Myopiaaccording to TCM
Symptom family: Vision Impairments and Disorders
Did you mean? Blurry Vision
What is Myopia?
Myopia, commonly known as nearsightedness, is a visual condition where close objects appear clear, but distant ones are blurry. This refractive error occurs when the eye's shape causes light rays to bend (refract) incorrectly, focusing images in front of the retina instead of on it.
How Does TCM View Myopia?
In Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), discerning a patient's "pattern" is essential for treatment. Patterns describe imbalances that lead to symptoms. Myopia in TCM isn't just an eye condition; it's a manifestation of a deeper disharmony such as Heart or Gallbladder Qi Deficiency or Phlegm. Identifying the correct pattern is critical, as it directs a tailored treatment strategy aimed at the underlying cause, ensuring a holistic healing approach.
Causes of Myopia According to TCM
TCM interprets myopia through two potential patterns. The first is Heart and Gallbladder Qi Deficiency, where a shortfall in vital energy leads to an inability of the Heart to support vision adequately.
The second, Heart Qi Deficiency and Stagnation due to Phlegm Turbidity, suggests that a blockage caused by viscous substances impairs the free flow of Qi, clouding the sensory orifices and leading to visual difficulties. Both patterns underscore the importance of Qi in maintaining clear vision and indicate that myopia may stem from systemic imbalances rather than solely an ocular issue.
TCM Herbal Formulas for Myopia
To address myopia, TCM recommends formulas that nurture Qi, clear stagnation, and dispel Phlegm. The Ding Zhi Wan formula is specifically tailored for patterns like Heart and Gallbladder Qi Deficiency and Heart Qi Deficiency with Stagnation due to Phlegm Turbidity.
By enhancing Qi and clearing the obstructive Phlegm, this formula helps to correct the underlying energetic imbalances believed to contribute to myopia. TCM practitioners might also include adjunct herbs to target specific symptoms and enhance the formula's effectiveness.
See more details below about Ding Zhi Wan, a herbal formula used to address myopia.
- By Formula Type
- Formulas that nourish the heart and calm the mind
Formulas that nourish the Heart and calm the Mind
Myopia can be treated by these formulas when it stems from a disharmony between the heart and the mind, often manifesting as emotional disturbances or sleep issues.
One such formula is Ding Zhi Wan, with ginseng as a key herb.
Acupoints for Myopia
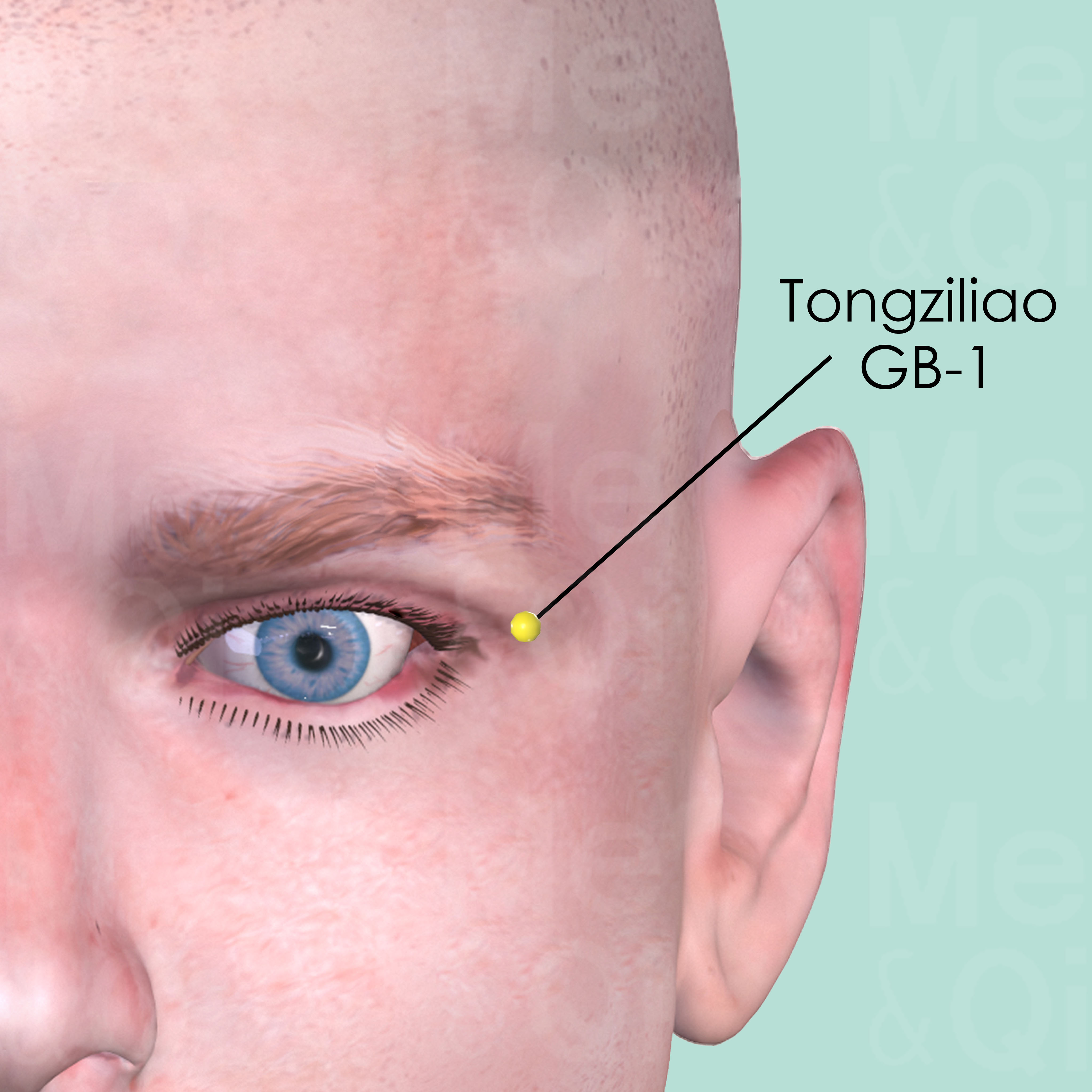
Acupuncture, a key component of TCM, offers additional support for myopia. Points like Guangming GB-37 and Tongziliao GB-1 are selected for their reputed efficacy in benefiting the eyes and addressing the patterns of Qi Deficiency and Stagnation. By stimulating these points, TCM aims to promote the flow of Qi and Blood to the eyes, alleviating the root causes of myopia from within the body's energetic framework.
Explore below some acupoints used to address myopia, organized by meridian.
- By Meridian
- Gall Bladder Channel
- Bladder Channel
- Stomach Channel
- Governing Vessel
- Extra Points: Head and Neck (EX-HN)
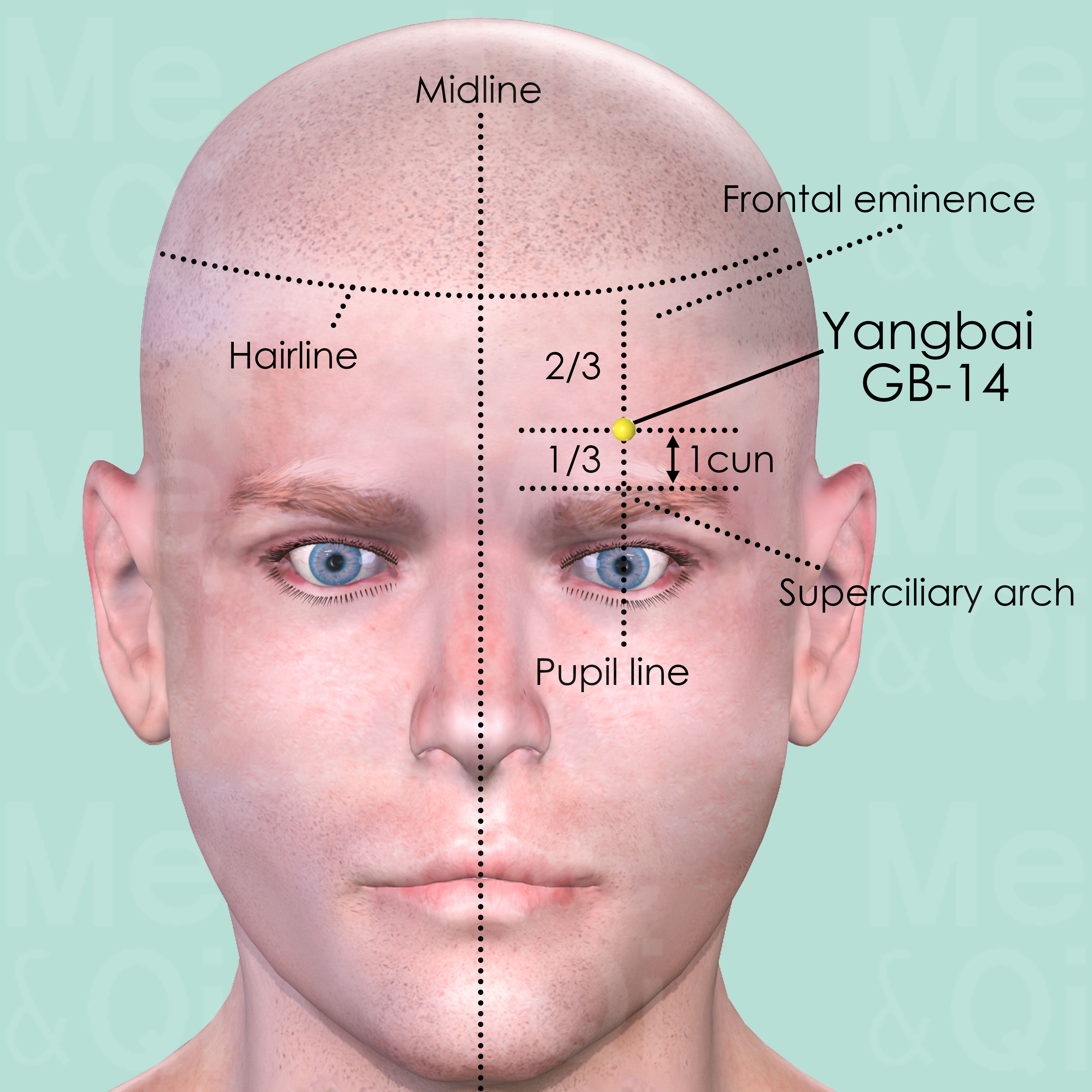
Yangbai GB-14
On the forehead, 1 cun above the midpoint of the eyebrow, approximately at the junction of the upper two-thirds and lower third of the vertical line draw from the anterior hairline to the eyebrow.
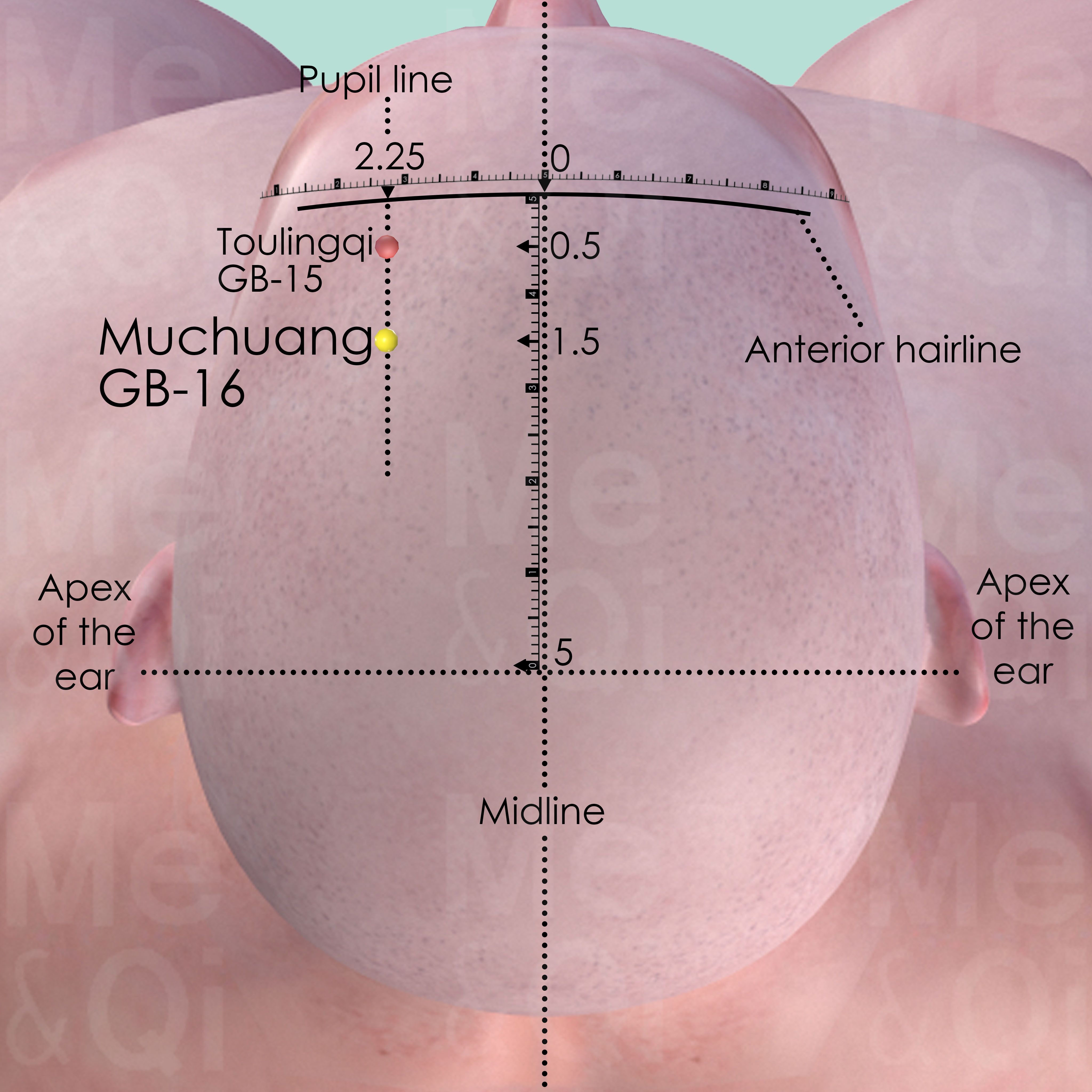
Muchuang GB-16
1 cun posterior to the Toulingqi GB-15 or 1.5 cun posterior to the anterior hairline, on the pupil line which is 2.25 cun lateral to the midline.
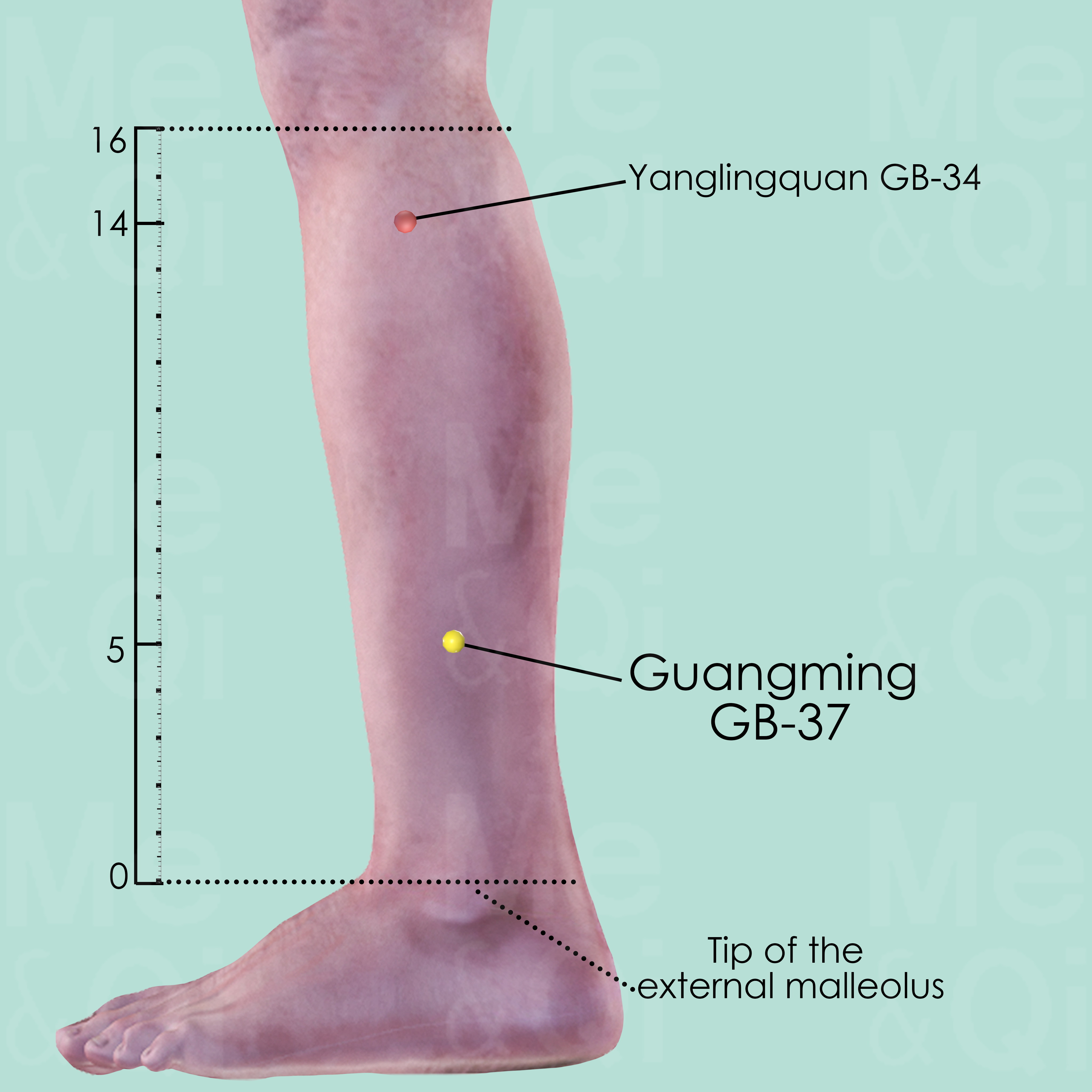
Guangming GB-37
5 cun directly above the tip of the external malleolus, on the anterior border of the fibula.
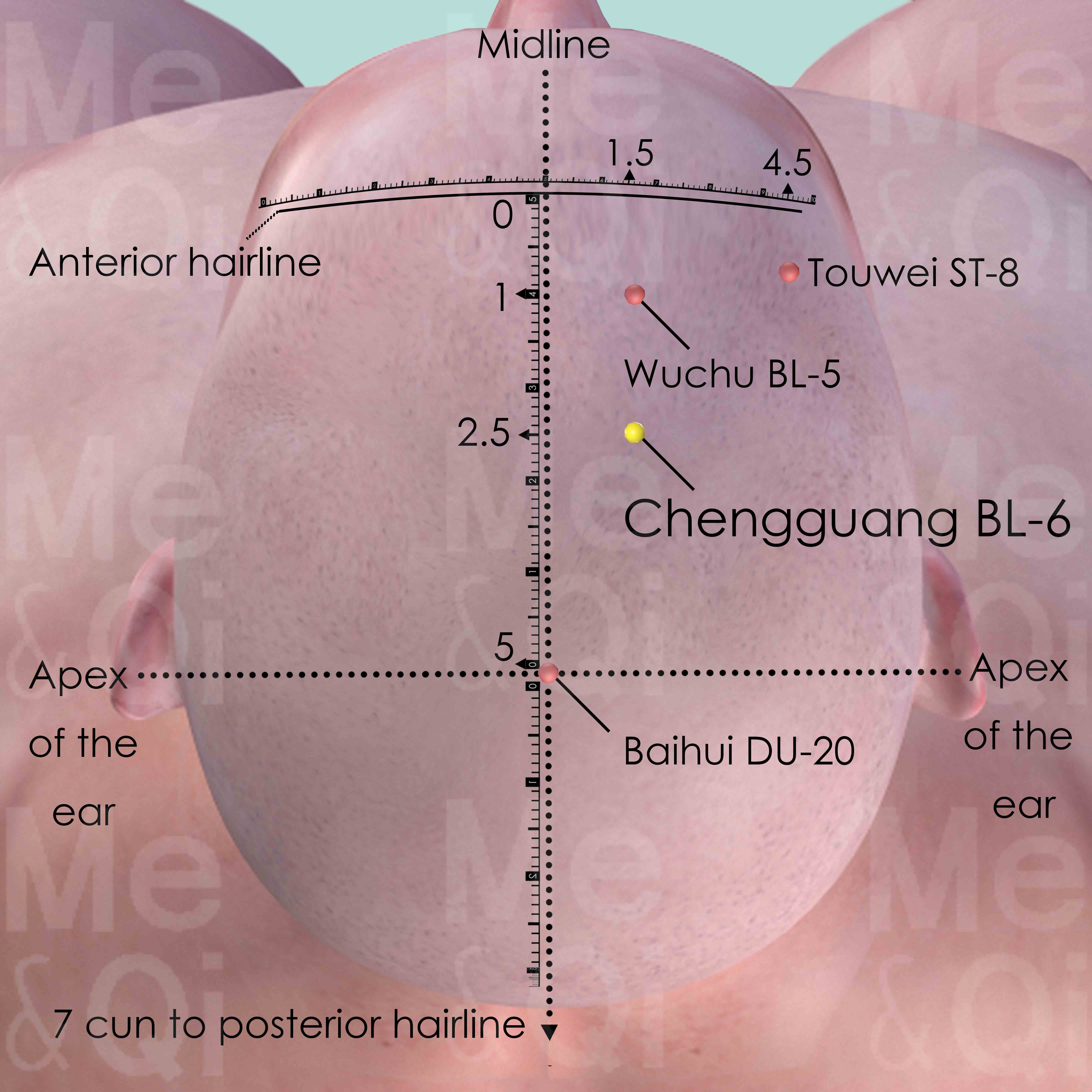
Chengguang BL-6
1.5 cun lateral to the anterior midline and 2.5 cun within the anterior hairline. On the other hand, this point is at the medial third and lateral two-thirds of the distance from anterior midline to the line vertically from Touwei ST-8. Chengguang BL-6 is also 1.5 cun posterior to Wuchu BL-5.
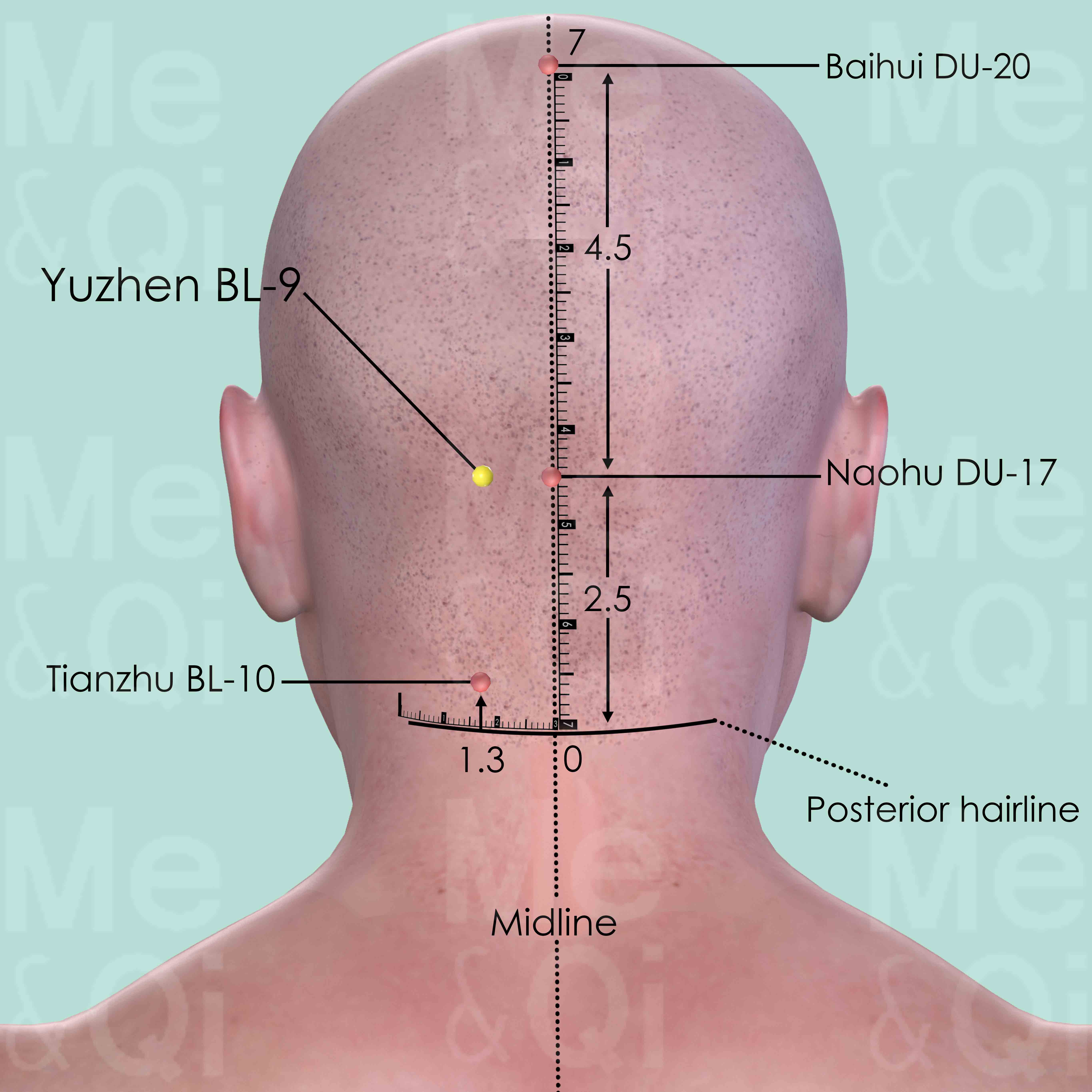
Yuzhen BL-9
First identify Naohu DU-17 which is on the superior border of the external occipital protuberance. Yuzhen BL-9 is 1.3 cun lateral to Naohu DU-17.
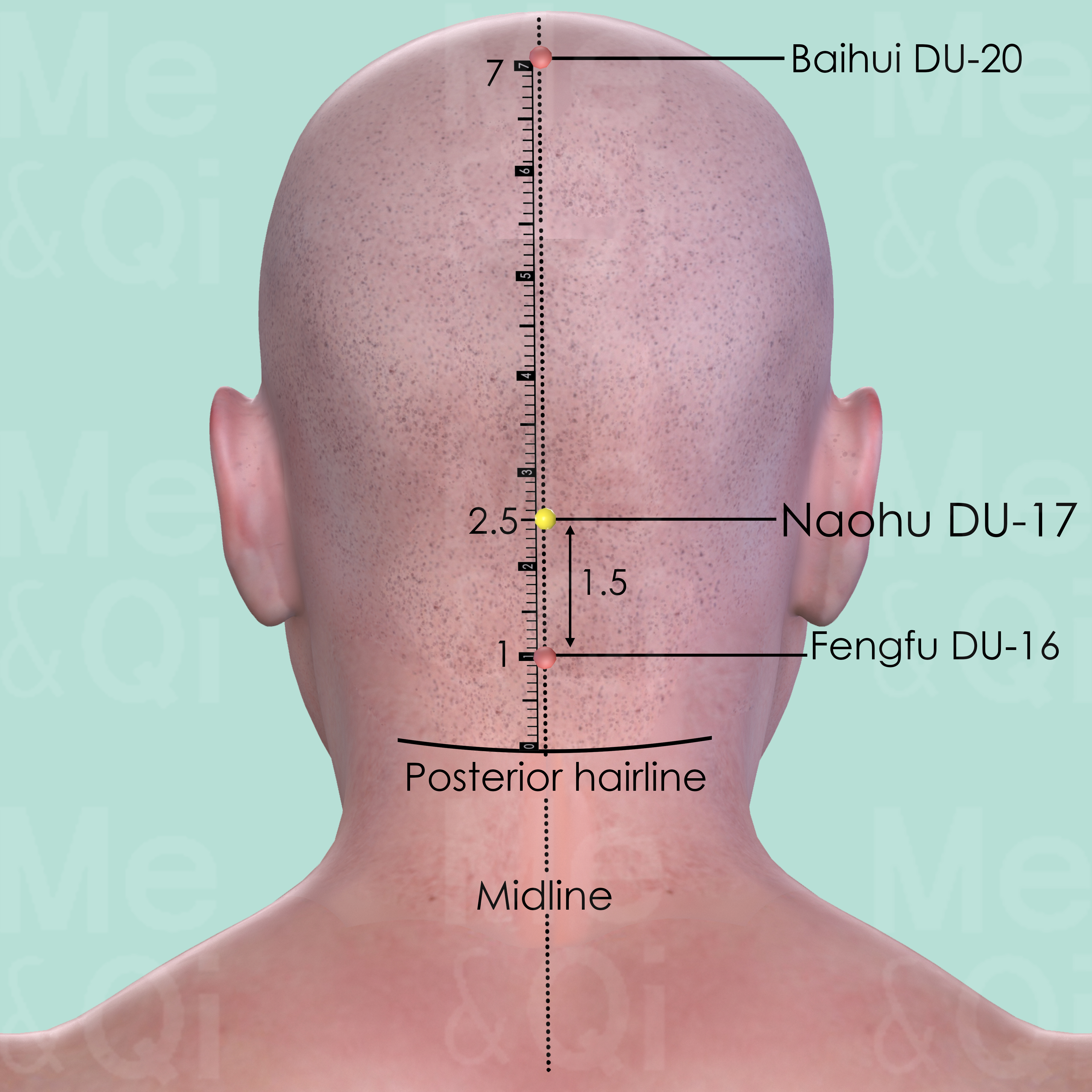
Naohu DU-17
1.5 cun above Fengfu DU-16 or 2.5 cun above the posterior hairline, in a depression superior to the external occipital protuberance.
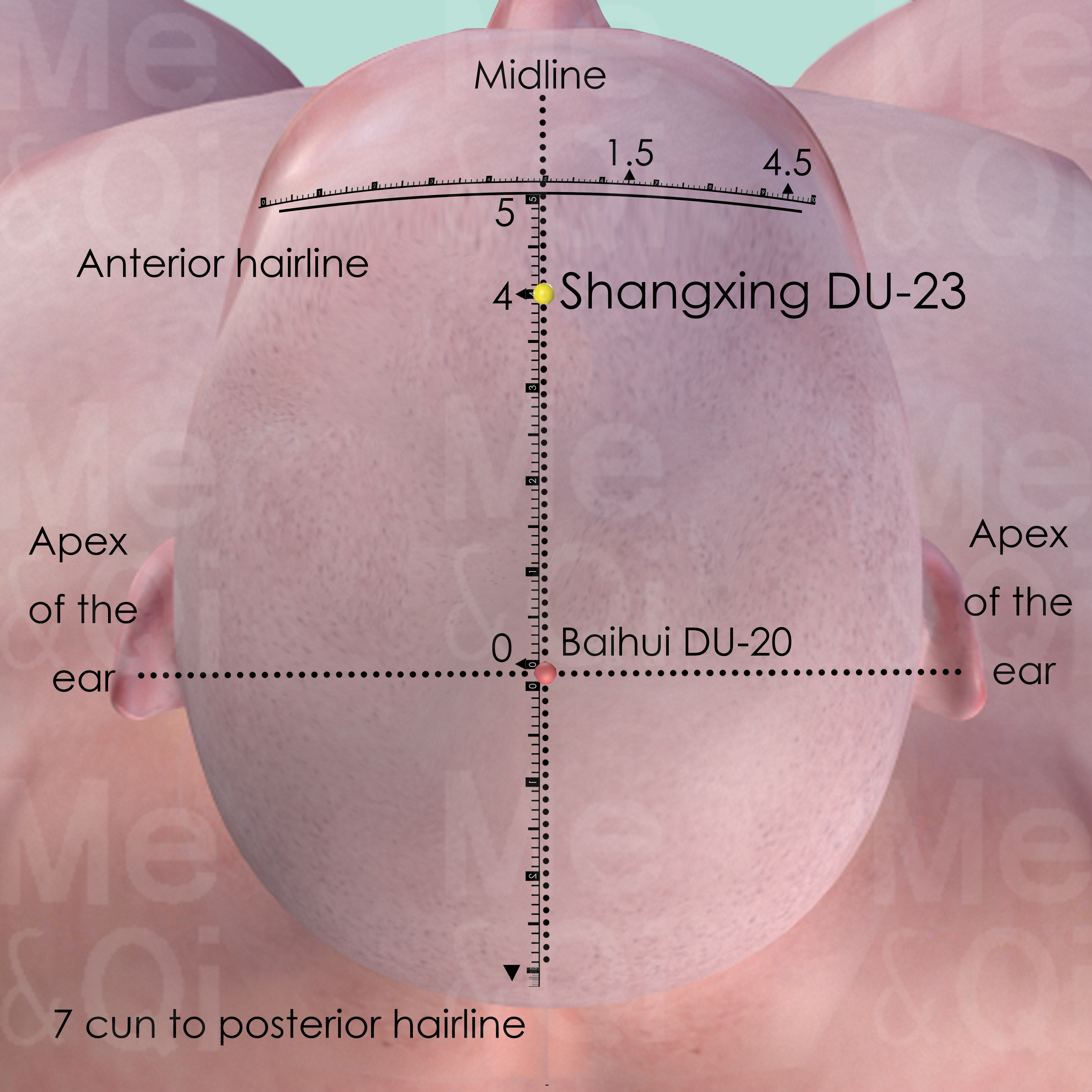
Shangxing DU-23
On the head midline, 1 cun within anterior to the front hairline, 4 cun anterior to Baihui DU-20.
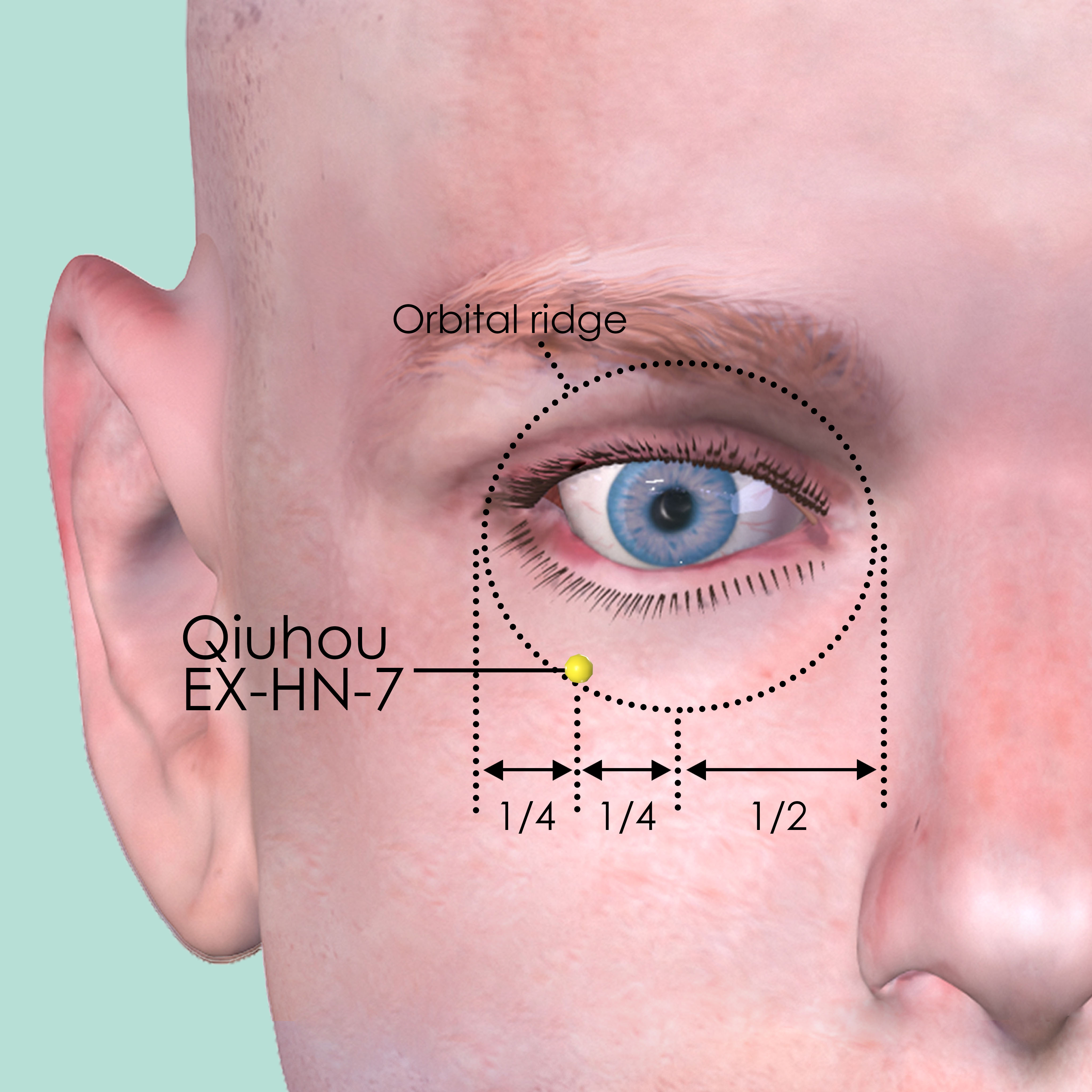
Qiuhou EX-HN-7
On the lower border of the orbital ridge, at the junction of the lateral quarter and the medial three quarters.
TCM Herbs for Myopia
Explore below some TCM herbs used to address myopia, organized by herb category.
- By Herb Category
- Aromatic herbs that transform dampness
- Tonic herbs for qi deficiency
Aromatic herbs that transform Dampness
Myopia can be treated by these herbs if it stems from damp accumulation, especially in the digestive system, using aromatic properties to transform and dispel dampness.
One such herb is Black Atractylodes Rhizomes (Cang Zhu), which is directly recommended for myopia.
Tonic herbs for Qi Deficiency
Myopia can be treated by these herbs when stemming from a lack of vital energy or Qi, helping to boost energy and overall vitality.
One such herb is Ginseng (Ren Shen), a key herb in some formulas recommended for myopia, like Ding Zhi Wan.