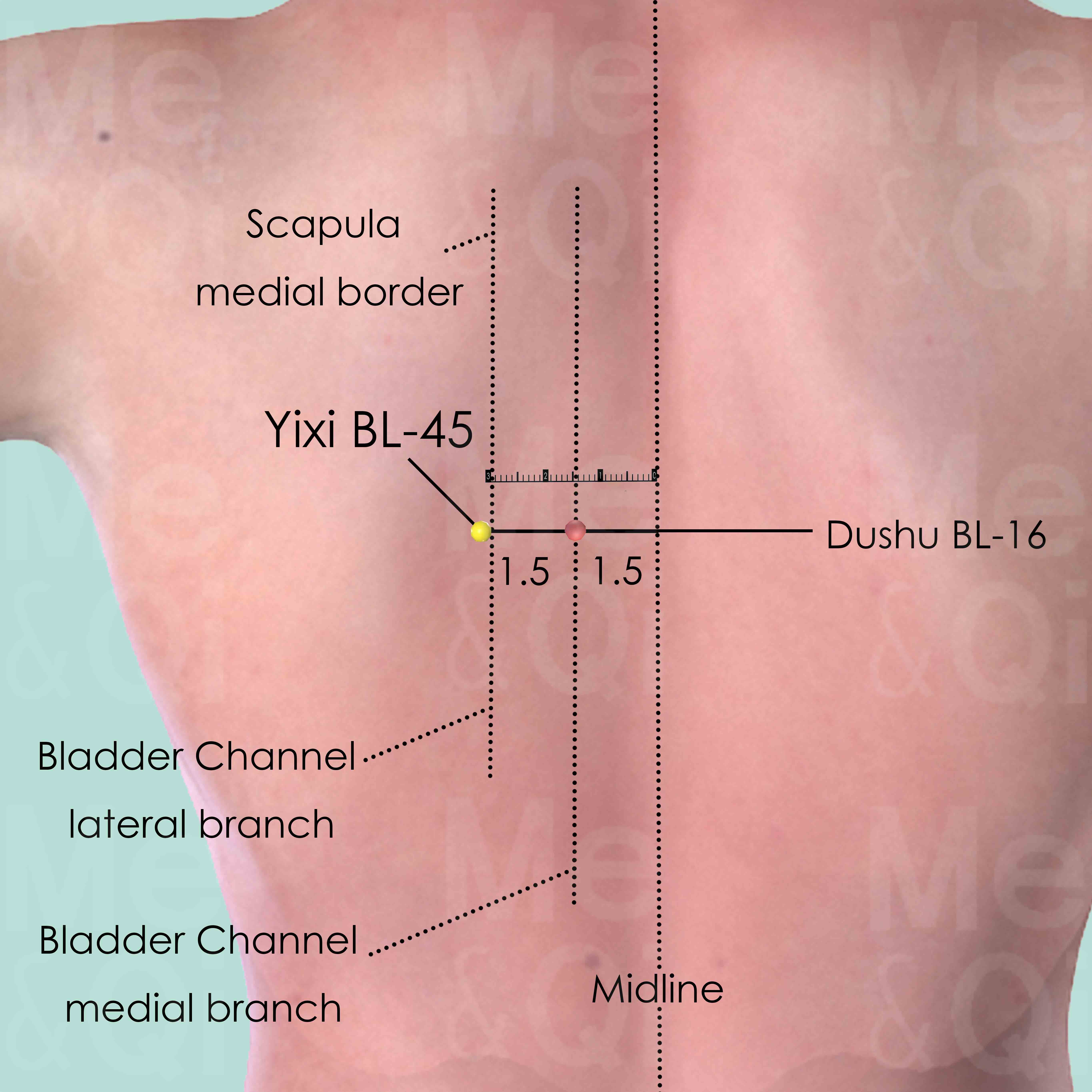
Yixi BL-45
3 cun (about 4 finger-breadths) lateral to the lower border of the spinous process of the 6th thoracic vertebra (T6).
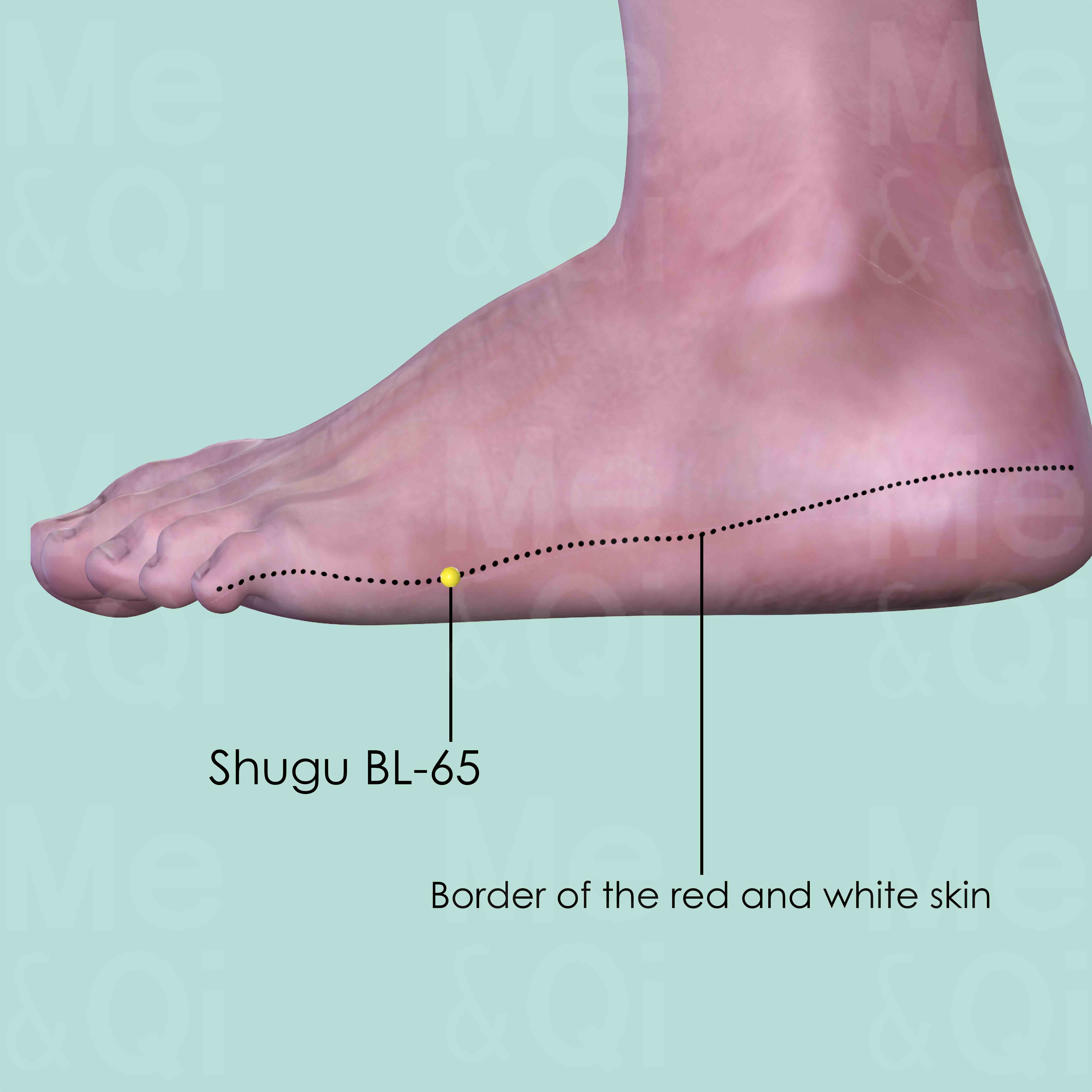
Shugu BL-65
On the lateral side of the foot dorsum, proximal to the head of the 5th metatarsal bone, at the border of the red and white skin.
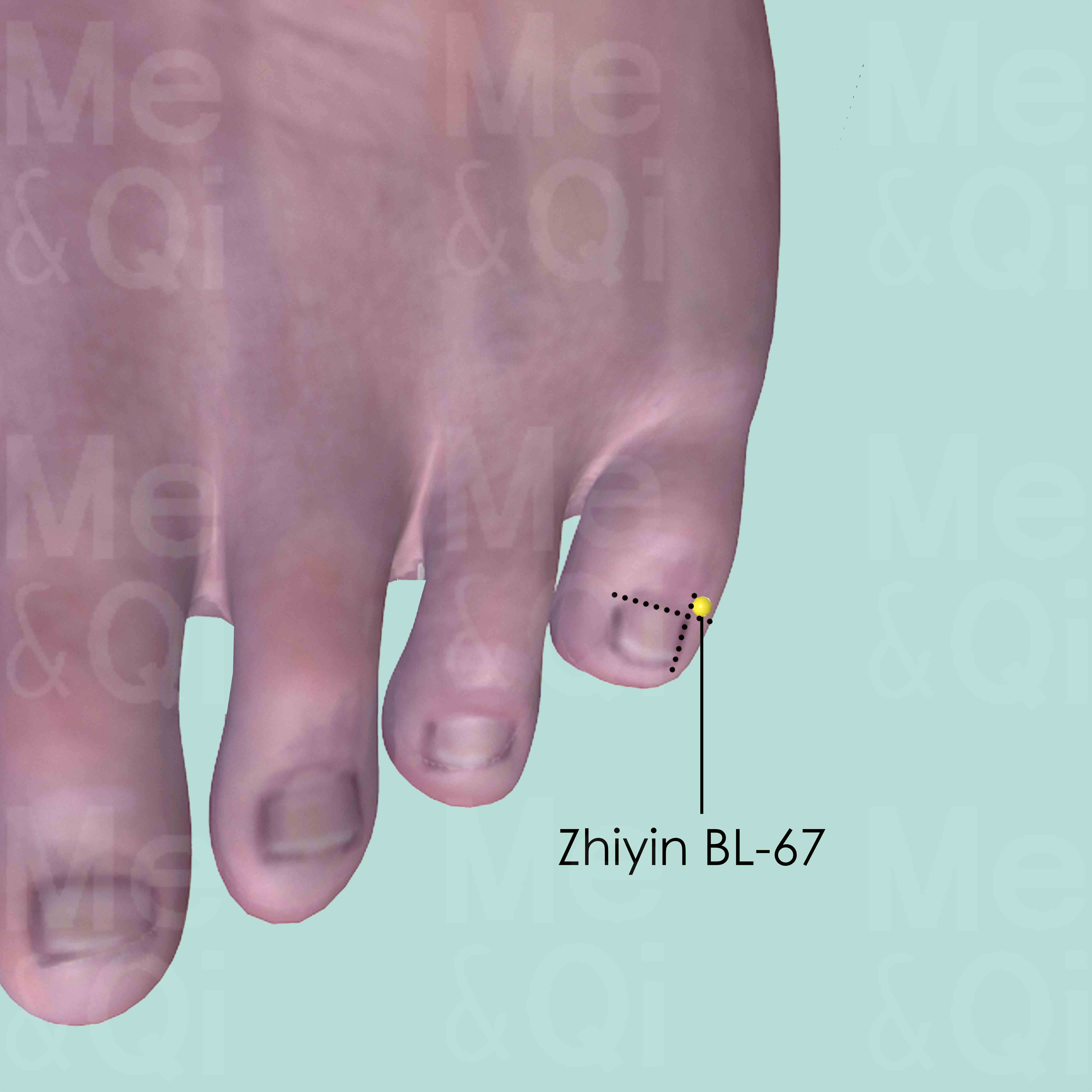
Zhiyin BL-67
On the lateral side of the little toe, about 0.1 cun posterior to the corner of the nail.
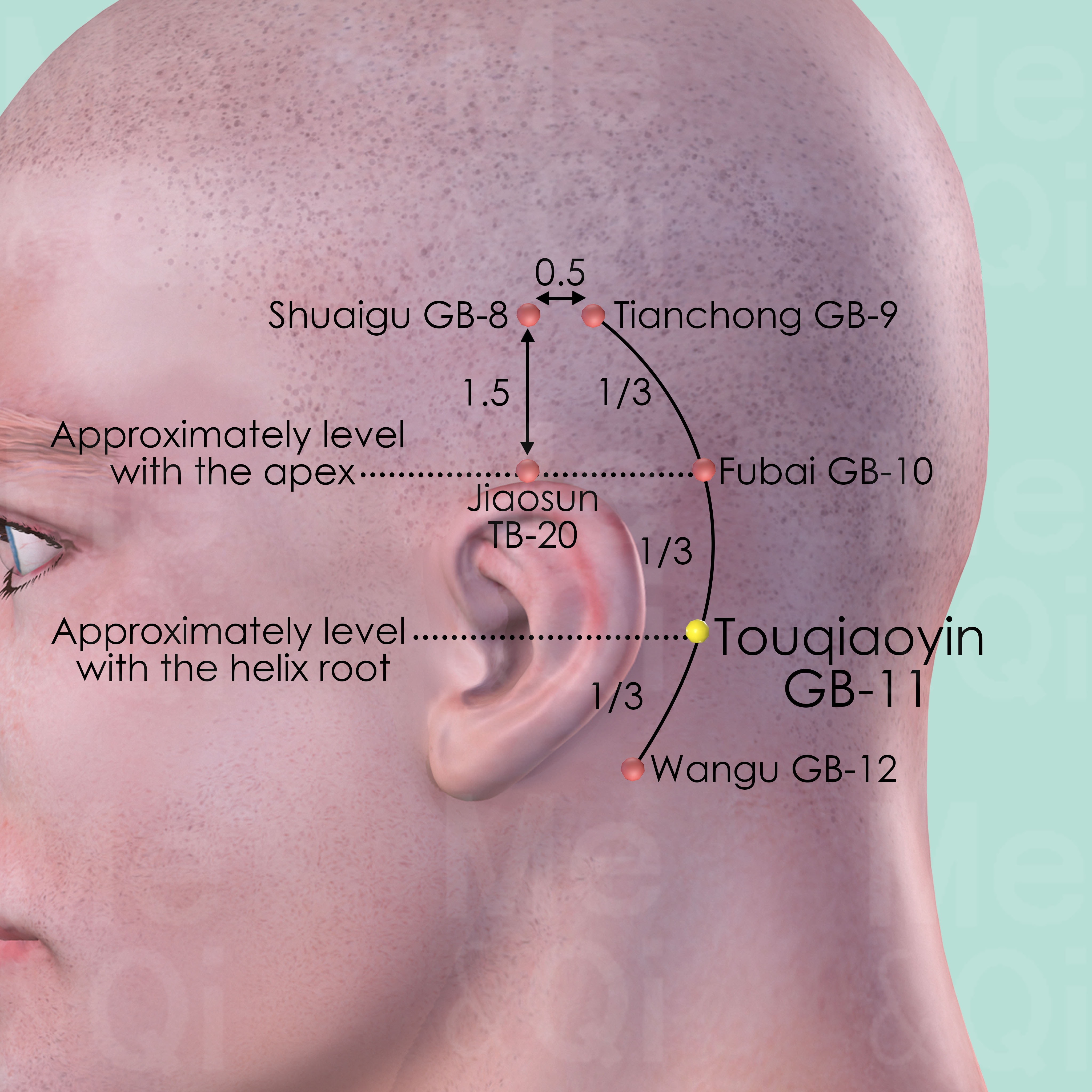
Touqiaoyin GB-11
Posterior and superior to the mastoid process, on the line connecting Tianchong GB-9, Fubai GB-10 and Wangu GB-12.
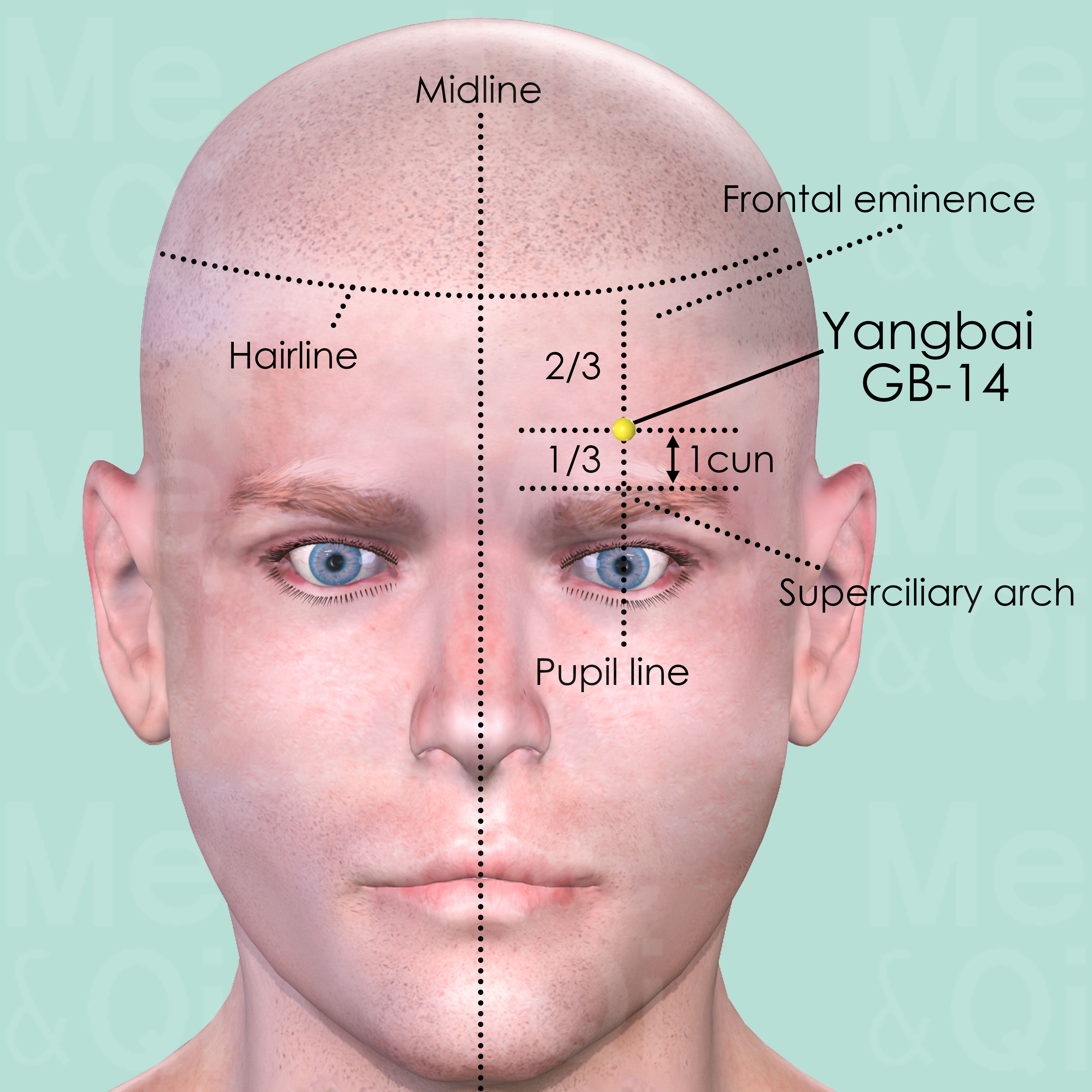
Yangbai GB-14
On the forehead, 1 cun above the midpoint of the eyebrow, approximately at the junction of the upper two-thirds and lower third of the vertical line draw from the anterior hairline to the eyebrow.
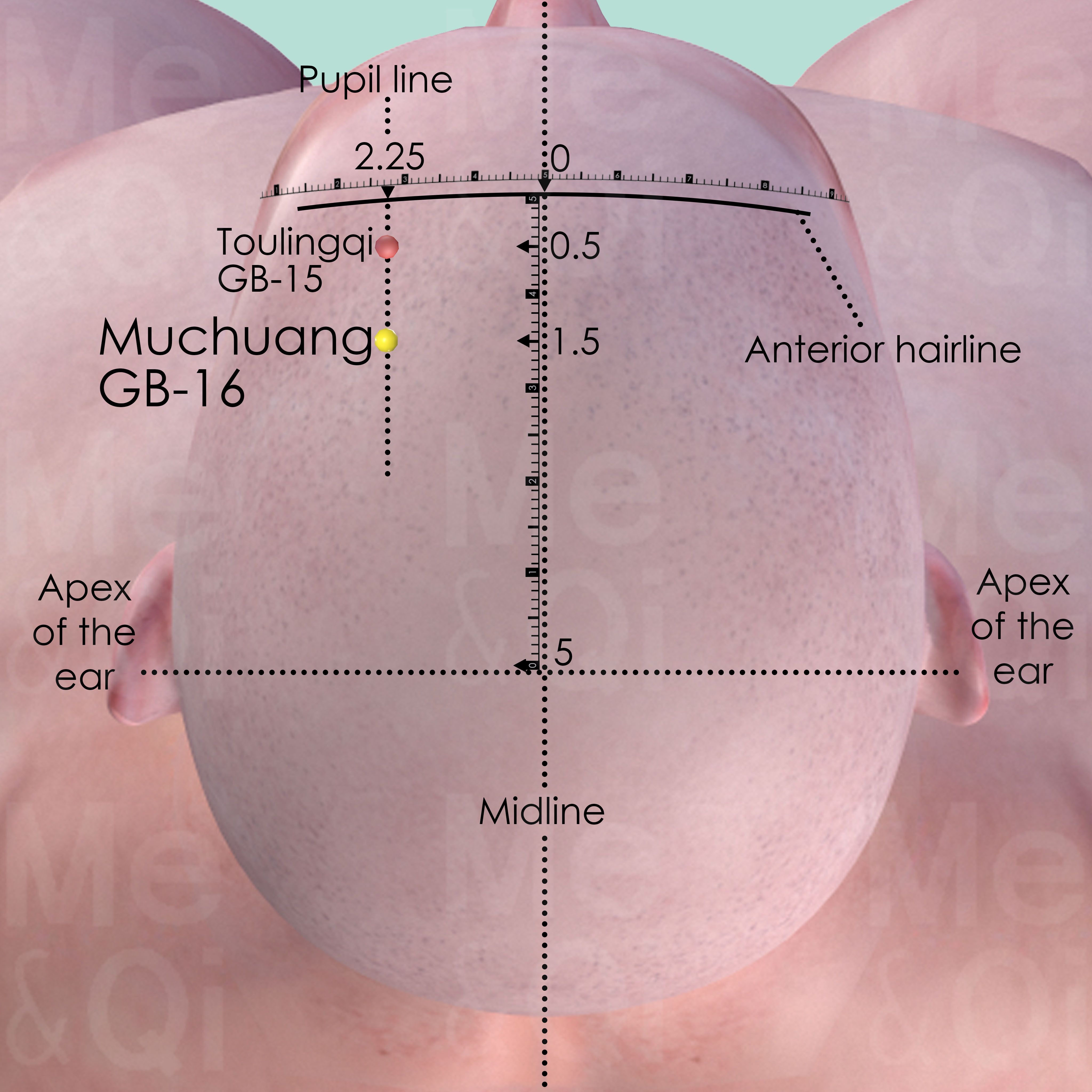
Muchuang GB-16
1 cun posterior to the Toulingqi GB-15 or 1.5 cun posterior to the anterior hairline, on the pupil line which is 2.25 cun lateral to the midline.
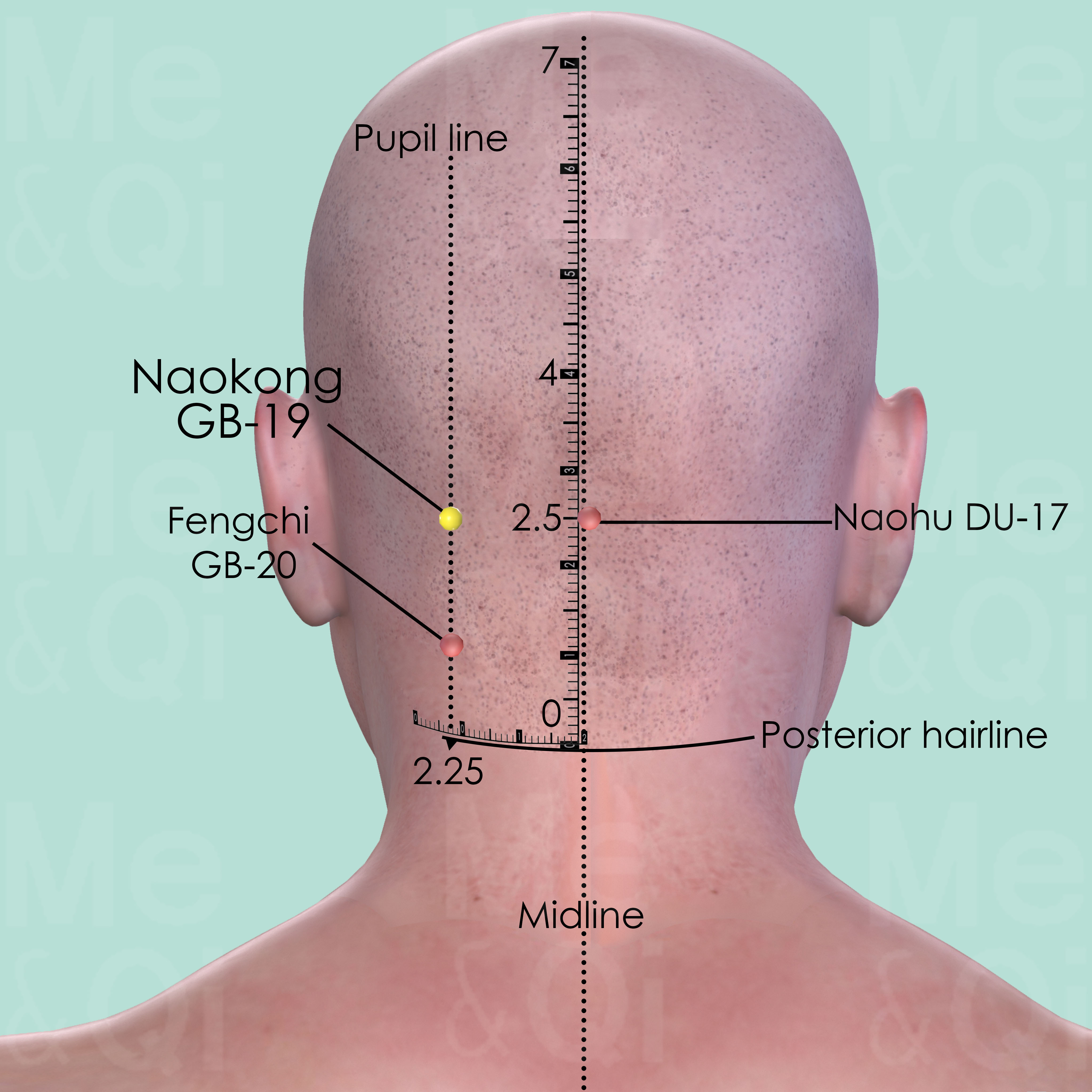
Naokong GB-19
Directly above Fengchi GB-20, level with Naohu DU-17, on the lateral side of the external occipital protuberance.
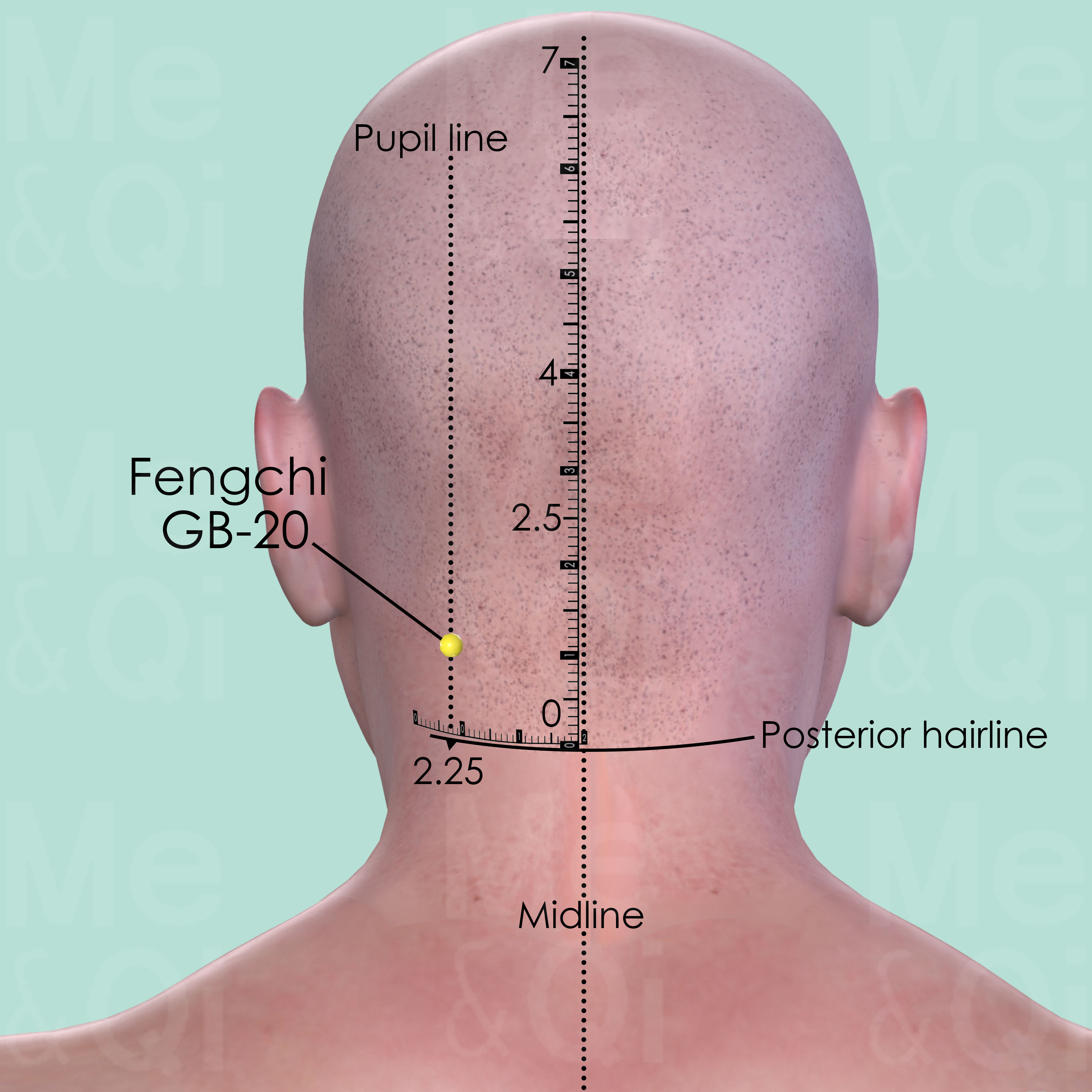
Fengchi GB-20
In the posterior aspect of the neck, below the occipital bone, in the depression between the upper portion of sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscle.
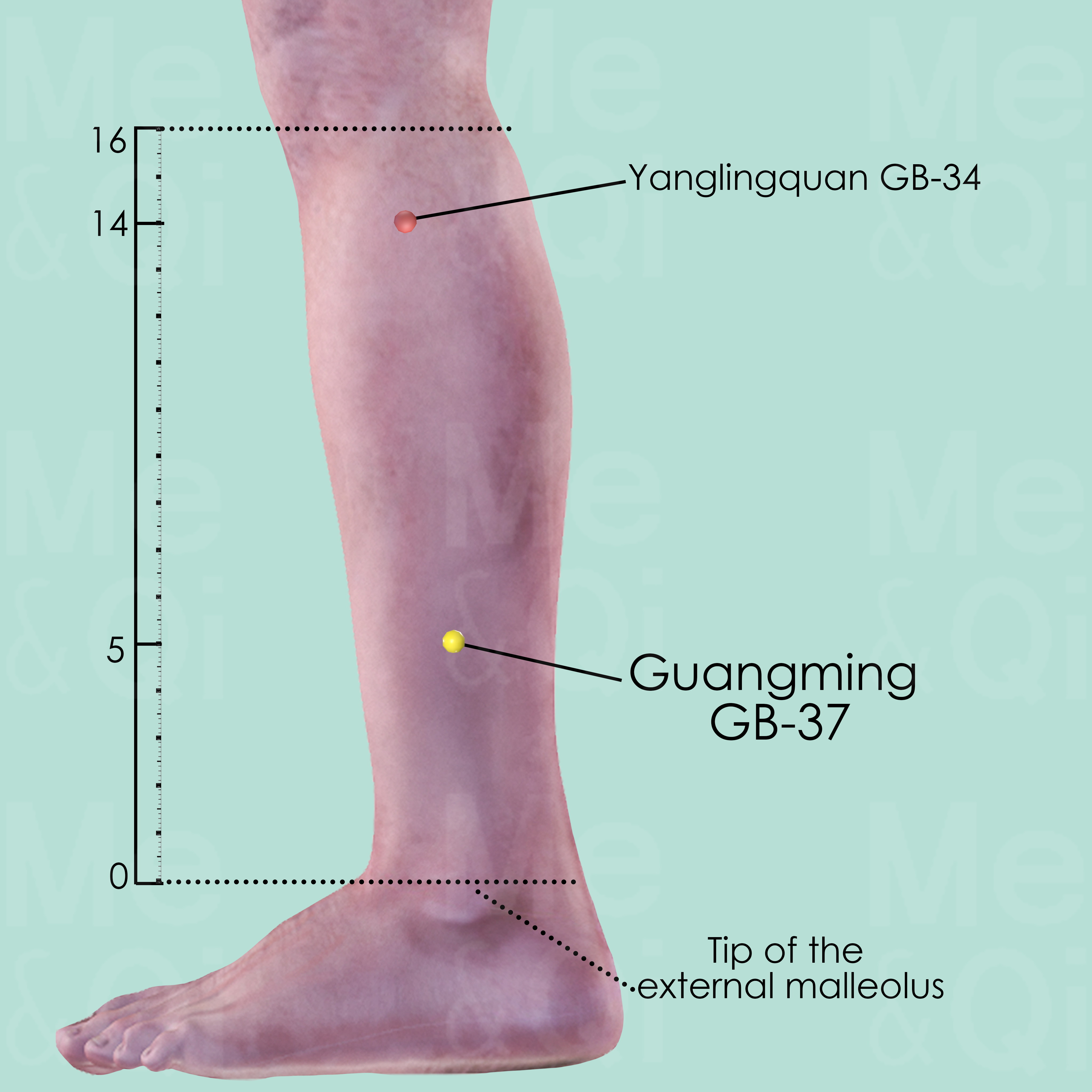
Guangming GB-37
5 cun directly above the tip of the external malleolus, on the anterior border of the fibula.
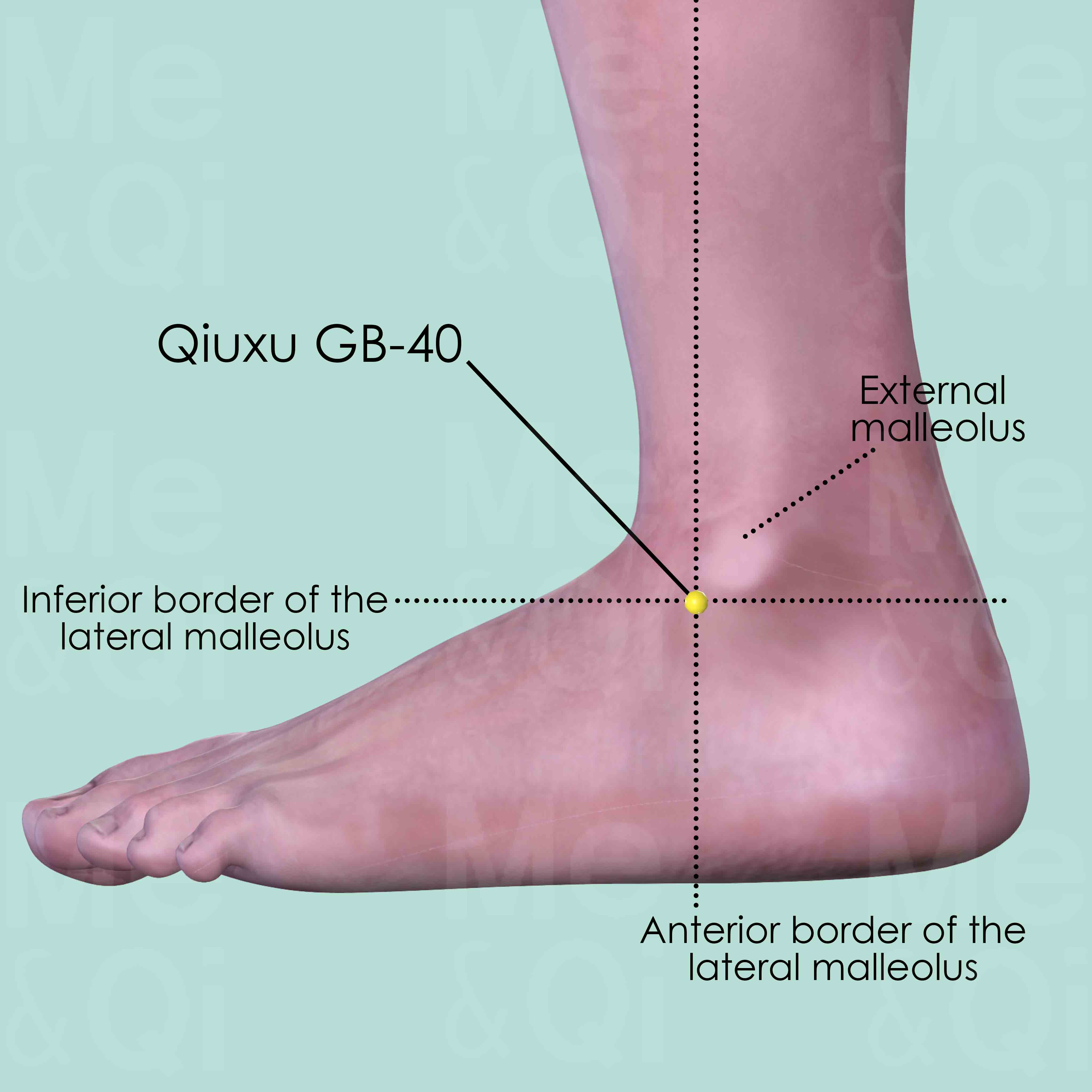
Qiuxu GB-40
Anterior and inferior to the external malleolus, in the depression on the lateral side of the tendon of extensor digitorum longus muscle that goes to the little toe.
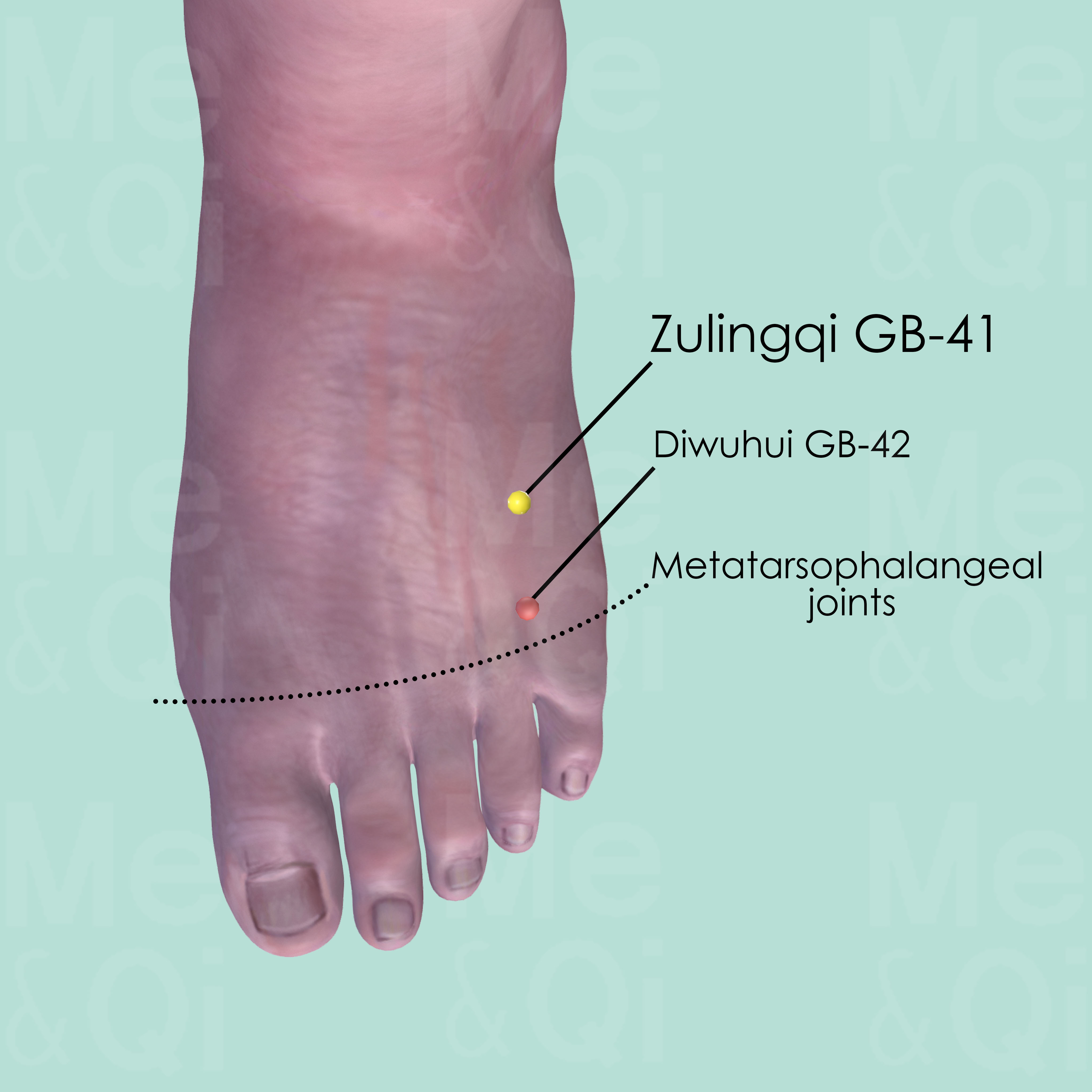
Zulingqi GB-41
In the depression distal to the junction of the 4th and 5th metatarsal bones, on the lateral side of the tendon of extensor digitorum longus muscle of the foot.
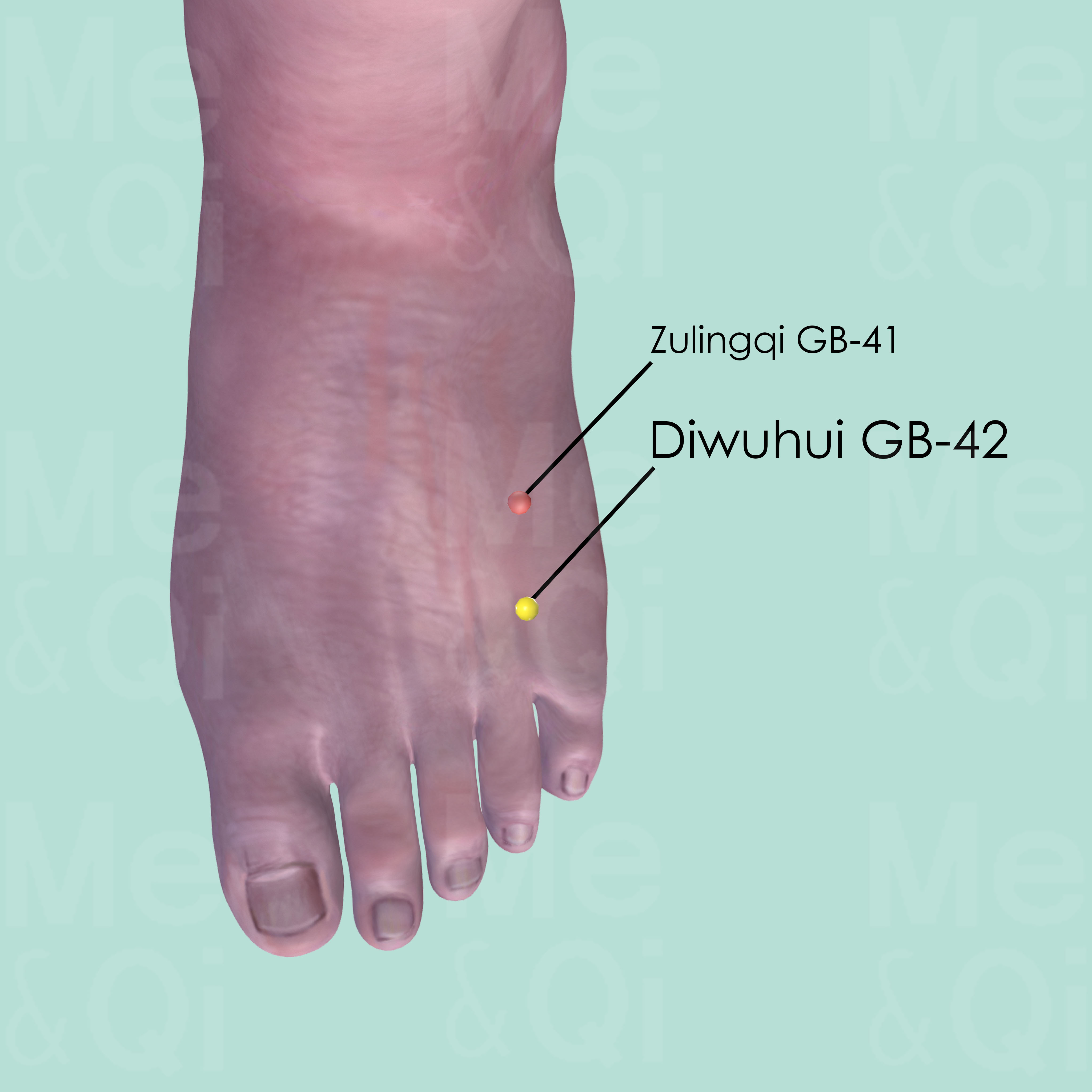
Diwuhui GB-42
Between the 4th and 5th metatarsal bones, on the medial side of the tendon of extensor digitorum longus muscle of the little toe.
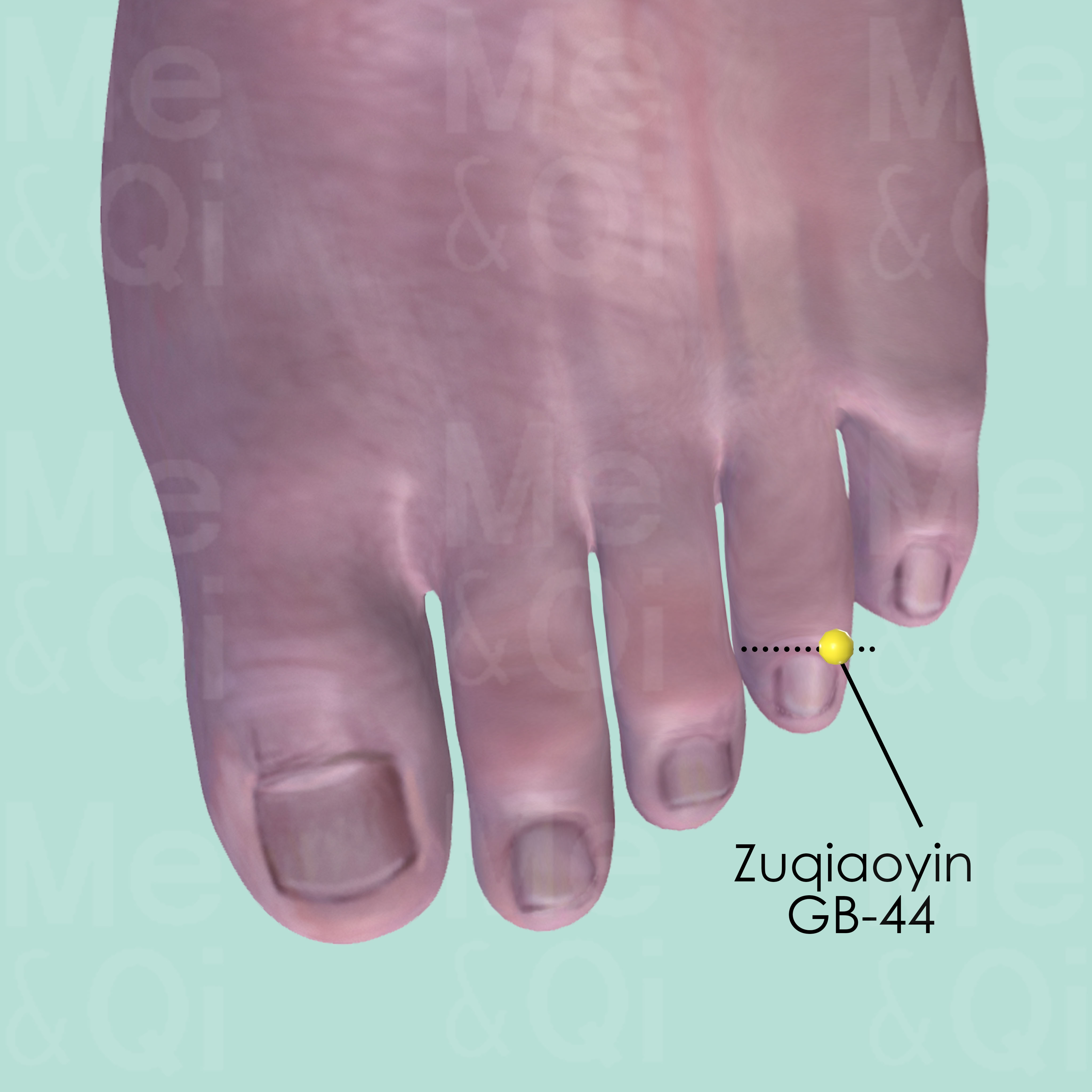
Zuqiaoyin GB-44
On the lateral side of the 4th toe, about 0.1 cun posterior to the corner of the nail.
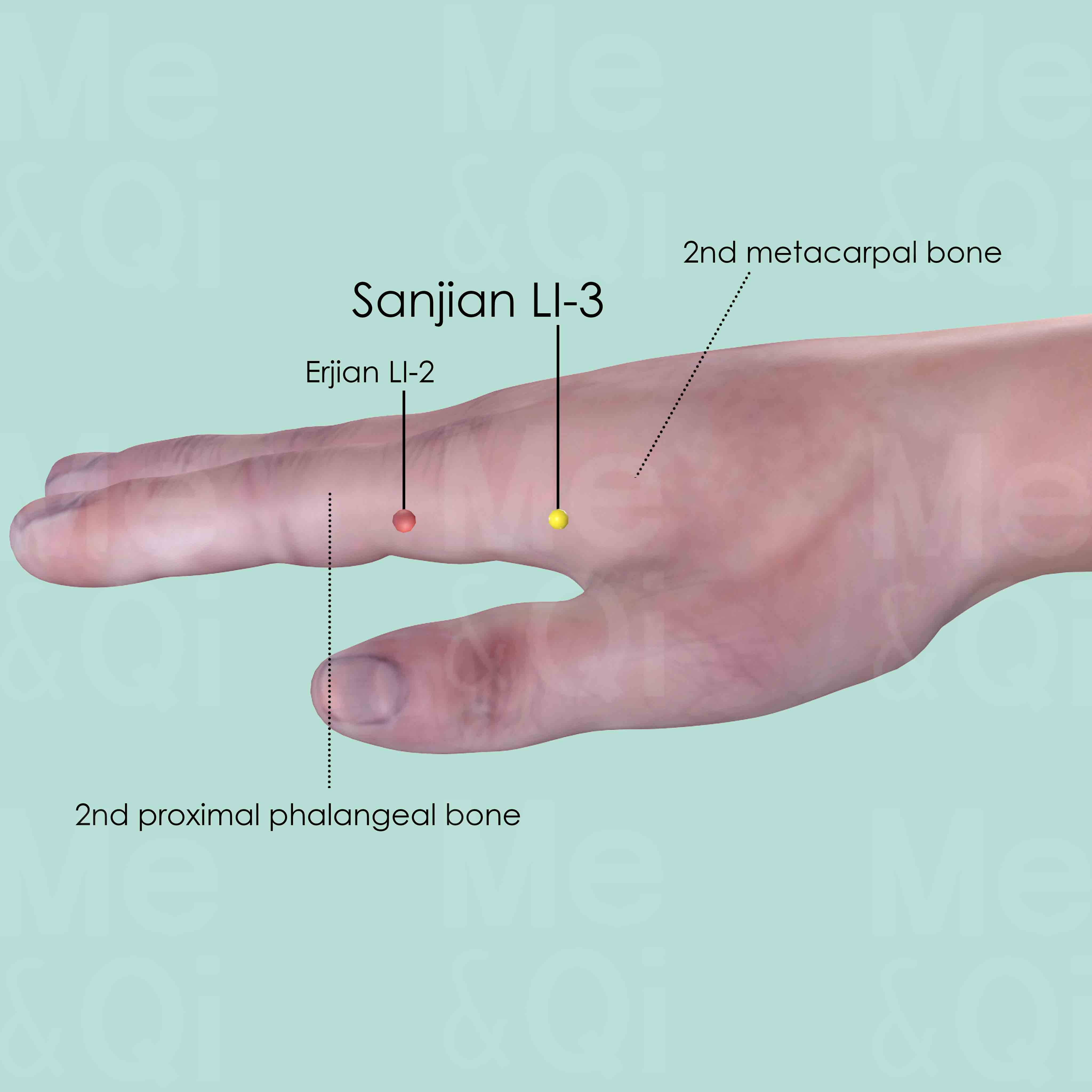
Sanjian LI-3
Located on the radial side of the index finger, in the depression proximal to the head of the 2nd metacarpal bone.
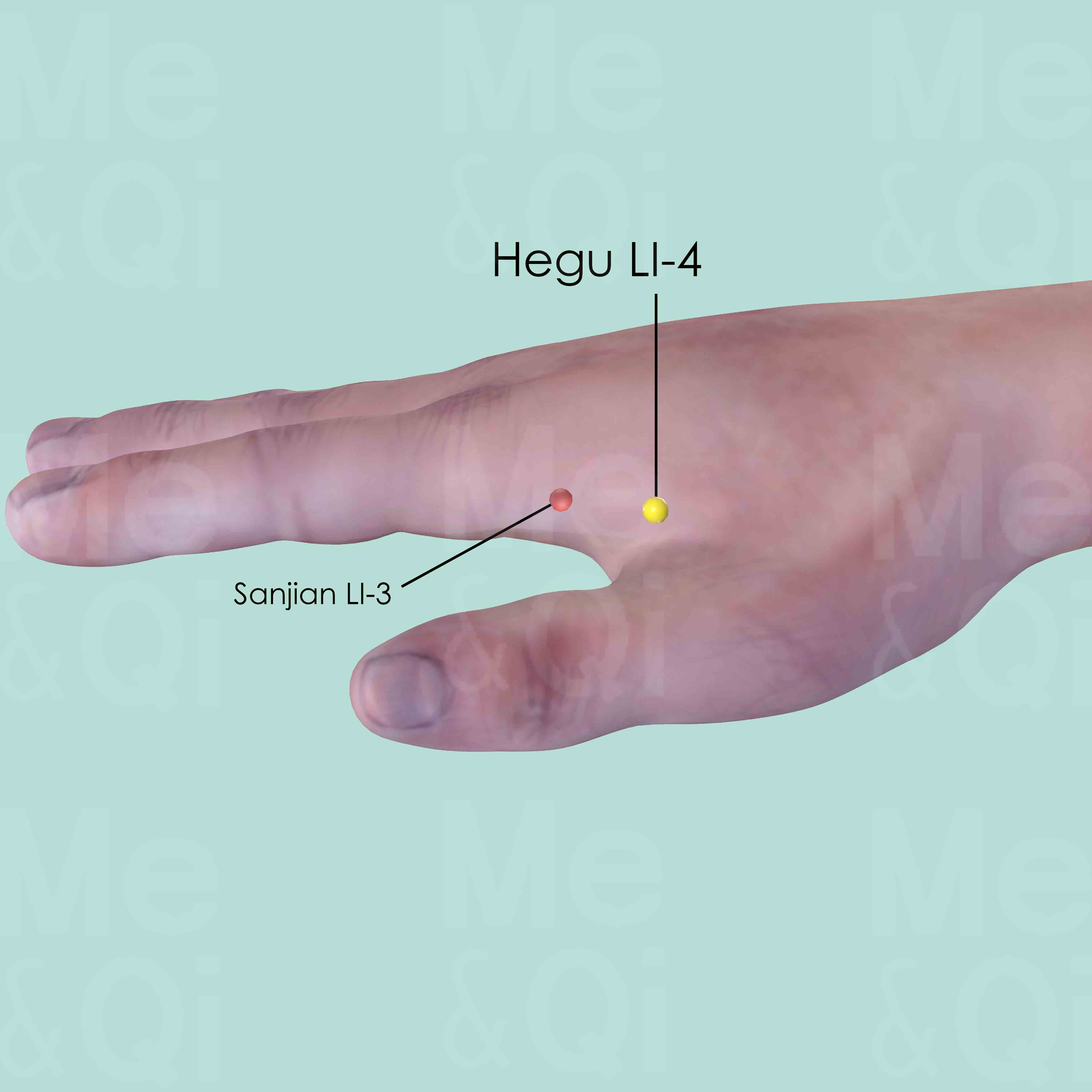
Hegu LI-4
Between the 1st and 2nd metacarpal bones, approximately in the middle of the 2nd metacarpal bone on the radial side.
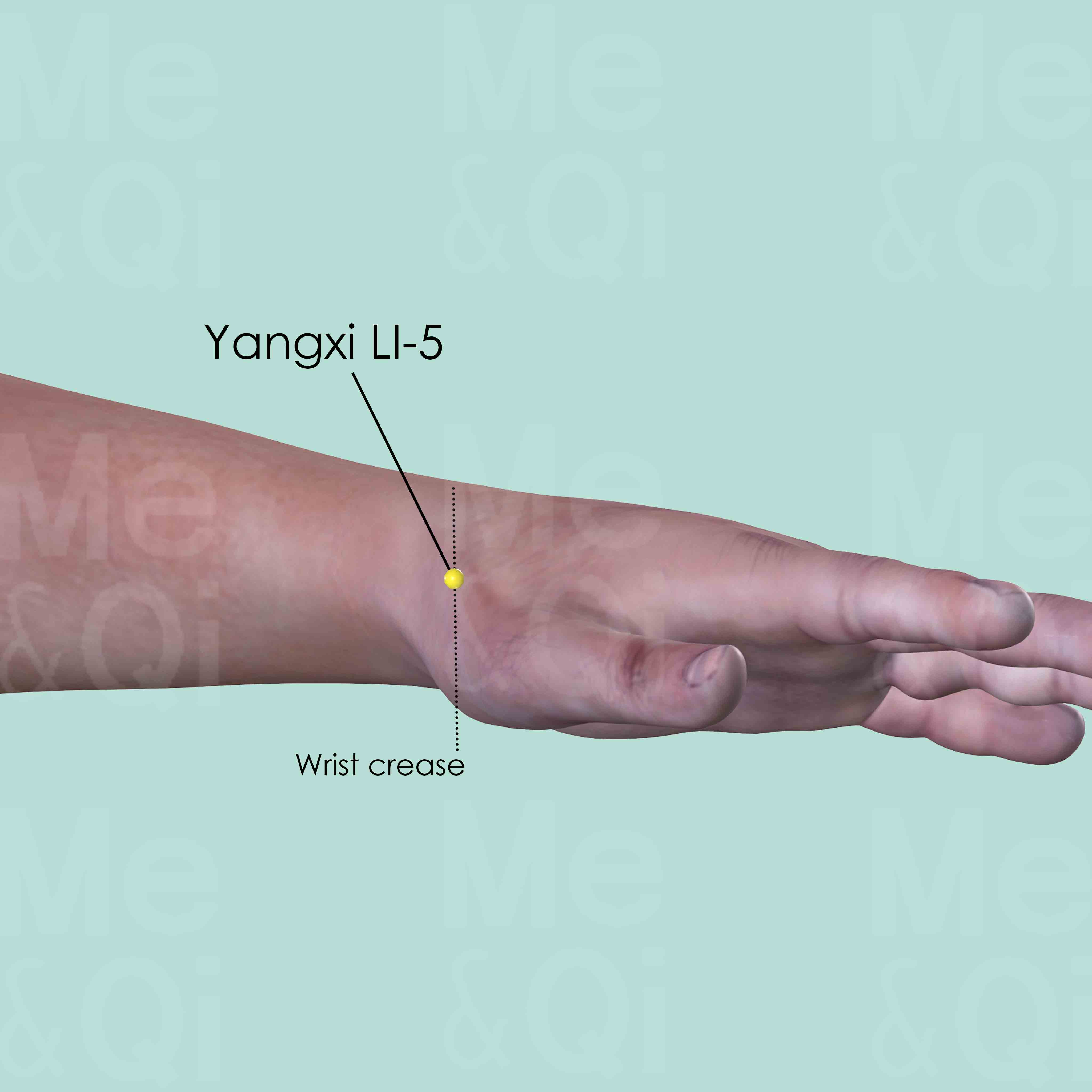
Yangxi LI-5
On the radial side of the wrist. When the thumb is tilted upward, it is in the depression on the wrist joint space (wrist crease) between the tendons of extensor pollicis longus and brevis muscles.
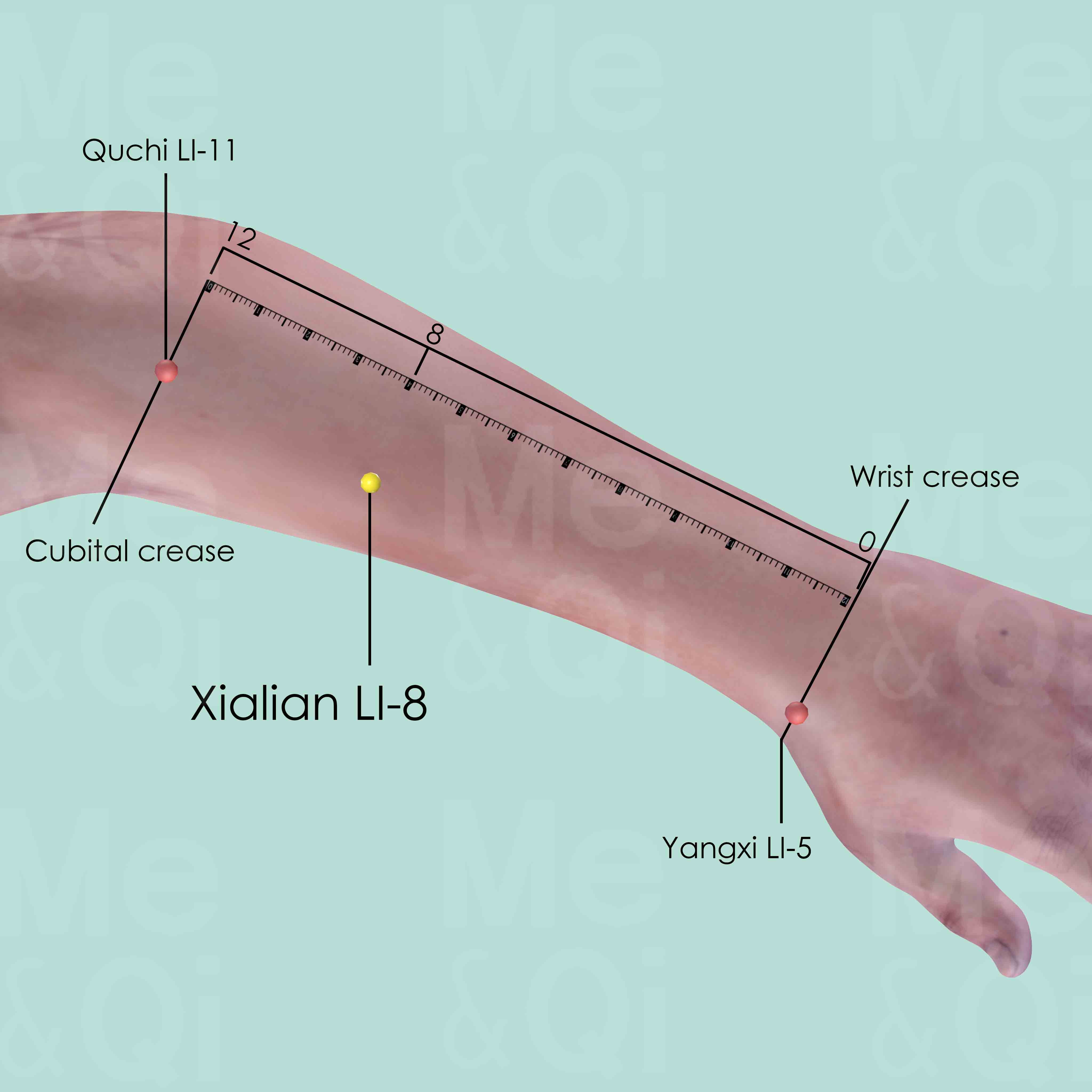
Xialian LI-8
When a fist is made, with the ulnar side downward and elbow flexed, the point is 4 cun distal to Quchi LI-11 of the line joining Yangxi LI-5 and Quchi LI-11.
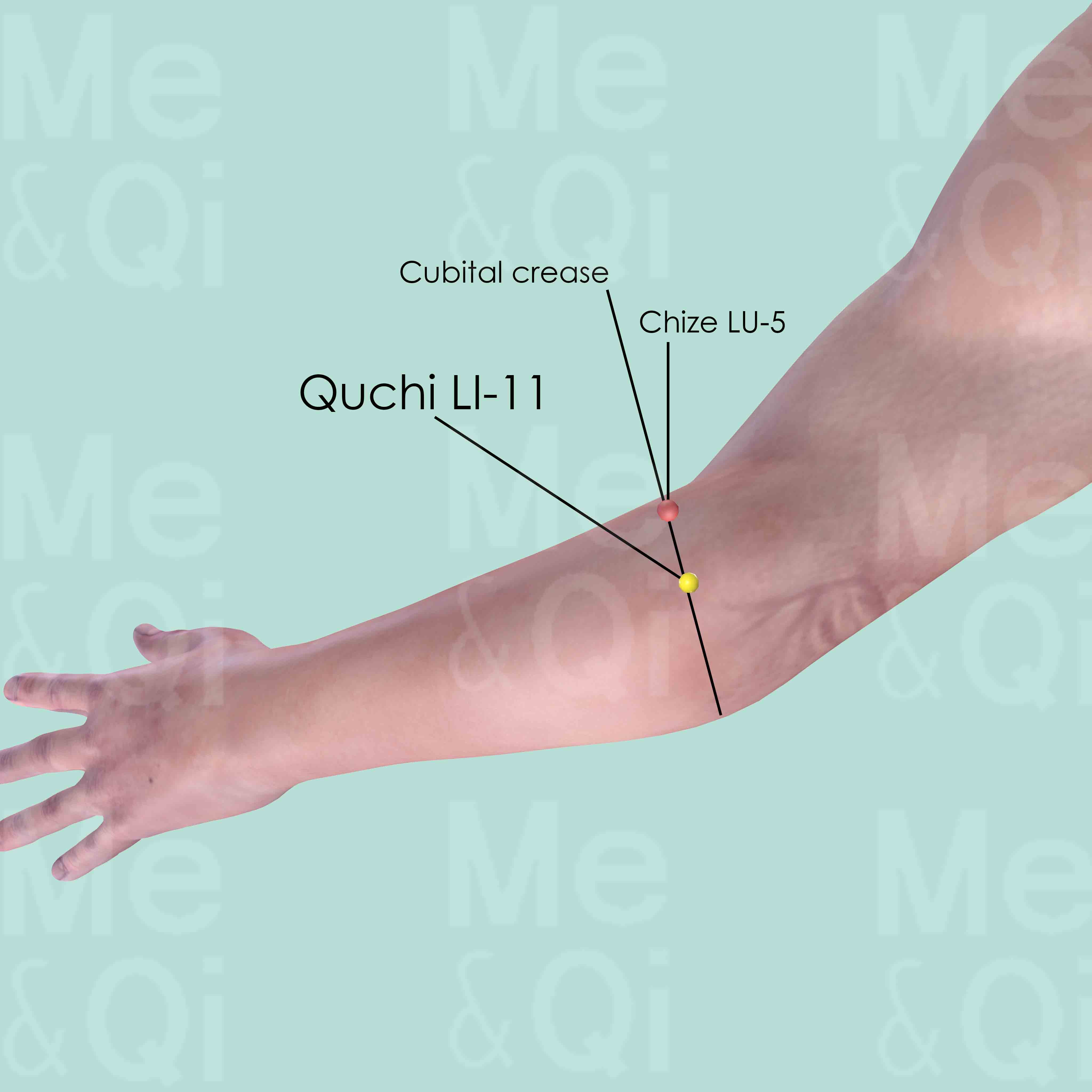
Quchi LI-11
When the elbow is flexed, Quchi LI-11 is in the depression at the lateral end of the cubital crease, midway between Chize LU-5 and the lateral epicondyle of the humerus.
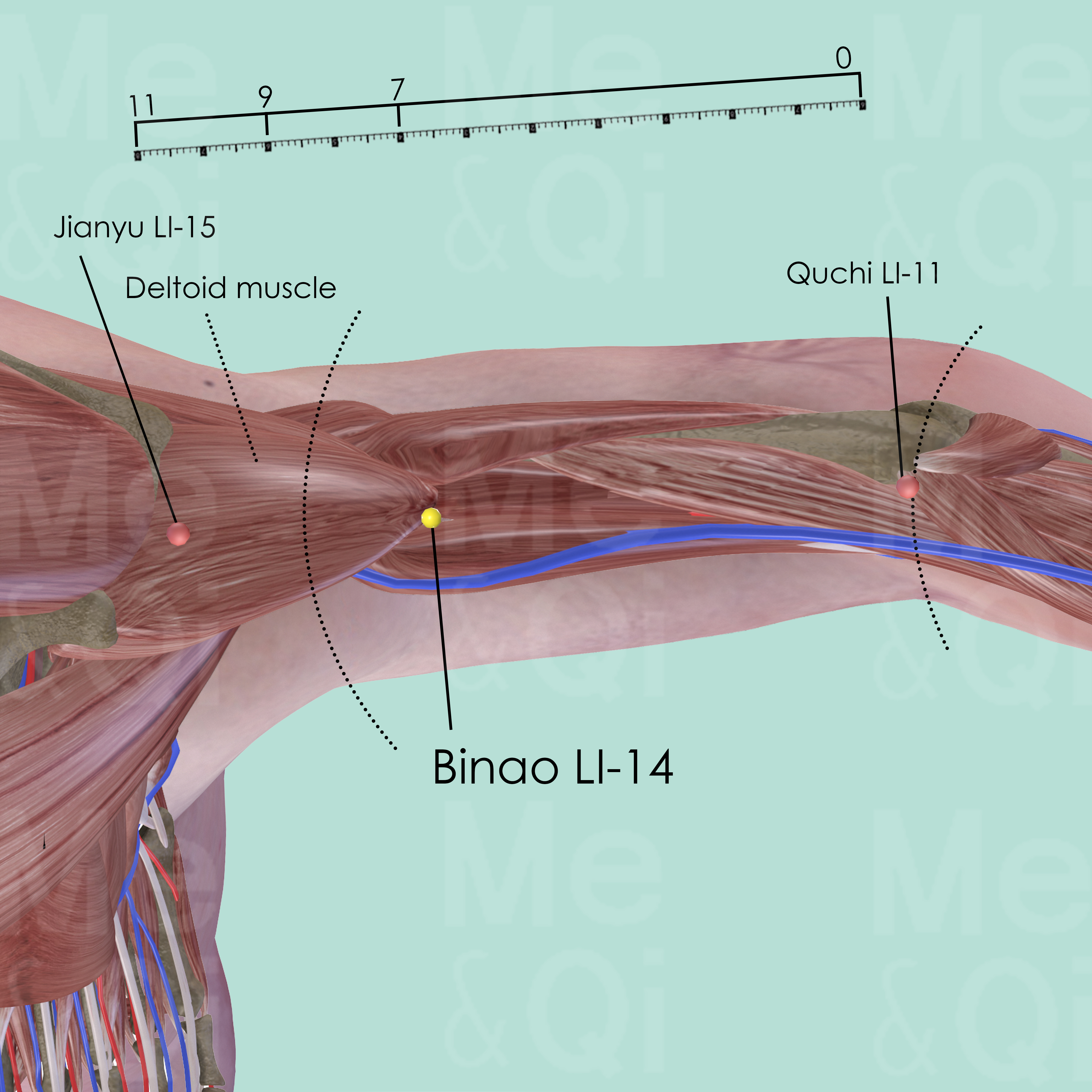
Binao LI-14
On the radial side of the humerus, superior to the lower end of deltoid muscle, on the line connecting Quchi LI-11 and Jianyu LI-15, 7 cun proximal to Quchi LI-11.
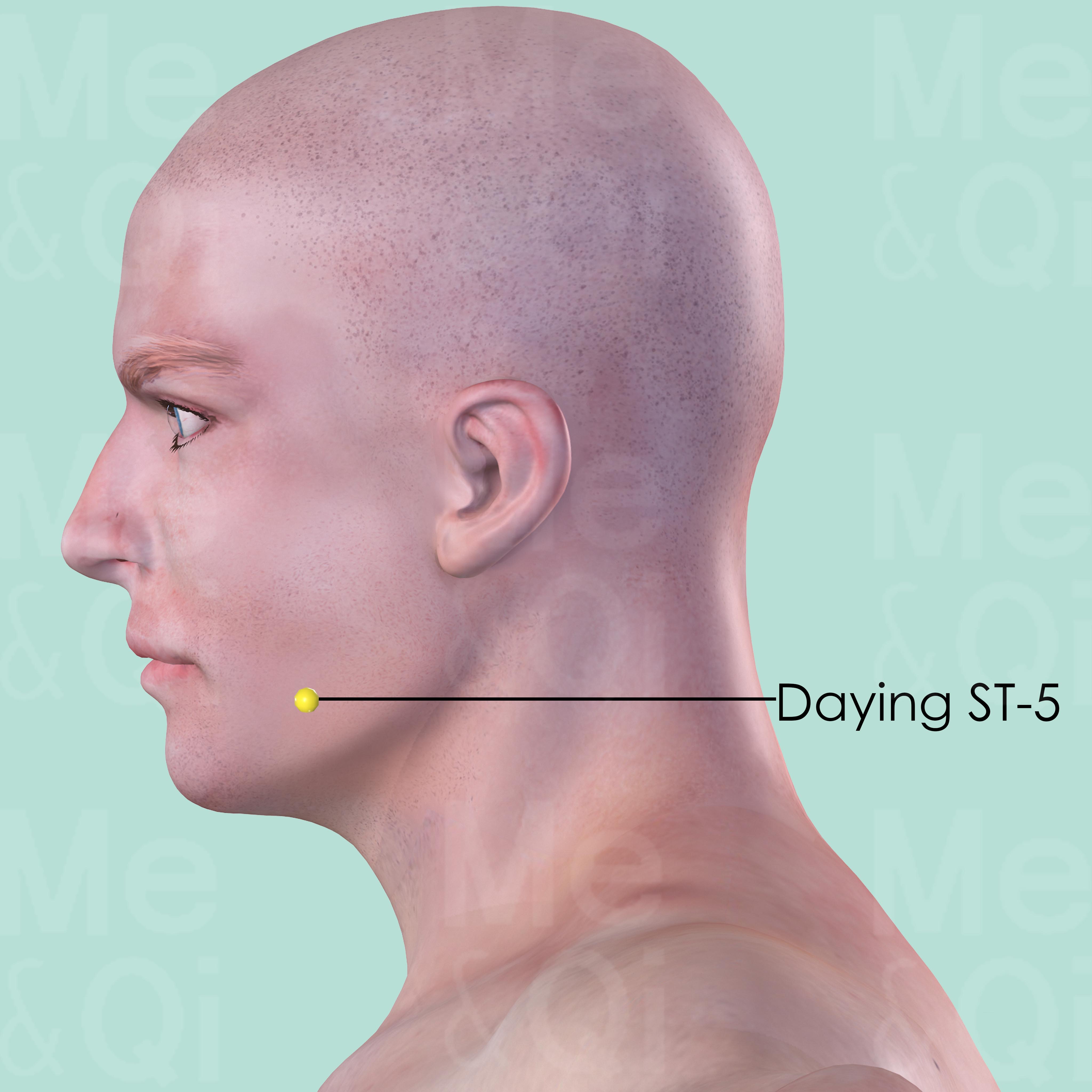
Daying ST-5
On the lateral mandible, on the anterior border of masseter muscle, in the groove-like depression appearing when the cheek is bulged.
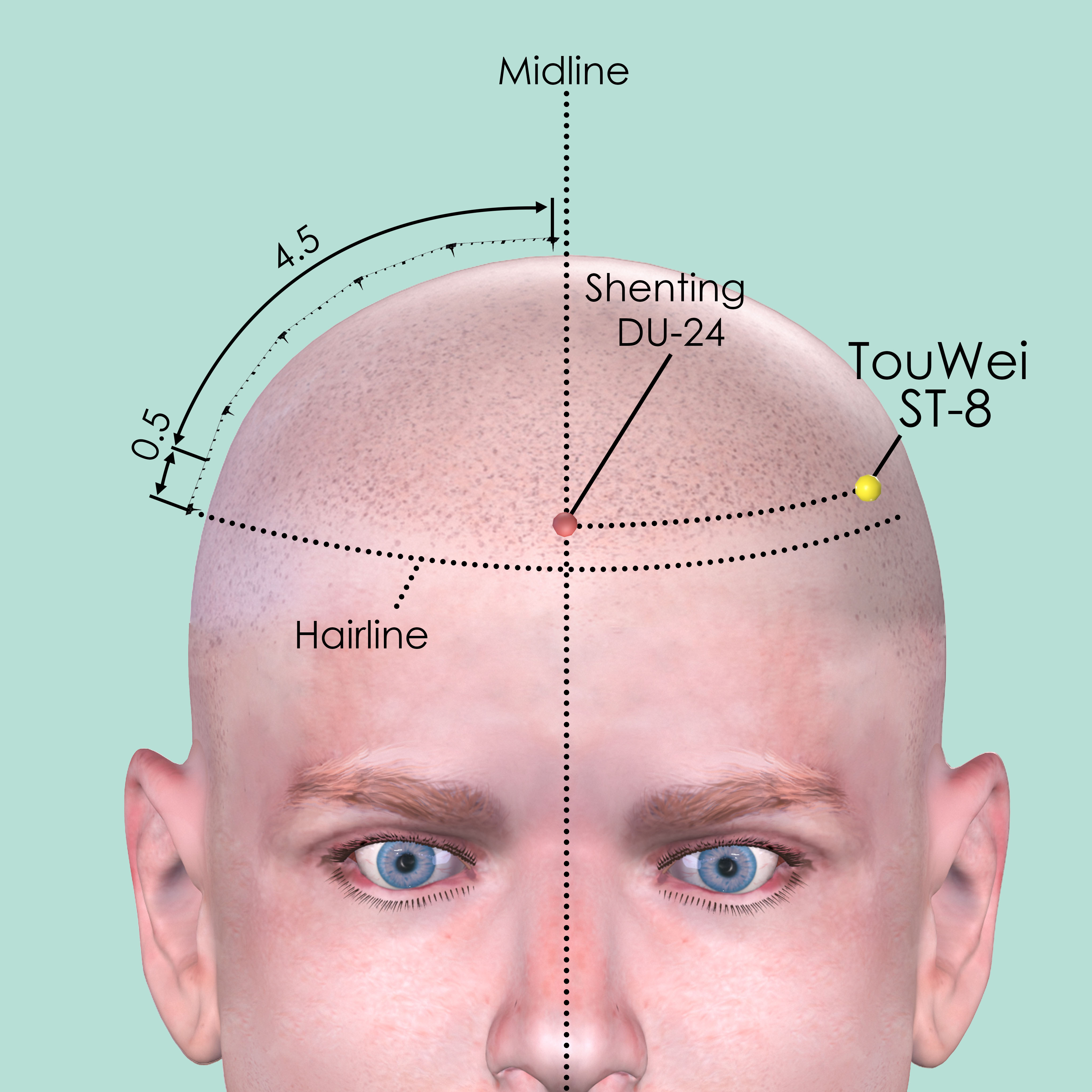
Touwei ST-8
At the temporal corner of the forehead, on the border of the temporalis muscle. 0.5 cun within the anterior hairline at the corner of the forehead and 4.5 cun lateral to the anterior midline.
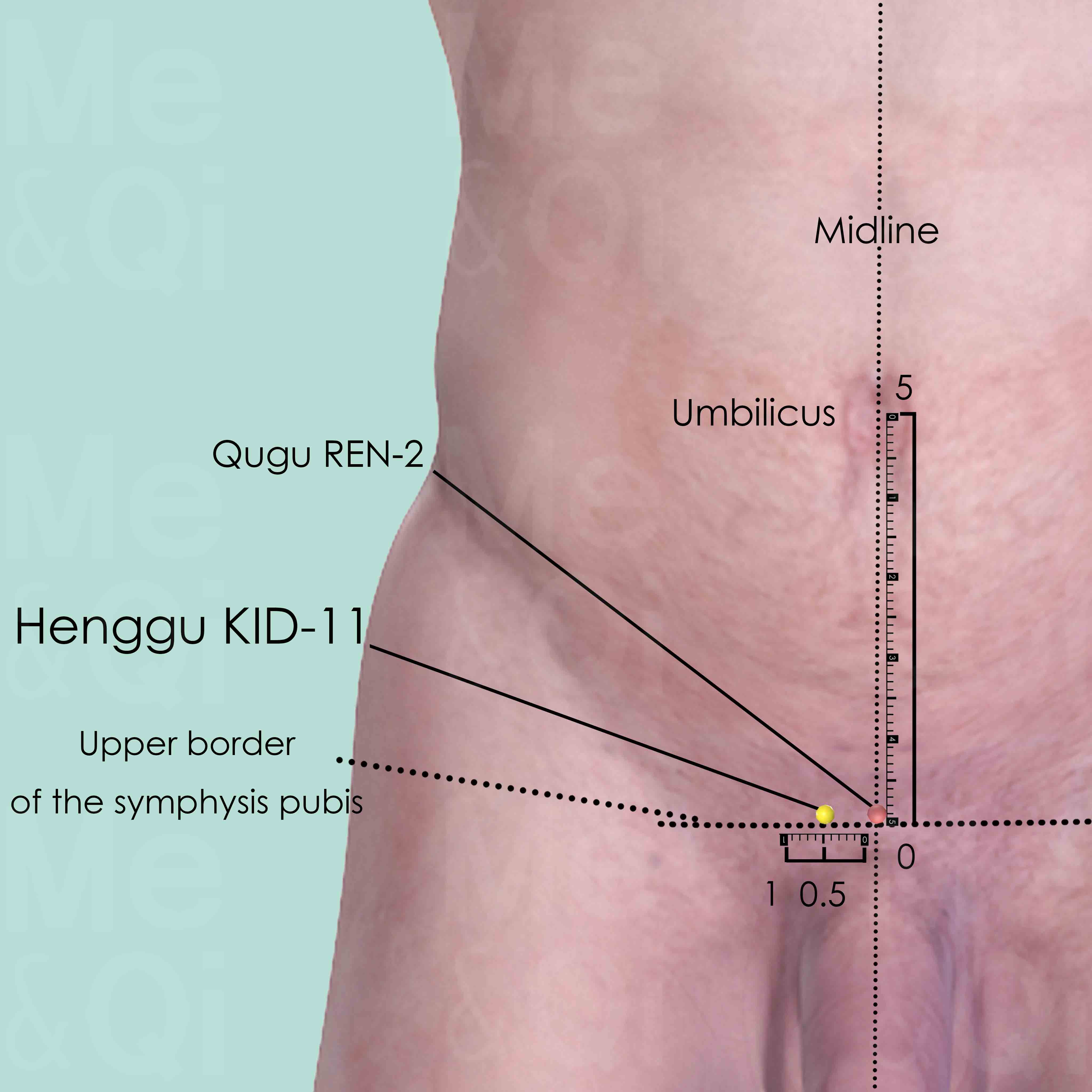
Henggu KID-11
5 cun below the umbilicus, on the upper border of symphysis pubis, 0.5 cun lateral to the anterior midline. It is at the same level as Qugu REN-2 which is at the anterior midline.
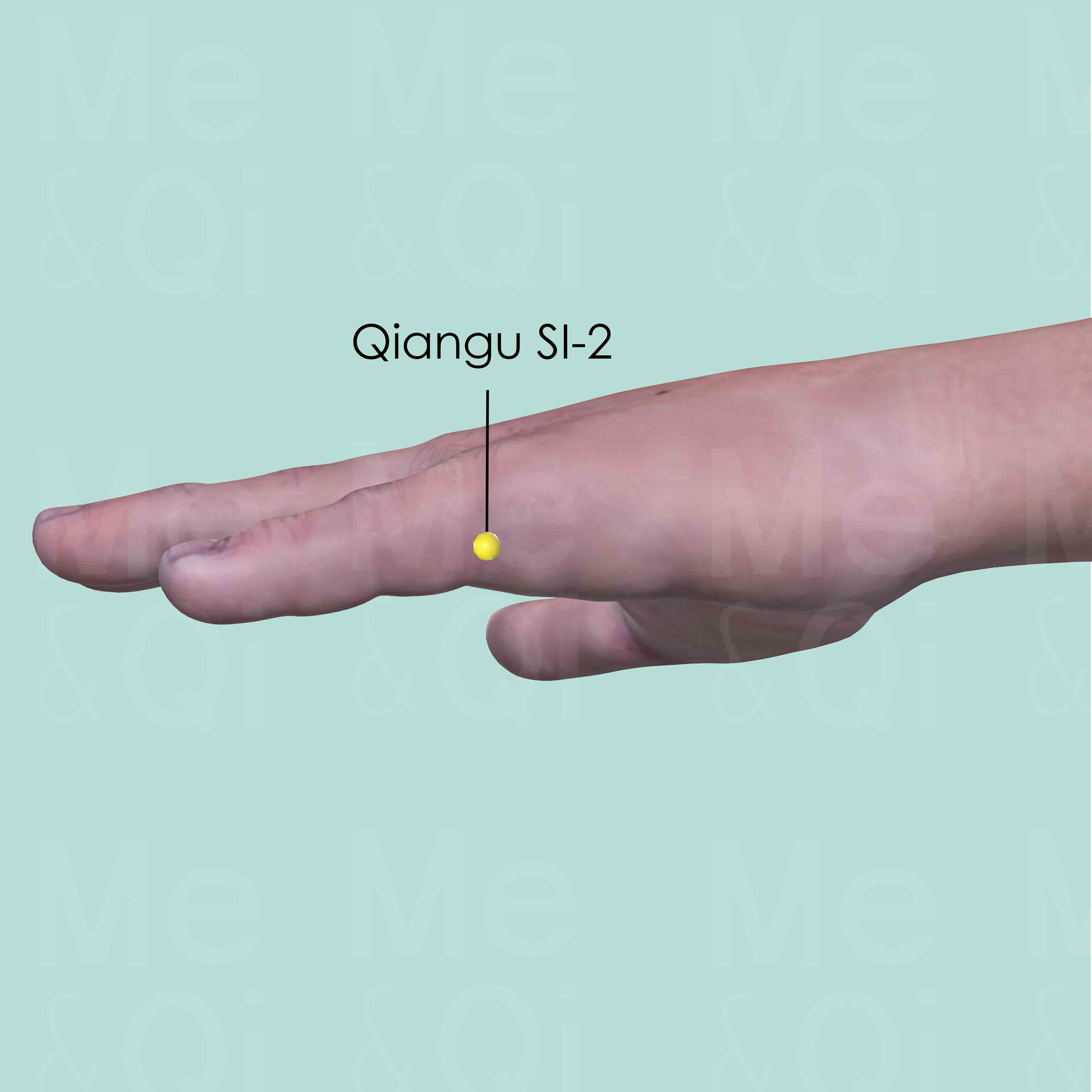
Qiangu SI-2
On the ulnar aspect of the little finger, distal to the metacarpophalangeal joint, at the junction of the shaft and the base of the proximal phalanx.
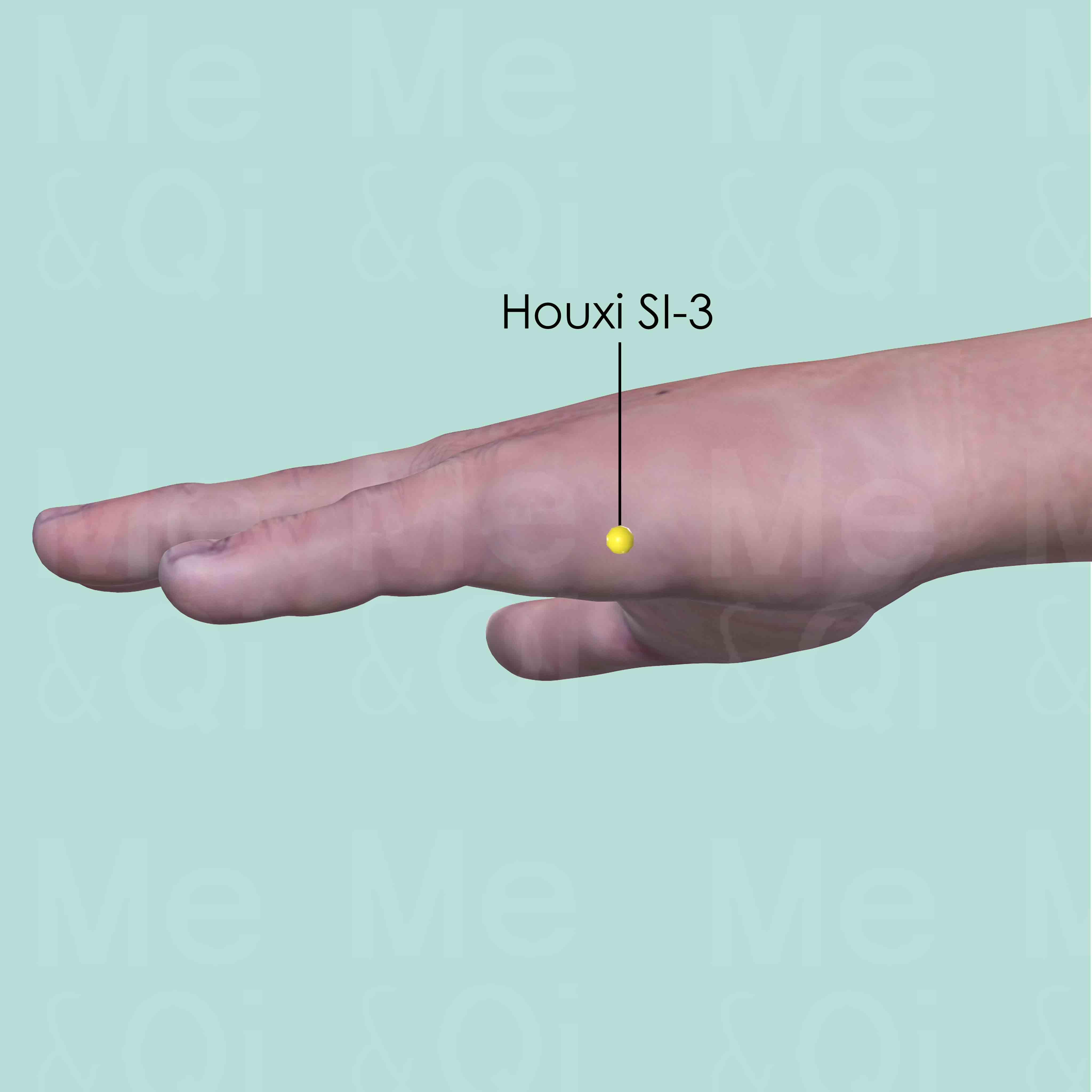
Houxi SI-3
Proximal to the head of the 5th metacarpal bone on the ulnar side, in the depression at the junction of the red and white skin.
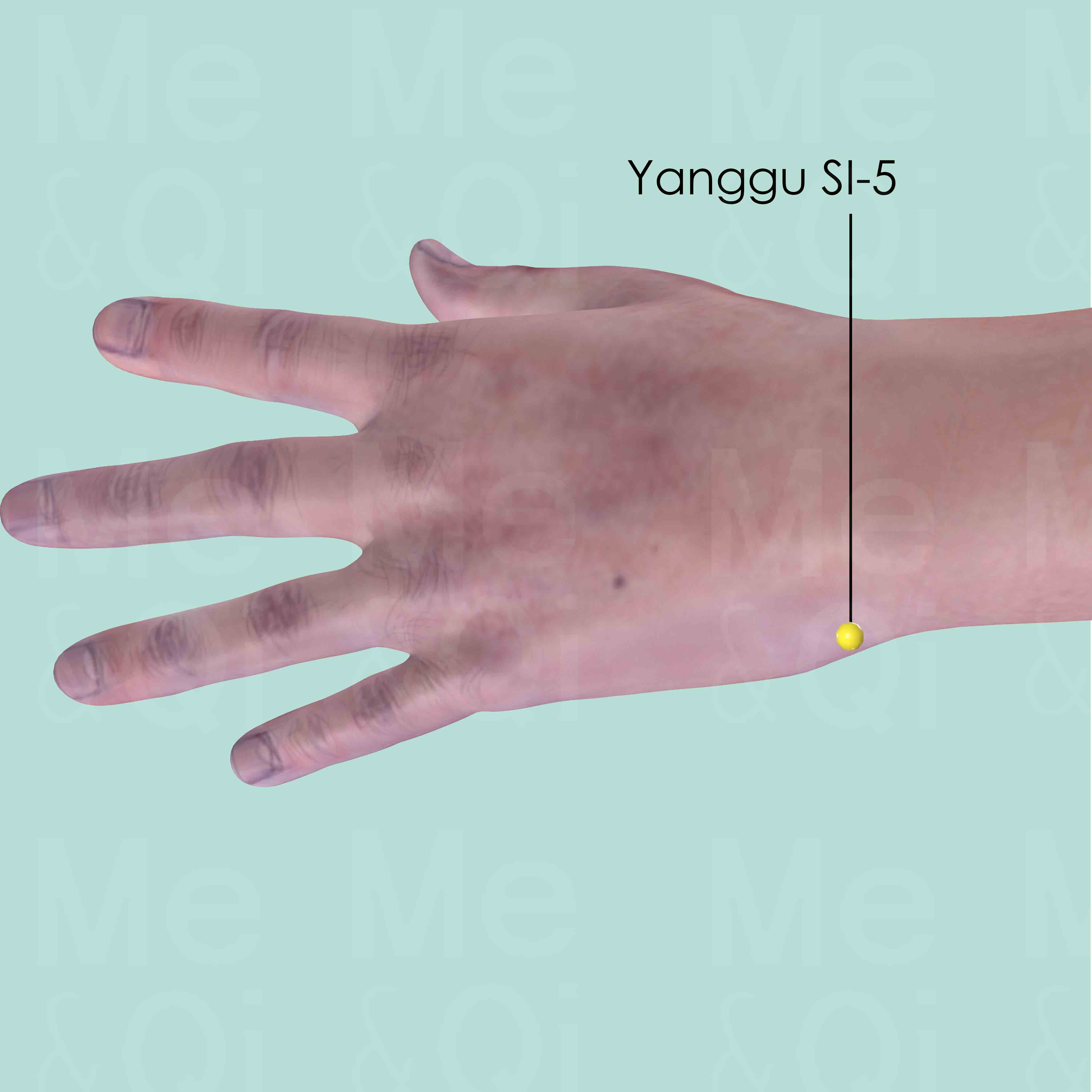
Yanggu SI-5
On the ulnar side of the wrist, in the depression between the styloid process of the ulna and the triquetral bone.

Yanglao SI-6
Dorsal to the head of the ulna. When the palm faces the chest, Yanglao SI-6 is in the bony depression on the radial side of the styloid process of the ulna.
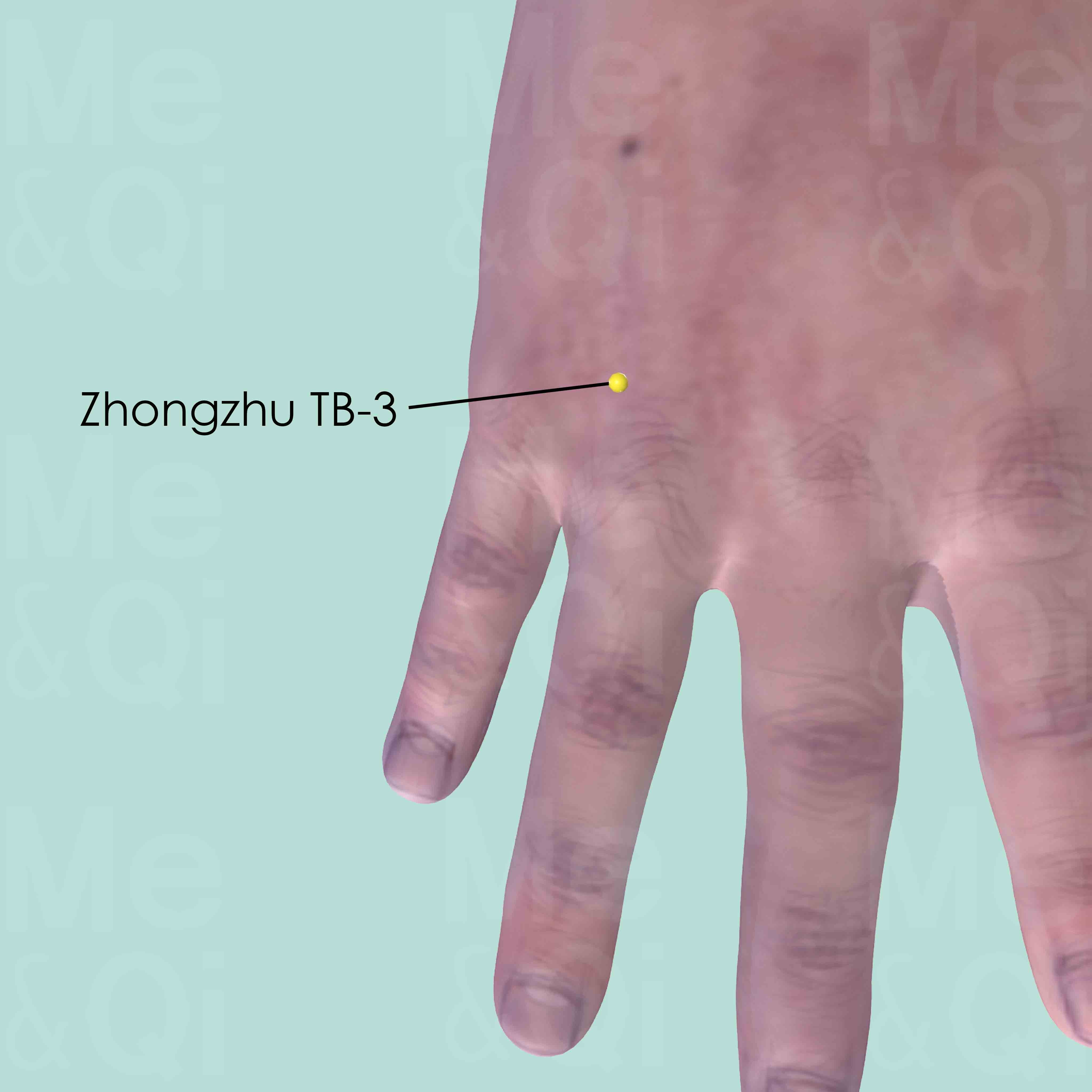
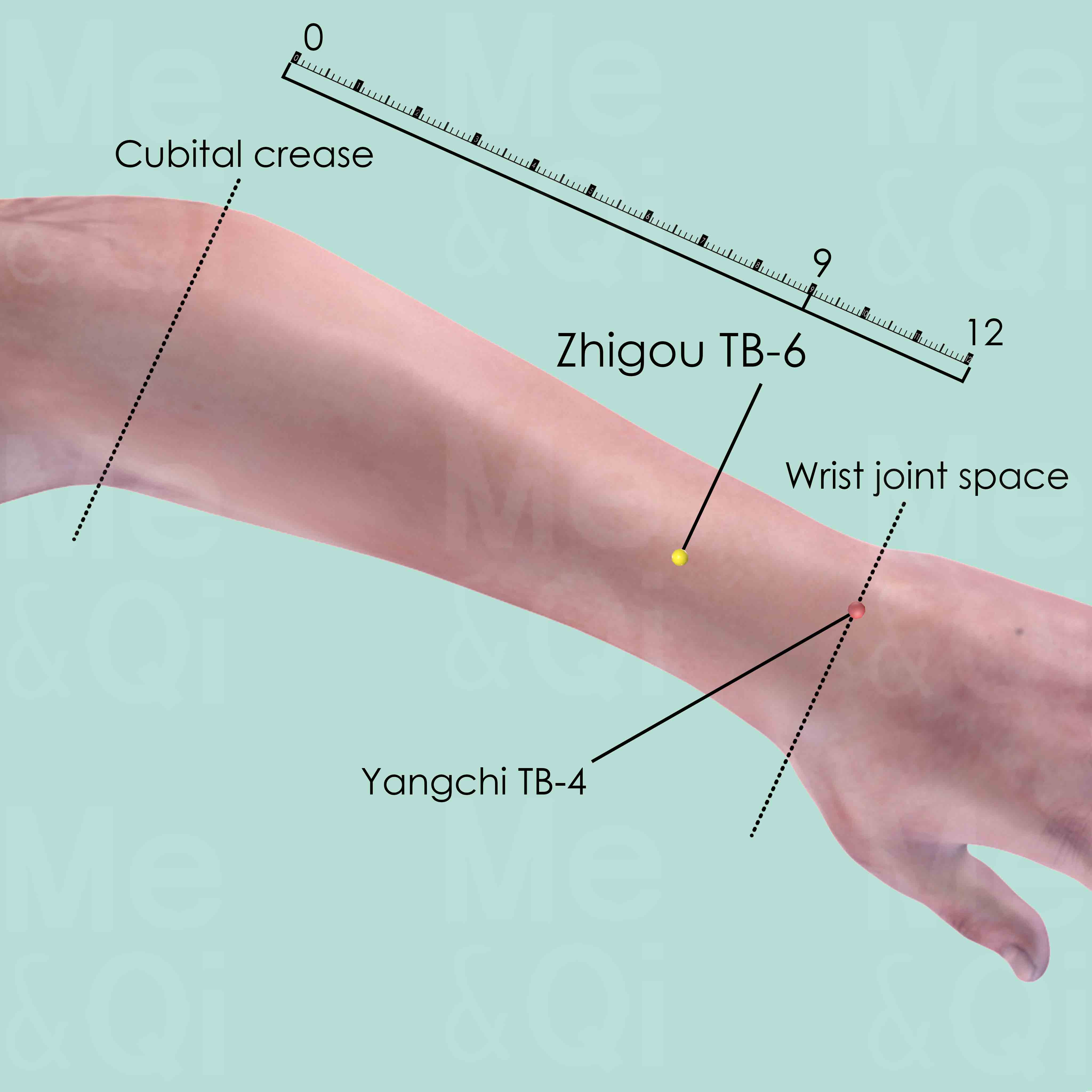
Zhongzhu TB-3
When the hand is placed with the palm facing downward, Zhongzhu TB-3 is on the hand dorsum between the 4th and 5th metacarpal bones, in the depression proximal to the metacarpophalangeal joints, at the junction between the heads and shaft of the two metacarpal bones.
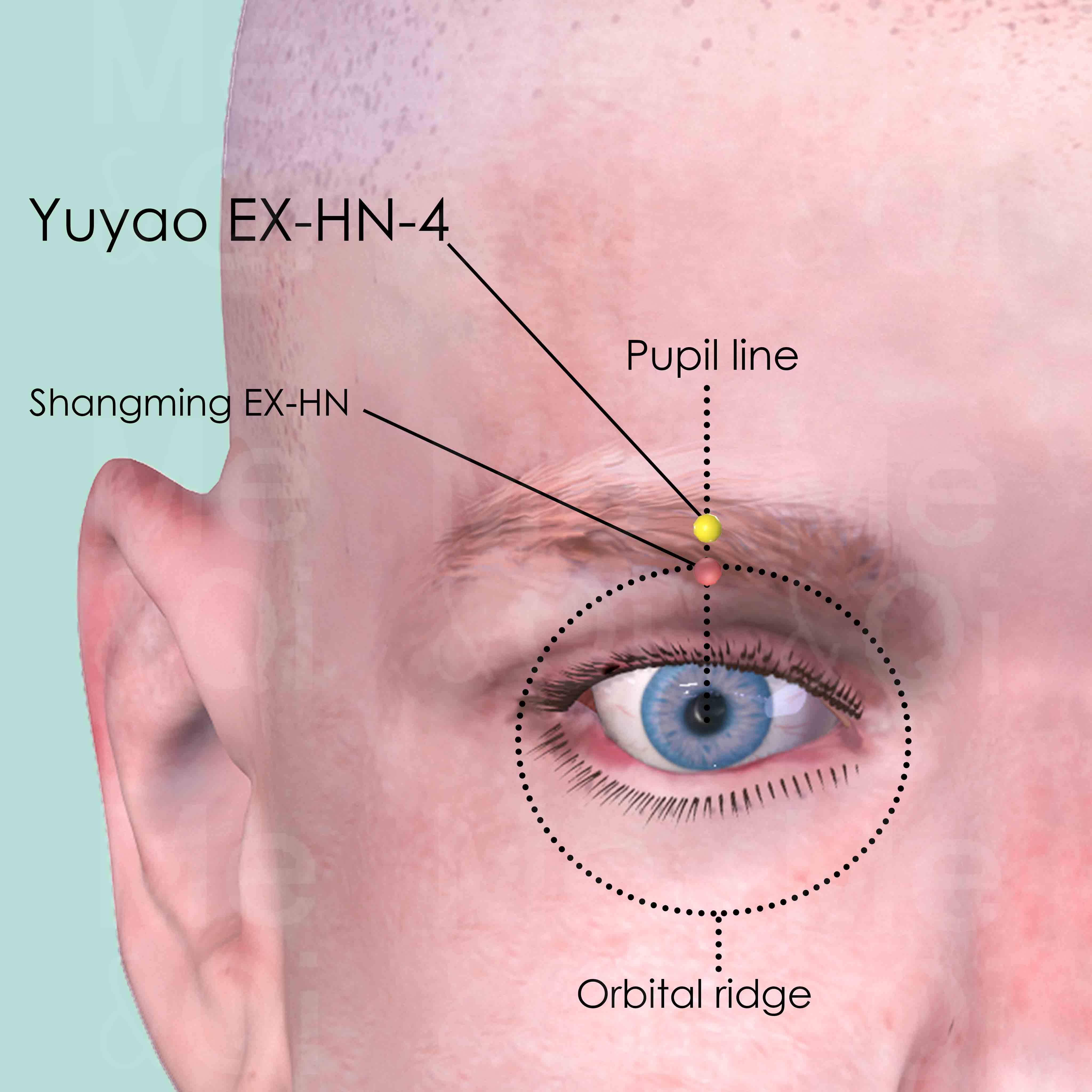
Yuyao EX-HN-4
When the patient looks straight forward, Yuyao EX-HN-4 is located directly above the pupil, in the midline of the eyebrow.
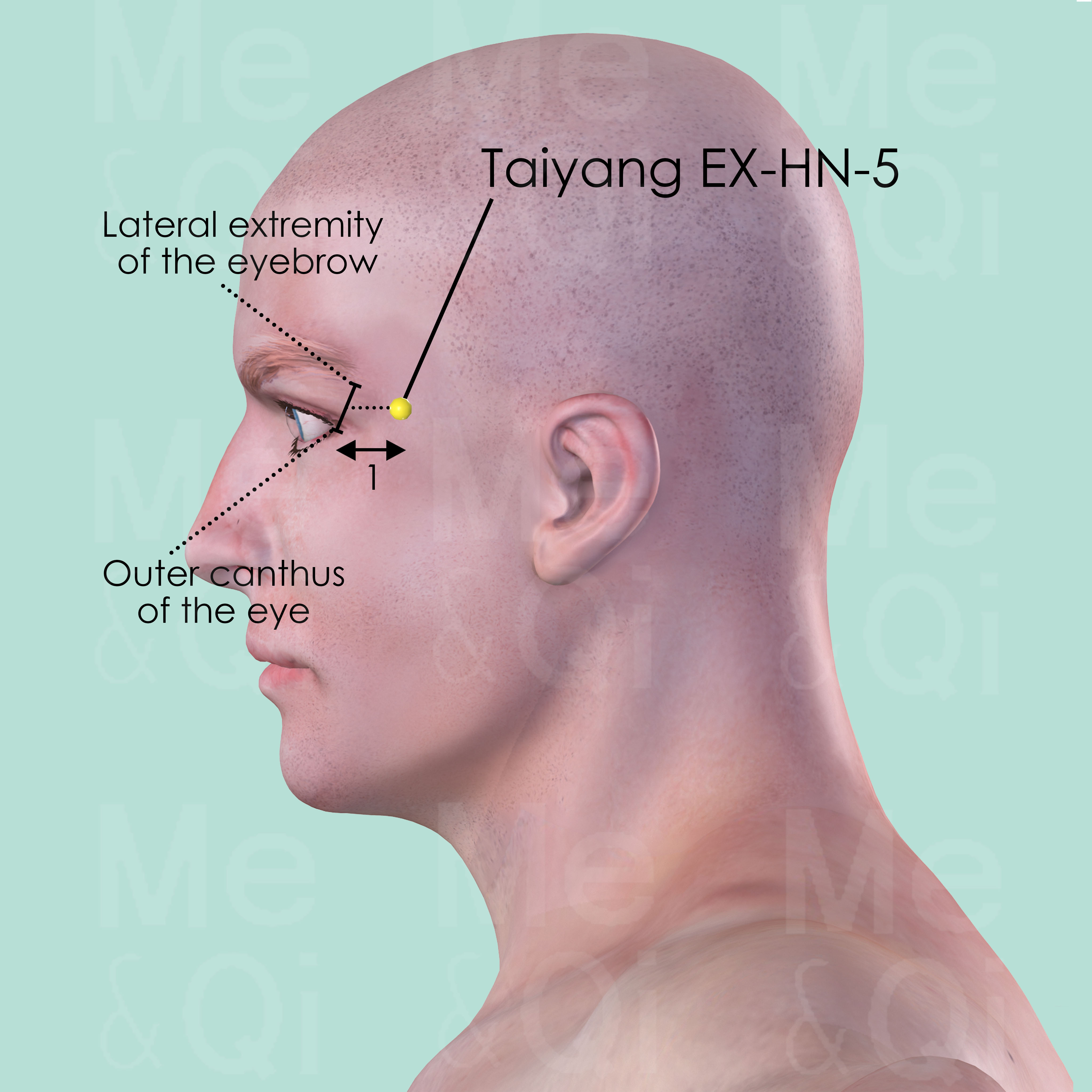
Taiyang EX-HN-5
At the temple, in the tender depression approximately 1 cun posterior to the midpoint between the lateral extremity of the eyebrow and the outer canthus of the eye.
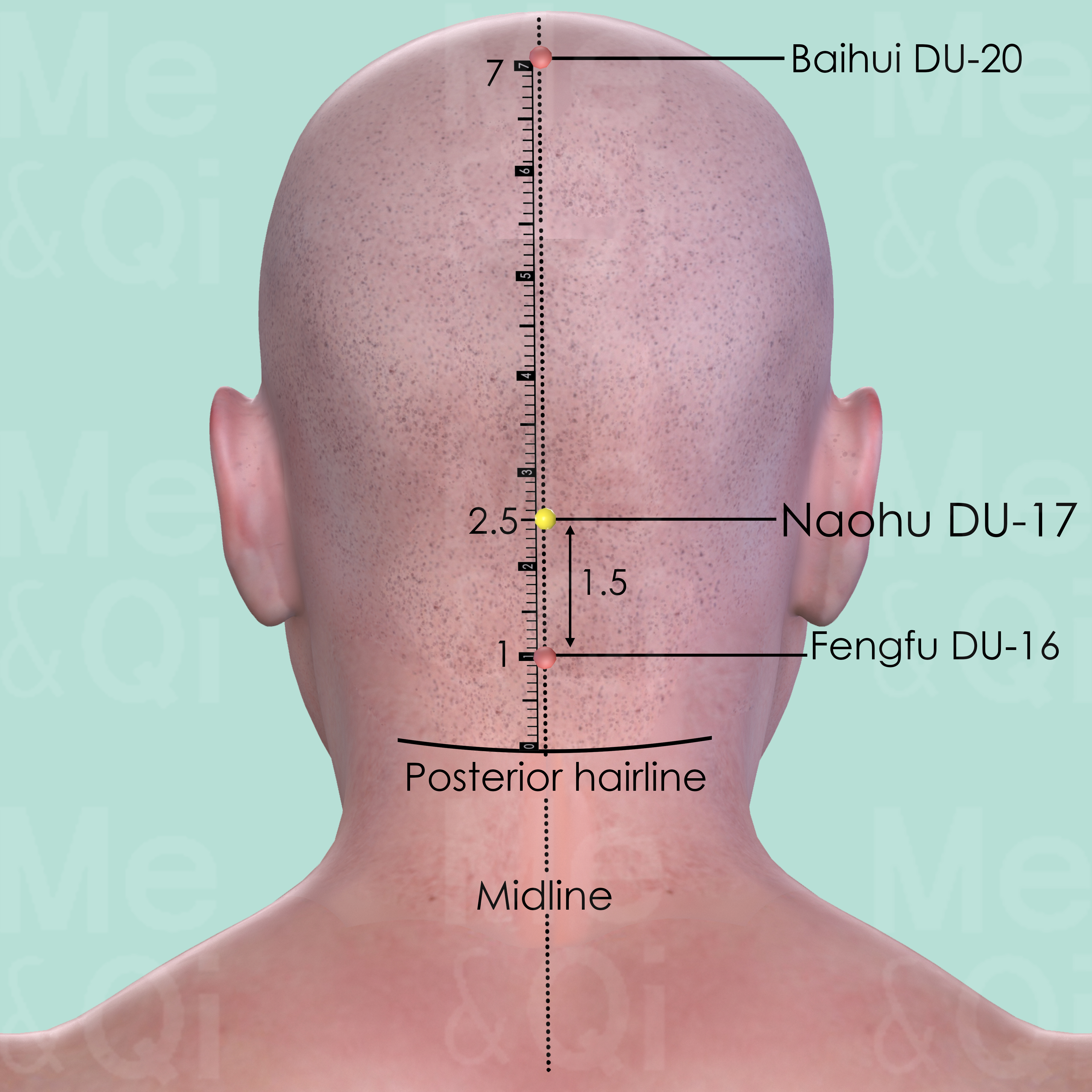
Naohu DU-17
1.5 cun above Fengfu DU-16 or 2.5 cun above the posterior hairline, in a depression superior to the external occipital protuberance.
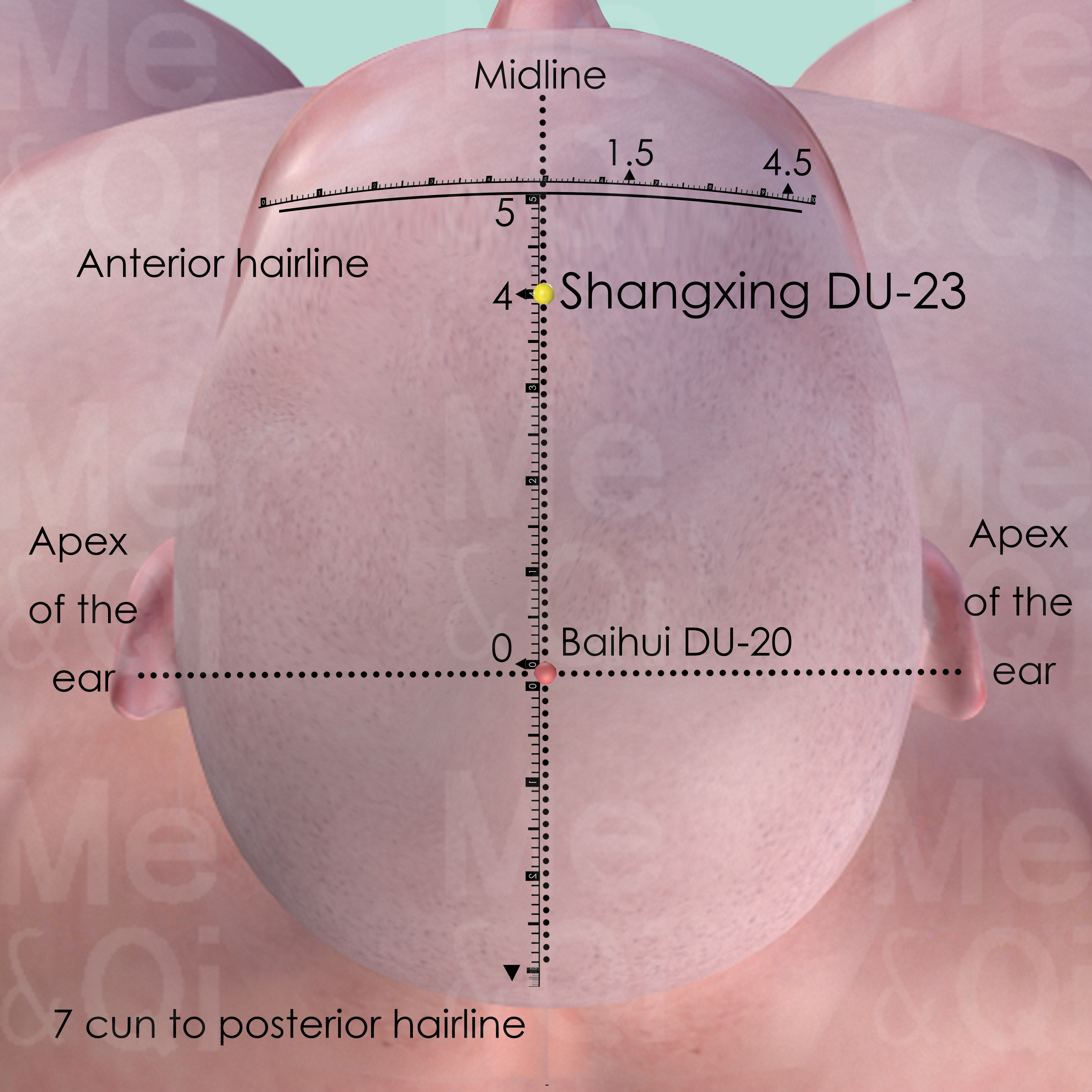
Shangxing DU-23
On the head midline, 1 cun within anterior to the front hairline, 4 cun anterior to Baihui DU-20.
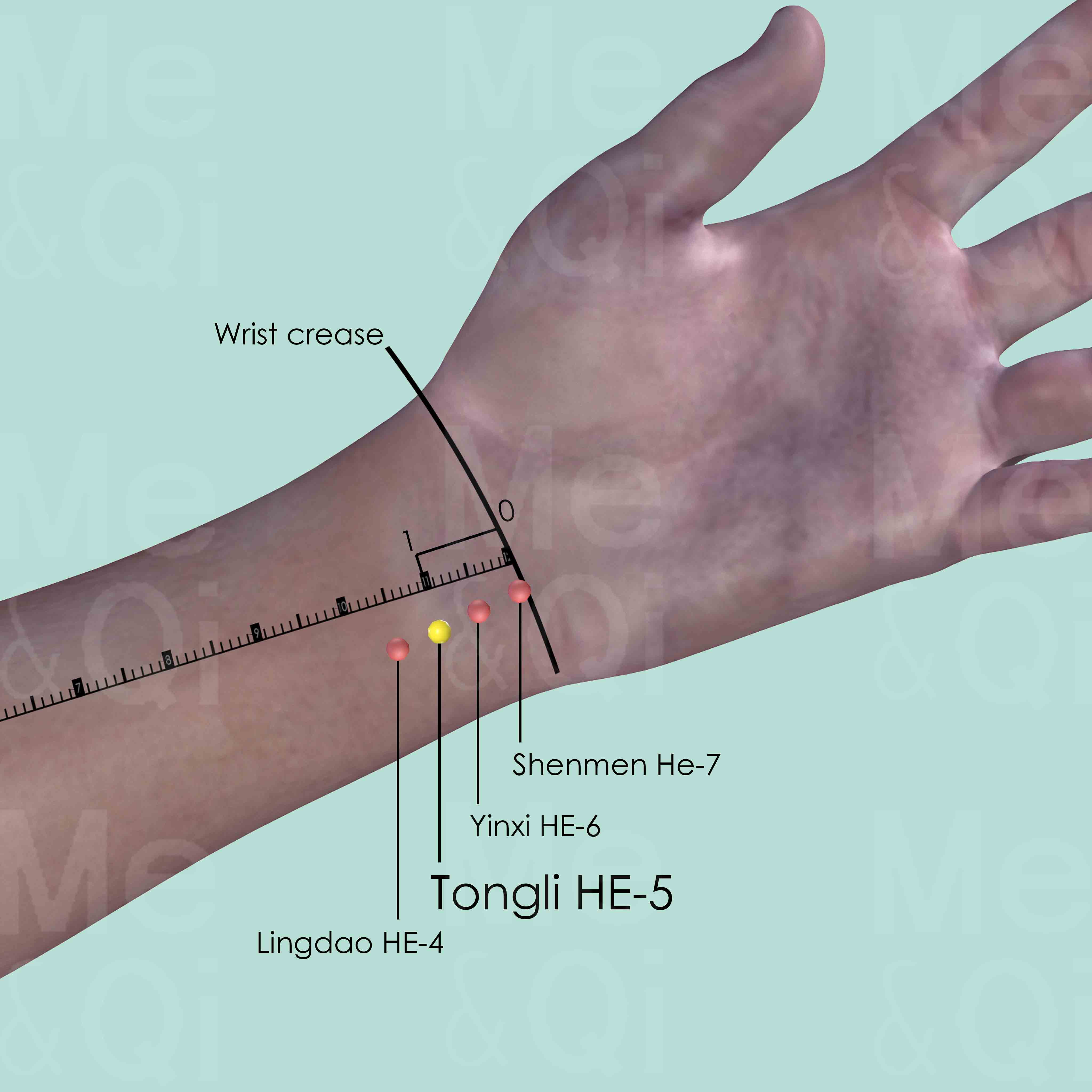
Tongli HE-5
On the radial side of the tendon of flexor carpi ulnaris muscle, 1 cun above the transverse crease of the wrist when the palm faces upward.
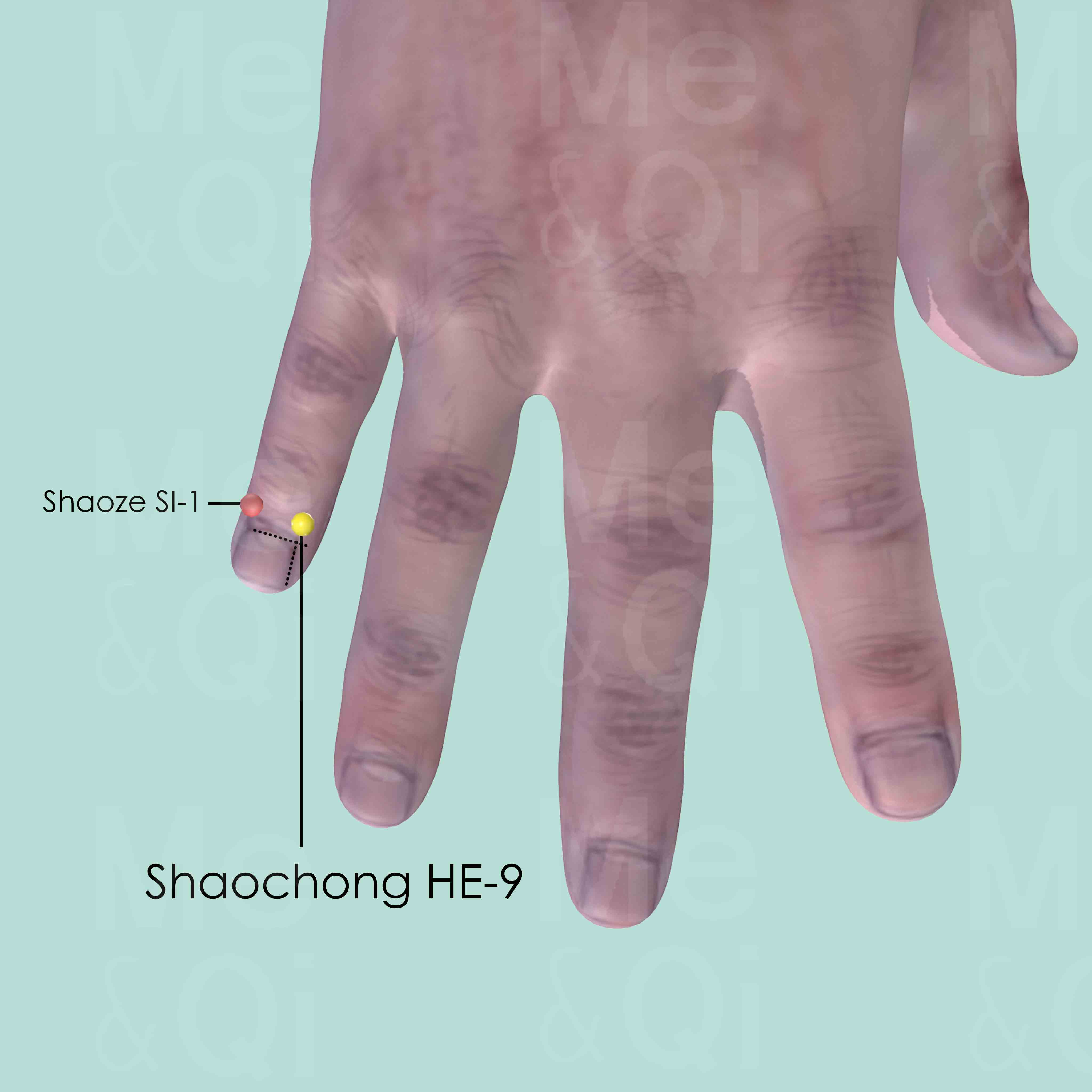
Shaochong HE-9
On the radial side of the little finger, about 0.1 cun posterior to the corner of the nail.
TCM Herbs for Painful Eyes
Explore below some TCM herbs used to address painful eyes, organized by herb category.
- By Herb Category
- Herbs that clear heat and purge fire and/or clear summer heat
- Herbs that pacify internal liver wind and stop tremors
- Herbs that clear heat and dry dampness
- Herbs for external application
- Herbs that invigorate the blood
- Cool/Acrid herbs that release the exterior
- Tonic herbs for blood deficiency
Herbs that clear Heat and purge Fire and/or clear Summer Heat
Painful eyes can be treated by these herbs when it arises from excessive internal heat or fire, aiding in cooling the body and balancing internal temperature.
One such herb is Climbing Groundsel Herbs (Qian Li Guang), which is directly recommended for painful eyes.
Other herbs of this category are listed in the table below.
"Herbs that clear Heat and purge Fire and/or clear Summer Heat" recommended for painful eyes
| Herb | Formulas they belong to (if applicable) |
|---|---|
| Climbing Groundsel Herbs (Qian Li Guang) | Not applicable |
| Heal-All Spikes (Xia Ku Cao) | Not applicable |
| Buddleia Flowers (Mi Meng Hua) | Not applicable |
Herbs that pacify Internal Liver Wind and stop Tremors
Painful eyes can be treated by these herbs when caused by internal wind from Liver disharmony, often manifesting in symptoms like spasms or tremors.
One such herb is Puncture Vine Fruits (Ji Li), which is directly recommended for painful eyes.
Other herbs of this category are listed in the table below.
"Herbs that pacify Internal Liver Wind and stop Tremors" recommended for painful eyes
| Herb | Formulas they belong to (if applicable) |
|---|---|
| Puncture Vine Fruits (Ji Li) | Not applicable |
| Silkworms (Jiang Can) | Not applicable |
Herbs that clear Heat and dry Dampness
Painful eyes can be treated by these herbs when caused by excessive dampness and heat within the body, aiming to restore balance by drying dampness and clearing heat.
One such herb is Ash Barks (Qin Pi), which is directly recommended for painful eyes.
Herbs for external application
Painful eyes can be treated by these herbs when the condition is external or superficial, requiring topical treatment to alleviate symptoms or heal the affected area.
One such herb is Borax (Peng Sha), which is directly recommended for painful eyes.
Herbs that invigorate the Blood
Painful eyes can be treated by these herbs when it stems from stagnation or poor circulation of blood, helping to improve blood flow and alleviate related discomfort.
One such herb is Motherwort Fruits (Chong Wei Zi), which is directly recommended for painful eyes.
Cool/Acrid herbs that release the Exterior
Painful eyes can be treated by these herbs when the body needs to harmonize with external environmental changes, particularly when there's a need to expel pathogenic factors like wind or cold without overly cooling the body.
One such herb is Vitex Fruits (Man Jing Zi), which is directly recommended for painful eyes.
Tonic herbs for Blood Deficiency
Painful eyes can be treated by these herbs in cases of blood deficiency, working to nourish and replenish the body's blood supply.
One such herb is Prepared Rehmannia (Shu Di huang), a key herb in some formulas recommended for painful eyes, like Qi Ju Di Huang Wan.