Leg Swellingaccording to TCM
Symptom family: Legs disorders and Symptoms
What is Leg Swelling?
Leg swelling, medically known as lower limb edema, is a condition characterized by an accumulation of fluid in the tissues of the leg, leading to noticeable swelling.
This condition can affect both legs and may extend to the feet. It can be a result of various health issues, ranging from circulatory problems to lymphatic system disorders. Leg swelling is often accompanied by discomfort and sometimes pain, and it can significantly impact mobility and quality of life.
How Does TCM View Leg Swelling?
Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) approaches leg swelling from a perspective of energy and fluid imbalances in the body. According to TCM, this condition often arises from the Stagnation of Qi (vital energy) and the accumulation of pathogenic factors like Dampness or Phlegm.
TCM practitioners aim to identify the underlying pattern of disharmony causing the swelling, whether it is due to a Deficiency in the body's energy systems or an excess of pathogenic factors.
Root Causes of Leg Swelling in TCM
In Traditional Chinese Medicine, leg swelling is often seen as a manifestation of imbalances in the body's Qi (energy) and its ability to process and regulate Body Fluids. Two common TCM patterns associated with leg swelling are Damp-Phlegm and Phlegm-Fluids in the limbs.
Damp-Phlegm is characterized by symptoms like swollen limbs, a feeling of heaviness, and often a sensation of fullness or congestion in the chest and abdomen. Phlegm-Fluids in the limbs are identified by the presence of swelling accompanied by a sense of heaviness, muscle pain, and possibly difficulty with urination or a lack of sweating. These patterns reflect an underlying disharmony in the body's natural systems, leading to the accumulation of fluids in the lower extremities.
Explore below more details about what might cause Leg swelling according to TCM.
- By Syndrome
- Phlegm
- Dampness
Phlegm
In TCM "Phlegm" as a pattern of disharmony is a complex concept that extends beyond the physical manifestation of mucus. It represents a pathological factor that can disrupt the flow of Qi (vital energy) and blood, leading to various health issues. Phlegm in TCM is seen as a sticky, turbid substance arising from the body's inability to metabolize fluids properly, often due to a dysfunction of the spleen. It's not only associated with respiratory problems like cough and congestion but also with systemic issues. Symptoms can include a feeling of heaviness, mental cloudiness, dizziness, and in some cases, the formation of lumps or masses. Phlegm can even be "invisible," contributing to emotional disturbances like depression or stress. ... see more
Phlegm Patterns That Can Lead to Leg Swelling
Common Symptoms: Profuse White Sputum Absence Of Thirst Focal Distention Of The Chest Upper Abdominal Focal Distention Nausea Sticky Taste In The Mouth Obesity Abdominal Fat
| Pattern Name | Relevant Symptoms | Relevant Formulas |
|---|---|---|
| Damp-Phlegm | Swollen limbs, Profuse white sputum, Focal distention of the chest, Upper abdominal focal distention, Nausea, Sticky taste in the mouth, Absence of thirst, Obesity, Abdominal fat... see more | Er Chen Tang | Xiang Sha Liu Jun Zi Tang | Shen Qi Wan |
| Phlegm-Fluids in the limbs | Swollen limbs, Feeling of heaviness, Muscle pain, Lack of sweating, Absence of thirst, Profuse white sputum, Urinary dysfunction... see more | Da Qing Long Tang | Xiao Qing Long Tang |
Dampness
"Dampness" in TCM is a concept that describes a pattern of disharmony where the body accumulates excess moisture. Imagine the heavy, sticky feeling you get on a very humid day; that's similar to what dampness feels like internally. It can manifest as a sense of heaviness, bloating, sluggishness, or even a foggy mind. This condition is often thought to arise from environmental factors like living in a damp place, dietary habits that promote moisture in the body, or internal imbalances that hinder the body's ability to process fluids properly. In TCM, dampness can obstruct the normal flow of energy and fluids in the body, leading to various symptoms.... see more
Dampness Patterns That Can Lead to Leg Swelling
| Pattern Name | Relevant Symptoms | Relevant Formulas |
|---|---|---|
| Damp-Phlegm | Swollen limbs, Profuse white sputum, Focal distention of the chest, Upper abdominal focal distention, Nausea, Sticky taste in the mouth, Absence of thirst, Obesity, Abdominal fat... see more | Er Chen Tang | Xiang Sha Liu Jun Zi Tang | Shen Qi Wan |
TCM Herbal Formulas for Leg Swelling
To address leg swelling, TCM practitioners typically recommend formulas based on the underlying disharmony identified. For Damp-Phlegm, a formula like Er Chen Tang, which includes Crow-Dipper Rhizomes (Ban Xia), is used to dry Dampness and transform Phlegm. This helps in reducing the fluid accumulation causing the swelling.
For Phlegm-Fluids in the limbs, Da Qing Long Tang, which contains Ephedra (Ma Huang), is often prescribed. This formula is known for its ability to expel pathogenic factors and manage fluid imbalances in the body. These herbal formulas are tailored to the individual's specific TCM diagnosis and are intended to restore balance by promoting the proper flow of Qi and fluids.
Explore below some TCM herbal formulas used to address leg swelling, organized by cause and by formula type.
- By Cause
- By Formula Type
- Phlegm
- Dampness
- Formulas that clear wind-Cold
- Formulas that dry dampness and transform phlegm
- Formulas that dispel phlegm
- Formulas that warm yang and tonify
Top Formula for Phlegm:
Er Chen Tang
Suitable for Phlegm patterns that may cause leg swelling, such as Damp-Phlegm
Learn moreAll Formulas Recommended for Leg Swelling Caused by Phlegm
| Formula | Patterns Suitable For |
|---|---|
| Er Chen Tang | Damp-Phlegm |
| Xiang Sha Liu Jun Zi Tang | Damp-Phlegm |
| Shen Qi Wan | Damp-Phlegm |
| Da Qing Long Tang | Phlegm-Fluids in the limbs |
| Xiao Qing Long Tang | Phlegm-Fluids in the limbs |
Top Formula for Dampness:
Er Chen Tang
Suitable for Dampness patterns that may cause leg swelling, such as Damp-Phlegm
Learn moreAll Formulas Recommended for Leg Swelling Caused by Dampness
| Formula | Patterns Suitable For |
|---|---|
| Er Chen Tang | Damp-Phlegm |
| Xiang Sha Liu Jun Zi Tang | Damp-Phlegm |
| Shen Qi Wan | Damp-Phlegm |
Formulas that clear Wind-Cold
These formulas are suitable for some leg swelling-causing patterns like Phlegm-Fluids in the limbs.
One such formula is Da Qing Long Tang, with ephedra as a key herb.
Other formulas of this category are listed in the table below.
All "formulas that clear wind-Cold" recommended for leg swelling
| Formula | Patterns Suitable For (if applicable) |
|---|---|
| Da Qing Long Tang | Phlegm-Fluids in the limbs |
| Xiao Qing Long Tang | Phlegm-Fluids in the limbs |
Formulas that dry Dampness and transform Phlegm
These formulas are suitable for some leg swelling-causing patterns like Damp-Phlegm.
One such formula is Er Chen Tang, with crow-dipper rhizome as a key herb.
Formulas that dispel Phlegm
These formulas are suitable for some leg swelling-causing patterns like Damp-Phlegm.
One such formula is Xiang Sha Liu Jun Zi Tang, with ginseng as a key herb.
Formulas that warm Yang and tonify
These formulas are suitable for some leg swelling-causing patterns like Damp-Phlegm.
One such formula is Shen Qi Wan, with prepared aconite as a key herb.
Acupoints for Leg Swelling
TCM also utilizes acupressure points to alleviate leg swelling. Tiaokou ST-38, located on the leg, is used for dispelling Wind-Damp and benefiting the shoulder, while Yinlingquan SP-9, situated on the medial aspect of the lower leg, is excellent for regulating the Spleen and resolving Dampness.
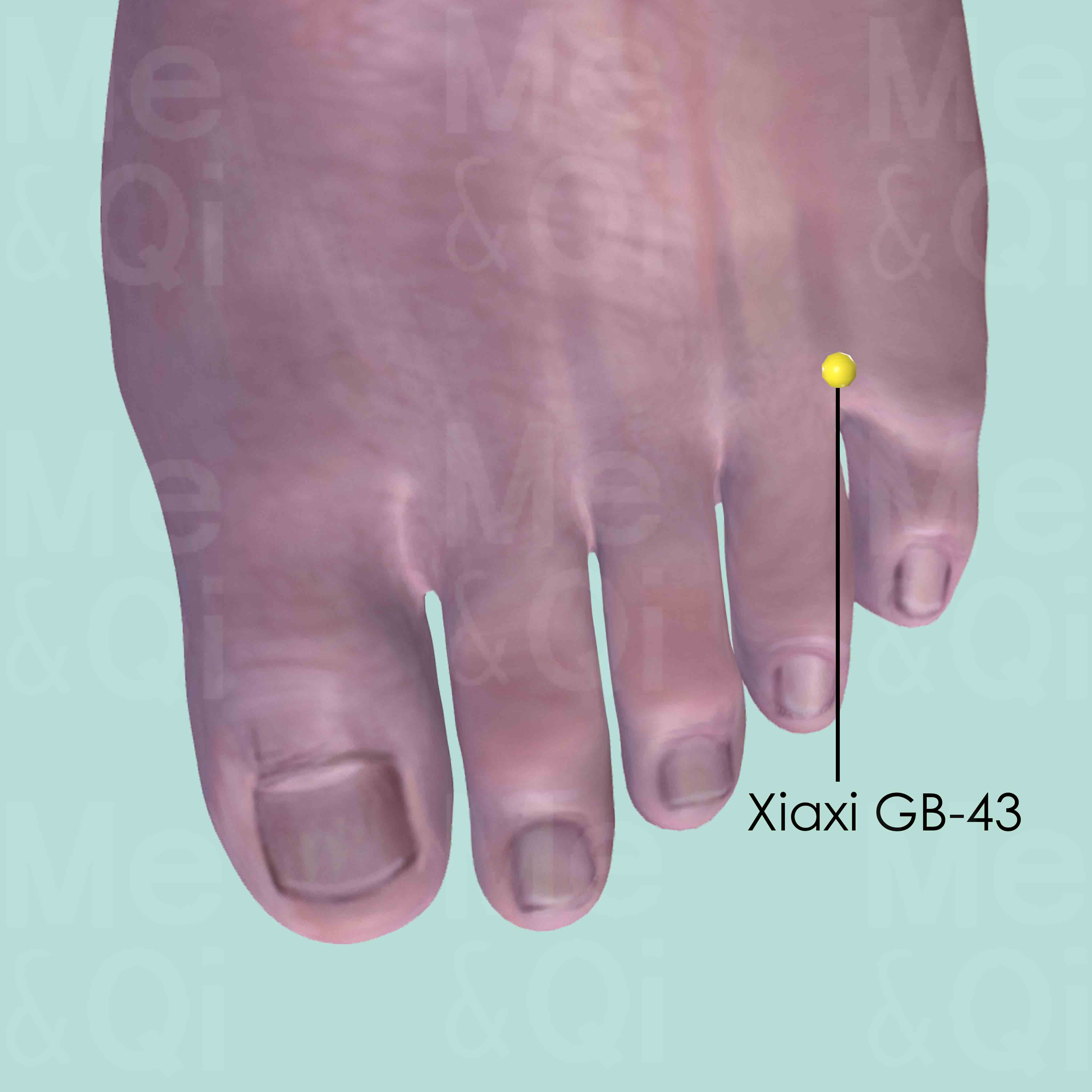
Other valuable points include Yangchi TB-4 on the wrist for regulating body fluids in the lower burner and Xiaxi GB-43 between the toes for subduing Liver Yang and expelling Damp-Heat. These acupoints are selected based on their ability to address the underlying TCM patterns contributing to leg swelling.
Explore below some acupoints used to address leg swelling, organized by meridian.
- By Meridian
- Stomach Channel
- Triple Burner Channel
- Spleen Channel
- Gall Bladder Channel
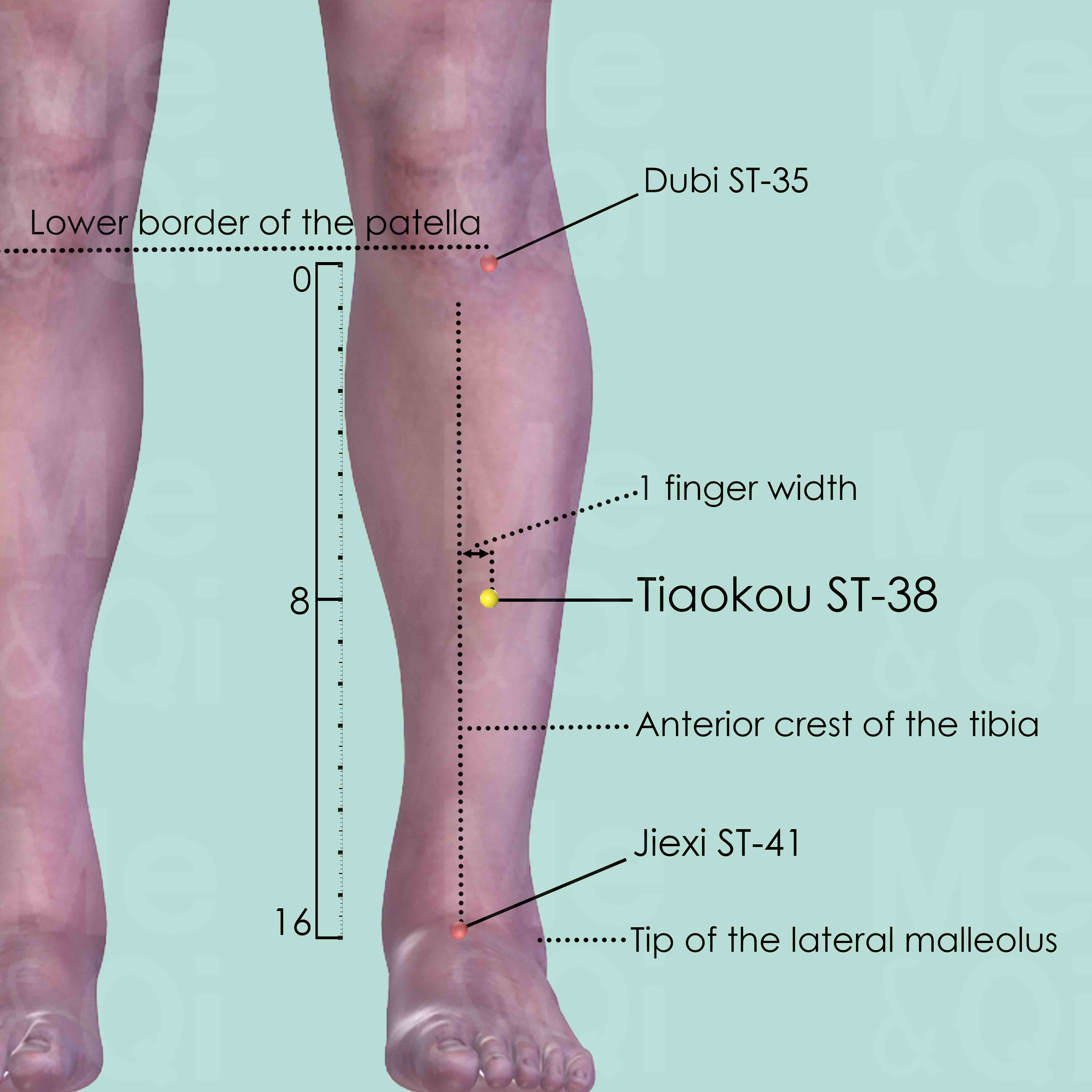
Tiaokou ST-38
8 cun below Dubi ST-35, midway between Dubi ST-35 and Jiexi ST-41, one middle finger-width from the anterior crest of the tibia.
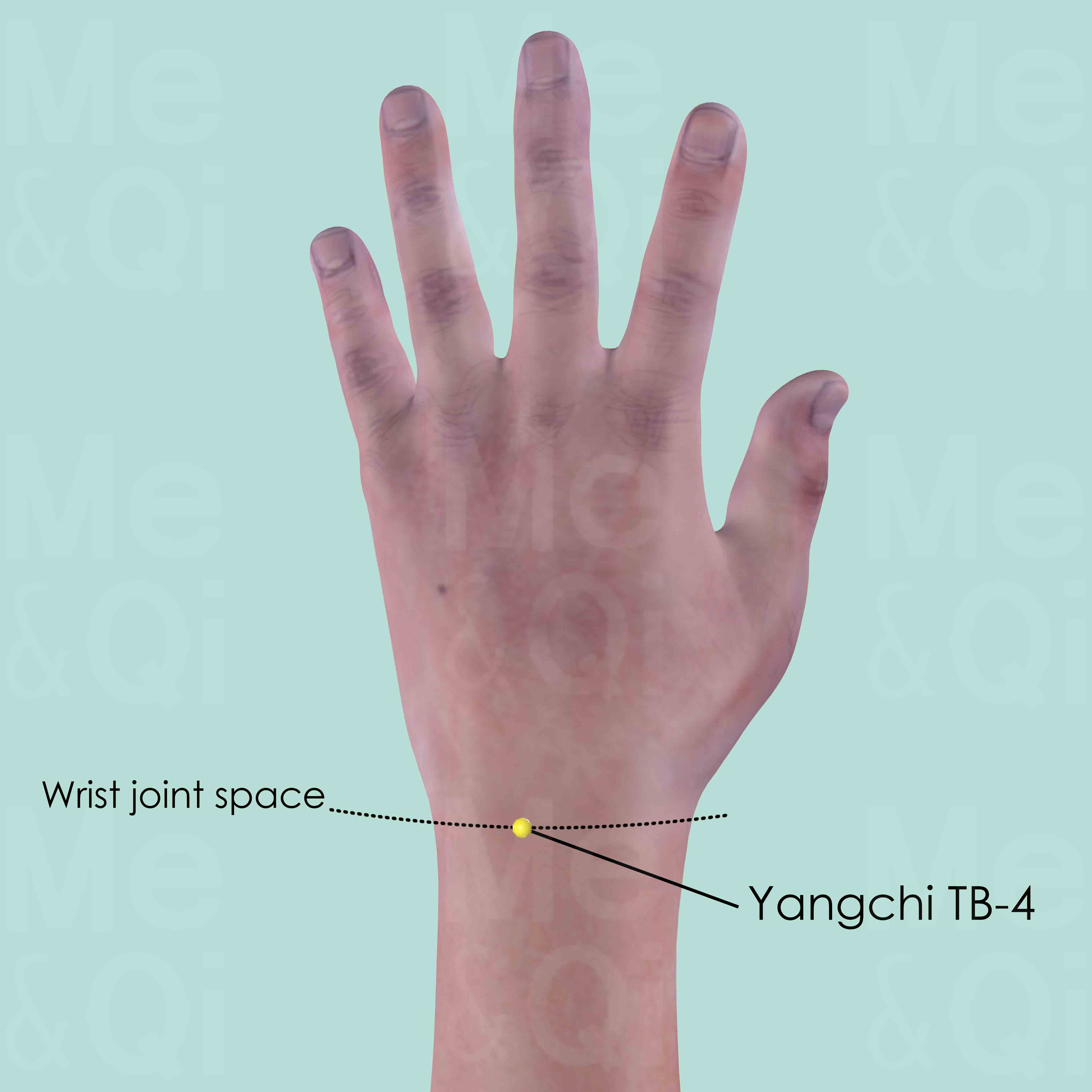
Yangchi TB-4
At the junction of the ulna carpal bones of the wrist dorsum, in the depression lateral to the tendon of extensor digitorum and extensor digiti minimi muscle.
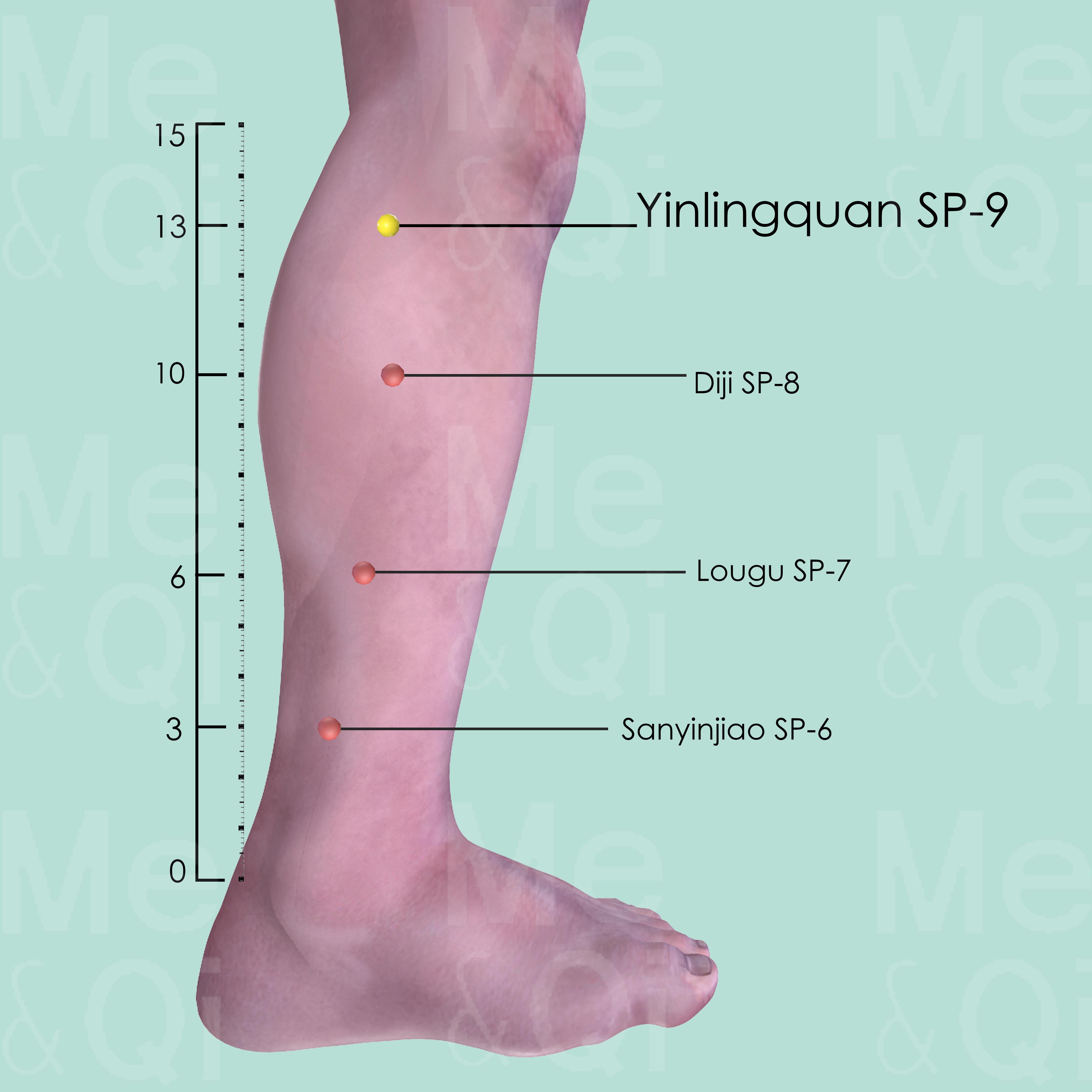
Yinlingquan SP-9
On the lower border of the medial condyle of the tibia, in the depression between the posterior border of the tibia and gastrocnemius muscle.