Facial Edemaaccording to TCM
Symptom families: Edema-associated Concerns, Face Conditions and Symptoms
Parent symptom: Edema
Did you mean? Facial Swelling
What is Facial Edema?
Facial edema, also known as swelling of the face, is a condition characterized by the accumulation of excess fluid in the facial tissues. This symptom can arise from various causes, ranging from allergies and sinus infections to more complex health issues such as heart or kidney problems. Facial edema can affect anyone, leading not only to physical discomfort but also to concerns over appearance and well-being. It is crucial to understand the underlying causes of this condition to provide effective treatment and relief.
How does TCM view Facial Edema?
From the perspective of Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), facial edema is seen as an imbalance within the body's natural systems. TCM interprets this condition as a manifestation of Dampness accumulation, Yang Deficiency, or a disturbance in the flow of Qi and Blood, often exacerbated by external factors such as Wind and Cold.
Identifying the specific pattern of disharmony underlying the edema is essential in TCM, as it guides the choice of treatment strategy aimed at rebalancing the body's energies and resolving the swelling.
Root Causes of Facial Edema in TCM
TCM attributes facial edema to several key patterns, notably Dampness accumulation and Yang Deficiency. Dampness can cause fluid to stagnate in the body, leading to swelling, while Yang Deficiency—particularly of the Spleen and Kidney—can impair the body's ability to metabolize fluids properly. These imbalances reflect deeper issues within the body's energetic system, necessitating targeted treatment approaches to restore harmony and alleviate the symptoms of facial edema.
Explore below more details about what might cause Facial edema according to TCM.
Dampness
"Dampness" in TCM is a concept that describes a pattern of disharmony where the body accumulates excess moisture. Imagine the heavy, sticky feeling you get on a very humid day; that's similar to what dampness feels like internally. It can manifest as a sense of heaviness, bloating, sluggishness, or even a foggy mind. This condition is often thought to arise from environmental factors like living in a damp place, dietary habits that promote moisture in the body, or internal imbalances that hinder the body's ability to process fluids properly. In TCM, dampness can obstruct the normal flow of energy and fluids in the body, leading to various symptoms.... see more
Dampness Patterns That Can Lead to Facial Edema
Common Symptoms: Ocular Swelling Shortness Of Breath Abdominal Edema Ankle Edema Foot Edema Oedema Of Hands Leg Edema Abdominal Distention
| Pattern Name | Relevant Symptoms | Relevant Formulas |
|---|---|---|
| Oedema | Oedema of face, Abdominal edema, Ankle edema, Facial edema, Foot edema, Oedema of hands, Leg edema, Ocular swelling, Abdominal distention... see more | Wu Ling San | Fang Ji Huang Qi Tang | Ping Wei San | Wu Pi Yin | Ling Gui Zhu Gan Tang | Zhen Wu Tang | Shen Qi Wan | Yu Gong San | Zhou Che Wan |
| Wind-Cold-Water invading the Lungs | Oedema of face, Ocular swelling, Shiny complexion, Scanty clear urination, Fever, Coughing, Shortness of breath, Aversion to cold, Facial edema... see more | Xiao Qing Long Tang |
Yang Deficiency
Yang deficiency in TCM refers to a state where the body's Yang energy, which is responsible for warmth, activity, and function, is weakened or diminished. This pattern of disharmony often arises from chronic illness, aging, or inherent constitutional weakness. Symptoms of Yang deficiency are typically associated with cold and sluggishness, such as a feeling of coldness, cold extremities, pale complexion, low energy or fatigue, and a desire for warmth. Digestive issues like poor appetite, loose stools, and water retention can also be indicative of Yang deficiency.... see more
Yang Deficiency Patterns That Can Lead to Facial Edema
| Pattern Name | Relevant Symptoms | Relevant Formulas |
|---|---|---|
| Spleen and Kidney Yang Deficiency | Oedema of face, Pale face, Facial edema, Oedema of limbs, Abdominal distention, Cold extremities, Shortness of breath, Diarrhea, Frequent urination, Lupus... see more | Wu Ling San |
Phlegm
In TCM "Phlegm" as a pattern of disharmony is a complex concept that extends beyond the physical manifestation of mucus. It represents a pathological factor that can disrupt the flow of Qi (vital energy) and blood, leading to various health issues. Phlegm in TCM is seen as a sticky, turbid substance arising from the body's inability to metabolize fluids properly, often due to a dysfunction of the spleen. It's not only associated with respiratory problems like cough and congestion but also with systemic issues. Symptoms can include a feeling of heaviness, mental cloudiness, dizziness, and in some cases, the formation of lumps or masses. Phlegm can even be "invisible," contributing to emotional disturbances like depression or stress. ... see more
Phlegm Patterns That Can Lead to Facial Edema
| Pattern Name | Relevant Symptoms | Relevant Formulas |
|---|---|---|
| Oedema | Oedema of face, Abdominal edema, Ankle edema, Facial edema, Foot edema, Oedema of hands, Leg edema, Ocular swelling, Abdominal distention... see more | Wu Ling San | Fang Ji Huang Qi Tang | Ping Wei San | Wu Pi Yin | Ling Gui Zhu Gan Tang | Zhen Wu Tang | Shen Qi Wan | Yu Gong San | Zhou Che Wan |
Wind
In TCM "Wind" is a concept that represents a pattern of disharmony, often characterized by its sudden and unpredictable nature, much like a gusty wind changing direction without warning. This pattern is associated with symptoms that come and go quickly or move around the body, such as itching, tremors, or even certain types of pain. Wind is considered to be a primary cause of illnesses that have these rapidly changing characteristics. In TCM, external Wind often refers to illnesses that start suddenly, like the common cold, believed to be caused by external pathogenic factors like climatic changes. On the other hand, internal Wind can be linked to internal imbalances and can manifest in conditions like dizziness or spasms. ... see more
Wind Patterns That Can Lead to Facial Edema
| Pattern Name | Relevant Symptoms | Relevant Formulas |
|---|---|---|
| Wind-Cold-Water invading the Lungs | Oedema of face, Ocular swelling, Shiny complexion, Scanty clear urination, Fever, Coughing, Shortness of breath, Aversion to cold, Facial edema... see more | Xiao Qing Long Tang |
Cold
In TCM "Cold" as a pattern of disharmony refers to a specific type of imbalance within the body's systems, often linked to a deficiency or weakness. It's not about feeling physically cold or having a common cold, but rather a metaphorical description of certain symptoms and underlying conditions. When a TCM practitioner says someone suffers from "Cold," it usually implies that the body's Yang energy, which is warm and active, is insufficient or overpowered by Yin energy, which is cool and passive. Symptoms of Cold in TCM can include a general feeling of coldness, cold limbs, pale complexion, low energy, slow metabolism, and a preference for warmth. ... see more
Cold Patterns That Can Lead to Facial Edema
| Pattern Name | Relevant Symptoms | Relevant Formulas |
|---|---|---|
| Wind-Cold-Water invading the Lungs | Oedema of face, Ocular swelling, Shiny complexion, Scanty clear urination, Fever, Coughing, Shortness of breath, Aversion to cold, Facial edema... see more | Xiao Qing Long Tang |
Kidney
In TCM the Kidneys are regarded as the body's most fundamental reservoir of Essence, known as Jing, which influences growth, reproduction, and aging. They are not just organs for filtering blood, but a holistic system governing vital life forces. When the Kidneys malfunction in TCM, it can manifest as a variety of health issues, such as chronic fatigue, reproductive problems, imbalances in fluid metabolism leading to edema or dryness, lower back pain, and a sense of fear or insecurity.... see more
Kidney Patterns That Can Lead to Facial Edema
Common Symptoms: Cold Extremities Pale Face Oedema Of Limbs Abdominal Distention Shortness Of Breath Diarrhea Frequent Urination Lupus
| Pattern Name | Relevant Symptoms | Relevant Formulas |
|---|---|---|
| Kidneys failing to receive Qi | Swelling of the face, Exertional dyspnea, Rapid respiration, Weak respiratory, Difficulty breathing in, Chronic coughing, Asthma, Spontaneous sweat, Cold extremities, Facial edema, Emaciation, Low energy, Lower back pain, Dizziness, Tinnitus, Clear urination... see more | You Gui Wan | Su Zi Jiang Qi Tang | Ren Shen Ge Jie San |
| Spleen and Kidney Yang Deficiency | Oedema of face, Pale face, Facial edema, Oedema of limbs, Abdominal distention, Cold extremities, Shortness of breath, Diarrhea, Frequent urination, Lupus... see more | Wu Ling San |
Spleen
In TCM the Spleen plays a vital role in digestion and transformation, converting food into energy and nutrients, and overseeing the distribution of Qi and Blood. It's also crucial in maintaining the health of muscles and limbs and ensuring the blood remains within the vessels. When the Spleen malfunctions in TCM, it can lead to a variety of issues such as digestive disorders, fatigue, weak muscles, bloating, and a feeling of heaviness. It can also cause a pale complexion, poor appetite, and a tendency to bruise easily. Emotionally, a Spleen imbalance is often associated with excessive worry or overthinking, reflecting its role in the interplay between physical and mental health.... see more
Spleen Patterns That Can Lead to Facial Edema
| Pattern Name | Relevant Symptoms | Relevant Formulas |
|---|---|---|
| Spleen and Kidney Yang Deficiency | Oedema of face, Pale face, Facial edema, Oedema of limbs, Abdominal distention, Cold extremities, Shortness of breath, Diarrhea, Frequent urination, Lupus... see more | Wu Ling San |
Lung
In TCM the Lungs are seen as the organ responsible for controlling Qi and respiration, as well as being a key part of the body's defensive system. They are thought to maintain the balance and flow of air and moisture, and are closely linked to the skin and hair. When the Lungs are imbalanced or malfunctioning in TCM, it can lead to respiratory issues like coughing or asthma, a weakened immune system, dry skin, and emotional disturbances such as sadness or grief. These symptoms are believed to arise from disruptions in the Lungs' ability to regulate Qi and protect the body, highlighting their central role in maintaining overall health and well-being.... see more
Lung Patterns That Can Lead to Facial Edema
| Pattern Name | Relevant Symptoms | Relevant Formulas |
|---|---|---|
| Wind-Cold-Water invading the Lungs | Oedema of face, Ocular swelling, Shiny complexion, Scanty clear urination, Fever, Coughing, Shortness of breath, Aversion to cold, Facial edema... see more | Xiao Qing Long Tang |
TCM Herbal Formulas for Facial Edema
To address the underlying causes of facial edema, TCM recommends specific herbal formulas. For Dampness-related edema, Wu Ling San, containing Water plantain (Ze Xie), is frequently prescribed to promote urination and leach out Dampness.
Xiao Qing Long Tang, with Ephedra (Ma Huang), is another formula used to clear Wind-Cold and support the Lungs in cases where external factors contribute to facial swelling. These formulas exemplify the holistic approach of TCM, aiming not only to reduce edema but also to correct the imbalances causing it.
Explore below some TCM herbal formulas used to address facial edema, organized by cause and by formula type.
- By Cause
- By Formula Type
- Dampness
- Yang Deficiency
- Phlegm
- Wind
- Cold
- View More Causes
- Formulas that promote urination and leach out dampness
- Formulas that tonify qi
- Formulas that warm and transform water and dampness
- Formulas that warm yang and tonify
- Formulas that drive out excess water
- Formulas that transform dampness and harmonize stomach
- Formulas that clear wind-Cold
- Formulas for a rebellious qi
Top Formula for Dampness:
Wu Ling San
Suitable for Dampness patterns that may cause facial edema, such as Oedema
Learn moreAll Formulas Recommended for Facial Edema Caused by Dampness
| Formula | Patterns Suitable For |
|---|---|
| Wu Ling San | Oedema |
| Fang Ji Huang Qi Tang | Oedema |
| Ping Wei San | Oedema |
| Wu Pi Yin | Oedema |
| Ling Gui Zhu Gan Tang | Oedema |
| Zhen Wu Tang | Oedema |
| Shen Qi Wan | Oedema |
| Yu Gong San | Oedema |
| Zhou Che Wan | Oedema |
| Xiao Qing Long Tang | Wind-Cold-Water invading the Lungs |
Top Formula for Yang Deficiency:
Wu Ling San
Suitable for Yang Deficiency patterns that may cause facial edema, such as Spleen and Kidney Yang Deficiency
Learn moreTop Formula for Phlegm:
Wu Ling San
Suitable for Phlegm patterns that may cause facial edema, such as Oedema
Learn moreAll Formulas Recommended for Facial Edema Caused by Phlegm
| Formula | Patterns Suitable For |
|---|---|
| Wu Ling San | Oedema |
| Fang Ji Huang Qi Tang | Oedema |
| Ping Wei San | Oedema |
| Wu Pi Yin | Oedema |
| Ling Gui Zhu Gan Tang | Oedema |
| Zhen Wu Tang | Oedema |
| Shen Qi Wan | Oedema |
| Yu Gong San | Oedema |
| Zhou Che Wan | Oedema |
Top Formula for Wind:
Xiao Qing Long Tang
Suitable for Wind patterns that may cause facial edema, such as Wind-Cold-Water invading the Lungs
Learn moreTop Formula for Cold:
Xiao Qing Long Tang
Suitable for Cold patterns that may cause facial edema, such as Wind-Cold-Water invading the Lungs
Learn moreFormulas that promote urination and leach out Dampness
These formulas are suitable for some facial edema-causing patterns like Spleen and Kidney Yang Deficiency or Oedema.
One such formula is Wu Ling San, with water plantain as a key herb.
Other formulas of this category are listed in the table below.
All "formulas that promote urination and leach out dampness" recommended for facial edema
| Formula | Patterns Suitable For (if applicable) |
|---|---|
| Wu Ling San | Spleen and Kidney Yang Deficiency, Oedema |
| Fang Ji Huang Qi Tang | Oedema |
| Wu Pi Yin | Oedema |
Formulas that warm Yang and tonify
These formulas are suitable for some facial edema-causing patterns like Oedema.
One such formula is Shen Qi Wan, with prepared aconite as a key herb.
Other formulas of this category are listed in the table below.
All "formulas that warm yang and tonify" recommended for facial edema
| Formula | Patterns Suitable For (if applicable) |
|---|---|
| Shen Qi Wan | Oedema |
| You Gui Wan | Kidneys failing to receive Qi |
Formulas that tonify Qi
These formulas are suitable for some facial edema-causing patterns like Kidneys failing to receive Qi.
One such formula is Ren Shen Ge Jie San, with tokay geckos as a key herb.
Other formulas of this category are listed in the table below.
All "formulas that tonify qi" recommended for facial edema
| Formula | Patterns Suitable For (if applicable) |
|---|---|
| Ren Shen Ge Jie San | Kidneys failing to receive Qi |
| Bu Fei Tang | Not applicable |
Formulas that warm and transform water and Dampness
These formulas are suitable for some facial edema-causing patterns like Oedema.
One such formula is Ling Gui Zhu Gan Tang, with poria-cocos mushroom as a key herb.
Other formulas of this category are listed in the table below.
All "formulas that warm and transform water and dampness" recommended for facial edema
| Formula | Patterns Suitable For (if applicable) |
|---|---|
| Ling Gui Zhu Gan Tang | Oedema |
| Zhen Wu Tang | Oedema |
Formulas that drive out excess water
These formulas are suitable for some facial edema-causing patterns like Oedema.
One such formula is Yu Gong San, with morning glory seeds as a key herb.
Other formulas of this category are listed in the table below.
All "formulas that drive out excess water" recommended for facial edema
| Formula | Patterns Suitable For (if applicable) |
|---|---|
| Yu Gong San | Oedema |
| Zhou Che Wan | Oedema |
Formulas that transform Dampness and harmonize Stomach
These formulas are suitable for some facial edema-causing patterns like Oedema.
One such formula is Ping Wei San, with black atractylodes rhizome as a key herb.
Formulas that clear Wind-Cold
These formulas are suitable for some facial edema-causing patterns like Wind-Cold-Water invading the Lungs.
One such formula is Xiao Qing Long Tang, with ephedra as a key herb.
Formulas for a rebellious Qi
These formulas are suitable for some facial edema-causing patterns like Kidneys failing to receive Qi.
One such formula is Su Zi Jiang Qi Tang, with perilla seeds as a key herb.
Acupoints for Facial Edema
In addition to herbal medicine, TCM utilizes acupuncture to enhance the treatment of facial edema. Acupoints such as Xiangu ST-43 and Fenglong ST-40 are targeted to regulate the Stomach and Spleen and resolve Dampness, while Hegu LI-4 and Yingxiang LI-20 are selected to expel Wind and benefit the facial area directly. By stimulating specific points, acupuncture seeks to improve the flow of Qi and Blood, reduce swelling, and support the body's natural healing mechanisms, offering a complementary strategy alongside herbal treatment.
Explore below some acupoints used to address facial edema, organized by meridian.
- By Meridian
- Stomach Channel
- Large Intestine Channel
- Governing Vessel
- Directing Vessel
- Gall Bladder Channel
- Small Intestine Channel
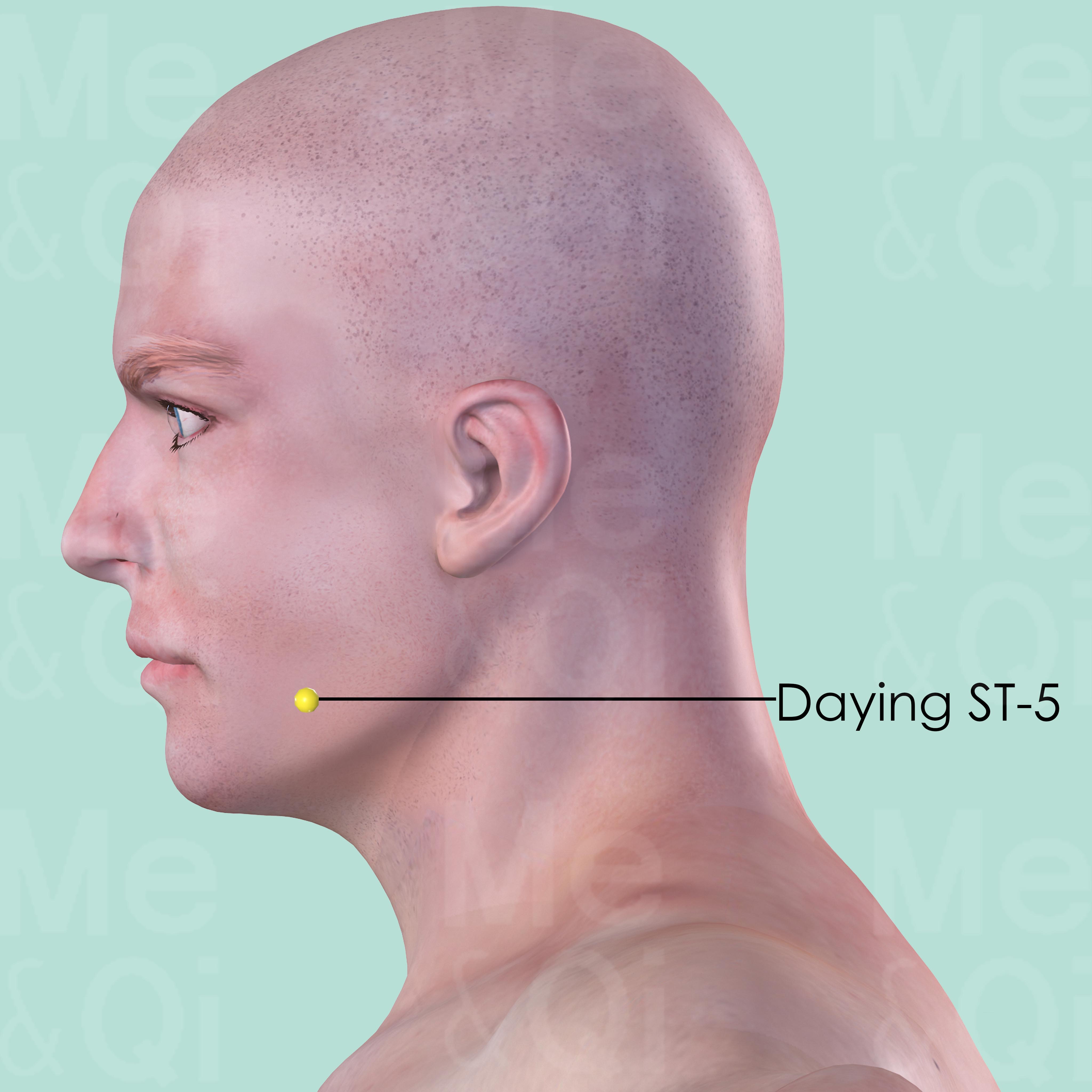
Daying ST-5
On the lateral mandible, on the anterior border of masseter muscle, in the groove-like depression appearing when the cheek is bulged.
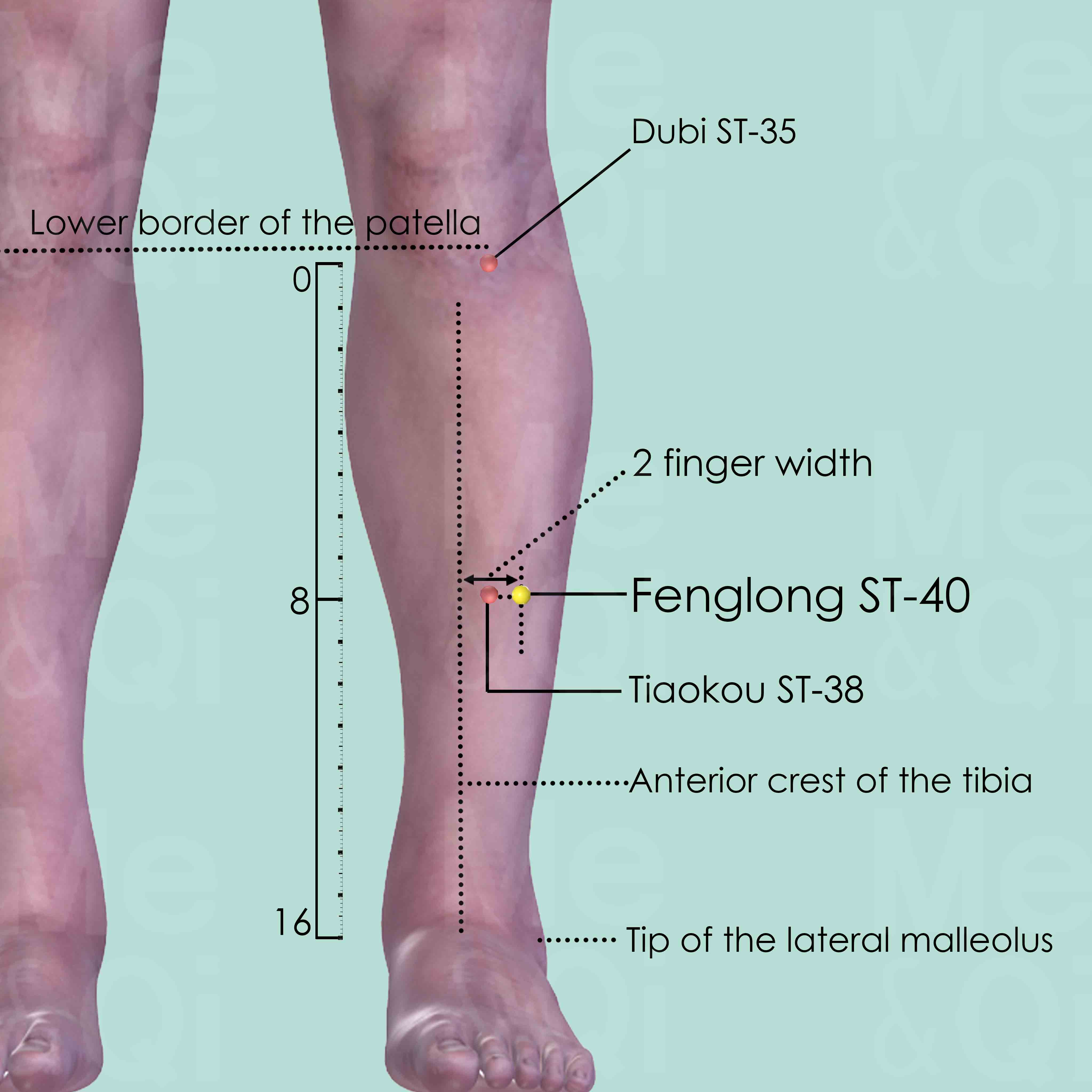
Fenglong ST-40
Midway between Dubi ST-35 and Jiexi ST-41, two middle finger-width from the anterior crest of the tibia, or one middle finger-width from Tiaokou ST-38.
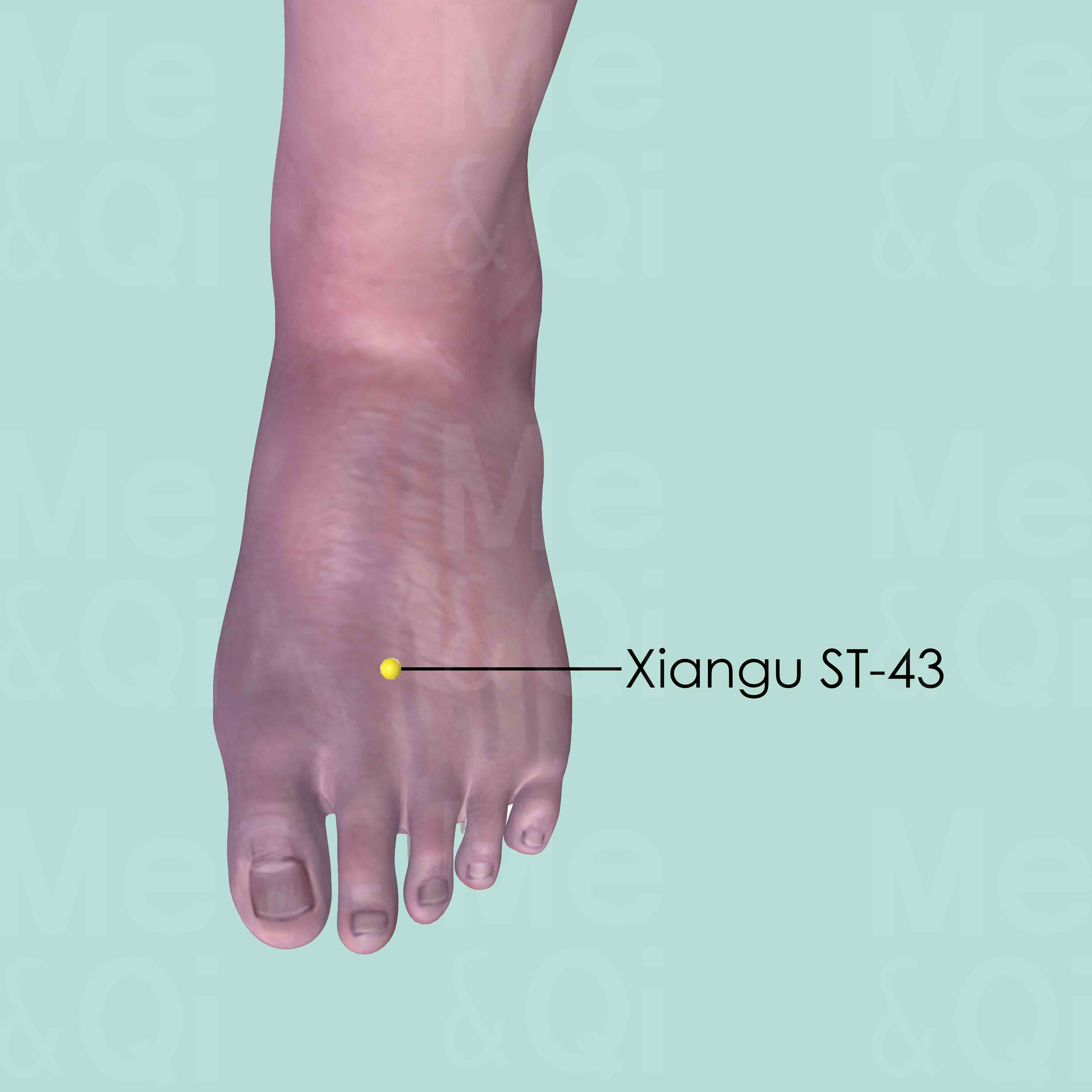
Xiangu ST-43
On the dorsum of the foot, in the depression between the 2nd and 3rd metatarsal bones, at the level of the junction of the shafts and the heads of these metatarsal bones.
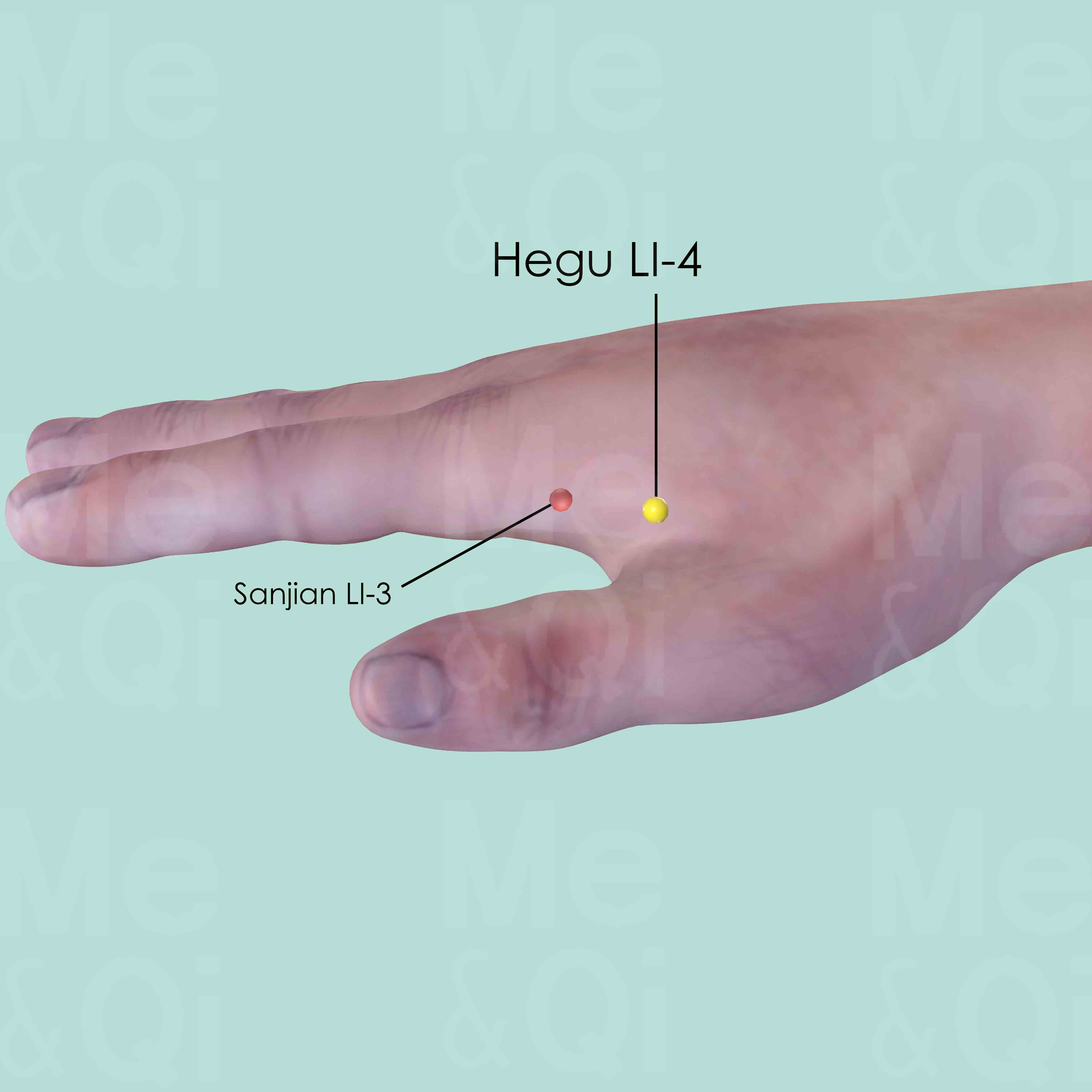
Hegu LI-4
Between the 1st and 2nd metacarpal bones, approximately in the middle of the 2nd metacarpal bone on the radial side.
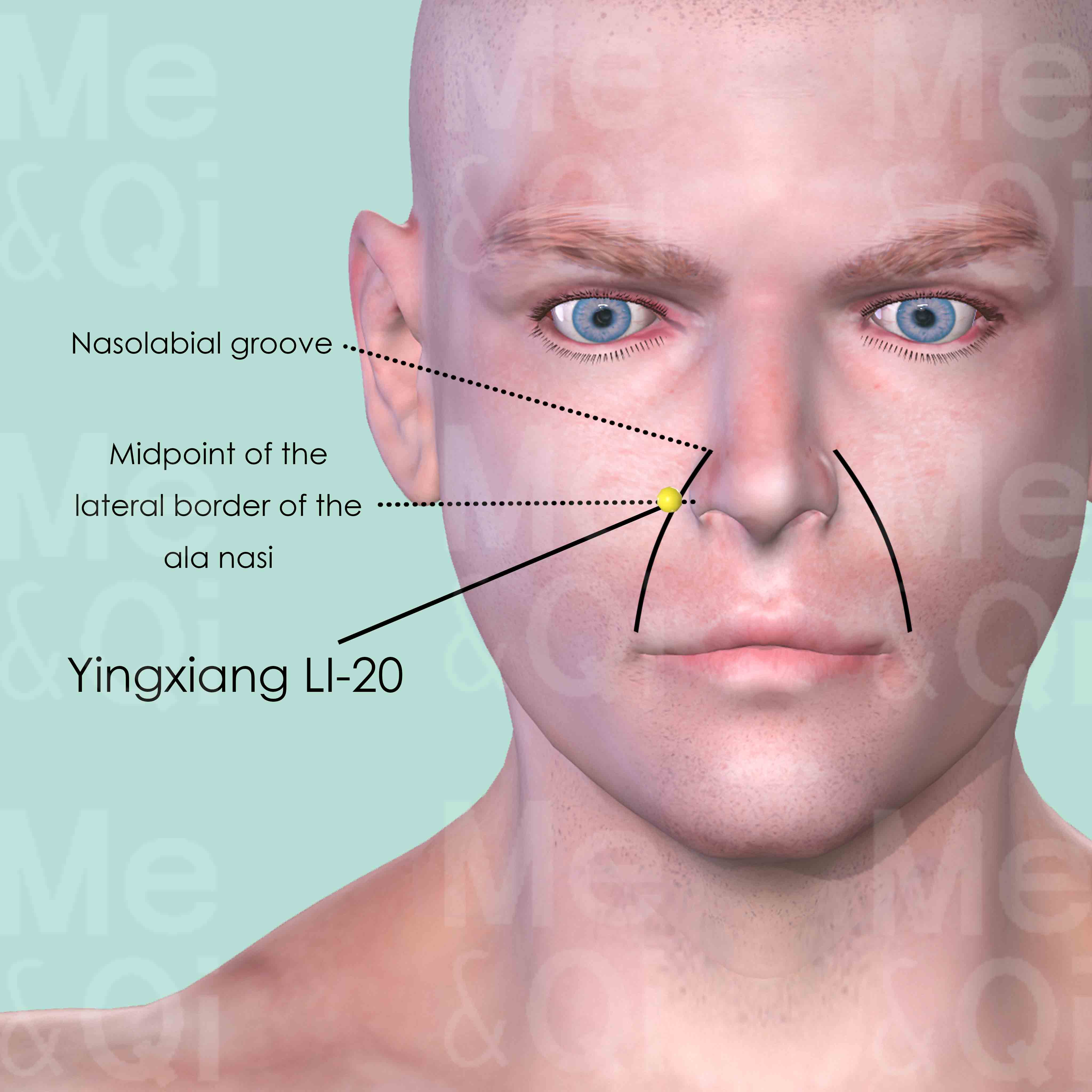
Yingxiang LI-20
In the nasolabrial groove, at the level of the midpoint of the lateral border of ala nasi.
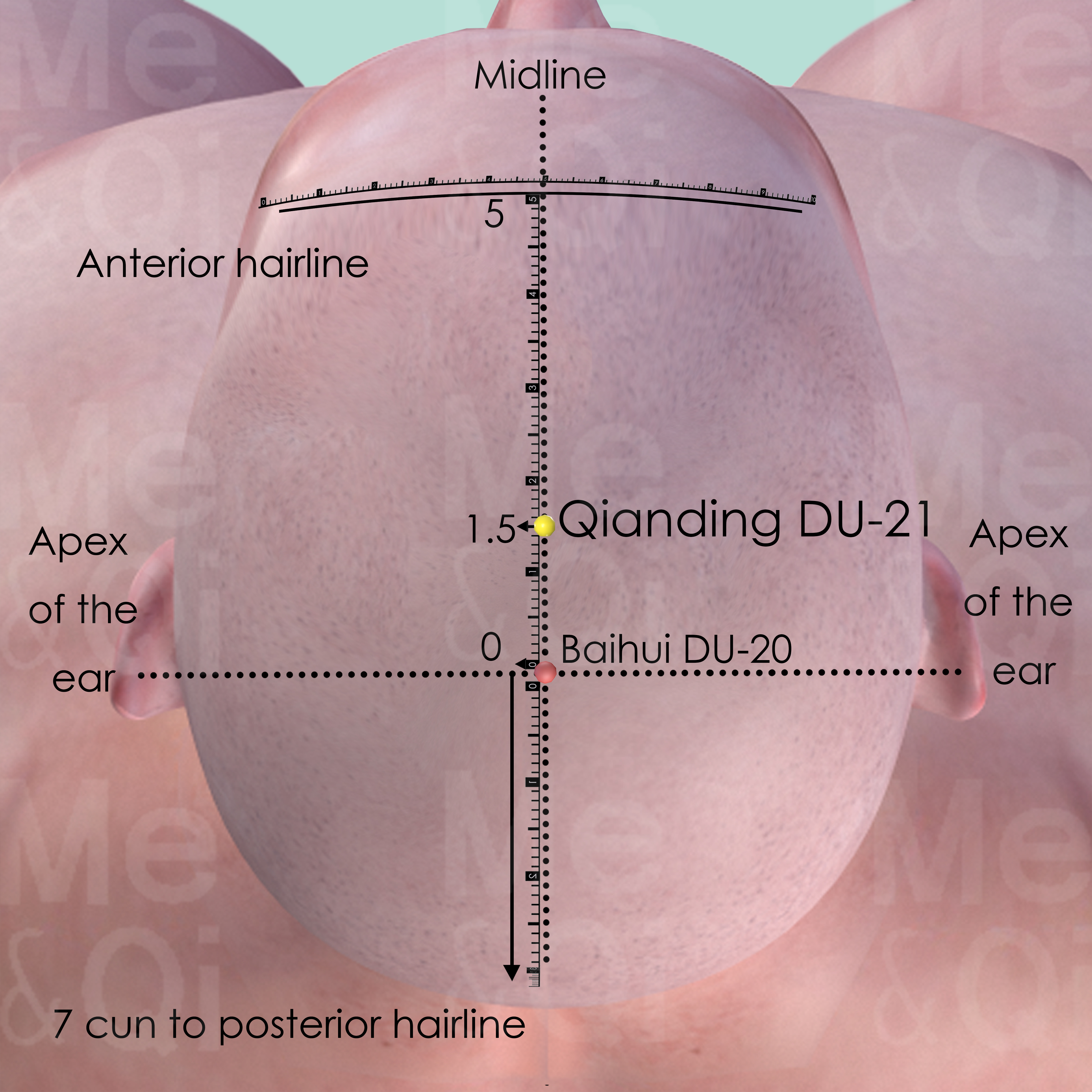
Qianding DU-21
On the midline, 1.5 cun anterior to Baihui DU-20 or 3.5 cun posterior to the anterior hairline.

Xinhui DU-22
On the head midline, 3 cun anterior to Baihui DU-20, 2 cun posterior to the front hairline.
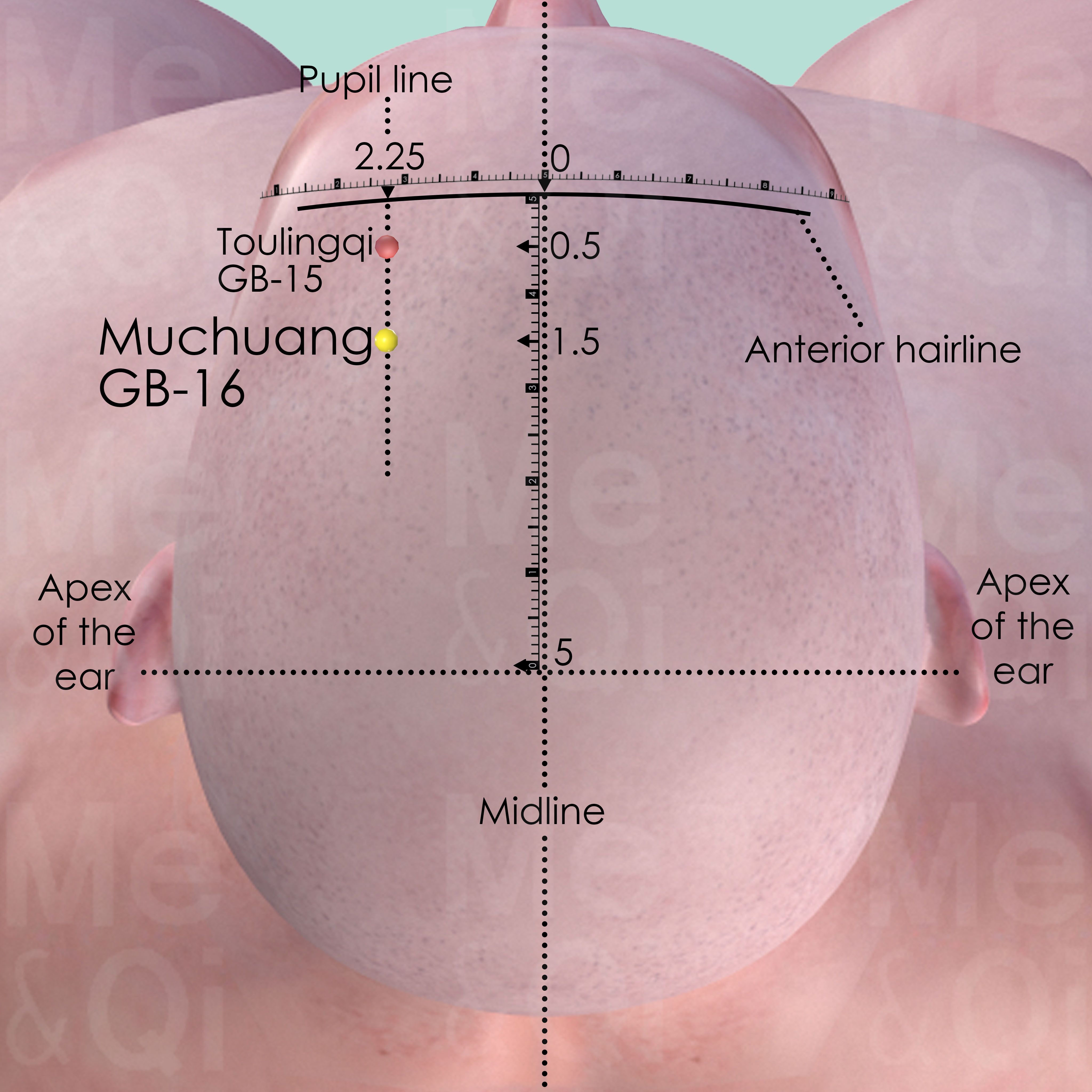
Muchuang GB-16
1 cun posterior to the Toulingqi GB-15 or 1.5 cun posterior to the anterior hairline, on the pupil line which is 2.25 cun lateral to the midline.