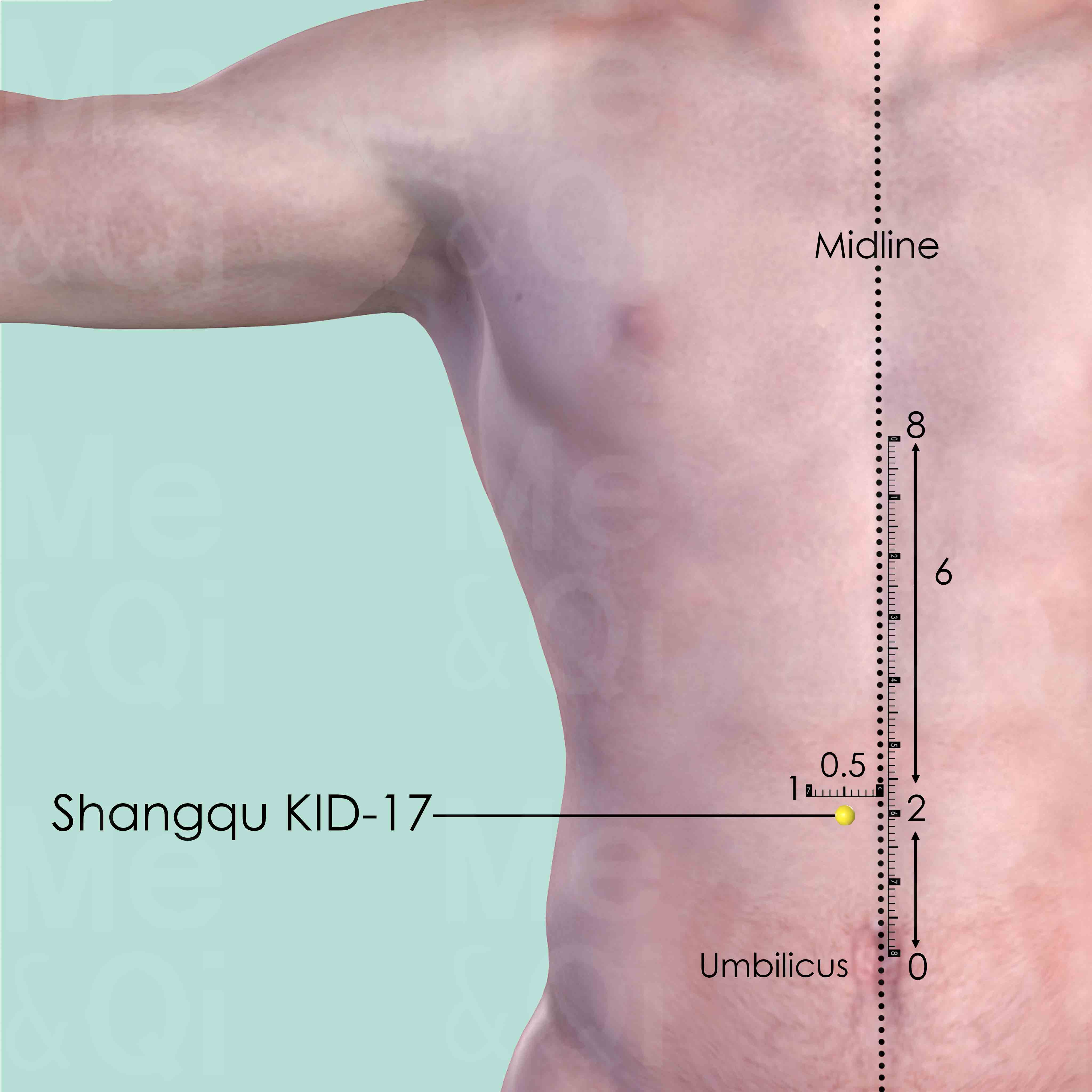
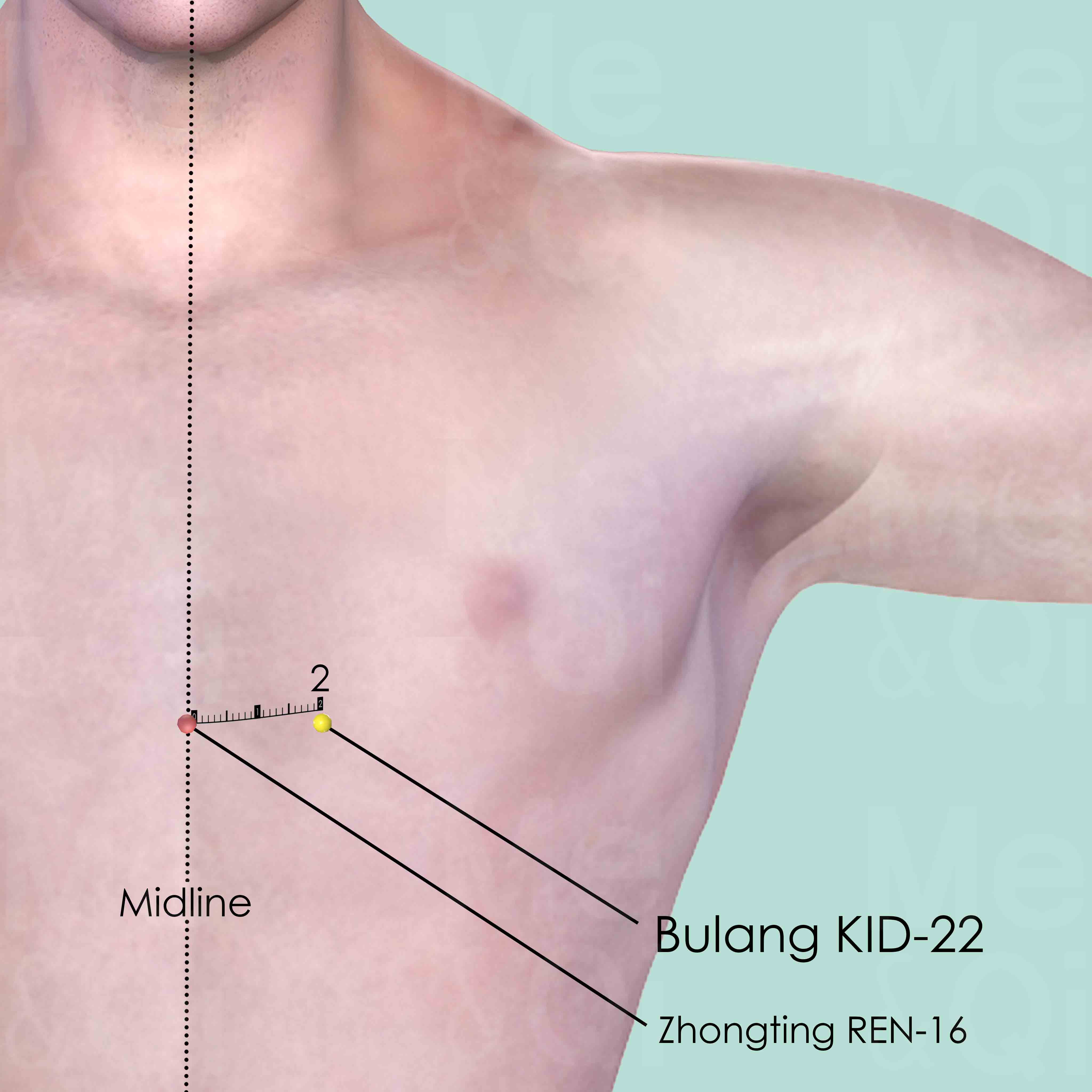
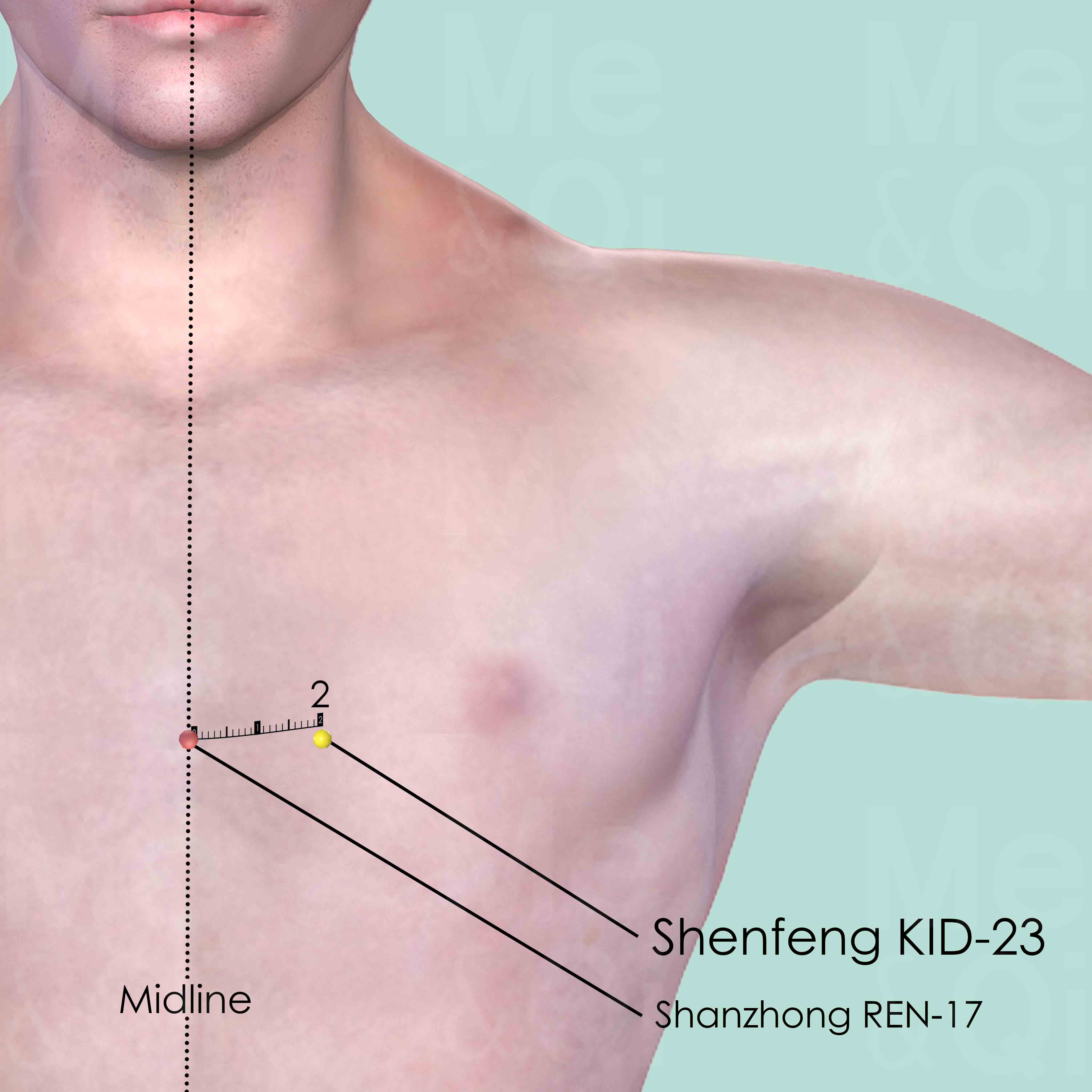
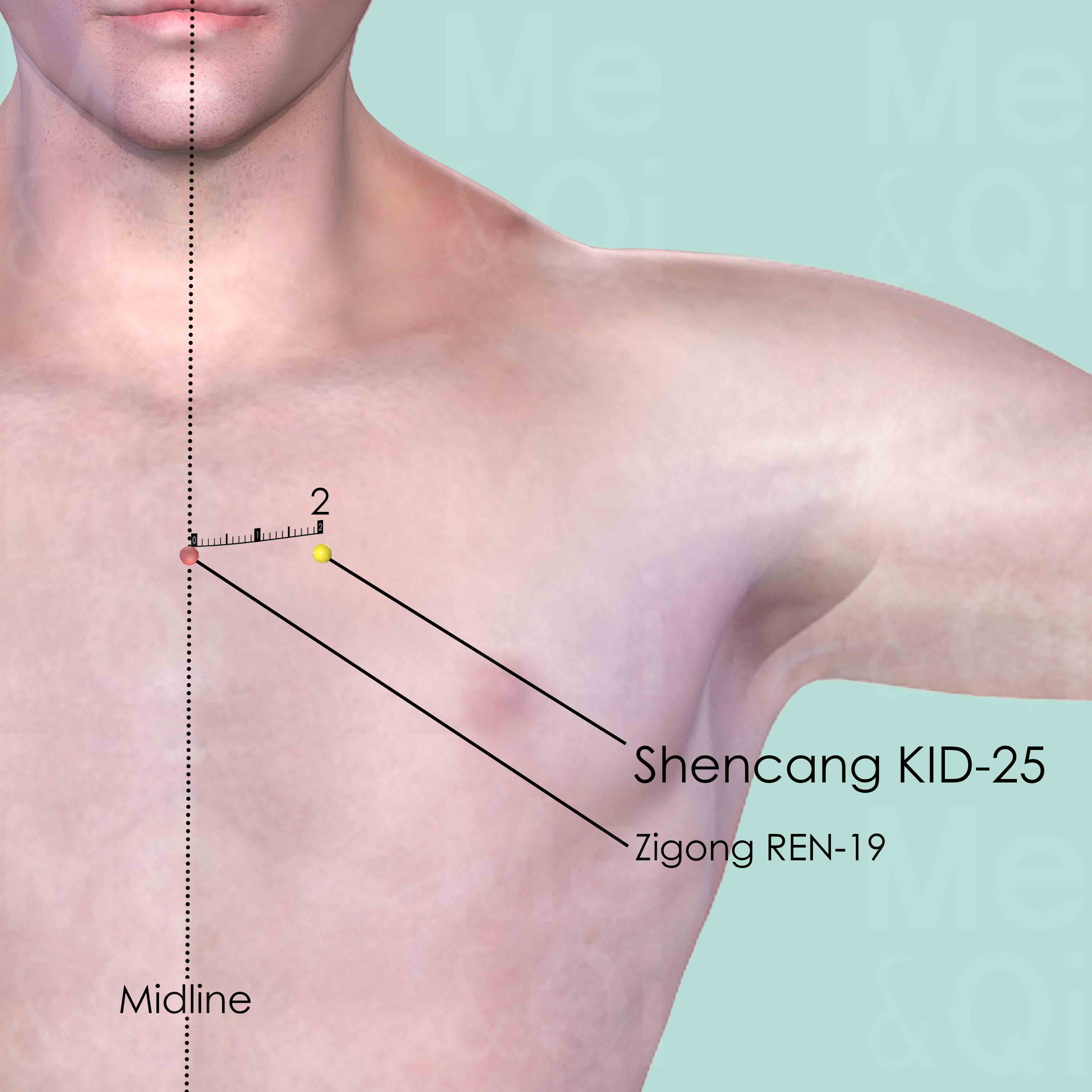
Lack Of Appetiteaccording to TCM
Symptom family: Appetite Disorders
Root Causes of Lack Of Appetite in TCM
Explore below more details about what might cause Lack of appetite according to TCM.
- By Syndrome
- By Organ
- Qi Deficiency
- Qi Stagnation
- Heat
- Blood Deficiency
- Dampness
- Yang Deficiency
- Cold
- Phlegm
- Yin Deficiency
- Qi Sinking
- Blood Stasis
- Yin Excess
- Summer Heat
- View More Causes
- Spleen
- Stomach
- Liver
- Heart
- Kidney
- Lung
- Uterus
- Large Intestine
- Pericardium
- View More Organs
Qi Deficiency
Qi Deficiency in TCM is like running low on battery power. Qi is the vital energy that powers every function in your body. When there's a Qi Deficiency, it means your body doesn't have enough of this essential energy. This can make you feel tired all the time, weak, or even cause shortness of breath. It's similar to how you feel when you haven't had enough sleep or nutritious food. Your body just doesn't have the energy it needs to perform at its best. Unlike modern medicine, which often focuses on specific physical causes for fatigue and weakness, TCM views Qi Deficiency as an overall energy depletion that affects your entire well-being, and it seeks to replenish and balance this vital energy.... see more
Qi Deficiency Patterns That Can Lead to Lack Of Appetite
Common Symptoms: Generalized Fatigue Diarrhea General Weakness Shortness Of Breath Weak Limbs Pale Face Weak Voice Palpitations
| Pattern Name | Relevant Symptoms | Relevant Formulas |
|---|---|---|
| Qi Deficiency | Poor appetite, General weakness, Weak voice, Generalized fatigue, Low energy, Reluctance to speak, Spontaneous sweat, Frequent colds or flu, Lack of appetite, Diarrhea, Shortness of breath... see more | Bu Zhong Yi Qi Tang | Gui Pi Tang | Gu Ben Zhi Beng Tang | Liu Jun Zi Tang | Si Jun Zi Tang |
| Qi and Blood Deficiency | Poor appetite, General weakness, Generalized fatigue, Weak voice, Pale face, Shortness of breath, Palpitations, Dizziness, Poor memory, Insomnia, Reluctance to speak, Lack of appetite, Limb numbness, Skin numbness... see more | Bu Zhong Yi Qi Tang | Gui Pi Tang | Ren Shen Yang Rong Tang | Shi Quan Da Bu Tang | Ba Zhen Tang | Si Wu Tang | Tong Ru Dan | Guo Qi Yin | Zhi Gan Cao Tang |
| Spleen Qi Deficiency | Poor appetite, Slight abdominal distension after eating, General weakness, Desire to lie down, Slight abdominal pain, Excessive gas and flatulence, Bloated abdomen, Dyspepsia, Swollen complexion, Obesity... see more | Ba Zhen Tang | Liu Jun Zi Tang | Si Jun Zi Tang | Fei Er Wan |
| Spleen and Kidney Qi Deficiency | Poor appetite, Excessive menstruation, Pale menstrual flow, Thin menstrual blood, Prolonged menstrual periods, Shortness of breath, Palpitations... see more | Fu Tu Dan |
| Liver Qi Deficiency | Poor appetite, Dizziness, Blurry vision, Eye floaters, Nervousness, Timidity, Easily startled, Lack of bravery, Indecision, Sighing, Vivid dreaming, Depression, Irritability, Hypochondriac distention, Irregular periods, Lack of appetite, Generalized fatigue, Abdominal distention... see more | Bu Zhong Yi Qi Tang | Si Wu Tang | Xiao Yao San |
| Spleen and Lung Qi Deficiency | Poor appetite, Lack of appetite, Slight abdominal distension after eating, Generalized fatigue, General weakness, Pale face, Weak limbs, Diarrhea, Obesity, Shortness of breath, Coughing, Weak voice, Spontaneous sweat, Reluctance to speak, Frequent colds or flu, Aversion to cold... see more | Liu Jun Zi Tang | Si Jun Zi Tang |
| Stomach and Spleen Qi Deficiency | Poor appetite, Lack of appetite, Slight abdominal distension after eating, Generalized fatigue, General weakness, Pale face, Weak limbs, Diarrhea, Upper abdominal discomfort, Loss of taste... see more | Shen Ling Bai Zhu San | Si Jun Zi Tang | Sheng Yang Yi Wei Tang | Xiang Sha Yang Wei Wan |
| Stomach Qi Deficiency | Poor appetite, Morning fatigue | Si Jun Zi Tang |
| Spleen Deficiency | Poor appetite, Sticky vaginal discharge, Generalized fatigue, Depression, Cold extremities, Diarrhea, White vaginal discharge, Lack of appetite, Amenorrhea, Dull shallow face, Weak limbs... see more | Bu Zhong Yi Qi Tang | Wan Dai Tang | Yi Huang Tang |
| Spleen and Stomach Qi Deficiency | Poor appetite, Dizziness, Unsteadiness, Blurry vision, Deafness, Tinnitus, Shortness of breath, Weak voice, Pale face, Lack of appetite, Diarrhea... see more | Bu Zhong Yi Qi Tang | Ren Shen Yang Rong Tang | Ba Zhen Tang | Xiang Sha Liu Jun Zi Tang |
| Heart and Spleen Deficiency | Poor appetite, Palpitations, Insomnia, Lack of appetite, Generalized fatigue, Anxiety, Pale face, Poor memory, Diarrhea, Scanty menstruation, Pale lips... see more | Gui Pi Tang |
| Stomach Deficiency | Poor appetite, Nausea or vomiting, Generalized fatigue, Chills, Lack of appetite, Depression, Dry mouth, Morning sickness... see more | Mai Men Dong Tang | Xiang Sha Liu Jun Zi Tang | Er Chen Tang |
| Heart and Spleen Qi and Blood Deficiency | Poor appetite, Palpitations, Poor memory, Restless sleeplessness, Fever, Lack of appetite, Generalized fatigue, Coughing, Shortness of breath, Exertional dyspnea, Weight loss... see more | Ren Shen Yang Rong Tang |
Qi Stagnation
Qi Stagnation in TCM is like having a traffic jam in your body's energy system. Qi, the vital life force that flows through your body, is supposed to move smoothly to maintain health and balance. But with Qi Stagnation, this flow gets blocked or slowed down, like cars stuck on a highway. This can lead to symptoms like feeling stressed, emotional mood swings, and physical discomfort, often described as a feeling of fullness or tightness, especially in the chest or abdomen. It's as though the body's internal energy circulation is disrupted, causing various issues. TCM sees this as an energy flow problem, different from modern medicine's focus on specific physiological processes.... see more
Qi Stagnation Patterns That Can Lead to Lack Of Appetite
Common Symptoms: Irritability Depression Sighing Nausea Upper Abdominal Distension Hypochondriac Pain Abdominal Distention Irregular Periods
| Pattern Name | Relevant Symptoms | Relevant Formulas |
|---|---|---|
| Obstruction Of the Spleen By Dampness with Liver Qi Stagnation | No appetite, Upper abdominal oppression, Nausea, Lack of appetite, Diarrhea, Feeling of heaviness, Dry mouth without desire to drink, Dull shallow face, Irritability, Upper abdominal distension, Hypochondriac distention, Hypochondriac pain... see more | Ping Wei San | Dang Gui Shao Yao San |
| Heart Qi Stagnation | Poor appetite, Palpitations, Chest distension, Feeling of oppression of the chest, Depression | Ban Xia Hou Pu Tang |
| Liver Qi Stagnation | Poor appetite, Hypochondriac distention, Chest distension, Upper abdominal distension, Abdominal distention, Sighing, Melancholia, Depression, Mood swings, Irregular periods, Globus sensation, Pre menstrual breast distension, Pre menstrual tension, Anxiety, Anger... see more | Xiao Yao San | Jia Wei Xiao Yao San | Yue Ju Wan | Chai Hu Shu Gan San | Yi Guan Jian |
| Pericardium Qi Stagnation | Poor appetite, Mild chest pain, Chest distension, Stifling sensation in the chest, Sighing, Throat lumps, Palpitations, Depression, Irritability, Lack of appetite, Weak limbs, Cold extremities... see more | Ban Xia Hou Pu Tang |
| Qi Stagnation | Poor appetite, General fullness, Moving pain, Depression, Irritability, Mood swings, Sighing | Yue Ju Wan |
| Blood and Qi Deficiency with Blood Stagnation | Poor appetite, Lack of appetite, Weak limbs, Lower back pain, Abdominal distention, Irregular periods, Red and white vaginal discharge, Infertility... see more | Ba Zhen Yi Mu Tang |
| Liver Qi Stagnation invading the Stomach | Poor appetite, Belching, Abdominal distention, Upper abdominal distension, Depression, Irritability, Dry mouth, Lack of appetite, Craving for sour foods, Dry throat, Acid reflux... see more | Ban Xia Hou Pu Tang | Zuo Jin Wan |
| Phlegm clogging the Lungs with Qi Stagnation | Poor appetite, Coughing and wheezing with copious sputum, Focal distention of the chest, Lack of appetite, Dyspepsia, Chronic bronchitis, Bronchial asthma, Emphysema, Childhood asthma, Diaphragm pain... see more | San Zi Yang Qin Tang |
Heat
In TCM "Heat" signifies an excess of Yang energy, leading to an imbalance where heat predominates over the body's cool Yin aspects. This condition is metaphorically akin to an internal over-heating. Symptoms indicative of Heat can include feelings of warmth, fever, sweating, irritability, red face, thirst with a preference for cold drinks, and a rapid pulse. The tongue may appear red with a yellow coating. Unlike the common interpretation of heat in terms of temperature, in TCM, it represents a state of hyperactivity or inflammation in the body.... see more
Heat Patterns That Can Lead to Lack Of Appetite
Common Symptoms: Feeling Of Heaviness Bitter Taste In The Mouth Nausea Abdominal Fullness Diarrhea Dry Mouth Without Desire To Drink Fever Sticky Taste In The Mouth
| Pattern Name | Relevant Symptoms | Relevant Formulas |
|---|---|---|
| Obstruction Of the Spleen By Dampness with Liver Qi Stagnation | No appetite, Upper abdominal oppression, Nausea, Lack of appetite, Diarrhea, Feeling of heaviness, Dry mouth without desire to drink, Dull shallow face, Irritability, Upper abdominal distension, Hypochondriac distention, Hypochondriac pain... see more | Ping Wei San | Dang Gui Shao Yao San |
| Damp-Heat | Poor appetite, Fever, Neck gland swelling, Headaches, Tight feeling in chest and stomach, Sticky taste in the mouth, Absence of thirst, Feeling hot, Feeling of heaviness, Bitter taste in the mouth, Acne... see more | Yi Huang Tang | Long Dan Xie Gan Tang | Ba Zheng San |
| Cold-Phlegm | Poor appetite, White and watery sputum, Feeling of oppression of the chest, Cold extremities, Nausea, Lack of appetite... see more | Ling Gan Wu Wei Jiang Xin Tang | San Zi Yang Qin Tang |
| Damp-Heat in the Liver | Poor appetite, Hypochondrial fullness with warmth relief, Abdominal fullness, Lower abdominal fullness, Bitter taste in the mouth, Sticky taste in the mouth, Lack of appetite, Nausea, Feeling of heaviness, Yellow vaginal discharge, Vaginal itching, Vulvar eczema, Vulvar sores, Bleeding between periods, Midcycle bleeding pain, Red and swollen scrotum, Red and swelling genital, Papules, Itchy vesicular rashes, Urinary dysfunction, Urinary burning, Dark urine... see more | Long Dan Xie Gan Tang | Yin Chen Hao Tang |
| Damp-Heat invading the Spleen | Poor appetite, Lack of appetite, Feeling of heaviness, Dry mouth without desire to drink, Nausea or vomiting, Malodorous diarrhea, Anal burning, Feeling hot, Scanty and dark urine, Low grade fever, Dull headache, Dull yellow complexion, Yellow sclera, Oily sweat, Itchy rashes, Bitter taste in the mouth, Upper abdominal fullness, Upper abdominal pain... see more | Lian Po Yin |
| Half Exterior Half Interior | Poor appetite, Chest distension, Bitter taste in the mouth, Dry cough, Anxiety, Restlessness, Vomit, Lack of appetite, Dizziness, Blurry vision... see more | Xiao Chai Hu Tang |
| Phlegm-Heat in the Middle Burner | Poor appetite, Upper abdominal focal distention, Abdominal fullness, Dry heaving, Borborygmi with diarrhea, Lack of appetite, Peptic ulcer, Gastroesophageal reflux disease, Gastritis, Chronic cholecystitis, Colitis... see more | Ban Xia Xie Xin Tang |
| Stomach Deficiency | Poor appetite, Nausea or vomiting, Generalized fatigue, Chills, Lack of appetite, Depression, Dry mouth, Morning sickness... see more | Mai Men Dong Tang | Xiang Sha Liu Jun Zi Tang | Er Chen Tang |
Blood Deficiency
Blood Deficiency in TCM is like when your body's tank runs low on the vital energy that blood provides. It's not exactly the same as anemia in modern medicine, which is about having too few red blood cells. Instead, Blood Deficiency in TCM is about your body not having enough of the life-giving qualities that blood brings, like nourishment and moisture. This can make you feel tired, look pale, and even feel dizzy or have blurry vision. It's like a garden not getting enough water to stay lush and vibrant. TCM sees this as an imbalance where the body isn't being nourished as it should be, impacting overall health and well-being.... see more
Blood Deficiency Patterns That Can Lead to Lack Of Appetite
Common Symptoms: Generalized Fatigue Palpitations Dizziness Poor Memory Insomnia Anemia Scanty Menstruation Diarrhea
| Pattern Name | Relevant Symptoms | Relevant Formulas |
|---|---|---|
| Qi and Blood Deficiency | Poor appetite, General weakness, Generalized fatigue, Weak voice, Pale face, Shortness of breath, Palpitations, Dizziness, Poor memory, Insomnia, Reluctance to speak, Lack of appetite, Limb numbness, Skin numbness... see more | Bu Zhong Yi Qi Tang | Gui Pi Tang | Ren Shen Yang Rong Tang | Shi Quan Da Bu Tang | Ba Zhen Tang | Si Wu Tang | Tong Ru Dan | Guo Qi Yin | Zhi Gan Cao Tang |
| Spleen and Heart Blood Deficiency | Poor appetite, Palpitations, Dizziness, Insomnia, Vivid dreaming, Poor memory, Anxiety, Easily startled, Dull pale complexion, Pale lips, Generalized fatigue, Muscle weakness, Diarrhea, Lack of appetite, Scanty menstruation... see more | Gui Pi Tang |
| Spleen Blood Deficiency | Poor appetite, Lack of appetite, Generalized fatigue, General weakness, Pale face, Weak limbs, Diarrhea, Depression, Emaciation, Scanty menstruation, Amenorrhea, Insomnia, Slight abdominal distension after eating... see more | Gui Pi Tang |
| Blood and Qi Deficiency with Blood Stagnation | Poor appetite, Lack of appetite, Weak limbs, Lower back pain, Abdominal distention, Irregular periods, Red and white vaginal discharge, Infertility... see more | Ba Zhen Yi Mu Tang |
| Heart and Spleen Deficiency | Poor appetite, Palpitations, Insomnia, Lack of appetite, Generalized fatigue, Anxiety, Pale face, Poor memory, Diarrhea, Scanty menstruation, Pale lips... see more | Gui Pi Tang |
| Heart and Spleen Qi and Blood Deficiency | Poor appetite, Palpitations, Poor memory, Restless sleeplessness, Fever, Lack of appetite, Generalized fatigue, Coughing, Shortness of breath, Exertional dyspnea, Weight loss... see more | Ren Shen Yang Rong Tang |
| Blood Deficiency with disharmony of Liver and Spleen | Poor appetite, Chest distension, Chest pain, Anemia, Dizziness, Headaches, Dry mouth, Dry throat, Lack of appetite, Irregular periods, Leukorrhea... see more | Xiao Yao San |
Dampness
"Dampness" in TCM is a concept that describes a pattern of disharmony where the body accumulates excess moisture. Imagine the heavy, sticky feeling you get on a very humid day; that's similar to what dampness feels like internally. It can manifest as a sense of heaviness, bloating, sluggishness, or even a foggy mind. This condition is often thought to arise from environmental factors like living in a damp place, dietary habits that promote moisture in the body, or internal imbalances that hinder the body's ability to process fluids properly. In TCM, dampness can obstruct the normal flow of energy and fluids in the body, leading to various symptoms.... see more
Dampness Patterns That Can Lead to Lack Of Appetite
Common Symptoms: Feeling Of Heaviness Diarrhea Nausea Fever Bitter Taste In The Mouth Generalized Fatigue Dry Mouth Without Desire To Drink Headaches
| Pattern Name | Relevant Symptoms | Relevant Formulas |
|---|---|---|
| Obstruction Of the Spleen By Dampness with Liver Qi Stagnation | No appetite, Upper abdominal oppression, Nausea, Lack of appetite, Diarrhea, Feeling of heaviness, Dry mouth without desire to drink, Dull shallow face, Irritability, Upper abdominal distension, Hypochondriac distention, Hypochondriac pain... see more | Ping Wei San | Dang Gui Shao Yao San |
| Damp-Heat | Poor appetite, Fever, Neck gland swelling, Headaches, Tight feeling in chest and stomach, Sticky taste in the mouth, Absence of thirst, Feeling hot, Feeling of heaviness, Bitter taste in the mouth, Acne... see more | Yi Huang Tang | Long Dan Xie Gan Tang | Ba Zheng San |
| Cold-Damp invading the Spleen | Poor appetite, Lack of appetite, Epigastric coldness, Head and body heaviness, Sweet taste in mouth, Absence of thirst, Diarrhea, General weakness, Generalized fatigue, Nausea, Edema, Dull pale complexion, White vaginal discharge, Upper abdominal fullness... see more | Ping Wei San |
| Damp-Heat in the Liver | Poor appetite, Hypochondrial fullness with warmth relief, Abdominal fullness, Lower abdominal fullness, Bitter taste in the mouth, Sticky taste in the mouth, Lack of appetite, Nausea, Feeling of heaviness, Yellow vaginal discharge, Vaginal itching, Vulvar eczema, Vulvar sores, Bleeding between periods, Midcycle bleeding pain, Red and swollen scrotum, Red and swelling genital, Papules, Itchy vesicular rashes, Urinary dysfunction, Urinary burning, Dark urine... see more | Long Dan Xie Gan Tang | Yin Chen Hao Tang |
| Damp-Heat invading the Spleen | Poor appetite, Lack of appetite, Feeling of heaviness, Dry mouth without desire to drink, Nausea or vomiting, Malodorous diarrhea, Anal burning, Feeling hot, Scanty and dark urine, Low grade fever, Dull headache, Dull yellow complexion, Yellow sclera, Oily sweat, Itchy rashes, Bitter taste in the mouth, Upper abdominal fullness, Upper abdominal pain... see more | Lian Po Yin |
| Oedema | Poor appetite, Abdominal edema, Ankle edema, Facial edema, Foot edema, Oedema of hands, Leg edema, Ocular swelling, Abdominal distention... see more | Ping Wei San | Wu Ling San | Fang Ji Huang Qi Tang | Wu Pi Yin | Ling Gui Zhu Gan Tang | Zhen Wu Tang | Shen Qi Wan | Yu Gong San | Zhou Che Wan |
| Summer Heat with Dampness | Poor appetite, Fever, Aversion to cold, Perspiration, Headaches, Feeling of heaviness, Tight feeling in chest and stomach, Anxiety, Thirst, Chest distension, Lack of appetite... see more | Huo Xiang Zheng Qi San | Xiang Ru San | Gui Ling Gan Lu Yin |
Yang Deficiency
Yang deficiency in TCM refers to a state where the body's Yang energy, which is responsible for warmth, activity, and function, is weakened or diminished. This pattern of disharmony often arises from chronic illness, aging, or inherent constitutional weakness. Symptoms of Yang deficiency are typically associated with cold and sluggishness, such as a feeling of coldness, cold extremities, pale complexion, low energy or fatigue, and a desire for warmth. Digestive issues like poor appetite, loose stools, and water retention can also be indicative of Yang deficiency.... see more
Yang Deficiency Patterns That Can Lead to Lack Of Appetite
Common Symptoms: Generalized Fatigue Chills Diarrhea Cold Extremities Pale Face Absence Of Thirst General Weakness Weak Limbs
| Pattern Name | Relevant Symptoms | Relevant Formulas |
|---|---|---|
| Greater Yin stage | No appetite, Lack of appetite, Vomit, Abdominal fullness, Chills, Diarrhea, Absence of thirst, Generalized fatigue... see more | Li Zhong Wan |
| Kidney and Spleen Yang Deficiency | Poor appetite, Lower back pain, Weak and cold knees, Back cold sensation, Chills, Weak legs, Bright pale face, Erectile dysfunction, Premature ejaculation, Oligospermia, Watery ejaculate, Low sex drive, Generalized fatigue, General weakness, Clear urination, Nocturia, Apathy, Leg edema, Female infertility, Diarrhea, Depression, Lack of appetite, Slight abdominal distention, Desire to lie down... see more | Li Zhong Wan |
| Lung Yang Deficiency | Poor appetite, Coughing and wheezing with copious sputum, Cold extremities, Spontaneous sweat, Frequent colds or flu, Pale face, Generalized fatigue, Shortness of breath, Absence of thirst, Wheezing, Weak voice... see more | Gan Cao Gan Jiang Tang | Si Jun Zi Tang | Sheng Mai San |
| Kidney Yang Deficiency | Poor appetite, Lower back pain, Dizziness, Tinnitus, Weak and cold knees, Lower back coldness, Chills, Weak legs, Bright pale face, Generalized fatigue, General weakness, Leg edema, Female infertility, Diarrhea, Depression, Erectile dysfunction, Premature ejaculation, Oligospermia, Low sex drive, Pale and abudant urination... see more | You Gui Wan |
| Spleen Yang Deficiency | Poor appetite, Slight abdominal distension after eating, General weakness, Desire to lie in fetal position, Pale face, Cold extremities, Chills, Undigested food in stools, Excessive gas and flatulence, Bloated abdomen, Abdominal pain relieved by pressure and warmth, Dull shallow face... see more | Bu Zhong Yi Qi Tang | Yi Huang Tang | Zhen Wu Tang | Huang Tu Tang |
| Stomach Yang Deficient and Cold | Poor appetite, Epigastric pain relieved with pressure or eating, Lack of appetite, Desire for hot beverages and foods, Vomiting clear liquid, Absence of thirst, Weak limbs, Cold extremities, Generalized fatigue, Pale face... see more | Huang Qi Jian Zhong Tang | Xiang Sha Yang Wei Wan | Xiao Jian Zhong Tang | Wu Zhu Yu Tang |
Cold
In TCM "Cold" as a pattern of disharmony refers to a specific type of imbalance within the body's systems, often linked to a deficiency or weakness. It's not about feeling physically cold or having a common cold, but rather a metaphorical description of certain symptoms and underlying conditions. When a TCM practitioner says someone suffers from "Cold," it usually implies that the body's Yang energy, which is warm and active, is insufficient or overpowered by Yin energy, which is cool and passive. Symptoms of Cold in TCM can include a general feeling of coldness, cold limbs, pale complexion, low energy, slow metabolism, and a preference for warmth. ... see more
Cold Patterns That Can Lead to Lack Of Appetite
Common Symptoms: Chills Diarrhea Generalized Fatigue Absence Of Thirst Cold Extremities General Weakness Scanty Menstruation Menstrual Cramps
| Pattern Name | Relevant Symptoms | Relevant Formulas |
|---|---|---|
| Greater Yin stage | No appetite, Lack of appetite, Vomit, Abdominal fullness, Chills, Diarrhea, Absence of thirst, Generalized fatigue... see more | Li Zhong Wan |
| Cold in the Uterus | Poor appetite, Diarrhea, Lack of appetite, Generalized fatigue, General weakness, Thin vaginal discharge... see more | Wen Jing Tang | Shao Fu Zhu Yu Tang | Wen Qi Hua Shi Tang |
| Cold-Damp invading the Spleen | Poor appetite, Lack of appetite, Epigastric coldness, Head and body heaviness, Sweet taste in mouth, Absence of thirst, Diarrhea, General weakness, Generalized fatigue, Nausea, Edema, Dull pale complexion, White vaginal discharge, Upper abdominal fullness... see more | Ping Wei San |
| Cold-Phlegm | Poor appetite, White and watery sputum, Feeling of oppression of the chest, Cold extremities, Nausea, Lack of appetite... see more | Ling Gan Wu Wei Jiang Xin Tang | San Zi Yang Qin Tang |
| Empty-Cold | Poor appetite, Chills, Cold extremities, Pale face, Absence of thirst, Low energy, Perspiration, Diarrhea, Clear urination, Frequent urination... see more | Huang Qi Jian Zhong Tang | Da Jian Zhong Tang |
| Stomach Deficiency | Poor appetite, Nausea or vomiting, Generalized fatigue, Chills, Lack of appetite, Depression, Dry mouth, Morning sickness... see more | Mai Men Dong Tang | Xiang Sha Liu Jun Zi Tang | Er Chen Tang |
Phlegm
In TCM "Phlegm" as a pattern of disharmony is a complex concept that extends beyond the physical manifestation of mucus. It represents a pathological factor that can disrupt the flow of Qi (vital energy) and blood, leading to various health issues. Phlegm in TCM is seen as a sticky, turbid substance arising from the body's inability to metabolize fluids properly, often due to a dysfunction of the spleen. It's not only associated with respiratory problems like cough and congestion but also with systemic issues. Symptoms can include a feeling of heaviness, mental cloudiness, dizziness, and in some cases, the formation of lumps or masses. Phlegm can even be "invisible," contributing to emotional disturbances like depression or stress. ... see more
Phlegm Patterns That Can Lead to Lack Of Appetite
Common Symptoms: Abdominal Fullness Hepatitis Feeling Of Oppression Of The Chest Cold Extremities Nausea Chronic Bronchitis Feeling Of Heaviness Congestive Heart Failure
| Pattern Name | Relevant Symptoms | Relevant Formulas |
|---|---|---|
| Cold-Phlegm | Poor appetite, White and watery sputum, Feeling of oppression of the chest, Cold extremities, Nausea, Lack of appetite... see more | Ling Gan Wu Wei Jiang Xin Tang | San Zi Yang Qin Tang |
| Phlegm | Poor appetite, Feeling of oppression of the chest, Head fog, Dizziness | Ban Xia Hou Pu Tang | Yue Ju Wan | Wen Dan Tang |
| Oedema | Poor appetite, Abdominal edema, Ankle edema, Facial edema, Foot edema, Oedema of hands, Leg edema, Ocular swelling, Abdominal distention... see more | Ping Wei San | Wu Ling San | Fang Ji Huang Qi Tang | Wu Pi Yin | Ling Gui Zhu Gan Tang | Zhen Wu Tang | Shen Qi Wan | Yu Gong San | Zhou Che Wan |
| Phlegm-Heat in the Middle Burner | Poor appetite, Upper abdominal focal distention, Abdominal fullness, Dry heaving, Borborygmi with diarrhea, Lack of appetite, Peptic ulcer, Gastroesophageal reflux disease, Gastritis, Chronic cholecystitis, Colitis... see more | Ban Xia Xie Xin Tang |
| Phlegm clogging the Lungs with Qi Stagnation | Poor appetite, Coughing and wheezing with copious sputum, Focal distention of the chest, Lack of appetite, Dyspepsia, Chronic bronchitis, Bronchial asthma, Emphysema, Childhood asthma, Diaphragm pain... see more | San Zi Yang Qin Tang |
Yin Deficiency
Yin deficiency in TCM is a pattern of disharmony characterized by a depletion of the body's Yin energy, which represents the cooling, moistening, and nurturing aspects of our physiology. This condition often arises from factors like chronic stress, overwork, insufficient rest, or prolonged illness. Symptoms of Yin deficiency can include a sensation of heat, especially in the afternoon or evening, night sweats, insomnia, a dry mouth or throat, and a red tongue with little coating. There might also be a general feeling of restlessness or irritability. Since Yin is essential for balancing the body's active and warm Yang energy, its deficiency leads to a relative excess of Yang, manifesting as heat or dryness symptoms.... see more
Yin Deficiency Patterns That Can Lead to Lack Of Appetite
Common Symptoms: Dry Mouth Preference For Sipping Dry Stools Generalized Fatigue Slight Abdominal Distension After Eating Upper Abdominal Pain Afternoon Heat Sensation Dry Throat
| Pattern Name | Relevant Symptoms | Relevant Formulas |
|---|---|---|
| Stomach Yin Deficiency | Poor appetite, No desire to eat, Lack of appetite, Preference for sipping, Slight abdominal distension after eating... see more | Mai Men Dong Tang | Yi Wei Tang | Shen Ling Bai Zhu San |
| Stomach and Spleen Yin Deficiency | Poor appetite, Lack of appetite, Dry mouth, Preference for sipping, Dry stools, Dry lips, Nausea, Generalized fatigue, Upper abdominal discomfort, Loss of taste... see more | Shen Ling Bai Zhu San |
| Stomach Deficiency | Poor appetite, Nausea or vomiting, Generalized fatigue, Chills, Lack of appetite, Depression, Dry mouth, Morning sickness... see more | Mai Men Dong Tang | Xiang Sha Liu Jun Zi Tang | Er Chen Tang |
Qi Sinking
Qi Sinking is a pattern of disharmony in TCM where the body's energy, or Qi, is thought to "sink" or drop down. Imagine a balloon slowly deflating and falling; that's similar to what happens with Qi Sinking. This can lead to feelings of heaviness, fatigue, and even physical symptoms like prolapse of organs or frequent urination. It's as if the body's energy, which usually supports and holds things in place, isn't able to do its job properly. TCM views this as an imbalance where the uplifting and supporting qualities of Qi are weakened.... see more
Qi Sinking Patterns That Can Lead to Lack Of Appetite
Common Symptoms: Anus Prolapse Hemorrhoids Generalized Fatigue Chronic Diarrhea Uterine Prolapse Prolapsed Bladder Stomach Prolapse Diarrhea
| Pattern Name | Relevant Symptoms | Relevant Formulas |
|---|---|---|
| Large Intestine collapse | Poor appetite, Chronic diarrhea, Anus prolapse, Hemorrhoids, Generalized fatigue, Cold extremities, Lack of appetite, Mental exhaustion, Craving for hot beverages... see more | Bu Zhong Yi Qi Tang |
| Qi Collapsing or Qi Sinking | Poor appetite, Uterine prolapse, Prolapsed bladder, Stomach prolapse, Nephroptosis, Anus prolapse, Bearing down sensation in abdomen, Hemorrhoids, Chronic diarrhea, Frequent and urgent urination, Urinary incontinence, Generalized fatigue, Low energy, Intestines prolapse, Vaginal prolapse... see more | Bu Zhong Yi Qi Tang | Du Shen Tang |
| Spleen Qi Sinking | Poor appetite, Lack of appetite, Slight abdominal distension after eating | Bu Zhong Yi Qi Tang |
Blood Stasis
Blood Stasis in TCM is a concept where the blood flow in the body is not as smooth or efficient as it should be. Imagine a river that's supposed to flow freely, but instead, it's getting blocked or moving too slowly in some parts. This can lead to various health issues, like pain that feels sharp or stabbing, dark bruises, and a complexion that looks purplish. TCM believes that good health relies on the smooth and vibrant flow of Qi and blood throughout the body, so when blood gets stuck, it's like a traffic jam in your body, leading to discomfort or health problems.... see more
Blood Stasis Patterns That Can Lead to Lack Of Appetite
Common Symptoms: Weak Limbs Lower Back Pain Abdominal Distention Irregular Periods Red And White Vaginal Discharge Infertility Slight Abdominal Distension After Eating Generalized Fatigue
| Pattern Name | Relevant Symptoms | Relevant Formulas |
|---|---|---|
| Spleen and Liver Blood Deficiency | Poor appetite, Lack of appetite, Slight abdominal distension after eating, Generalized fatigue, General weakness, Dull pale complexion, Weak limbs, Diarrhea, Emaciation, Scanty menstruation, Amenorrhea, Insomnia, Limb numbness, Dizziness, Blurry vision, Eye floaters, Night blindness, Pale lips, Muscle weakness, Muscle cramps, Withered and brittle nails, Dry hair, Skin dryness, Depression, Lack of direction... see more | Dang Gui Shao Yao San | Gui Pi Tang | Shao Yao Gan Cao Tang |
| Blood and Qi Deficiency with Blood Stagnation | Poor appetite, Lack of appetite, Weak limbs, Lower back pain, Abdominal distention, Irregular periods, Red and white vaginal discharge, Infertility... see more | Ba Zhen Yi Mu Tang |
Yin Excess
Yin Excess in TCM is a pattern of disharmony characterized by an overabundance of Yin energy, leading to symptoms of dampness and coldness in the body. This condition often results from an imbalance where the cooling, moistening aspects of Yin overshadow the warm, active qualities of Yang energy. Symptoms can include a feeling of heaviness, lethargy, cold sensations, pale complexion, and possibly edema or fluid retention. Digestive issues such as poor appetite, bloating, and loose stools may also be present, reflecting the impact of excess Yin on the body's metabolic processes. Treatment in TCM for Yin Excess focuses on reducing the excess Yin and stimulating Yang energy to restore balance. ... see more
Yin Excess Patterns That Can Lead to Lack Of Appetite
| Pattern Name | Relevant Symptoms | Relevant Formulas |
|---|---|---|
| Yin Excess | Poor appetite, Absence of thirst, Slow and forceful movement, Epigastric pain worsen by pressure, Polyuria, Feeling of oppression of the chest, Nausea, Excessive vaginal discharge, Lack of appetite, Pain relieved by heat, Chills, Cold extremities, Pale urine... see more | Wu Ling San | Wu Pi Yin |
Summer Heat
"Summer-Heat" in TCM is a unique concept that refers to a pattern of disharmony often associated with the hot summer months. Imagine the intense heat of summer stressing your body, like being in a sweltering, humid environment for too long. This can lead to symptoms like feeling overheated, excessive sweating, a feeling of irritation, and sometimes even nausea or dizziness. In TCM, this condition is thought to arise from the external environment's heat affecting the body's internal balance. It's similar to how we might feel uncomfortable and out of sorts on a very hot day. ... see more
Summer Heat Patterns That Can Lead to Lack Of Appetite
| Pattern Name | Relevant Symptoms | Relevant Formulas |
|---|---|---|
| Summer Heat with Dampness | Poor appetite, Fever, Aversion to cold, Perspiration, Headaches, Feeling of heaviness, Tight feeling in chest and stomach, Anxiety, Thirst, Chest distension, Lack of appetite... see more | Huo Xiang Zheng Qi San | Xiang Ru San | Gui Ling Gan Lu Yin |
Spleen
In TCM the Spleen plays a vital role in digestion and transformation, converting food into energy and nutrients, and overseeing the distribution of Qi and Blood. It's also crucial in maintaining the health of muscles and limbs and ensuring the blood remains within the vessels. When the Spleen malfunctions in TCM, it can lead to a variety of issues such as digestive disorders, fatigue, weak muscles, bloating, and a feeling of heaviness. It can also cause a pale complexion, poor appetite, and a tendency to bruise easily. Emotionally, a Spleen imbalance is often associated with excessive worry or overthinking, reflecting its role in the interplay between physical and mental health.... see more
Spleen Patterns That Can Lead to Lack Of Appetite
Common Symptoms: Generalized Fatigue Diarrhea General Weakness Weak Limbs Pale Face Slight Abdominal Distension After Eating Depression Dizziness
| Pattern Name | Relevant Symptoms | Relevant Formulas |
|---|---|---|
| Greater Yin stage | No appetite, Lack of appetite, Vomit, Abdominal fullness, Chills, Diarrhea, Absence of thirst, Generalized fatigue... see more | Li Zhong Wan |
| Obstruction Of the Spleen By Dampness with Liver Qi Stagnation | No appetite, Upper abdominal oppression, Nausea, Lack of appetite, Diarrhea, Feeling of heaviness, Dry mouth without desire to drink, Dull shallow face, Irritability, Upper abdominal distension, Hypochondriac distention, Hypochondriac pain... see more | Ping Wei San | Dang Gui Shao Yao San |
| Spleen Qi Deficiency | Poor appetite, Slight abdominal distension after eating, General weakness, Desire to lie down, Slight abdominal pain, Excessive gas and flatulence, Bloated abdomen, Dyspepsia, Swollen complexion, Obesity... see more | Ba Zhen Tang | Liu Jun Zi Tang | Si Jun Zi Tang | Fei Er Wan |
| Cold-Damp invading the Spleen | Poor appetite, Lack of appetite, Epigastric coldness, Head and body heaviness, Sweet taste in mouth, Absence of thirst, Diarrhea, General weakness, Generalized fatigue, Nausea, Edema, Dull pale complexion, White vaginal discharge, Upper abdominal fullness... see more | Ping Wei San |
| Damp-Heat invading the Spleen | Poor appetite, Lack of appetite, Feeling of heaviness, Dry mouth without desire to drink, Nausea or vomiting, Malodorous diarrhea, Anal burning, Feeling hot, Scanty and dark urine, Low grade fever, Dull headache, Dull yellow complexion, Yellow sclera, Oily sweat, Itchy rashes, Bitter taste in the mouth, Upper abdominal fullness, Upper abdominal pain... see more | Lian Po Yin |
| Spleen and Kidney Qi Deficiency | Poor appetite, Excessive menstruation, Pale menstrual flow, Thin menstrual blood, Prolonged menstrual periods, Shortness of breath, Palpitations... see more | Fu Tu Dan |
| Kidney and Spleen Yang Deficiency | Poor appetite, Lower back pain, Weak and cold knees, Back cold sensation, Chills, Weak legs, Bright pale face, Erectile dysfunction, Premature ejaculation, Oligospermia, Watery ejaculate, Low sex drive, Generalized fatigue, General weakness, Clear urination, Nocturia, Apathy, Leg edema, Female infertility, Diarrhea, Depression, Lack of appetite, Slight abdominal distention, Desire to lie down... see more | Li Zhong Wan |
| Spleen and Heart Blood Deficiency | Poor appetite, Palpitations, Dizziness, Insomnia, Vivid dreaming, Poor memory, Anxiety, Easily startled, Dull pale complexion, Pale lips, Generalized fatigue, Muscle weakness, Diarrhea, Lack of appetite, Scanty menstruation... see more | Gui Pi Tang |
| Spleen and Liver Blood Deficiency | Poor appetite, Lack of appetite, Slight abdominal distension after eating, Generalized fatigue, General weakness, Dull pale complexion, Weak limbs, Diarrhea, Emaciation, Scanty menstruation, Amenorrhea, Insomnia, Limb numbness, Dizziness, Blurry vision, Eye floaters, Night blindness, Pale lips, Muscle weakness, Muscle cramps, Withered and brittle nails, Dry hair, Skin dryness, Depression, Lack of direction... see more | Dang Gui Shao Yao San | Gui Pi Tang | Shao Yao Gan Cao Tang |
| Spleen and Lung Qi Deficiency | Poor appetite, Lack of appetite, Slight abdominal distension after eating, Generalized fatigue, General weakness, Pale face, Weak limbs, Diarrhea, Obesity, Shortness of breath, Coughing, Weak voice, Spontaneous sweat, Reluctance to speak, Frequent colds or flu, Aversion to cold... see more | Liu Jun Zi Tang | Si Jun Zi Tang |
| Spleen Blood Deficiency | Poor appetite, Lack of appetite, Generalized fatigue, General weakness, Pale face, Weak limbs, Diarrhea, Depression, Emaciation, Scanty menstruation, Amenorrhea, Insomnia, Slight abdominal distension after eating... see more | Gui Pi Tang |
| Spleen Qi Sinking | Poor appetite, Lack of appetite, Slight abdominal distension after eating | Bu Zhong Yi Qi Tang |
| Spleen Yang Deficiency | Poor appetite, Slight abdominal distension after eating, General weakness, Desire to lie in fetal position, Pale face, Cold extremities, Chills, Undigested food in stools, Excessive gas and flatulence, Bloated abdomen, Abdominal pain relieved by pressure and warmth, Dull shallow face... see more | Bu Zhong Yi Qi Tang | Yi Huang Tang | Zhen Wu Tang | Huang Tu Tang |
| Stomach and Spleen Qi Deficiency | Poor appetite, Lack of appetite, Slight abdominal distension after eating, Generalized fatigue, General weakness, Pale face, Weak limbs, Diarrhea, Upper abdominal discomfort, Loss of taste... see more | Shen Ling Bai Zhu San | Si Jun Zi Tang | Sheng Yang Yi Wei Tang | Xiang Sha Yang Wei Wan |
| Stomach and Spleen Yin Deficiency | Poor appetite, Lack of appetite, Dry mouth, Preference for sipping, Dry stools, Dry lips, Nausea, Generalized fatigue, Upper abdominal discomfort, Loss of taste... see more | Shen Ling Bai Zhu San |
| Spleen Deficiency | Poor appetite, Sticky vaginal discharge, Generalized fatigue, Depression, Cold extremities, Diarrhea, White vaginal discharge, Lack of appetite, Amenorrhea, Dull shallow face, Weak limbs... see more | Bu Zhong Yi Qi Tang | Wan Dai Tang | Yi Huang Tang |
| Spleen and Stomach Qi Deficiency | Poor appetite, Dizziness, Unsteadiness, Blurry vision, Deafness, Tinnitus, Shortness of breath, Weak voice, Pale face, Lack of appetite, Diarrhea... see more | Bu Zhong Yi Qi Tang | Ren Shen Yang Rong Tang | Ba Zhen Tang | Xiang Sha Liu Jun Zi Tang |
| Heart and Spleen Deficiency | Poor appetite, Palpitations, Insomnia, Lack of appetite, Generalized fatigue, Anxiety, Pale face, Poor memory, Diarrhea, Scanty menstruation, Pale lips... see more | Gui Pi Tang |
| Heart and Spleen Qi and Blood Deficiency | Poor appetite, Palpitations, Poor memory, Restless sleeplessness, Fever, Lack of appetite, Generalized fatigue, Coughing, Shortness of breath, Exertional dyspnea, Weight loss... see more | Ren Shen Yang Rong Tang |
| Blood Deficiency with disharmony of Liver and Spleen | Poor appetite, Chest distension, Chest pain, Anemia, Dizziness, Headaches, Dry mouth, Dry throat, Lack of appetite, Irregular periods, Leukorrhea... see more | Xiao Yao San |
Stomach
In TCM the Stomach is regarded as the "sea of nourishment," pivotal for digesting food and transforming it into Qi and blood. It works closely with the Spleen to distribute these essential nutrients throughout the body. When the Stomach is out of balance or malfunctions in TCM, it often leads to digestive problems such as bloating, nausea, vomiting, poor appetite, or a feeling of fullness. There may also be issues like acid reflux or a sour taste in the mouth. Emotionally, an imbalanced Stomach can contribute to excessive worry and overthinking, reflecting the TCM belief that physical and emotional well-being are deeply interconnected.... see more
Stomach Patterns That Can Lead to Lack Of Appetite
Common Symptoms: Generalized Fatigue Dry Mouth Pale Face Diarrhea Belching Weak Limbs Upper Abdominal Discomfort Loss Of Taste
| Pattern Name | Relevant Symptoms | Relevant Formulas |
|---|---|---|
| Stomach Yin Deficiency | Poor appetite, No desire to eat, Lack of appetite, Preference for sipping, Slight abdominal distension after eating... see more | Mai Men Dong Tang | Yi Wei Tang | Shen Ling Bai Zhu San |
| Food Stagnation in the Stomach | Poor appetite, Epigastric fullness and pain relieved by vomiting, Nausea, Vomiting of sour fluids, Bad breath, Acid reflux, Belching, Insomnia, Alternating diarrhea and constipation, Lack of appetite, Abdominal pain due to overeating... see more | Bao He Wan | Zhi Shi Dao Zhi Wan | Gua Di San |
| Stomach and Spleen Qi Deficiency | Poor appetite, Lack of appetite, Slight abdominal distension after eating, Generalized fatigue, General weakness, Pale face, Weak limbs, Diarrhea, Upper abdominal discomfort, Loss of taste... see more | Shen Ling Bai Zhu San | Si Jun Zi Tang | Sheng Yang Yi Wei Tang | Xiang Sha Yang Wei Wan |
| Stomach and Spleen Yin Deficiency | Poor appetite, Lack of appetite, Dry mouth, Preference for sipping, Dry stools, Dry lips, Nausea, Generalized fatigue, Upper abdominal discomfort, Loss of taste... see more | Shen Ling Bai Zhu San |
| Stomach Qi Deficiency | Poor appetite, Morning fatigue | Si Jun Zi Tang |
| Stomach Yang Deficient and Cold | Poor appetite, Epigastric pain relieved with pressure or eating, Lack of appetite, Desire for hot beverages and foods, Vomiting clear liquid, Absence of thirst, Weak limbs, Cold extremities, Generalized fatigue, Pale face... see more | Huang Qi Jian Zhong Tang | Xiang Sha Yang Wei Wan | Xiao Jian Zhong Tang | Wu Zhu Yu Tang |
| Phlegm-Heat in the Middle Burner | Poor appetite, Upper abdominal focal distention, Abdominal fullness, Dry heaving, Borborygmi with diarrhea, Lack of appetite, Peptic ulcer, Gastroesophageal reflux disease, Gastritis, Chronic cholecystitis, Colitis... see more | Ban Xia Xie Xin Tang |
| Spleen and Stomach Qi Deficiency | Poor appetite, Dizziness, Unsteadiness, Blurry vision, Deafness, Tinnitus, Shortness of breath, Weak voice, Pale face, Lack of appetite, Diarrhea... see more | Bu Zhong Yi Qi Tang | Ren Shen Yang Rong Tang | Ba Zhen Tang | Xiang Sha Liu Jun Zi Tang |
| Stomach Deficiency | Poor appetite, Nausea or vomiting, Generalized fatigue, Chills, Lack of appetite, Depression, Dry mouth, Morning sickness... see more | Mai Men Dong Tang | Xiang Sha Liu Jun Zi Tang | Er Chen Tang |
| Liver Qi Stagnation invading the Stomach | Poor appetite, Belching, Abdominal distention, Upper abdominal distension, Depression, Irritability, Dry mouth, Lack of appetite, Craving for sour foods, Dry throat, Acid reflux... see more | Ban Xia Hou Pu Tang | Zuo Jin Wan |
Liver
In TCM the Liver is viewed as the organ responsible for the smooth flow of Qi, Blood, and emotions throughout the body. It plays a key role in regulating mood, storing blood, supporting digestion, and ensuring the health of tendons and eyes. When the Liver malfunctions or is imbalanced in TCM, it can lead to a range of issues such as irritability, mood swings, menstrual irregularities, eye problems, and muscular stiffness or pain. A malfunctioning Liver in TCM reflects not only physical disturbances but also emotional and mental disharmony, emphasizing the holistic approach of TCM in addressing health and wellness.... see more
Liver Patterns That Can Lead to Lack Of Appetite
Common Symptoms: Irritability Irregular Periods Depression Nausea Diarrhea Upper Abdominal Distension Hypochondriac Distention Dizziness
| Pattern Name | Relevant Symptoms | Relevant Formulas |
|---|---|---|
| Obstruction Of the Spleen By Dampness with Liver Qi Stagnation | No appetite, Upper abdominal oppression, Nausea, Lack of appetite, Diarrhea, Feeling of heaviness, Dry mouth without desire to drink, Dull shallow face, Irritability, Upper abdominal distension, Hypochondriac distention, Hypochondriac pain... see more | Ping Wei San | Dang Gui Shao Yao San |
| Damp-Heat in the Liver | Poor appetite, Hypochondrial fullness with warmth relief, Abdominal fullness, Lower abdominal fullness, Bitter taste in the mouth, Sticky taste in the mouth, Lack of appetite, Nausea, Feeling of heaviness, Yellow vaginal discharge, Vaginal itching, Vulvar eczema, Vulvar sores, Bleeding between periods, Midcycle bleeding pain, Red and swollen scrotum, Red and swelling genital, Papules, Itchy vesicular rashes, Urinary dysfunction, Urinary burning, Dark urine... see more | Long Dan Xie Gan Tang | Yin Chen Hao Tang |
| Liver Qi Deficiency | Poor appetite, Dizziness, Blurry vision, Eye floaters, Nervousness, Timidity, Easily startled, Lack of bravery, Indecision, Sighing, Vivid dreaming, Depression, Irritability, Hypochondriac distention, Irregular periods, Lack of appetite, Generalized fatigue, Abdominal distention... see more | Bu Zhong Yi Qi Tang | Si Wu Tang | Xiao Yao San |
| Liver Qi Stagnation | Poor appetite, Hypochondriac distention, Chest distension, Upper abdominal distension, Abdominal distention, Sighing, Melancholia, Depression, Mood swings, Irregular periods, Globus sensation, Pre menstrual breast distension, Pre menstrual tension, Anxiety, Anger... see more | Xiao Yao San | Jia Wei Xiao Yao San | Yue Ju Wan | Chai Hu Shu Gan San | Yi Guan Jian |
| Spleen and Liver Blood Deficiency | Poor appetite, Lack of appetite, Slight abdominal distension after eating, Generalized fatigue, General weakness, Dull pale complexion, Weak limbs, Diarrhea, Emaciation, Scanty menstruation, Amenorrhea, Insomnia, Limb numbness, Dizziness, Blurry vision, Eye floaters, Night blindness, Pale lips, Muscle weakness, Muscle cramps, Withered and brittle nails, Dry hair, Skin dryness, Depression, Lack of direction... see more | Dang Gui Shao Yao San | Gui Pi Tang | Shao Yao Gan Cao Tang |
| Liver Qi Stagnation invading the Stomach | Poor appetite, Belching, Abdominal distention, Upper abdominal distension, Depression, Irritability, Dry mouth, Lack of appetite, Craving for sour foods, Dry throat, Acid reflux... see more | Ban Xia Hou Pu Tang | Zuo Jin Wan |
| Blood Deficiency with disharmony of Liver and Spleen | Poor appetite, Chest distension, Chest pain, Anemia, Dizziness, Headaches, Dry mouth, Dry throat, Lack of appetite, Irregular periods, Leukorrhea... see more | Xiao Yao San |
Heart
In TCM the Heart is considered the "emperor" of all organs, primarily responsible for governing Blood and housing the mind, known as "Shen." It plays a crucial role in maintaining mental-emotional equilibrium and controlling the circulation of Qi and blood throughout the body. When the Heart is imbalanced or malfunctions in TCM, it can lead to a range of issues like heart palpitations, insomnia, dream-disturbed sleep, anxiety, and a flushed complexion. Emotional disturbances such as excessive joy or lack of joy are also seen as signs of Heart disharmony. These symptoms reflect not just physical heart conditions but also the state of one's Shen, indicating the interconnectedness of physical and emotional well-being in TCM.... see more
Heart Patterns That Can Lead to Lack Of Appetite
Common Symptoms: Palpitations Generalized Fatigue Poor Memory Insomnia Anxiety Pale Face Diarrhea Scanty Menstruation
| Pattern Name | Relevant Symptoms | Relevant Formulas |
|---|---|---|
| Heart Qi Stagnation | Poor appetite, Palpitations, Chest distension, Feeling of oppression of the chest, Depression | Ban Xia Hou Pu Tang |
| Spleen and Heart Blood Deficiency | Poor appetite, Palpitations, Dizziness, Insomnia, Vivid dreaming, Poor memory, Anxiety, Easily startled, Dull pale complexion, Pale lips, Generalized fatigue, Muscle weakness, Diarrhea, Lack of appetite, Scanty menstruation... see more | Gui Pi Tang |
| Heart and Spleen Deficiency | Poor appetite, Palpitations, Insomnia, Lack of appetite, Generalized fatigue, Anxiety, Pale face, Poor memory, Diarrhea, Scanty menstruation, Pale lips... see more | Gui Pi Tang |
| Heart and Spleen Qi and Blood Deficiency | Poor appetite, Palpitations, Poor memory, Restless sleeplessness, Fever, Lack of appetite, Generalized fatigue, Coughing, Shortness of breath, Exertional dyspnea, Weight loss... see more | Ren Shen Yang Rong Tang |
Kidney
In TCM the Kidneys are regarded as the body's most fundamental reservoir of Essence, known as Jing, which influences growth, reproduction, and aging. They are not just organs for filtering blood, but a holistic system governing vital life forces. When the Kidneys malfunction in TCM, it can manifest as a variety of health issues, such as chronic fatigue, reproductive problems, imbalances in fluid metabolism leading to edema or dryness, lower back pain, and a sense of fear or insecurity.... see more
Kidney Patterns That Can Lead to Lack Of Appetite
Common Symptoms: Bright Pale Face Pale Menstrual Flow Thin Menstrual Blood Nocturnal Emission Lower Back Pain Weak And Cold Knees Chills Weak Legs
| Pattern Name | Relevant Symptoms | Relevant Formulas |
|---|---|---|
| Spleen and Kidney Qi Deficiency | Poor appetite, Excessive menstruation, Pale menstrual flow, Thin menstrual blood, Prolonged menstrual periods, Shortness of breath, Palpitations... see more | Fu Tu Dan |
| Kidney and Spleen Yang Deficiency | Poor appetite, Lower back pain, Weak and cold knees, Back cold sensation, Chills, Weak legs, Bright pale face, Erectile dysfunction, Premature ejaculation, Oligospermia, Watery ejaculate, Low sex drive, Generalized fatigue, General weakness, Clear urination, Nocturia, Apathy, Leg edema, Female infertility, Diarrhea, Depression, Lack of appetite, Slight abdominal distention, Desire to lie down... see more | Li Zhong Wan |
| Kidney Yang Deficiency | Poor appetite, Lower back pain, Dizziness, Tinnitus, Weak and cold knees, Lower back coldness, Chills, Weak legs, Bright pale face, Generalized fatigue, General weakness, Leg edema, Female infertility, Diarrhea, Depression, Erectile dysfunction, Premature ejaculation, Oligospermia, Low sex drive, Pale and abudant urination... see more | You Gui Wan |
Lung
In TCM the Lungs are seen as the organ responsible for controlling Qi and respiration, as well as being a key part of the body's defensive system. They are thought to maintain the balance and flow of air and moisture, and are closely linked to the skin and hair. When the Lungs are imbalanced or malfunctioning in TCM, it can lead to respiratory issues like coughing or asthma, a weakened immune system, dry skin, and emotional disturbances such as sadness or grief. These symptoms are believed to arise from disruptions in the Lungs' ability to regulate Qi and protect the body, highlighting their central role in maintaining overall health and well-being.... see more
Lung Patterns That Can Lead to Lack Of Appetite
Common Symptoms: Coughing And Wheezing With Copious Sputum Spontaneous Sweat Frequent Colds Or Flu Pale Face Generalized Fatigue Shortness Of Breath Weak Voice Cold Extremities
| Pattern Name | Relevant Symptoms | Relevant Formulas |
|---|---|---|
| Lung Yang Deficiency | Poor appetite, Coughing and wheezing with copious sputum, Cold extremities, Spontaneous sweat, Frequent colds or flu, Pale face, Generalized fatigue, Shortness of breath, Absence of thirst, Wheezing, Weak voice... see more | Gan Cao Gan Jiang Tang | Si Jun Zi Tang | Sheng Mai San |
| Spleen and Lung Qi Deficiency | Poor appetite, Lack of appetite, Slight abdominal distension after eating, Generalized fatigue, General weakness, Pale face, Weak limbs, Diarrhea, Obesity, Shortness of breath, Coughing, Weak voice, Spontaneous sweat, Reluctance to speak, Frequent colds or flu, Aversion to cold... see more | Liu Jun Zi Tang | Si Jun Zi Tang |
| Phlegm clogging the Lungs with Qi Stagnation | Poor appetite, Coughing and wheezing with copious sputum, Focal distention of the chest, Lack of appetite, Dyspepsia, Chronic bronchitis, Bronchial asthma, Emphysema, Childhood asthma, Diaphragm pain... see more | San Zi Yang Qin Tang |
Uterus
In TCM the Uterus (or "Bao Gong") is not just a reproductive organ but a vital system closely linked to Kidney energy, responsible for menstrual health, fertility, and pregnancy. It's also connected to the Heart and Liver, reflecting the importance of emotional and blood health in reproductive wellness. In TCM, the Uterus is seen as a reservoir of Blood and Qi, crucial for reproductive health and general vitality. When the Uterus malfunctions or is imbalanced, it can lead to menstrual irregularities, infertility, miscarriages, or menopausal symptoms. Additionally, there might be symptoms like lower abdominal pain or emotional disturbances such as mood swings, often linked to Liver Qi stagnation. These manifestations highlight the TCM perspective that the health of the Uterus is intertwined with the overall balance of energy and blood in the body, as well as emotional well-being.... see more
Uterus Patterns That Can Lead to Lack Of Appetite
| Pattern Name | Relevant Symptoms | Relevant Formulas |
|---|---|---|
| Cold in the Uterus | Poor appetite, Diarrhea, Lack of appetite, Generalized fatigue, General weakness, Thin vaginal discharge... see more | Wen Jing Tang | Shao Fu Zhu Yu Tang | Wen Qi Hua Shi Tang |
Large Intestine
In TCM the Large Intestine is primarily seen as responsible for the absorption of fluids and the excretion of waste. It is closely related to the Lung in terms of energy flow and function, reflecting the interconnectedness of organ systems in TCM. When the Large Intestine malfunctions, it can lead to issues such as constipation or diarrhea, abdominal pain, and an inability to let go of emotional waste, like holding onto grief or stress. This is in line with the TCM view that the physical and emotional aspects of health are deeply connected. An imbalanced Large Intestine can also manifest as skin problems, signifying the organ’s role in eliminating toxins and maintaining balance in the body’s internal environment.... see more
Large Intestine Patterns That Can Lead to Lack Of Appetite
| Pattern Name | Relevant Symptoms | Relevant Formulas |
|---|---|---|
| Large Intestine collapse | Poor appetite, Chronic diarrhea, Anus prolapse, Hemorrhoids, Generalized fatigue, Cold extremities, Lack of appetite, Mental exhaustion, Craving for hot beverages... see more | Bu Zhong Yi Qi Tang |
Pericardium
In TCM the Pericardium is more than a physical membrane protecting the heart; it's considered an organ system that acts as the "Heart's protector." It plays a crucial role in safeguarding the heart from external pathogenic factors and emotional disturbances. The Pericardium is also involved in regulating blood circulation and influencing emotional well-being, especially in terms of relationships and intimacy. When the Pericardium malfunctions or is imbalanced in TCM, it can lead to symptoms that mirror heart issues, such as chest pain or palpitations, but often with an emotional component like difficulty in forming emotional connections or excessive vulnerability to external stressors. Additionally, a disturbed Pericardium can result in sleep disturbances, anxiety, and in severe cases, mental confusion, reflecting its integral role in both physical heart protection and emotional balance.... see more
Pericardium Patterns That Can Lead to Lack Of Appetite
| Pattern Name | Relevant Symptoms | Relevant Formulas |
|---|---|---|
| Pericardium Qi Stagnation | Poor appetite, Mild chest pain, Chest distension, Stifling sensation in the chest, Sighing, Throat lumps, Palpitations, Depression, Irritability, Lack of appetite, Weak limbs, Cold extremities... see more | Ban Xia Hou Pu Tang |
TCM Herbal Formulas for Lack Of Appetite
Explore below some TCM herbal formulas used to address lack of appetite, organized by cause and by formula type.
- By Cause
- By Formula Type
- Qi Deficiency
- Qi Stagnation
- Heat
- Blood Deficiency
- Dampness
- Yang Deficiency
- Cold
- Phlegm
- Yin Deficiency
- Qi Sinking
- Blood Stasis
- Yin Excess
- Summer Heat
- View More Causes
- Formulas that tonify qi
- Formulas that warm the middle and dispel cold
- Formulas that tonify qi and blood
- Formulas that invigorate blood and dispel blood stagnation
- Formulas that clear heat and expel dampness
- Formulas that reduce food accumulation and transform stagnation
- Formulas that promote qi movement
- Formulas that tonify blood
- Formulas that promote urination and leach out dampness
- Formulas that transform dampness and harmonize stomach
- Formulas that nourish yin and tonify
- Formulas that secure irregular uterine bleeding and stop vaginal discharge
- Formulas that tonify
- Formulas that warm and transform phlegm-Cold
- Formulas that harmonize liver-Spleen
- Formulas that warm yang and tonify
- Formulas that dry dampness and transform phlegm
- Formulas that warm and transform water and dampness
- Formulas that drive out excess water
- Formulas that harmonize lesser yang-warp disorders
- Formulas that enrich yin and moisten dryness
- Formulas that clear heat from the organs
- Formulas that tonify yin and yang
- Formulas that harmonize stomach-Intestines
- Formulas that induce vomiting
- Formulas that secure essence and stop enuresis
- Formulas that regulate blood
- Formulas that warm interior cold
- Formulas that dispel phlegm
- Formulas that clear heat
- Formulas that rescue devastated yang
- Formulas that stop bleeding
- Formulas that dispel summer-Heat and resolve exterior
- Formulas that dispel summer-Heat and facilitate resolution of dampness
Top Formula for Qi Deficiency:
Bu Zhong Yi Qi Tang
Suitable for Qi Deficiency patterns that may cause lack of appetite, such as Qi Deficiency or Spleen Deficiency
Learn moreAll Formulas Recommended for Lack Of Appetite Caused by Qi Deficiency
| Formula | Patterns Suitable For |
|---|---|
| Bu Zhong Yi Qi Tang | Qi Deficiency, Spleen Deficiency, Qi and Blood Deficiency, Spleen and Stomach Qi Deficiency, Liver Qi Deficiency... see more |
| Si Jun Zi Tang | Qi Deficiency, Spleen Qi Deficiency, Spleen and Lung Qi Deficiency, Stomach and Spleen Qi Deficiency, Stomach Qi Deficiency... see more |
| Gui Pi Tang | Qi Deficiency, Qi and Blood Deficiency, Heart and Spleen Deficiency |
| Liu Jun Zi Tang | Qi Deficiency, Spleen Qi Deficiency, Spleen and Lung Qi Deficiency |
| Ren Shen Yang Rong Tang | Qi and Blood Deficiency, Spleen and Stomach Qi Deficiency, Heart and Spleen Qi and Blood Deficiency... see more |
| Ba Zhen Tang | Qi and Blood Deficiency, Spleen Qi Deficiency, Spleen and Stomach Qi Deficiency |
| Si Wu Tang | Qi and Blood Deficiency, Liver Qi Deficiency |
| Xiang Sha Liu Jun Zi Tang | Spleen and Stomach Qi Deficiency, Stomach Deficiency |
| Yi Huang Tang | Spleen Deficiency |
| Xiao Yao San | Liver Qi Deficiency |
| Shen Ling Bai Zhu San | Stomach and Spleen Qi Deficiency |
| Mai Men Dong Tang | Stomach Deficiency |
| Xiang Sha Yang Wei Wan | Stomach and Spleen Qi Deficiency |
| Gu Ben Zhi Beng Tang | Qi Deficiency |
| Wan Dai Tang | Spleen Deficiency |
| Shi Quan Da Bu Tang | Qi and Blood Deficiency |
| Tong Ru Dan | Qi and Blood Deficiency |
| Guo Qi Yin | Qi and Blood Deficiency |
| Zhi Gan Cao Tang | Qi and Blood Deficiency |
| Fei Er Wan | Spleen Qi Deficiency |
| Fu Tu Dan | Spleen and Kidney Qi Deficiency |
| Er Chen Tang | Stomach Deficiency |
| Sheng Yang Yi Wei Tang | Stomach and Spleen Qi Deficiency |
Top Formula for Qi Stagnation:
Ban Xia Hou Pu Tang
Suitable for Qi Stagnation patterns that may cause lack of appetite, such as Heart Qi Stagnation or Liver Qi Stagnation invading the Stomach
Learn moreAll Formulas Recommended for Lack Of Appetite Caused by Qi Stagnation
| Formula | Patterns Suitable For |
|---|---|
| Ban Xia Hou Pu Tang | Heart Qi Stagnation, Liver Qi Stagnation invading the Stomach, Pericardium Qi Stagnation... see more |
| Yue Ju Wan | Liver Qi Stagnation, Qi Stagnation |
| Ping Wei San | Obstruction Of the Spleen By Dampness with Liver Qi Stagnation |
| Xiao Yao San | Liver Qi Stagnation |
| Dang Gui Shao Yao San | Obstruction Of the Spleen By Dampness with Liver Qi Stagnation |
| San Zi Yang Qin Tang | Phlegm clogging the Lungs with Qi Stagnation |
| Ba Zhen Yi Mu Tang | Blood and Qi Deficiency with Blood Stagnation |
| Jia Wei Xiao Yao San | Liver Qi Stagnation |
| Chai Hu Shu Gan San | Liver Qi Stagnation |
| Yi Guan Jian | Liver Qi Stagnation |
| Zuo Jin Wan | Liver Qi Stagnation invading the Stomach |
Top Formula for Heat:
Long Dan Xie Gan Tang
Suitable for Heat patterns that may cause lack of appetite, such as Damp-Heat or Damp-Heat in the Liver
Learn moreAll Formulas Recommended for Lack Of Appetite Caused by Heat
| Formula | Patterns Suitable For |
|---|---|
| Long Dan Xie Gan Tang | Damp-Heat, Damp-Heat in the Liver |
| Ping Wei San | Obstruction Of the Spleen By Dampness with Liver Qi Stagnation |
| Yi Huang Tang | Damp-Heat |
| Dang Gui Shao Yao San | Obstruction Of the Spleen By Dampness with Liver Qi Stagnation |
| San Zi Yang Qin Tang | Cold-Phlegm |
| Xiao Chai Hu Tang | Half Exterior Half Interior |
| Mai Men Dong Tang | Stomach Deficiency |
| Xiang Sha Liu Jun Zi Tang | Stomach Deficiency |
| Ba Zheng San | Damp-Heat |
| Ban Xia Xie Xin Tang | Phlegm-Heat in the Middle Burner |
| Ling Gan Wu Wei Jiang Xin Tang | Cold-Phlegm |
| Yin Chen Hao Tang | Damp-Heat in the Liver |
| Lian Po Yin | Damp-Heat invading the Spleen |
| Er Chen Tang | Stomach Deficiency |
Top Formula for Blood Deficiency:
Gui Pi Tang
Suitable for Blood Deficiency patterns that may cause lack of appetite, such as Qi and Blood Deficiency or Heart and Spleen Deficiency
Learn moreAll Formulas Recommended for Lack Of Appetite Caused by Blood Deficiency
| Formula | Patterns Suitable For |
|---|---|
| Gui Pi Tang | Qi and Blood Deficiency, Heart and Spleen Deficiency, Spleen and Heart Blood Deficiency, Spleen Blood Deficiency... see more |
| Ren Shen Yang Rong Tang | Qi and Blood Deficiency, Heart and Spleen Qi and Blood Deficiency |
| Bu Zhong Yi Qi Tang | Qi and Blood Deficiency |
| Ba Zhen Tang | Qi and Blood Deficiency |
| Xiao Yao San | Blood Deficiency with disharmony of Liver and Spleen |
| Si Wu Tang | Qi and Blood Deficiency |
| Shi Quan Da Bu Tang | Qi and Blood Deficiency |
| Tong Ru Dan | Qi and Blood Deficiency |
| Guo Qi Yin | Qi and Blood Deficiency |
| Zhi Gan Cao Tang | Qi and Blood Deficiency |
| Ba Zhen Yi Mu Tang | Blood and Qi Deficiency with Blood Stagnation |
Top Formula for Dampness:
Ping Wei San
Suitable for Dampness patterns that may cause lack of appetite, such as Obstruction Of the Spleen By Dampness with Liver Qi Stagnation or Cold-Damp invading the Spleen
Learn moreAll Formulas Recommended for Lack Of Appetite Caused by Dampness
| Formula | Patterns Suitable For |
|---|---|
| Ping Wei San | Obstruction Of the Spleen By Dampness with Liver Qi Stagnation, Cold-Damp invading the Spleen, Oedema... see more |
| Long Dan Xie Gan Tang | Damp-Heat, Damp-Heat in the Liver |
| Yi Huang Tang | Damp-Heat |
| Dang Gui Shao Yao San | Obstruction Of the Spleen By Dampness with Liver Qi Stagnation |
| Wu Ling San | Oedema |
| Wu Pi Yin | Oedema |
| Zhen Wu Tang | Oedema |
| Ba Zheng San | Damp-Heat |
| Yin Chen Hao Tang | Damp-Heat in the Liver |
| Lian Po Yin | Damp-Heat invading the Spleen |
| Fang Ji Huang Qi Tang | Oedema |
| Ling Gui Zhu Gan Tang | Oedema |
| Shen Qi Wan | Oedema |
| Yu Gong San | Oedema |
| Zhou Che Wan | Oedema |
| Huo Xiang Zheng Qi San | Summer Heat with Dampness |
| Xiang Ru San | Summer Heat with Dampness |
| Gui Ling Gan Lu Yin | Summer Heat with Dampness |
Top Formula for Yang Deficiency:
Li Zhong Wan
Suitable for Yang Deficiency patterns that may cause lack of appetite, such as Greater Yin stage or Kidney and Spleen Yang Deficiency
Learn moreAll Formulas Recommended for Lack Of Appetite Caused by Yang Deficiency
| Formula | Patterns Suitable For |
|---|---|
| Li Zhong Wan | Greater Yin stage, Kidney and Spleen Yang Deficiency |
| Bu Zhong Yi Qi Tang | Spleen Yang Deficiency |
| Si Jun Zi Tang | Lung Yang Deficiency |
| Yi Huang Tang | Spleen Yang Deficiency |
| Zhen Wu Tang | Spleen Yang Deficiency |
| Huang Qi Jian Zhong Tang | Stomach Yang Deficient and Cold |
| Xiang Sha Yang Wei Wan | Stomach Yang Deficient and Cold |
| Gan Cao Gan Jiang Tang | Lung Yang Deficiency |
| Sheng Mai San | Lung Yang Deficiency |
| You Gui Wan | Kidney Yang Deficiency |
| Huang Tu Tang | Spleen Yang Deficiency |
| Xiao Jian Zhong Tang | Stomach Yang Deficient and Cold |
| Wu Zhu Yu Tang | Stomach Yang Deficient and Cold |
Top Formula for Cold:
Ping Wei San
Suitable for Cold patterns that may cause lack of appetite, such as Cold-Damp invading the Spleen
Learn moreAll Formulas Recommended for Lack Of Appetite Caused by Cold
| Formula | Patterns Suitable For |
|---|---|
| Ping Wei San | Cold-Damp invading the Spleen |
| Li Zhong Wan | Greater Yin stage |
| San Zi Yang Qin Tang | Cold-Phlegm |
| Huang Qi Jian Zhong Tang | Empty-Cold |
| Mai Men Dong Tang | Stomach Deficiency |
| Xiang Sha Liu Jun Zi Tang | Stomach Deficiency |
| Wen Jing Tang | Cold in the Uterus |
| Shao Fu Zhu Yu Tang | Cold in the Uterus |
| Wen Qi Hua Shi Tang | Cold in the Uterus |
| Ling Gan Wu Wei Jiang Xin Tang | Cold-Phlegm |
| Da Jian Zhong Tang | Empty-Cold |
| Er Chen Tang | Stomach Deficiency |
Top Formula for Phlegm:
San Zi Yang Qin Tang
Suitable for Phlegm patterns that may cause lack of appetite, such as Cold-Phlegm or Phlegm clogging the Lungs with Qi Stagnation
Learn moreAll Formulas Recommended for Lack Of Appetite Caused by Phlegm
| Formula | Patterns Suitable For |
|---|---|
| San Zi Yang Qin Tang | Cold-Phlegm, Phlegm clogging the Lungs with Qi Stagnation |
| Ban Xia Hou Pu Tang | Phlegm |
| Yue Ju Wan | Phlegm |
| Ping Wei San | Oedema |
| Wu Ling San | Oedema |
| Wu Pi Yin | Oedema |
| Zhen Wu Tang | Oedema |
| Ban Xia Xie Xin Tang | Phlegm-Heat in the Middle Burner |
| Ling Gan Wu Wei Jiang Xin Tang | Cold-Phlegm |
| Wen Dan Tang | Phlegm |
| Fang Ji Huang Qi Tang | Oedema |
| Ling Gui Zhu Gan Tang | Oedema |
| Shen Qi Wan | Oedema |
| Yu Gong San | Oedema |
| Zhou Che Wan | Oedema |
Top Formula for Yin Deficiency:
Shen Ling Bai Zhu San
Suitable for Yin Deficiency patterns that may cause lack of appetite, such as Stomach Yin Deficiency or Stomach and Spleen Yin Deficiency
Learn moreAll Formulas Recommended for Lack Of Appetite Caused by Yin Deficiency
| Formula | Patterns Suitable For |
|---|---|
| Shen Ling Bai Zhu San | Stomach Yin Deficiency, Stomach and Spleen Yin Deficiency |
| Mai Men Dong Tang | Stomach Yin Deficiency, Stomach Deficiency |
| Xiang Sha Liu Jun Zi Tang | Stomach Deficiency |
| Yi Wei Tang | Stomach Yin Deficiency |
| Er Chen Tang | Stomach Deficiency |
Top Formula for Qi Sinking:
Bu Zhong Yi Qi Tang
Suitable for Qi Sinking patterns that may cause lack of appetite, such as Large Intestine collapse or Qi Collapsing or Qi Sinking
Learn moreAll Formulas Recommended for Lack Of Appetite Caused by Qi Sinking
| Formula | Patterns Suitable For |
|---|---|
| Bu Zhong Yi Qi Tang | Large Intestine collapse, Qi Collapsing or Qi Sinking, Spleen Qi Sinking |
| Du Shen Tang | Qi Collapsing or Qi Sinking |
Top Formula for Blood Stasis:
Gui Pi Tang
Suitable for Blood Stasis patterns that may cause lack of appetite, such as Spleen and Liver Blood Deficiency
Learn moreAll Formulas Recommended for Lack Of Appetite Caused by Blood Stasis
| Formula | Patterns Suitable For |
|---|---|
| Gui Pi Tang | Spleen and Liver Blood Deficiency |
| Dang Gui Shao Yao San | Spleen and Liver Blood Deficiency |
| Ba Zhen Yi Mu Tang | Blood and Qi Deficiency with Blood Stagnation |
| Shao Yao Gan Cao Tang | Spleen and Liver Blood Deficiency |
Top Formula for Yin Excess:
Wu Ling San
Suitable for Yin Excess patterns that may cause lack of appetite, such as Yin Excess
Learn moreAll Formulas Recommended for Lack Of Appetite Caused by Yin Excess
| Formula | Patterns Suitable For |
|---|---|
| Wu Ling San | Yin Excess |
| Wu Pi Yin | Yin Excess |
Top Formula for Summer Heat:
Huo Xiang Zheng Qi San
Suitable for Summer Heat patterns that may cause lack of appetite, such as Summer Heat with Dampness
Learn moreAll Formulas Recommended for Lack Of Appetite Caused by Summer Heat
| Formula | Patterns Suitable For |
|---|---|
| Huo Xiang Zheng Qi San | Summer Heat with Dampness |
| Xiang Ru San | Summer Heat with Dampness |
| Gui Ling Gan Lu Yin | Summer Heat with Dampness |
Formulas that tonify Qi
These formulas are suitable for some lack of appetite-causing patterns like Qi Deficiency or Spleen Deficiency.
One such formula is Bu Zhong Yi Qi Tang, with milkvetch root as a key herb.
Other formulas of this category are listed in the table below.
All "formulas that tonify qi" recommended for lack of appetite
| Formula | Patterns Suitable For (if applicable) |
|---|---|
| Bu Zhong Yi Qi Tang | Qi Deficiency, Spleen Deficiency, Qi and Blood Deficiency, Spleen and Stomach Qi Deficiency, Large Intestine collapse, Liver Qi Deficiency, Qi Collapsing or Qi Sinking, Spleen Qi Sinking, Spleen Yang Deficiency... see more |
| Si Jun Zi Tang | Lung Yang Deficiency, Qi Deficiency, Spleen Qi Deficiency, Spleen and Lung Qi Deficiency, Stomach and Spleen Qi Deficiency, Stomach Qi Deficiency... see more |
| Shen Ling Bai Zhu San | Stomach Yin Deficiency, Stomach and Spleen Qi Deficiency, Stomach and Spleen Yin Deficiency... see more |
| Liu Jun Zi Tang | Spleen Qi Deficiency, Qi Deficiency, Spleen and Lung Qi Deficiency |
| Xiang Sha Yang Wei Wan | Stomach and Spleen Qi Deficiency, Stomach Yang Deficient and Cold |
| Sheng Mai San | Lung Yang Deficiency |
| Sheng Yang Yi Wei Tang | Stomach and Spleen Qi Deficiency |
Formulas that tonify Qi and Blood
These formulas are suitable for some lack of appetite-causing patterns like Qi Deficiency or Qi and Blood Deficiency.
One such formula is Gui Pi Tang, with ginseng as a key herb.
Other formulas of this category are listed in the table below.
All "formulas that tonify qi and blood" recommended for lack of appetite
| Formula | Patterns Suitable For (if applicable) |
|---|---|
| Gui Pi Tang | Qi Deficiency, Qi and Blood Deficiency, Heart and Spleen Deficiency, Spleen and Heart Blood Deficiency, Spleen and Liver Blood Deficiency, Spleen Blood Deficiency, Spleen not controlling Blood... see more |
| Ba Zhen Tang | Spleen Qi Deficiency, Qi and Blood Deficiency, Spleen and Stomach Qi Deficiency |
| Gu Ben Zhi Beng Tang | Qi Deficiency |
| Zhi Gan Cao Tang | Qi and Blood Deficiency |
Formulas that promote Qi movement
These formulas are suitable for some lack of appetite-causing patterns like Heart Qi Stagnation or Phlegm.
One such formula is Ban Xia Hou Pu Tang, with crow-dipper rhizome as a key herb.
Other formulas of this category are listed in the table below.
All "formulas that promote qi movement" recommended for lack of appetite
| Formula | Patterns Suitable For (if applicable) |
|---|---|
| Ban Xia Hou Pu Tang | Heart Qi Stagnation, Phlegm, Liver Qi Stagnation invading the Stomach, Pericardium Qi Stagnation... see more |
| Yue Ju Wan | Liver Qi Stagnation, Phlegm, Qi Stagnation |
| Chai Hu Shu Gan San | Liver Qi Stagnation |
Formulas that warm the middle and dispel Cold
These formulas are suitable for some lack of appetite-causing patterns like Greater Yin stage or Kidney and Spleen Yang Deficiency.
One such formula is Li Zhong Wan, with dried ginger as a key herb.
Other formulas of this category are listed in the table below.
All "formulas that warm the middle and dispel cold" recommended for lack of appetite
| Formula | Patterns Suitable For (if applicable) |
|---|---|
| Li Zhong Wan | Greater Yin stage, Kidney and Spleen Yang Deficiency |
| Huang Qi Jian Zhong Tang | Empty-Cold, Stomach Yang Deficient and Cold |
| Wen Qi Hua Shi Tang | Cold in the Uterus |
| Da Jian Zhong Tang | Empty-Cold |
| Xiao Jian Zhong Tang | Stomach Yang Deficient and Cold |
| Wu Zhu Yu Tang | Stomach Yang Deficient and Cold |
Formulas that transform Dampness and harmonize Stomach
These formulas are suitable for some lack of appetite-causing patterns like Obstruction Of the Spleen By Dampness with Liver Qi Stagnation or Cold-Damp invading the Spleen.
One such formula is Ping Wei San, with black atractylodes rhizome as a key herb.
Other formulas of this category are listed in the table below.
All "formulas that transform dampness and harmonize stomach" recommended for lack of appetite
| Formula | Patterns Suitable For (if applicable) |
|---|---|
| Ping Wei San | Obstruction Of the Spleen By Dampness with Liver Qi Stagnation, Cold-Damp invading the Spleen, Oedema... see more |
| Huo Xiang Zheng Qi San | Summer Heat with Dampness |
Formulas that tonify
These formulas are suitable for some lack of appetite-causing patterns like Qi and Blood Deficiency or Spleen and Stomach Qi Deficiency.
One such formula is Ren Shen Yang Rong Tang, with ginseng as a key herb.
Other formulas of this category are listed in the table below.
All "formulas that tonify" recommended for lack of appetite
| Formula | Patterns Suitable For (if applicable) |
|---|---|
| Ren Shen Yang Rong Tang | Qi and Blood Deficiency, Heart and Spleen Qi and Blood Deficiency, Spleen and Stomach Qi Deficiency... see more |
| Ba Zhen Yi Mu Tang | Blood and Qi Deficiency with Blood Stagnation |
Formulas that invigorate Blood and dispel Blood Stagnation
These formulas are suitable for some lack of appetite-causing patterns like Obstruction Of the Spleen By Dampness with Liver Qi Stagnation or Spleen and Liver Blood Deficiency.
One such formula is Dang Gui Shao Yao San, with white peony root as a key herb.
Other formulas of this category are listed in the table below.
All "formulas that invigorate blood and dispel blood stagnation" recommended for lack of appetite
| Formula | Patterns Suitable For (if applicable) |
|---|---|
| Dang Gui Shao Yao San | Obstruction Of the Spleen By Dampness with Liver Qi Stagnation, Spleen and Liver Blood Deficiency... see more |
| Wen Jing Tang | Cold in the Uterus |
| Shao Fu Zhu Yu Tang | Cold in the Uterus |
Formulas that clear Heat and expel dampness
These formulas are suitable for some lack of appetite-causing patterns like Damp-Heat in the Liver.
One such formula is Yin Chen Hao Tang, with virgate wormwood as a key herb.
Other formulas of this category are listed in the table below.
All "formulas that clear heat and expel dampness" recommended for lack of appetite
| Formula | Patterns Suitable For (if applicable) |
|---|---|
| Yin Chen Hao Tang | Damp-Heat in the Liver |
| Lian Po Yin | Damp-Heat invading the Spleen |
| Ba Zheng San | Damp-Heat |
Formulas that tonify Blood
These formulas are suitable for some lack of appetite-causing patterns like Qi and Blood Deficiency or Liver Qi Deficiency.
One such formula is Si Wu Tang, with prepared rehmannia as a key herb.
Other formulas of this category are listed in the table below.
All "formulas that tonify blood" recommended for lack of appetite
| Formula | Patterns Suitable For (if applicable) |
|---|---|
| Si Wu Tang | Liver Qi Deficiency, Qi and Blood Deficiency |
| Guo Qi Yin | Qi and Blood Deficiency |
| Shao Yao Gan Cao Tang | Spleen and Liver Blood Deficiency |
Formulas that secure irregular uterine bleeding and stop vaginal discharge
These formulas are suitable for some lack of appetite-causing patterns like Spleen Deficiency or Damp-Heat.
One such formula is Yi Huang Tang, with yam as a key herb.
Other formulas of this category are listed in the table below.
All "formulas that secure irregular uterine bleeding and stop vaginal discharge" recommended for lack of appetite
| Formula | Patterns Suitable For (if applicable) |
|---|---|
| Yi Huang Tang | Spleen Deficiency, Damp-Heat, Spleen Yang Deficiency |
| Wan Dai Tang | Spleen Deficiency |
Formulas that harmonize Liver-Spleen
These formulas are suitable for some lack of appetite-causing patterns like Liver Qi Deficiency or Liver Qi Stagnation.
One such formula is Xiao Yao San, with bupleurum root as a key herb.
Other formulas of this category are listed in the table below.
All "formulas that harmonize liver-Spleen" recommended for lack of appetite
| Formula | Patterns Suitable For (if applicable) |
|---|---|
| Xiao Yao San | Liver Qi Deficiency, Liver Qi Stagnation, Blood Deficiency with disharmony of Liver and Spleen... see more |
| Jia Wei Xiao Yao San | Liver Qi Stagnation |
Formulas that reduce food accumulation and transform Stagnation
These formulas are suitable for some lack of appetite-causing patterns like Food Stagnation in the Stomach.
One such formula is Bao He Wan, with hawthorn berry as a key herb.
Other formulas of this category are listed in the table below.
All "formulas that reduce food accumulation and transform stagnation" recommended for lack of appetite
| Formula | Patterns Suitable For (if applicable) |
|---|---|
| Bao He Wan | Food Stagnation in the Stomach |
| Zhi Shi Dao Zhi Wan | Food Stagnation in the Stomach |
| Fei Er Wan | Spleen Qi Deficiency |
Formulas that promote urination and leach out Dampness
These formulas are suitable for some lack of appetite-causing patterns like Oedema or Yin Excess.
One such formula is Wu Ling San, with water plantain as a key herb.
Other formulas of this category are listed in the table below.
All "formulas that promote urination and leach out dampness" recommended for lack of appetite
| Formula | Patterns Suitable For (if applicable) |
|---|---|
| Wu Ling San | Oedema, Yin Excess |
| Wu Pi Yin | Oedema, Yin Excess |
| Fang Ji Huang Qi Tang | Oedema |
Formulas that nourish Yin and tonify
These formulas are suitable for some lack of appetite-causing patterns like Stomach Yin Deficiency.
One such formula is Yi Wei Tang, with unprepared rehmannia as a key herb.
Other formulas of this category are listed in the table below.
All "formulas that nourish yin and tonify" recommended for lack of appetite
| Formula | Patterns Suitable For (if applicable) |
|---|---|
| Yi Wei Tang | Stomach Yin Deficiency |
| Yi Guan Jian | Liver Qi Stagnation |
Formulas that warm and transform Phlegm-Cold
These formulas are suitable for some lack of appetite-causing patterns like Cold-Phlegm or Phlegm clogging the Lungs with Qi Stagnation.
One such formula is San Zi Yang Qin Tang, with white mustard seeds as a key herb.
Other formulas of this category are listed in the table below.
All "formulas that warm and transform phlegm-Cold" recommended for lack of appetite
| Formula | Patterns Suitable For (if applicable) |
|---|---|
| San Zi Yang Qin Tang | Cold-Phlegm, Phlegm clogging the Lungs with Qi Stagnation |
| Ling Gan Wu Wei Jiang Xin Tang | Cold-Phlegm |
Formulas that warm Yang and tonify
These formulas are suitable for some lack of appetite-causing patterns like Kidney Yang Deficiency.
One such formula is You Gui Wan, with prepared aconite as a key herb.
Other formulas of this category are listed in the table below.
All "formulas that warm yang and tonify" recommended for lack of appetite
| Formula | Patterns Suitable For (if applicable) |
|---|---|
| You Gui Wan | Kidney Yang Deficiency |
| Shen Qi Wan | Oedema |
Formulas that dry Dampness and transform Phlegm
These formulas are suitable for some lack of appetite-causing patterns like Phlegm.
One such formula is Wen Dan Tang, with crow-dipper rhizome as a key herb.
Other formulas of this category are listed in the table below.
All "formulas that dry dampness and transform phlegm" recommended for lack of appetite
| Formula | Patterns Suitable For (if applicable) |
|---|---|
| Wen Dan Tang | Phlegm |
| Er Chen Tang | Stomach Deficiency |
Formulas that warm and transform water and Dampness
These formulas are suitable for some lack of appetite-causing patterns like Oedema or Spleen Yang Deficiency.
One such formula is Zhen Wu Tang, with prepared aconite as a key herb.
Other formulas of this category are listed in the table below.
All "formulas that warm and transform water and dampness" recommended for lack of appetite
| Formula | Patterns Suitable For (if applicable) |
|---|---|
| Zhen Wu Tang | Oedema, Spleen Yang Deficiency |
| Ling Gui Zhu Gan Tang | Oedema |
Formulas that harmonize lesser Yang-warp disorders
These formulas are suitable for some lack of appetite-causing patterns like Lesser Yang stage or Half Exterior Half Interior.
One such formula is Xiao Chai Hu Tang, with bupleurum root as a key herb.
Formulas that enrich Yin and moisten Dryness
These formulas are suitable for some lack of appetite-causing patterns like Stomach Yin Deficiency or Stomach Deficiency.
One such formula is Mai Men Dong Tang, with dwarf lilyturf root as a key herb.
Formulas that clear Heat from the Organs
These formulas are suitable for some lack of appetite-causing patterns like Damp-Heat or Damp-Heat in the Liver.
One such formula is Long Dan Xie Gan Tang, with chinese gentian as a key herb.
Formulas that dispel Phlegm
These formulas are suitable for some lack of appetite-causing patterns like Spleen and Stomach Qi Deficiency or Stomach Deficiency.
One such formula is Xiang Sha Liu Jun Zi Tang, with ginseng as a key herb.
Formulas that drive out excess water
These formulas are suitable for some lack of appetite-causing patterns like Oedema.
One such formula is Yu Gong San, with morning glory seeds as a key herb.
Other formulas of this category are listed in the table below.
All "formulas that drive out excess water" recommended for lack of appetite
| Formula | Patterns Suitable For (if applicable) |
|---|---|
| Yu Gong San | Oedema |
| Zhou Che Wan | Oedema |
Formulas that tonify Yin and Yang
These formulas are suitable for some lack of appetite-causing patterns like Qi and Blood Deficiency.
One such formula is Shi Quan Da Bu Tang, with milkvetch root as a key herb.
Formulas that harmonize Stomach-Intestines
These formulas are suitable for some lack of appetite-causing patterns like Phlegm-Heat in the Middle Burner.
One such formula is Ban Xia Xie Xin Tang, with goldthread rhizome as a key herb.
Formulas that induce vomiting
These formulas are suitable for some lack of appetite-causing patterns like Food Stagnation in the Stomach.
One such formula is Gua Di San, with melon stalk as a key herb.
Formulas that secure Essence and stop enuresis
These formulas are suitable for some lack of appetite-causing patterns like Spleen and Kidney Qi Deficiency.
One such formula is Fu Tu Dan, with cuscuta seeds as a key herb.
Formulas that regulate Blood
These formulas are suitable for some lack of appetite-causing patterns like Qi and Blood Deficiency.
One such formula is Tong Ru Dan, with ginseng as a key herb.
Formulas that warm Interior Cold
These formulas are suitable for some lack of appetite-causing patterns like Lung Yang Deficiency.
One such formula is Gan Cao Gan Jiang Tang, with dried ginger as a key herb.
Formulas that clear Heat
These formulas are suitable for some lack of appetite-causing patterns like Liver Qi Stagnation invading the Stomach.
One such formula is Zuo Jin Wan, with goldthread rhizome as a key herb.
Formulas that rescue devastated Yang
These formulas are suitable for some lack of appetite-causing patterns like Qi Collapsing or Qi Sinking.
One such formula is Du Shen Tang, with ginseng as a key herb.
Formulas that stop bleeding
These formulas are suitable for some lack of appetite-causing patterns like Spleen Yang Deficiency.
One such formula is Huang Tu Tang, with stove earth as a key herb.
Formulas that dispel Summer-Heat and resolve Exterior
These formulas are suitable for some lack of appetite-causing patterns like Summer Heat with Dampness.
One such formula is Xiang Ru San, with vietnamese balm as a key herb.
Formulas that dispel Summer-Heat and facilitate resolution of Dampness
These formulas are suitable for some lack of appetite-causing patterns like Summer Heat with Dampness.
One such formula is Gui Ling Gan Lu Yin, with talc as a key herb.
Acupoints for Lack Of Appetite
Explore below some acupoints used to address lack of appetite, organized by meridian.
- By Meridian
- Kidney Channel
- Spleen Channel
- Stomach Channel
- Bladder Channel
- Gall Bladder Channel
- Governing Vessel
- Triple Burner Channel
- Directing Vessel
Youmen KID-21
6 cun above the umbilicus and 2 cun below the sternocostal angle, 0.5 cun lateral to the anterior midline.
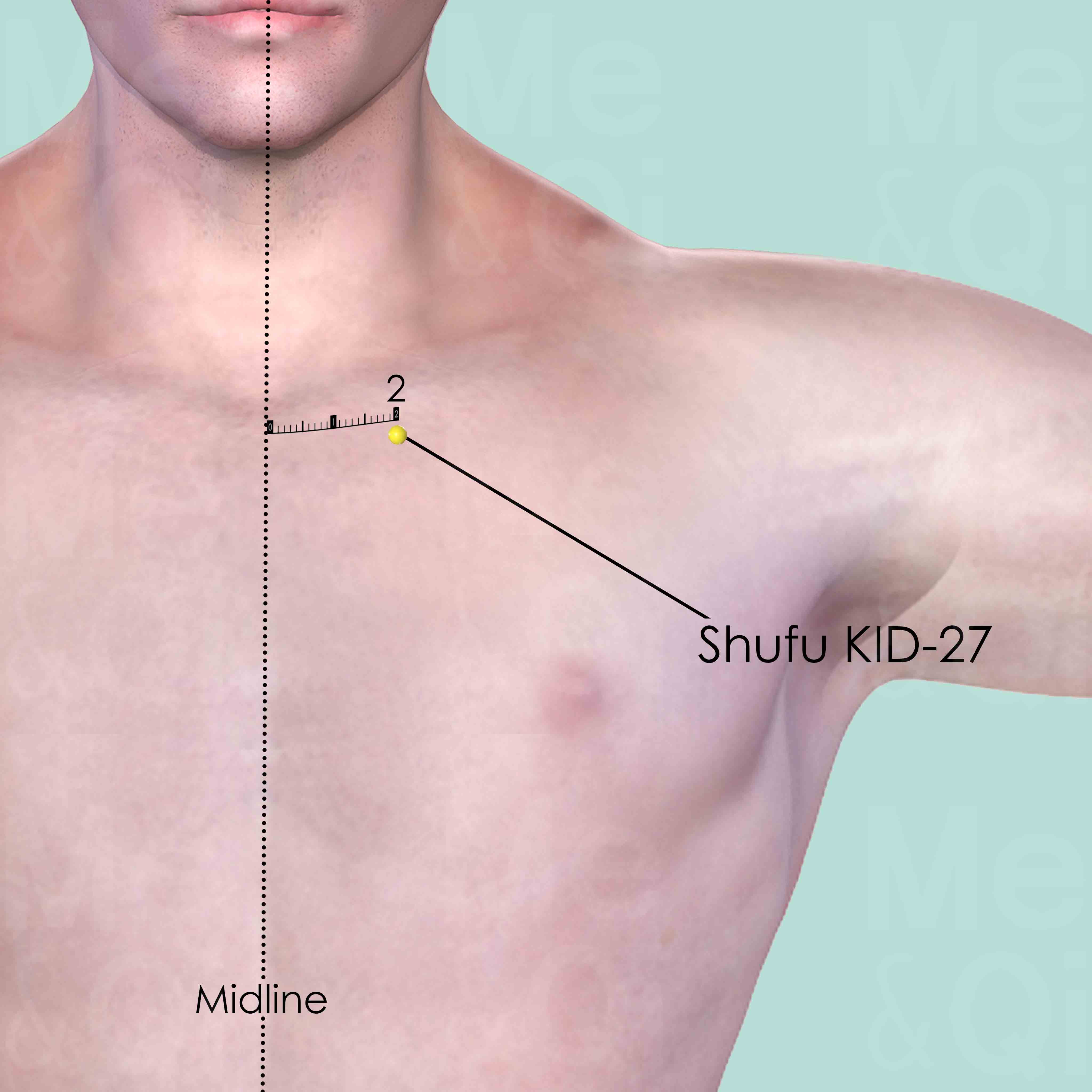
Shufu KID-27
In the depression on the lower border of the clavicle, 2 cun lateral to the anterior midline.
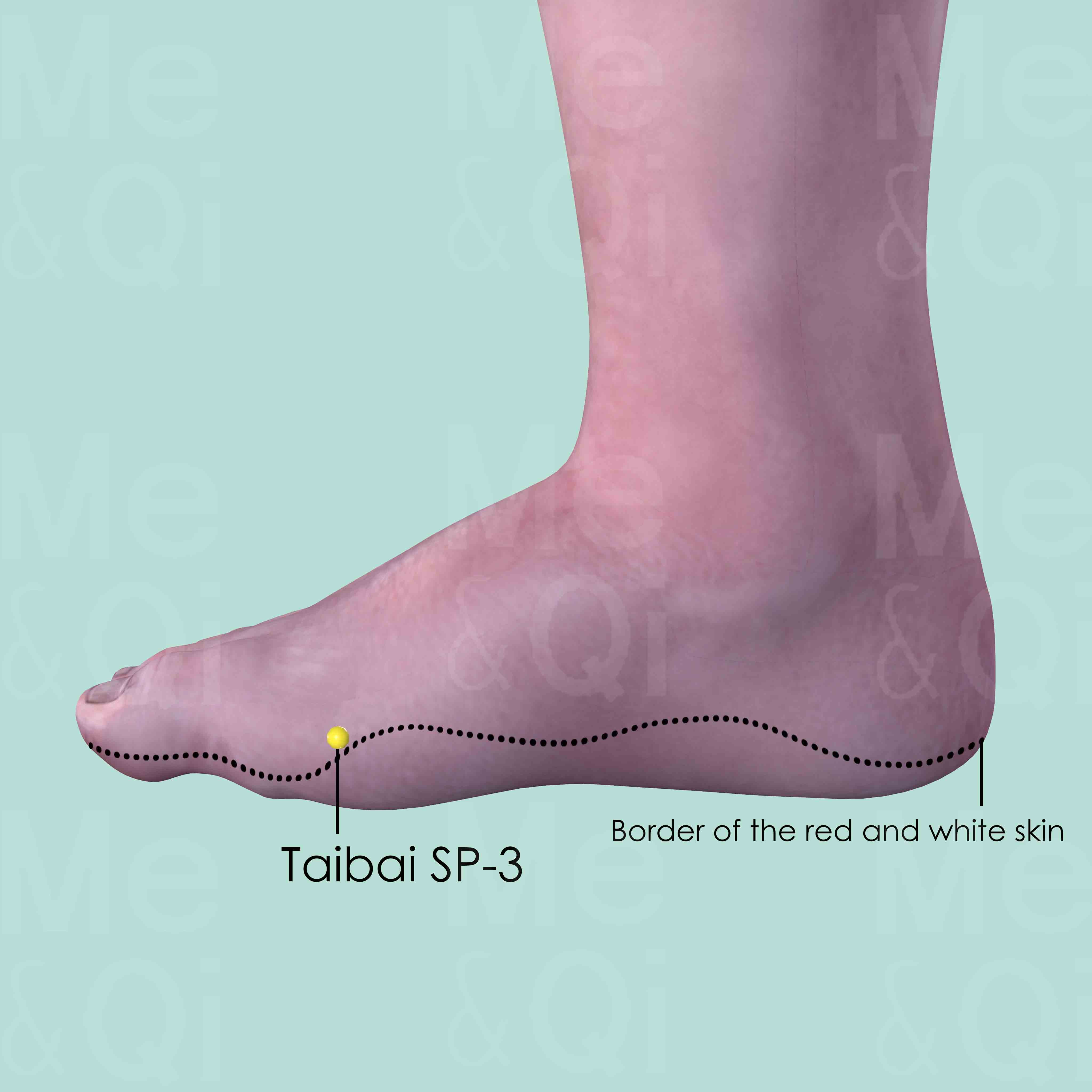
Taibai SP-3
Proximal and inferior to the head of the 1st metatarsal bone, at the border of the red and white skin.
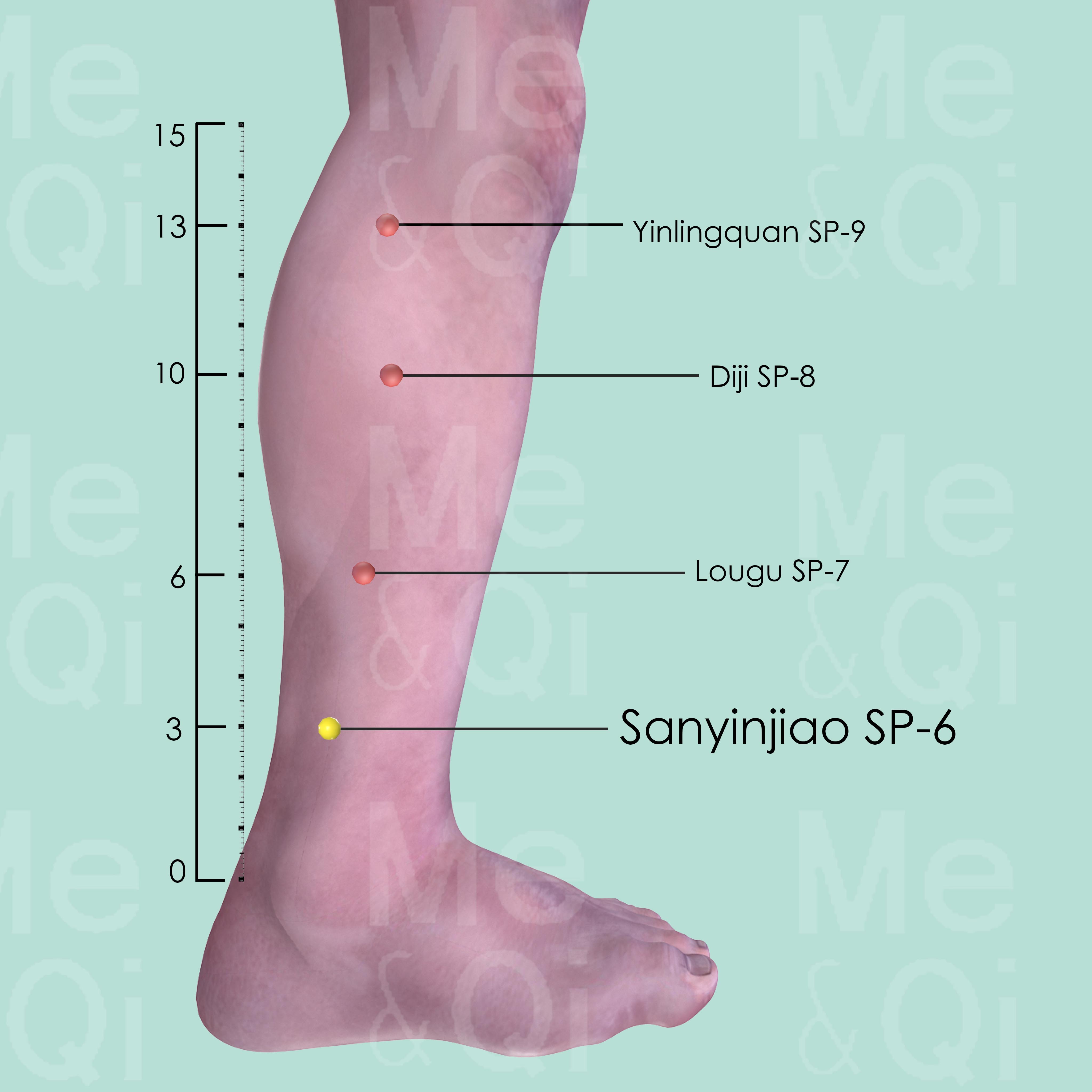
Sanyinjiao SP-6
3 cun directly above the tip of the medial malleolus, on the posterior border of the tibia, on the line drawn from the medial malleolus to Yinlingquan SP-9.
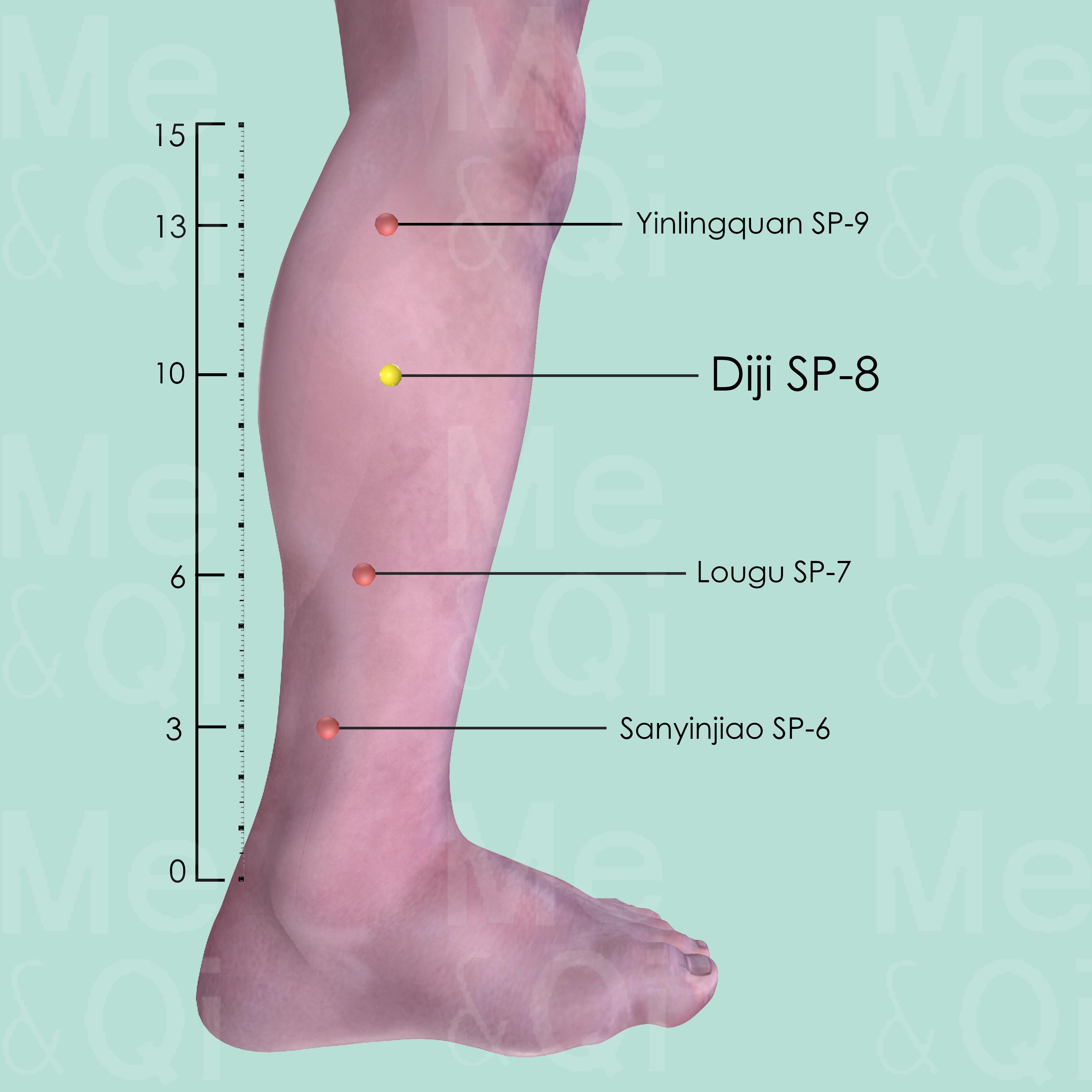
Diji SP-8
3 cun below the medial condyle of the tibia, on the line connecting Yinlingquan SP-9 and the the medial malleolus.
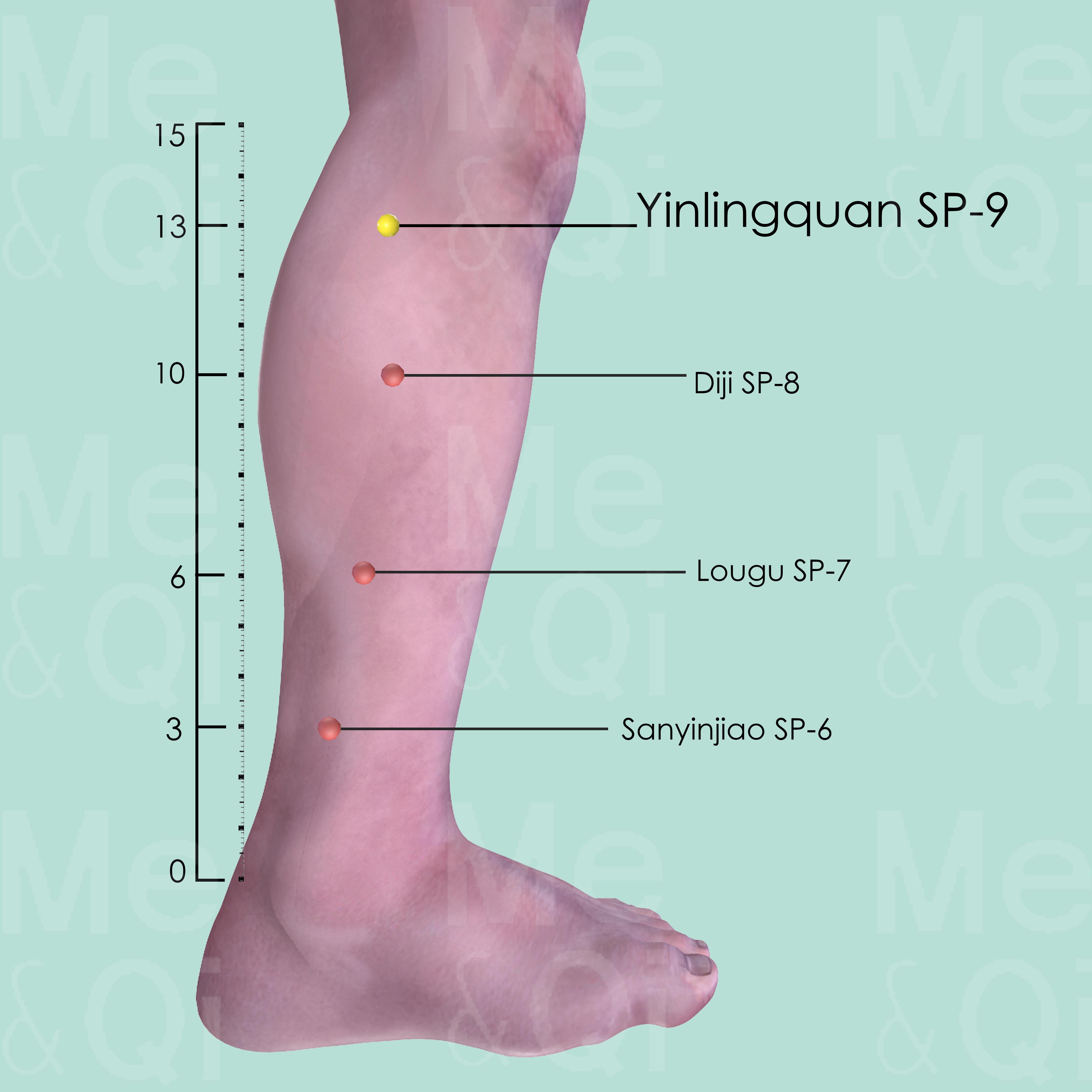
Yinlingquan SP-9
On the lower border of the medial condyle of the tibia, in the depression between the posterior border of the tibia and gastrocnemius muscle.
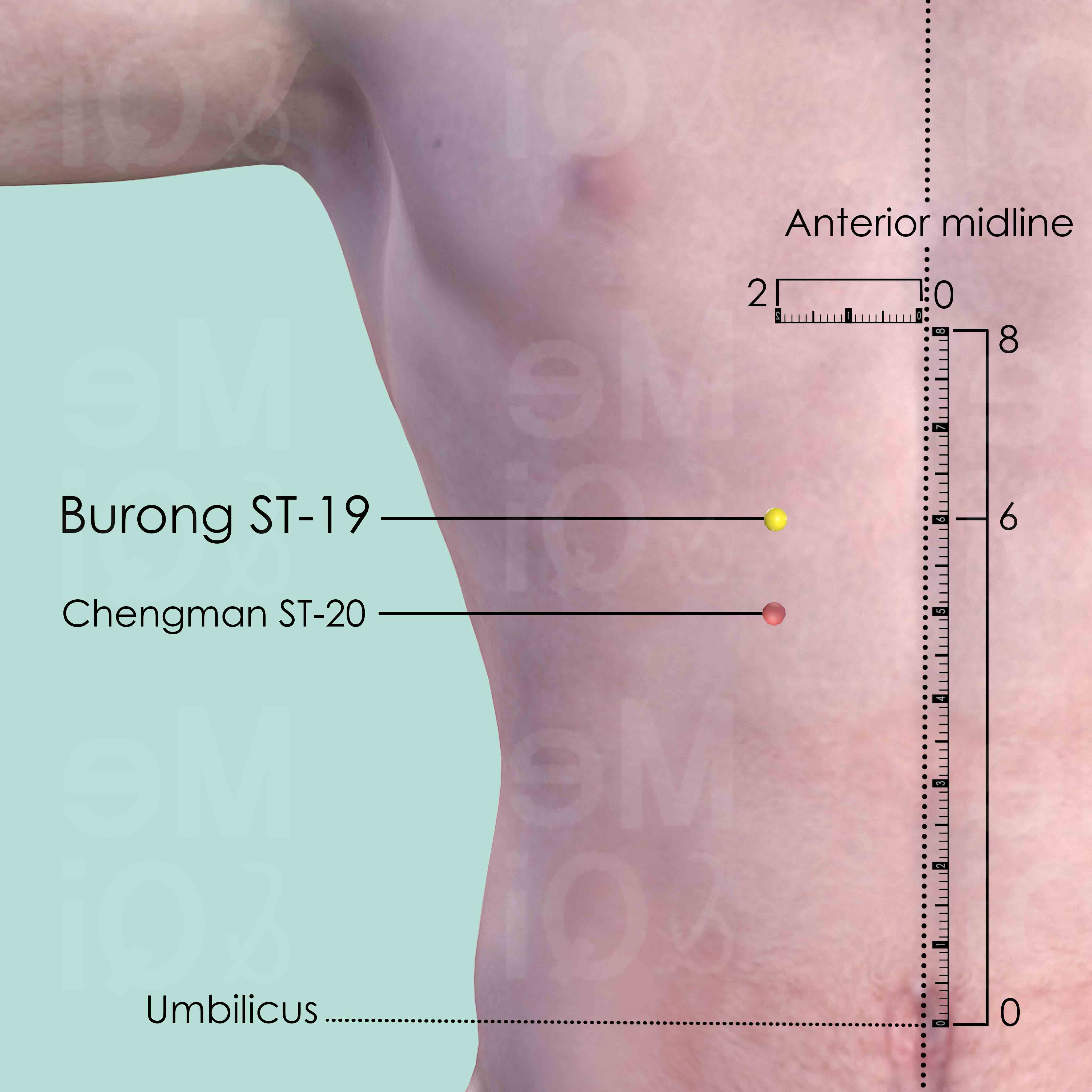
Burong ST-19
2 cun below the sternocostal angel and 6 cun above the umbilicus, 2 cun lateral to the anterior midline.
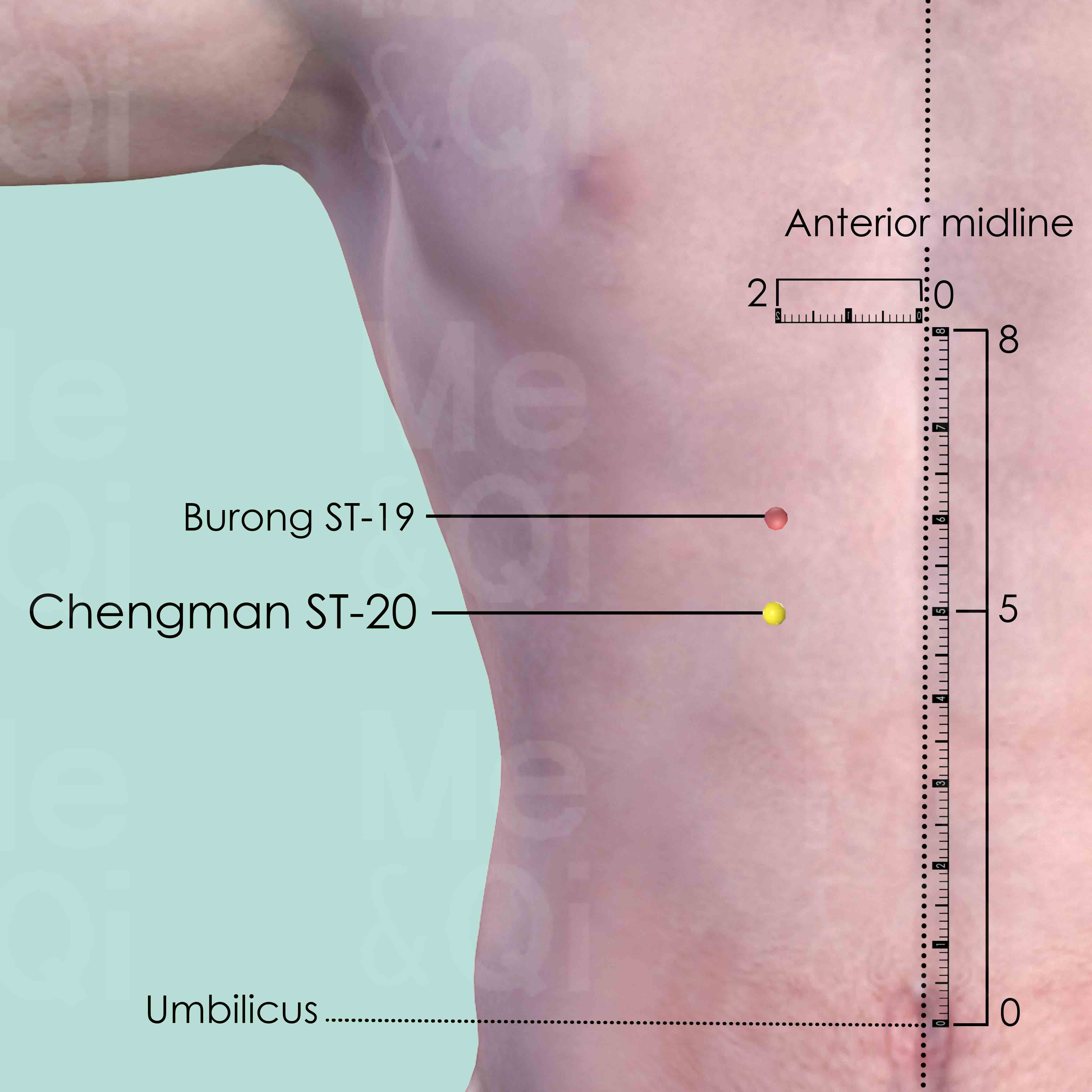
Chengman ST-20
5 cun above the umbilicus and 2 cun lateral to the anterior midline, or 1 cun below Burong ST-19.
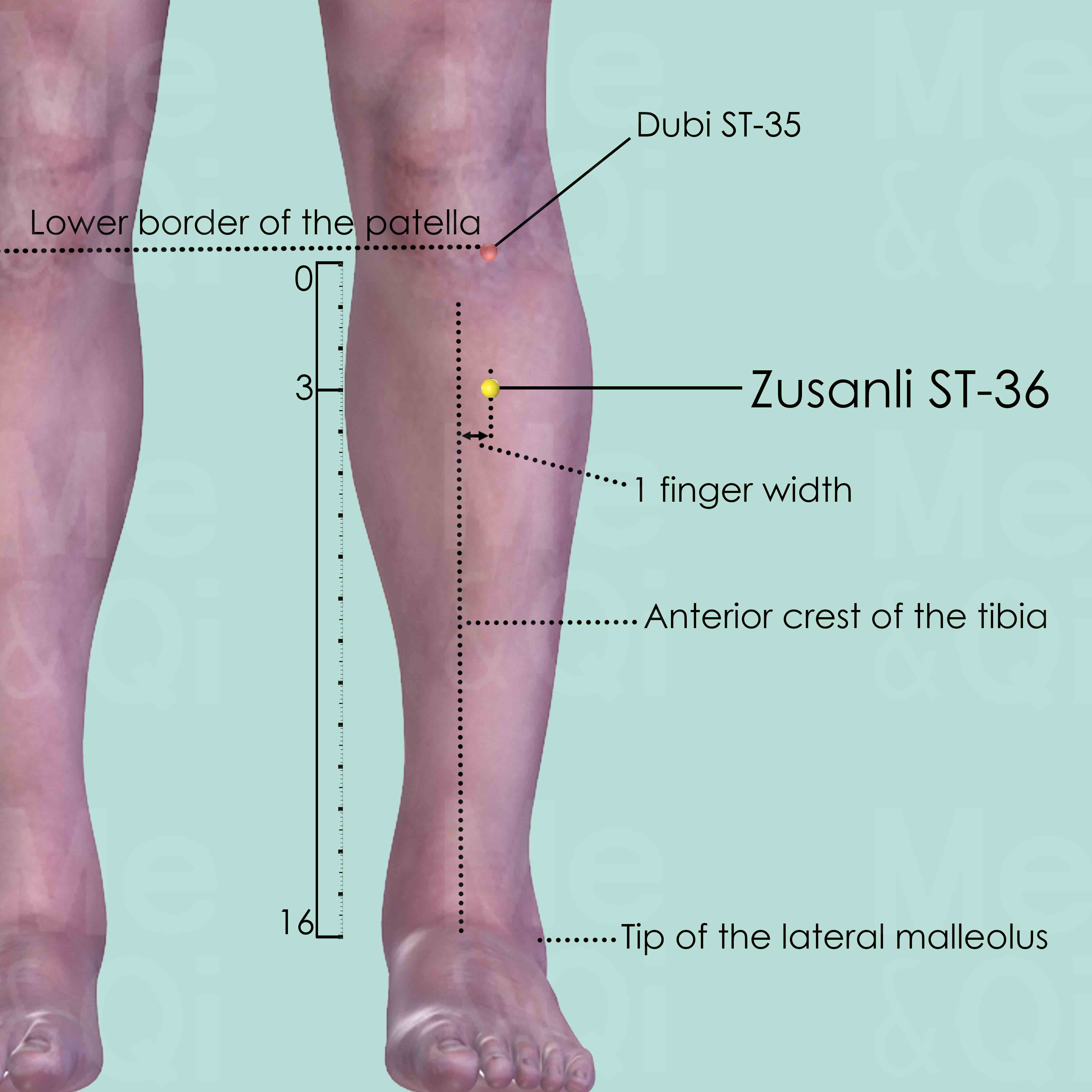
Zusanli ST-36
3 cun below Dubi ST-35, one finger breadth lateral to the anterior crest of the tibia, on the tibialis anterior muscle.
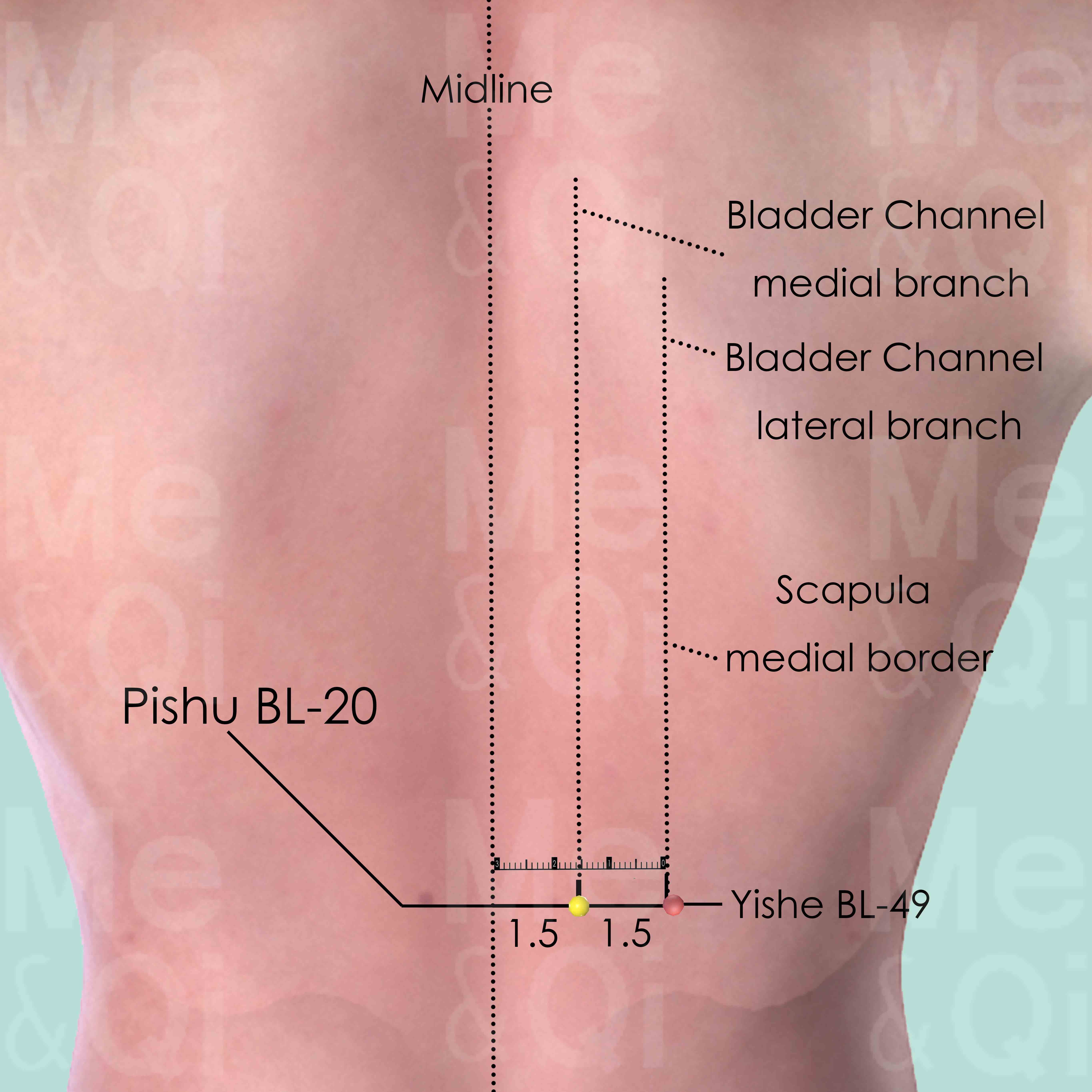
Pishu BL-20
1.5 cun lateral to the lower border of the spinous process of the 11th thoracic vertebra (T11).
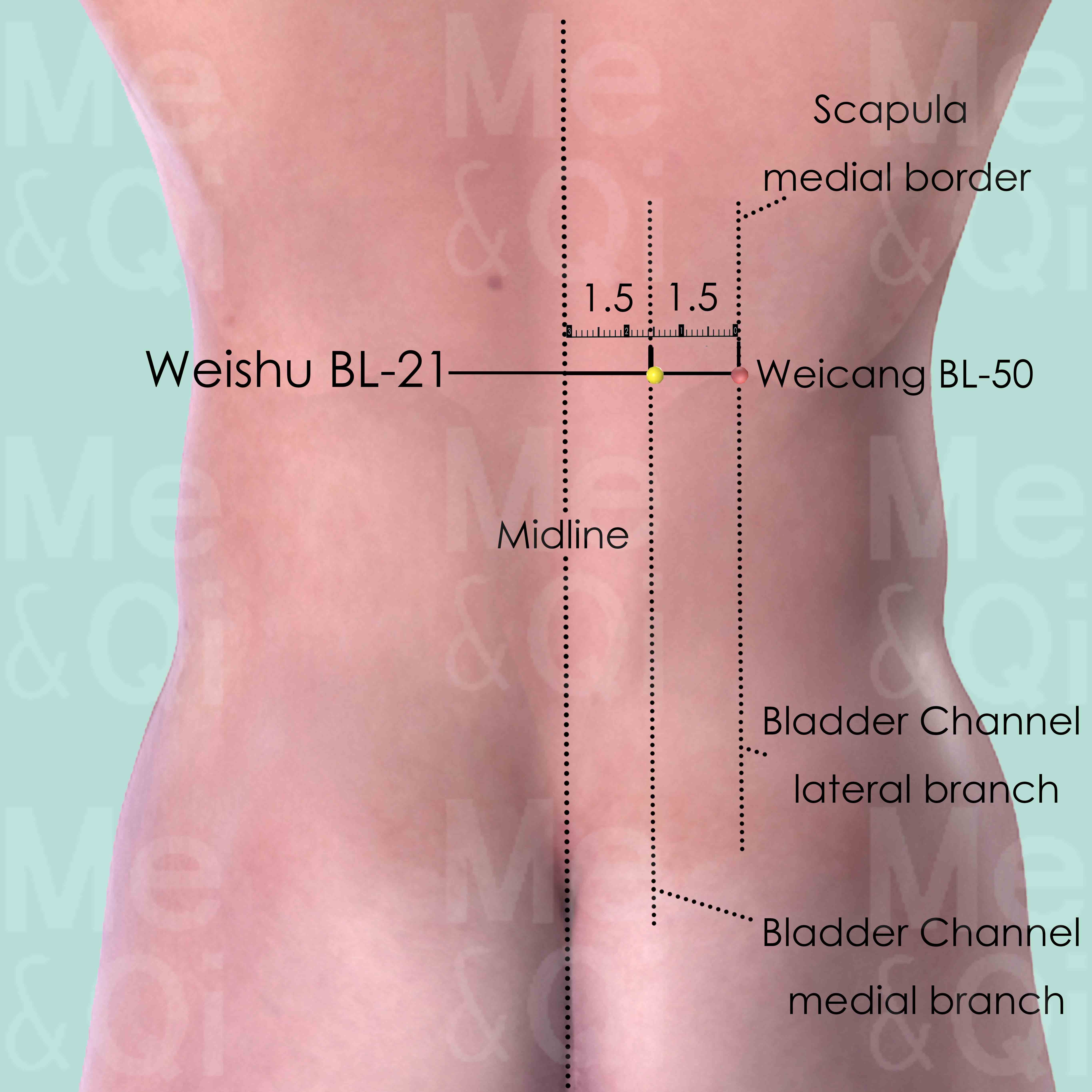
Weishu BL-21
1.5 cun lateral to the lower border of the spinous process of the 12th thoracic vertebra (T12).
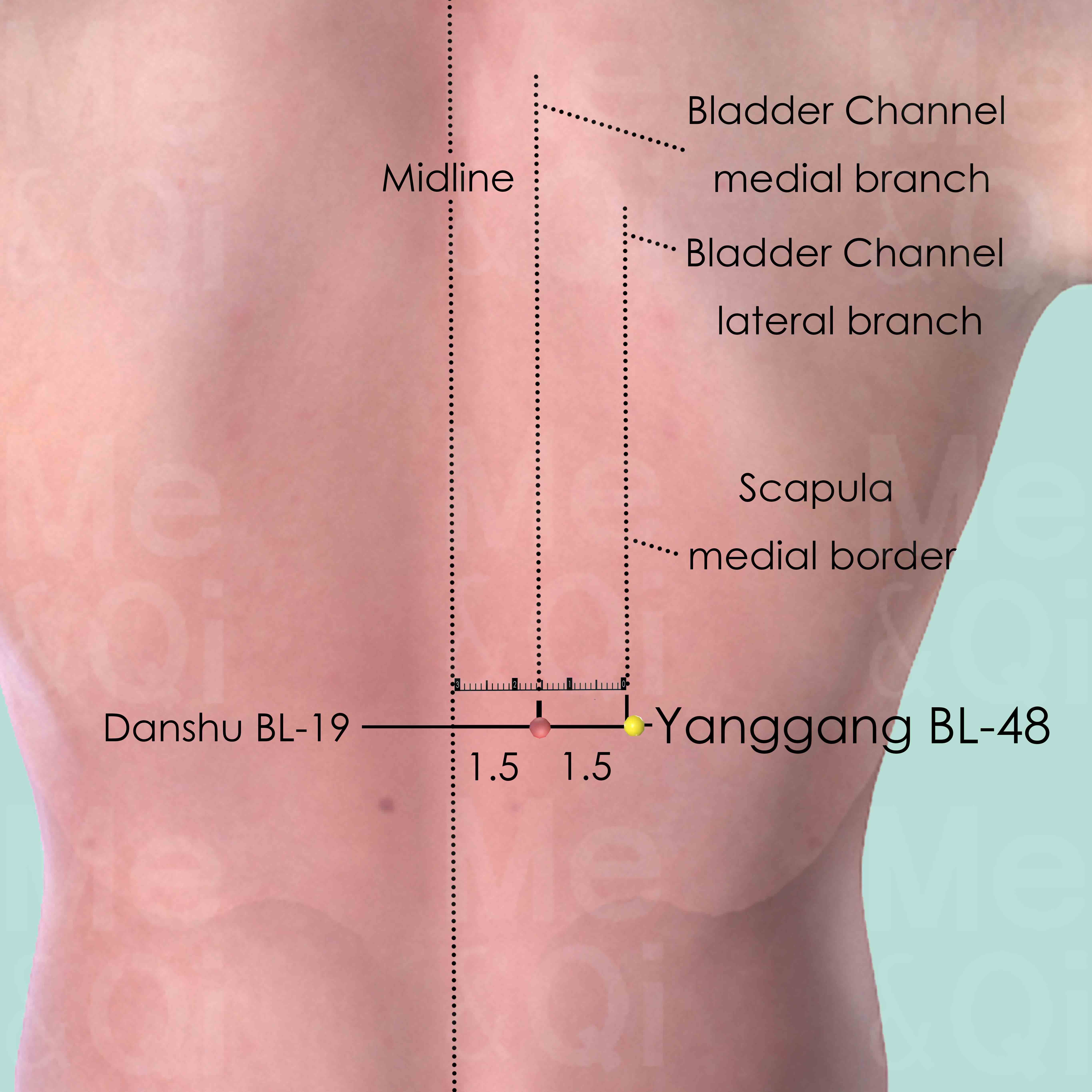
Yanggang BL-48
3 cun lateral to the lower border of the spinous process of the 10th thoracic vertebra (T10).
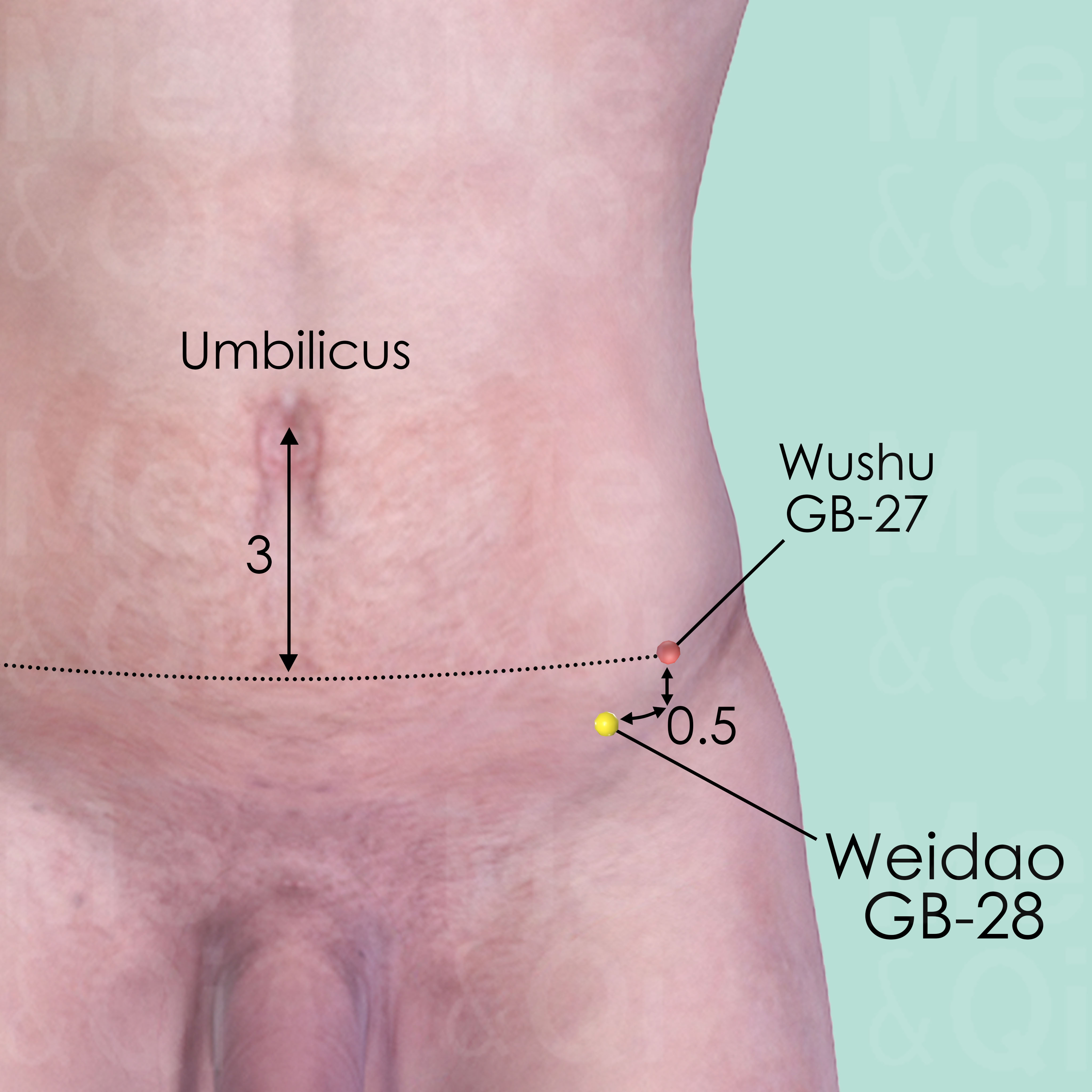
Weidao GB-28
Anterior and Inferior to the anterior superior iliac spine (ASIS), 0.5 cun anterior and inferior to Wushu GB-27.
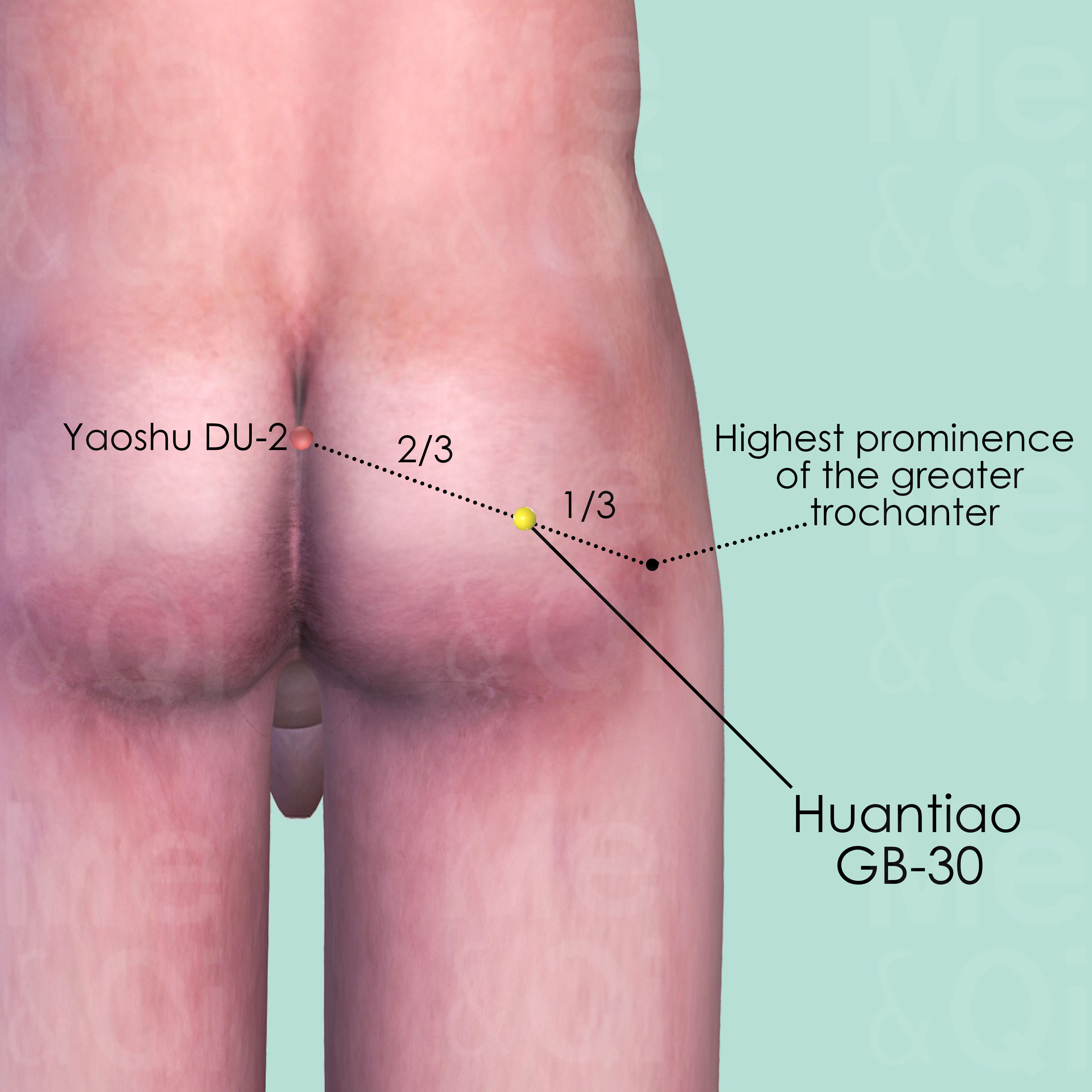
Huantiao GB-30
At the junction of the middle and lateral third of the distance between the great trochanter and Yaoshu DU-2 of the hiatus of the sacrum. When locating the point, put the patient in lateral recumbent position with the thigh flexed.
Jizhong DU-6
On the back midline, in the depression below the spinous process of the 11th thoracic vertebra (T11).
Zhongshu DU-7
On the back midline, in the depression below the spinous process of the 10th thoracic vertebra (T10).
Yangchi TB-4
At the junction of the ulna carpal bones of the wrist dorsum, in the depression lateral to the tendon of extensor digitorum and extensor digiti minimi muscle.
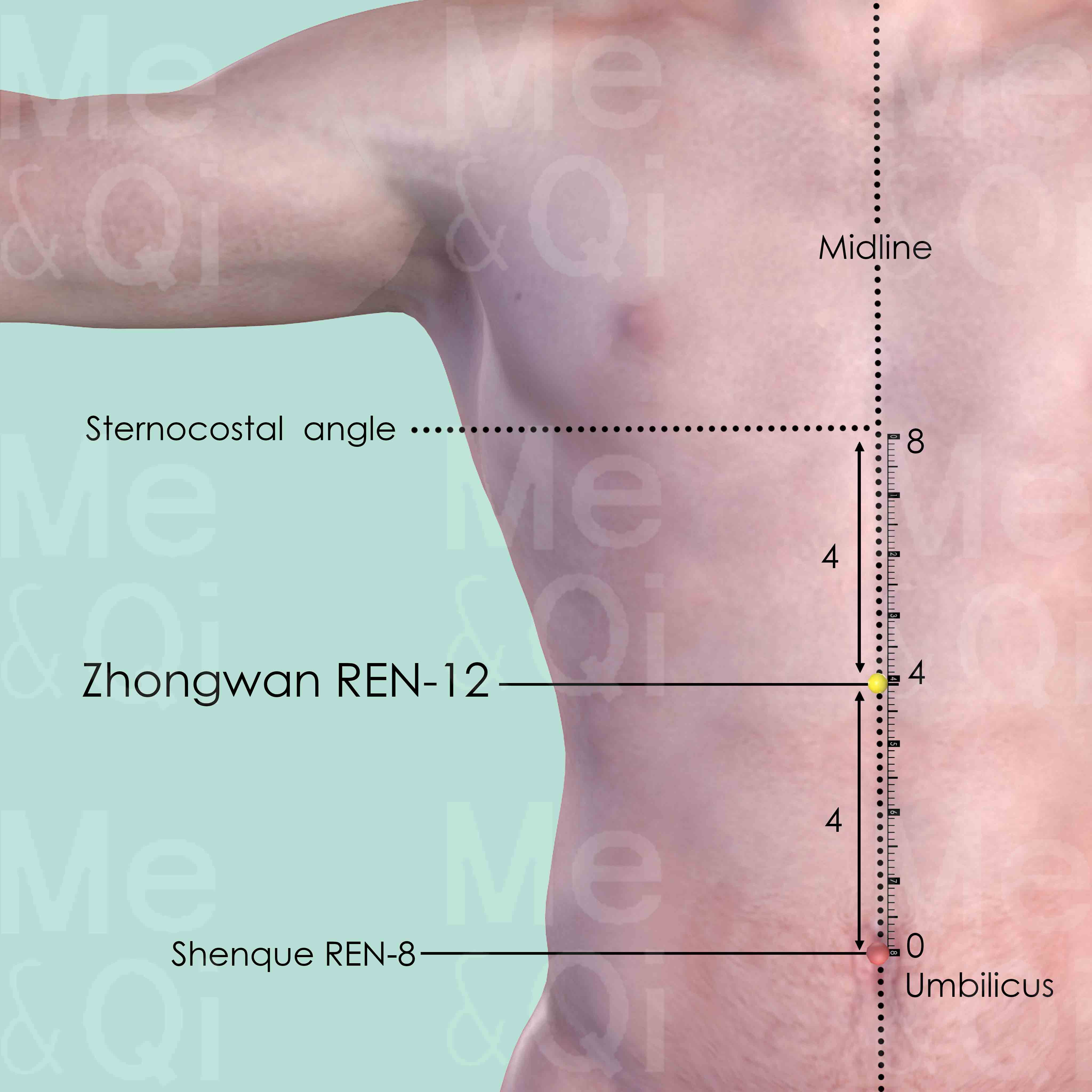
Zhongwan REN-12
On the midline of the abdomen, 4 cun above the umbilicus and 4 cun below the sternocostal angle.