Joint Stiffnessaccording to TCM
What is Joint Stiffness?
Joint stiffness encompasses the sensation of limited or restricted movement in one or more of the body’s joints. It is often accompanied by discomfort or pain, which can further inhibit free motion. This condition can present itself in a variety of forms, such as stiffness in specific areas like the neck, shoulders, or knees, or as a more generalized rigidity affecting multiple joints.
Joint stiffness can be a symptom of underlying health issues, including inflammatory conditions like arthritis or the natural aging process, and is a significant concern for its impact on daily functioning and quality of life.
How does TCM view Joint Stiffness?
In Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), joint stiffness is perceived through the concept of 'pattern differentiation.' A pattern in TCM is a complex framework used to diagnose the nature of a patient's disharmony by interpreting a constellation of symptoms and signs. It goes beyond the superficial manifestation of a condition, aiming to understand the underlying cause of symptoms such as joint stiffness.
Identifying the pattern is crucial because it guides the practitioner to a tailored treatment strategy. It ensures that the intervention—whether it be with acupuncture, herbs, or lifestyle modifications—addresses the root of the disharmony rather than just the surface symptom, fostering a more holistic healing process.
Root Causes of Joint Stiffness in TCM
In Traditional Chinese Medicine, joint stiffness is often attributed to the invasion of external pathogenic factors—namely Damp, Wind, Cold, and Heat—which can obstruct the flow of Qi and Blood in the channels and muscles. For instance, Cold can cause constriction and reduce circulation, leading to stiffness, while Dampness tends to create a sensation of heaviness and swelling in the joints.
Additionally, internal factors like Phlegm can accumulate in the channels, further impeding the movement of Qi and Blood and contributing to joint stiffness. Addressing these external and internal imbalances is essential in TCM for restoring ease of movement and alleviating discomfort.
Explore below more details about what might cause Joint stiffness according to TCM.
- By Syndrome
- By Organ
- Cold
- Dampness
- Heat
- Blood Deficiency
- Yin Deficiency
- Wind
- Phlegm
- Yang Deficiency
- Blood Stasis
- Yang Excess
- Qi Deficiency
- View More Causes
- Liver
- Kidney
Cold
In TCM "Cold" as a pattern of disharmony refers to a specific type of imbalance within the body's systems, often linked to a deficiency or weakness. It's not about feeling physically cold or having a common cold, but rather a metaphorical description of certain symptoms and underlying conditions. When a TCM practitioner says someone suffers from "Cold," it usually implies that the body's Yang energy, which is warm and active, is insufficient or overpowered by Yin energy, which is cool and passive. Symptoms of Cold in TCM can include a general feeling of coldness, cold limbs, pale complexion, low energy, slow metabolism, and a preference for warmth. ... see more
Cold Patterns That Can Lead to Joint Stiffness
Common Symptoms: Arthralgia Rheumatoid Arthritis Periarthritis Of The Shoulder Cold Extremities Fever Swollen And Painful Joints Worsening At Night Chills Without Sweating Weight Loss
| Pattern Name | Relevant Symptoms | Relevant Formulas |
|---|---|---|
| Cold invading the Channels joints and muscles | Joint stiff, Joint pain, Arthralgia, Joint stiffness, Muscle pain, Swollen joints, Muscle numbness, Stiff neck... see more | Wu Tou Tang | Xiao Huo Luo Dan |
| Damp-Cold | Joints pain, Mouth ulcers, White and watery sputum, Nasal discharge, Sneezing, Chills, Abdominal pain, Cold extremities, Arthralgia, Diarrhea, Feeling of heaviness... see more | Wei Ling Tang |
| Wind invading the Channels joints and muscles | Joints pain, Arthralgia, Anemophobia, Fever | Xiao Huo Luo Dan | Da Fang Feng Tang |
| Painful Obstruction with Wind-Cold-Damp | Reduced range of motion in the affected joints, Swollen and painful joints worsening at night, Joint stiffness, Chills without sweating, Weight loss, Headaches, Dizziness, Shortness of breath, Nausea, Rheumatoid arthritis, Connective tissue disorders... see more | Gui Zhi Shao Yao Zhi Mu Tang |
| Yang Deficiency with Cold-Damp | Aching bones and joints, Body pain, Bone and joint pain, Cold extremities, Absence of thirst, Aversion to cold, Migraine, Cluster headache, Trigeminal neuralgia, Piriformis syndrome, Rheumatoid arthritis... see more | Fu Zi Tang |
Dampness
"Dampness" in TCM is a concept that describes a pattern of disharmony where the body accumulates excess moisture. Imagine the heavy, sticky feeling you get on a very humid day; that's similar to what dampness feels like internally. It can manifest as a sense of heaviness, bloating, sluggishness, or even a foggy mind. This condition is often thought to arise from environmental factors like living in a damp place, dietary habits that promote moisture in the body, or internal imbalances that hinder the body's ability to process fluids properly. In TCM, dampness can obstruct the normal flow of energy and fluids in the body, leading to various symptoms.... see more
Dampness Patterns That Can Lead to Joint Stiffness
Common Symptoms: Arthralgia Headaches Dizziness Rheumatoid Arthritis Periarthritis Of The Shoulder Cold Extremities Absence Of Thirst Aversion To Cold
| Pattern Name | Relevant Symptoms | Relevant Formulas |
|---|---|---|
| Dampness invading the Channels joints and muscles | Joint stiff, Joint pain, Arthralgia, Joint stiffness, Swollen joints, Skin numbness, Heavy joint, Muscle numbness... see more | Xiao Huo Luo Dan | Shu Jing Huo Xue Tang |
| Damp-Heat | Joint pain, Fever, Neck gland swelling, Headaches, Tight feeling in chest and stomach, Sticky taste in the mouth, Absence of thirst, Feeling hot, Feeling of heaviness, Bitter taste in the mouth, Acne... see more | Ba Zheng San |
| Damp-Cold | Joints pain, Mouth ulcers, White and watery sputum, Nasal discharge, Sneezing, Chills, Abdominal pain, Cold extremities, Arthralgia, Diarrhea, Feeling of heaviness... see more | Wei Ling Tang |
| Painful Obstruction with Wind-Cold-Damp | Reduced range of motion in the affected joints, Swollen and painful joints worsening at night, Joint stiffness, Chills without sweating, Weight loss, Headaches, Dizziness, Shortness of breath, Nausea, Rheumatoid arthritis, Connective tissue disorders... see more | Gui Zhi Shao Yao Zhi Mu Tang |
| Yang Deficiency with Cold-Damp | Aching bones and joints, Body pain, Bone and joint pain, Cold extremities, Absence of thirst, Aversion to cold, Migraine, Cluster headache, Trigeminal neuralgia, Piriformis syndrome, Rheumatoid arthritis... see more | Fu Zi Tang |
Heat
In TCM "Heat" signifies an excess of Yang energy, leading to an imbalance where heat predominates over the body's cool Yin aspects. This condition is metaphorically akin to an internal over-heating. Symptoms indicative of Heat can include feelings of warmth, fever, sweating, irritability, red face, thirst with a preference for cold drinks, and a rapid pulse. The tongue may appear red with a yellow coating. Unlike the common interpretation of heat in terms of temperature, in TCM, it represents a state of hyperactivity or inflammation in the body.... see more
Heat Patterns That Can Lead to Joint Stiffness
Common Symptoms: Arthralgia Fever Thirst Generalized Fatigue Joints Red And Hot Anxiety Anemophobia Swollen Joints
| Pattern Name | Relevant Symptoms | Relevant Formulas |
|---|---|---|
| Heat invading the Channels joints and muscles | Joint stiff, Joints pain, Arthralgia, Joints red and hot, Fever, Thirst, Anxiety, Anemophobia, Swollen joints, Joint stiffness... see more | Xuan Bi Tang |
| Damp-Heat | Joint pain, Fever, Neck gland swelling, Headaches, Tight feeling in chest and stomach, Sticky taste in the mouth, Absence of thirst, Feeling hot, Feeling of heaviness, Bitter taste in the mouth, Acne... see more | Ba Zheng San |
| Empty-Heat caused by Yin Deficiency | Joint pain, Nighttime fever, Emaciation, Chronic pyelonephritis, Pulmonary tuberculosis, Renal tuberculosis, Tidal fever, Hot palms and soles, Red skin eruptions, Night sweats, Generalized fatigue... see more | Qing Hao Bie Jia Tang |
Blood Deficiency
Blood Deficiency in TCM is like when your body's tank runs low on the vital energy that blood provides. It's not exactly the same as anemia in modern medicine, which is about having too few red blood cells. Instead, Blood Deficiency in TCM is about your body not having enough of the life-giving qualities that blood brings, like nourishment and moisture. This can make you feel tired, look pale, and even feel dizzy or have blurry vision. It's like a garden not getting enough water to stay lush and vibrant. TCM sees this as an imbalance where the body isn't being nourished as it should be, impacting overall health and well-being.... see more
Blood Deficiency Patterns That Can Lead to Joint Stiffness
Common Symptoms: Limb Numbness Blurry Vision Dull Pale Complexion Scanty Menstruation Pale Lips Muscle Weakness Dizziness Tingling Of Limbs
| Pattern Name | Relevant Symptoms | Relevant Formulas |
|---|---|---|
| Liver Blood Deficiency | Joint pain, Blurry vision, Dull pale complexion, Scanty menstruation, Limb numbness, Pale lips, Muscle weakness, Dizziness, Tingling of limbs, Insomnia, Eye floaters, Night blindness, Amenorrhea, Withered and brittle nails, Dry hair, Skin dryness, Depression, Lack of direction, Vivid dreaming... see more | Si Wu Tang | Bu Gan Tang | Suan Zao Ren Tang | Qi Bao Mei Ran Dan |
| Painful Obstruction with Qi and Blood Deficiency | Stiffness in the neck shoulder and upper back, Feeling of heaviness, Limb numbness, Difficulty in moving, Stiffness in neck, shoulder, and upper back, Periarthritis of the shoulder, Rheumatoid arthritis... see more | Juan Bi Tang |
Yin Deficiency
Yin deficiency in TCM is a pattern of disharmony characterized by a depletion of the body's Yin energy, which represents the cooling, moistening, and nurturing aspects of our physiology. This condition often arises from factors like chronic stress, overwork, insufficient rest, or prolonged illness. Symptoms of Yin deficiency can include a sensation of heat, especially in the afternoon or evening, night sweats, insomnia, a dry mouth or throat, and a red tongue with little coating. There might also be a general feeling of restlessness or irritability. Since Yin is essential for balancing the body's active and warm Yang energy, its deficiency leads to a relative excess of Yang, manifesting as heat or dryness symptoms.... see more
Yin Deficiency Patterns That Can Lead to Joint Stiffness
Common Symptoms: Pulmonary Tuberculosis Renal Tuberculosis Hot Palms And Soles Night Sweats Generalized Fatigue Insomnia Arthralgia Nighttime Fever
| Pattern Name | Relevant Symptoms | Relevant Formulas |
|---|---|---|
| Kidney and Liver Yin Deficiency | Joint pain, Dizziness, Tinnitus, Hearing loss, Lower back pain, Vertical headaches, Occipital headache, Insomnia, Limb numbness, Tingling of limbs, Dry eyes, Blurry vision, Dry throat, Dry hair, Skin dryness, Withered and brittle nails, Vaginal dryness, Night sweats, Dry stools, Nocturnal emission, Scanty menstruation, Amenorrhea, Late menstruation, Infertility... see more | Qi Ju Di Huang Wan | Liu Wei Di Huang Wan | Gui Shao Di Huang Tang | Zuo Gui Yin |
| Empty-Heat caused by Yin Deficiency | Joint pain, Nighttime fever, Emaciation, Chronic pyelonephritis, Pulmonary tuberculosis, Renal tuberculosis, Tidal fever, Hot palms and soles, Red skin eruptions, Night sweats, Generalized fatigue... see more | Qing Hao Bie Jia Tang |
Wind
In TCM "Wind" is a concept that represents a pattern of disharmony, often characterized by its sudden and unpredictable nature, much like a gusty wind changing direction without warning. This pattern is associated with symptoms that come and go quickly or move around the body, such as itching, tremors, or even certain types of pain. Wind is considered to be a primary cause of illnesses that have these rapidly changing characteristics. In TCM, external Wind often refers to illnesses that start suddenly, like the common cold, believed to be caused by external pathogenic factors like climatic changes. On the other hand, internal Wind can be linked to internal imbalances and can manifest in conditions like dizziness or spasms. ... see more
Wind Patterns That Can Lead to Joint Stiffness
Common Symptoms: Headaches Swollen And Painful Joints Worsening At Night Chills Without Sweating Weight Loss Dizziness Shortness Of Breath Nausea Rheumatoid Arthritis
| Pattern Name | Relevant Symptoms | Relevant Formulas |
|---|---|---|
| Exterior Wind | Joint pain, Aversion to cold, Fever, Headaches, Anemophobia, Nasal discharge, Clear sputum, Itchy throat, Sneezing, Coughing, Muscle pain, Itchy skin... see more | Chuan Xiong Cha Tiao San |
| Painful Obstruction with Wind-Cold-Damp | Reduced range of motion in the affected joints, Swollen and painful joints worsening at night, Joint stiffness, Chills without sweating, Weight loss, Headaches, Dizziness, Shortness of breath, Nausea, Rheumatoid arthritis, Connective tissue disorders... see more | Gui Zhi Shao Yao Zhi Mu Tang |
Phlegm
In TCM "Phlegm" as a pattern of disharmony is a complex concept that extends beyond the physical manifestation of mucus. It represents a pathological factor that can disrupt the flow of Qi (vital energy) and blood, leading to various health issues. Phlegm in TCM is seen as a sticky, turbid substance arising from the body's inability to metabolize fluids properly, often due to a dysfunction of the spleen. It's not only associated with respiratory problems like cough and congestion but also with systemic issues. Symptoms can include a feeling of heaviness, mental cloudiness, dizziness, and in some cases, the formation of lumps or masses. Phlegm can even be "invisible," contributing to emotional disturbances like depression or stress. ... see more
Phlegm Patterns That Can Lead to Joint Stiffness
| Pattern Name | Relevant Symptoms | Relevant Formulas |
|---|---|---|
| Phlegm in the Channels joints and muscles | Joint stiff, Joints pain, Skin numbness, Skeletal deformities, Joint stiffness, Arthralgia, Muscle pain | Shen Tong Zhu Yu Tang |
Yang Deficiency
Yang deficiency in TCM refers to a state where the body's Yang energy, which is responsible for warmth, activity, and function, is weakened or diminished. This pattern of disharmony often arises from chronic illness, aging, or inherent constitutional weakness. Symptoms of Yang deficiency are typically associated with cold and sluggishness, such as a feeling of coldness, cold extremities, pale complexion, low energy or fatigue, and a desire for warmth. Digestive issues like poor appetite, loose stools, and water retention can also be indicative of Yang deficiency.... see more
Yang Deficiency Patterns That Can Lead to Joint Stiffness
| Pattern Name | Relevant Symptoms | Relevant Formulas |
|---|---|---|
| Yang Deficiency with Cold-Damp | Aching bones and joints, Body pain, Bone and joint pain, Cold extremities, Absence of thirst, Aversion to cold, Migraine, Cluster headache, Trigeminal neuralgia, Piriformis syndrome, Rheumatoid arthritis... see more | Fu Zi Tang |
Blood Stasis
Blood Stasis in TCM is a concept where the blood flow in the body is not as smooth or efficient as it should be. Imagine a river that's supposed to flow freely, but instead, it's getting blocked or moving too slowly in some parts. This can lead to various health issues, like pain that feels sharp or stabbing, dark bruises, and a complexion that looks purplish. TCM believes that good health relies on the smooth and vibrant flow of Qi and blood throughout the body, so when blood gets stuck, it's like a traffic jam in your body, leading to discomfort or health problems.... see more
Blood Stasis Patterns That Can Lead to Joint Stiffness
| Pattern Name | Relevant Symptoms | Relevant Formulas |
|---|---|---|
| Blood Stagnation | Shoulder stiffness, Dark face, Purple lips, Stabbing fixed pain, Abdominal masses, Purple nails, Menstrual cramps, Dark menstrual clots, Dark menstrual blood, Lumps... see more | Tao He Cheng Qi Tang | Da Huang Mu Dan Pi Tang | Gui Zhi Fu Ling Wan | Di Dang Tang | Dan Shen Yin | Da Huang Zhe Chong Wan | San Zhong Kui Jian Tang | Hai Tong Pi Tang | Huang Qi Gui Zhi Wu Wu Tang |
Yang Excess
Yang Excess in TCM refers to a state where there is an overabundance of Yang energy, leading to symptoms of heat and hyperactivity in the body. This pattern of disharmony often arises from factors like stress, excessive physical activity, overconsumption of spicy or heating foods, or an internal imbalance that causes Yang to flare up. Symptoms of Yang Excess include a feeling of heat, red face, irritability, restlessness, thirst, constipation, and a rapid, forceful pulse. Treatment in TCM for Yang Excess aims to cool down and subdue the excessive Yang while nurturing Yin energy to restore balance.... see more
Yang Excess Patterns That Can Lead to Joint Stiffness
| Pattern Name | Relevant Symptoms | Relevant Formulas |
|---|---|---|
| Liver Yang Rising | Stiff shoulder, Stiffness in the neck shoulder and upper back, Headaches, Dizziness, Tinnitus, Deafness, Blurry vision, Dry mouth, Dry throat, Insomnia, Irritability, Exhaustion, Anger, Stiff neck, Shoulder stiffness, Stiff upper back... see more | Qi Ju Di Huang Wan | Liu Wei Di Huang Wan | Tian Ma Gou Teng Yin | Ling Jiao Gou Teng Tang | Da Chai Hu Tang | Zhen Zhu Mu Wan | Zhen Xin An Shen Tang |
Qi Deficiency
Qi Deficiency in TCM is like running low on battery power. Qi is the vital energy that powers every function in your body. When there's a Qi Deficiency, it means your body doesn't have enough of this essential energy. This can make you feel tired all the time, weak, or even cause shortness of breath. It's similar to how you feel when you haven't had enough sleep or nutritious food. Your body just doesn't have the energy it needs to perform at its best. Unlike modern medicine, which often focuses on specific physical causes for fatigue and weakness, TCM views Qi Deficiency as an overall energy depletion that affects your entire well-being, and it seeks to replenish and balance this vital energy.... see more
Qi Deficiency Patterns That Can Lead to Joint Stiffness
| Pattern Name | Relevant Symptoms | Relevant Formulas |
|---|---|---|
| Painful Obstruction with Qi and Blood Deficiency | Stiffness in the neck shoulder and upper back, Feeling of heaviness, Limb numbness, Difficulty in moving, Stiffness in neck, shoulder, and upper back, Periarthritis of the shoulder, Rheumatoid arthritis... see more | Juan Bi Tang |
Liver
In TCM the Liver is viewed as the organ responsible for the smooth flow of Qi, Blood, and emotions throughout the body. It plays a key role in regulating mood, storing blood, supporting digestion, and ensuring the health of tendons and eyes. When the Liver malfunctions or is imbalanced in TCM, it can lead to a range of issues such as irritability, mood swings, menstrual irregularities, eye problems, and muscular stiffness or pain. A malfunctioning Liver in TCM reflects not only physical disturbances but also emotional and mental disharmony, emphasizing the holistic approach of TCM in addressing health and wellness.... see more
Liver Patterns That Can Lead to Joint Stiffness
Common Symptoms: Blurry Vision Dizziness Insomnia Scanty Menstruation Limb Numbness Tingling Of Limbs Amenorrhea Withered And Brittle Nails
| Pattern Name | Relevant Symptoms | Relevant Formulas |
|---|---|---|
| Liver Blood Deficiency | Joint pain, Blurry vision, Dull pale complexion, Scanty menstruation, Limb numbness, Pale lips, Muscle weakness, Dizziness, Tingling of limbs, Insomnia, Eye floaters, Night blindness, Amenorrhea, Withered and brittle nails, Dry hair, Skin dryness, Depression, Lack of direction, Vivid dreaming... see more | Si Wu Tang | Bu Gan Tang | Suan Zao Ren Tang | Qi Bao Mei Ran Dan |
| Kidney and Liver Yin Deficiency | Joint pain, Dizziness, Tinnitus, Hearing loss, Lower back pain, Vertical headaches, Occipital headache, Insomnia, Limb numbness, Tingling of limbs, Dry eyes, Blurry vision, Dry throat, Dry hair, Skin dryness, Withered and brittle nails, Vaginal dryness, Night sweats, Dry stools, Nocturnal emission, Scanty menstruation, Amenorrhea, Late menstruation, Infertility... see more | Qi Ju Di Huang Wan | Liu Wei Di Huang Wan | Gui Shao Di Huang Tang | Zuo Gui Yin |
| Liver Yang Rising | Stiff shoulder, Stiffness in the neck shoulder and upper back, Headaches, Dizziness, Tinnitus, Deafness, Blurry vision, Dry mouth, Dry throat, Insomnia, Irritability, Exhaustion, Anger, Stiff neck, Shoulder stiffness, Stiff upper back... see more | Qi Ju Di Huang Wan | Liu Wei Di Huang Wan | Tian Ma Gou Teng Yin | Ling Jiao Gou Teng Tang | Da Chai Hu Tang | Zhen Zhu Mu Wan | Zhen Xin An Shen Tang |
Kidney
In TCM the Kidneys are regarded as the body's most fundamental reservoir of Essence, known as Jing, which influences growth, reproduction, and aging. They are not just organs for filtering blood, but a holistic system governing vital life forces. When the Kidneys malfunction in TCM, it can manifest as a variety of health issues, such as chronic fatigue, reproductive problems, imbalances in fluid metabolism leading to edema or dryness, lower back pain, and a sense of fear or insecurity.... see more
Kidney Patterns That Can Lead to Joint Stiffness
| Pattern Name | Relevant Symptoms | Relevant Formulas |
|---|---|---|
| Kidney and Liver Yin Deficiency | Joint pain, Dizziness, Tinnitus, Hearing loss, Lower back pain, Vertical headaches, Occipital headache, Insomnia, Limb numbness, Tingling of limbs, Dry eyes, Blurry vision, Dry throat, Dry hair, Skin dryness, Withered and brittle nails, Vaginal dryness, Night sweats, Dry stools, Nocturnal emission, Scanty menstruation, Amenorrhea, Late menstruation, Infertility... see more | Qi Ju Di Huang Wan | Liu Wei Di Huang Wan | Gui Shao Di Huang Tang | Zuo Gui Yin |
TCM Herbal Formulas for Joint Stiffness
TCM utilizes a variety of herbs and formulas to counteract the external evils that contribute to joint stiffness. For conditions stemming from Cold and Dampness, warming and drying herbs are employed to restore the free flow of Qi and Blood.
Formulas like Wu Tou Tang and Gui Zhi Shao Yao Zhi Mu Tang, containing herbs like Prepared Sichuan Aconite and Cinnamon Twigs, are often prescribed to warm the channels and disperse Cold, as well as to alleviate the obstructive influence of Wind and Dampness. Herbs that resolve Phlegm, such as those found in Shen Tong Zhu Yu Tang, are used to clear internal blockages that can lead to stiffness.
Explore below some TCM herbal formulas used to address joint stiffness, organized by cause and by formula type.
- By Cause
- By Formula Type
- Cold
- Dampness
- Heat
- Blood Deficiency
- Yin Deficiency
- Wind
- Phlegm
- Yang Deficiency
- Blood Stasis
- Yang Excess
- Qi Deficiency
- View More Causes
- Formulas that invigorate blood and dispel blood stagnation
- Formulas that dispel wind-Damp
- Formulas that nourish yin and tonify
- Formulas that warm the meridians and disperse cold
- Formulas that dredge and disperse external wind
- Formulas that tonify blood
- Formulas that nourish the heart and calm the mind
- Formulas that pacify and extinguish internal wind
- Formulas that regulate blood
- Formulas that warm and transform water and dampness
- Formulas that expel dampness
- Formulas that clear heat and expel dampness
- Formulas that tonify yin and yang
- Formulas that clear heat from deficiency
- Formulas that clear internal abscesses and sores
- Formulas that clear external abscesses and sores
- External formulas for external disorders
- Formulas that release the exterior and purge the interior
- Formulas that sedate and calm the mind
Top Formula for Cold:
Xiao Huo Luo Dan
Suitable for Cold patterns that may cause joint stiffness, such as Cold invading the Channels joints and muscles or Wind invading the Channels joints and muscles
Learn moreAll Formulas Recommended for Joint Stiffness Caused by Cold
| Formula | Patterns Suitable For |
|---|---|
| Xiao Huo Luo Dan | Cold invading the Channels joints and muscles, Wind invading the Channels joints and muscles... see more |
| Wu Tou Tang | Cold invading the Channels joints and muscles |
| Da Fang Feng Tang | Wind invading the Channels joints and muscles |
| Gui Zhi Shao Yao Zhi Mu Tang | Painful Obstruction with Wind-Cold-Damp |
| Fu Zi Tang | Yang Deficiency with Cold-Damp |
| Wei Ling Tang | Damp-Cold |
Top Formula for Dampness:
Xiao Huo Luo Dan
Suitable for Dampness patterns that may cause joint stiffness, such as Dampness invading the Channels joints and muscles
Learn moreAll Formulas Recommended for Joint Stiffness Caused by Dampness
| Formula | Patterns Suitable For |
|---|---|
| Xiao Huo Luo Dan | Dampness invading the Channels joints and muscles |
| Gui Zhi Shao Yao Zhi Mu Tang | Painful Obstruction with Wind-Cold-Damp |
| Shu Jing Huo Xue Tang | Dampness invading the Channels joints and muscles |
| Fu Zi Tang | Yang Deficiency with Cold-Damp |
| Ba Zheng San | Damp-Heat |
| Wei Ling Tang | Damp-Cold |
Top Formula for Heat:
Xuan Bi Tang
Suitable for Heat patterns that may cause joint stiffness, such as Heat invading the Channels joints and muscles
Learn moreAll Formulas Recommended for Joint Stiffness Caused by Heat
| Formula | Patterns Suitable For |
|---|---|
| Xuan Bi Tang | Heat invading the Channels joints and muscles |
| Ba Zheng San | Damp-Heat |
| Qing Hao Bie Jia Tang | Empty-Heat caused by Yin Deficiency |
Top Formula for Blood Deficiency:
Si Wu Tang
Suitable for Blood Deficiency patterns that may cause joint stiffness, such as Liver Blood Deficiency
Learn moreAll Formulas Recommended for Joint Stiffness Caused by Blood Deficiency
| Formula | Patterns Suitable For |
|---|---|
| Si Wu Tang | Liver Blood Deficiency |
| Bu Gan Tang | Liver Blood Deficiency |
| Suan Zao Ren Tang | Liver Blood Deficiency |
| Qi Bao Mei Ran Dan | Liver Blood Deficiency |
| Juan Bi Tang | Painful Obstruction with Qi and Blood Deficiency |
Top Formula for Yin Deficiency:
Qi Ju Di Huang Wan
Suitable for Yin Deficiency patterns that may cause joint stiffness, such as Kidney and Liver Yin Deficiency
Learn moreAll Formulas Recommended for Joint Stiffness Caused by Yin Deficiency
| Formula | Patterns Suitable For |
|---|---|
| Qi Ju Di Huang Wan | Kidney and Liver Yin Deficiency |
| Liu Wei Di Huang Wan | Kidney and Liver Yin Deficiency |
| Qing Hao Bie Jia Tang | Empty-Heat caused by Yin Deficiency |
| Gui Shao Di Huang Tang | Kidney and Liver Yin Deficiency |
| Zuo Gui Yin | Kidney and Liver Yin Deficiency |
Top Formula for Wind:
Gui Zhi Shao Yao Zhi Mu Tang
Suitable for Wind patterns that may cause joint stiffness, such as Painful Obstruction with Wind-Cold-Damp
Learn moreAll Formulas Recommended for Joint Stiffness Caused by Wind
| Formula | Patterns Suitable For |
|---|---|
| Gui Zhi Shao Yao Zhi Mu Tang | Painful Obstruction with Wind-Cold-Damp |
| Chuan Xiong Cha Tiao San | Exterior Wind |
Top Formula for Phlegm:
Shen Tong Zhu Yu Tang
Suitable for Phlegm patterns that may cause joint stiffness, such as Phlegm in the Channels joints and muscles
Learn moreTop Formula for Yang Deficiency:
Fu Zi Tang
Suitable for Yang Deficiency patterns that may cause joint stiffness, such as Yang Deficiency with Cold-Damp
Learn moreTop Formula for Blood Stasis:
Tao He Cheng Qi Tang
Suitable for Blood Stasis patterns that may cause joint stiffness, such as Blood Stagnation
Learn moreAll Formulas Recommended for Joint Stiffness Caused by Blood Stasis
| Formula | Patterns Suitable For |
|---|---|
| Tao He Cheng Qi Tang | Blood Stagnation |
| Da Huang Mu Dan Pi Tang | Blood Stagnation |
| Gui Zhi Fu Ling Wan | Blood Stagnation |
| Di Dang Tang | Blood Stagnation |
| Dan Shen Yin | Blood Stagnation |
| Da Huang Zhe Chong Wan | Blood Stagnation |
| San Zhong Kui Jian Tang | Blood Stagnation |
| Hai Tong Pi Tang | Blood Stagnation |
| Huang Qi Gui Zhi Wu Wu Tang | Blood Stagnation |
Top Formula for Yang Excess:
Qi Ju Di Huang Wan
Suitable for Yang Excess patterns that may cause joint stiffness, such as Liver Yang Rising
Learn moreAll Formulas Recommended for Joint Stiffness Caused by Yang Excess
| Formula | Patterns Suitable For |
|---|---|
| Qi Ju Di Huang Wan | Liver Yang Rising |
| Liu Wei Di Huang Wan | Liver Yang Rising |
| Tian Ma Gou Teng Yin | Liver Yang Rising |
| Ling Jiao Gou Teng Tang | Liver Yang Rising |
| Da Chai Hu Tang | Liver Yang Rising |
| Zhen Zhu Mu Wan | Liver Yang Rising |
| Zhen Xin An Shen Tang | Liver Yang Rising |
Top Formula for Qi Deficiency:
Juan Bi Tang
Suitable for Qi Deficiency patterns that may cause joint stiffness, such as Painful Obstruction with Qi and Blood Deficiency
Learn moreFormulas that dispel Wind-Damp
These formulas are suitable for some joint stiffness-causing patterns like Painful Obstruction or Wind invading the Channels joints and muscles.
One such formula is Da Fang Feng Tang, with saposhnikovia root as a key herb.
Other formulas of this category are listed in the table below.
All "formulas that dispel wind-Damp" recommended for joint stiffness
| Formula | Patterns Suitable For (if applicable) |
|---|---|
| Da Fang Feng Tang | Painful Obstruction, Wind invading the Channels joints and muscles |
| Gui Zhi Shao Yao Zhi Mu Tang | Painful Obstruction with Wind-Cold-Damp |
| Xuan Bi Tang | Heat invading the Channels joints and muscles |
| Juan Bi Tang | Painful Obstruction with Qi and Blood Deficiency |
Formulas that dredge and disperse External Wind
These formulas are suitable for some joint stiffness-causing patterns like Cold invading the Channels joints and muscles or Dampness invading the Channels joints and muscles.
One such formula is Xiao Huo Luo Dan, with prepared kusnezoffii aconite as a key herb.
Other formulas of this category are listed in the table below.
All "formulas that dredge and disperse external wind" recommended for joint stiffness
| Formula | Patterns Suitable For (if applicable) |
|---|---|
| Xiao Huo Luo Dan | Cold invading the Channels joints and muscles, Dampness invading the Channels joints and muscles, Painful Obstruction, Wind invading the Channels joints and muscles... see more |
| Chuan Xiong Cha Tiao San | Exterior Wind |
Formulas that warm the Meridians and disperse Cold
These formulas are suitable for some joint stiffness-causing patterns like Cold invading the Channels joints and muscles or Painful Obstruction.
One such formula is Wu Tou Tang, with prepared sichuan aconite as a key herb.
Other formulas of this category are listed in the table below.
All "formulas that warm the meridians and disperse cold" recommended for joint stiffness
| Formula | Patterns Suitable For (if applicable) |
|---|---|
| Wu Tou Tang | Cold invading the Channels joints and muscles, Painful Obstruction |
| Huang Qi Gui Zhi Wu Wu Tang | Blood Stagnation |
Formulas that invigorate Blood and dispel Blood Stagnation
These formulas are suitable for some joint stiffness-causing patterns like Dampness invading the Channels joints and muscles.
One such formula is Shu Jing Huo Xue Tang, with dong quai as a key herb.
Other formulas of this category are listed in the table below.
All "formulas that invigorate blood and dispel blood stagnation" recommended for joint stiffness
| Formula | Patterns Suitable For (if applicable) |
|---|---|
| Shu Jing Huo Xue Tang | Dampness invading the Channels joints and muscles |
| Tao He Cheng Qi Tang | Blood Stagnation |
| Gui Zhi Fu Ling Wan | Blood Stagnation |
| Di Dang Tang | Blood Stagnation |
| Dan Shen Yin | Blood Stagnation |
| Da Huang Zhe Chong Wan | Blood Stagnation |
Formulas that nourish Yin and tonify
These formulas are suitable for some joint stiffness-causing patterns like Kidney and Liver Yin Deficiency or Liver Yang Rising.
One such formula is Qi Ju Di Huang Wan, with prepared rehmannia as a key herb.
Other formulas of this category are listed in the table below.
All "formulas that nourish yin and tonify" recommended for joint stiffness
| Formula | Patterns Suitable For (if applicable) |
|---|---|
| Qi Ju Di Huang Wan | Kidney and Liver Yin Deficiency, Liver Yang Rising |
| Liu Wei Di Huang Wan | Kidney and Liver Yin Deficiency, Liver Yang Rising |
| Gui Shao Di Huang Tang | Kidney and Liver Yin Deficiency |
| Zuo Gui Yin | Kidney and Liver Yin Deficiency |
Formulas that nourish the Heart and calm the Mind
These formulas are suitable for some joint stiffness-causing patterns like Liver Blood Deficiency.
One such formula is Suan Zao Ren Tang, with jujube seeds as a key herb.
Other formulas of this category are listed in the table below.
All "formulas that nourish the heart and calm the mind" recommended for joint stiffness
| Formula | Patterns Suitable For (if applicable) |
|---|---|
| Suan Zao Ren Tang | Liver Blood Deficiency |
| Zhen Xin An Shen Tang | Liver Yang Rising |
Formulas that tonify Blood
These formulas are suitable for some joint stiffness-causing patterns like Liver Blood Deficiency.
One such formula is Si Wu Tang, with prepared rehmannia as a key herb.
Other formulas of this category are listed in the table below.
All "formulas that tonify blood" recommended for joint stiffness
| Formula | Patterns Suitable For (if applicable) |
|---|---|
| Si Wu Tang | Liver Blood Deficiency |
| Bu Gan Tang | Liver Blood Deficiency |
Formulas that pacify and extinguish Internal Wind
These formulas are suitable for some joint stiffness-causing patterns like Liver Yang Rising.
One such formula is Tian Ma Gou Teng Yin, with gastrodia rhizome as a key herb.
Other formulas of this category are listed in the table below.
All "formulas that pacify and extinguish internal wind" recommended for joint stiffness
| Formula | Patterns Suitable For (if applicable) |
|---|---|
| Tian Ma Gou Teng Yin | Liver Yang Rising |
| Ling Jiao Gou Teng Tang | Liver Yang Rising |
Formulas that regulate Blood
These formulas are suitable for some joint stiffness-causing patterns like Phlegm in the Channels joints and muscles.
One such formula is Shen Tong Zhu Yu Tang, with peach kernel as a key herb.
Formulas that warm and transform water and Dampness
These formulas are suitable for some joint stiffness-causing patterns like Yang Deficiency with Cold-Damp.
One such formula is Fu Zi Tang, with prepared aconite as a key herb.
Formulas that expel Dampness
These formulas are suitable for some joint stiffness-causing patterns like Damp-Cold.
One such formula is Wei Ling Tang, with water plantain as a key herb.
Formulas that clear Heat and expel dampness
These formulas are suitable for some joint stiffness-causing patterns like Damp-Heat.
One such formula is Ba Zheng San, with chinese pink herb as a key herb.
Formulas that tonify Yin and Yang
These formulas are suitable for some joint stiffness-causing patterns like Liver Blood Deficiency.
One such formula is Qi Bao Mei Ran Dan, with fleeceflower root as a key herb.
Formulas that clear Heat from Deficiency
These formulas are suitable for some joint stiffness-causing patterns like Empty-Heat caused by Yin Deficiency.
One such formula is Qing Hao Bie Jia Tang, with softshell turtle shell as a key herb.
Formulas that clear internal abscesses and sores
These formulas are suitable for some joint stiffness-causing patterns like Blood Stagnation.
One such formula is Da Huang Mu Dan Pi Tang, with rhubarb as a key herb.
Formulas that clear external abscesses and sores
These formulas are suitable for some joint stiffness-causing patterns like Blood Stagnation.
One such formula is San Zhong Kui Jian Tang, with phellodendron bark as a key herb.
External formulas for External disorders
These formulas are suitable for some joint stiffness-causing patterns like Blood Stagnation.
One such formula is Hai Tong Pi Tang, with erythrinae bark as a key herb.
Formulas that release the Exterior and purge the Interior
These formulas are suitable for some joint stiffness-causing patterns like Liver Yang Rising.
One such formula is Da Chai Hu Tang, with bupleurum root as a key herb.
Formulas that sedate and calm the Mind
These formulas are suitable for some joint stiffness-causing patterns like Liver Yang Rising.
One such formula is Zhen Zhu Mu Wan, with mother of pearl as a key herb.
Acupoints for Joint Stiffness
Acupuncture is another cornerstone of TCM treatment for joint stiffness. Specific acupoints are chosen to expel pathogenic factors and stimulate the body's healing response. Points such as Huatuojiaji (EX-B-2) are selected for their ability to harmonize the organs and remove obstructions caused by external evils like Dampness and Cold.
Other points along the Bladder Channel, such as Geguan (BL-46), are utilized to regulate Qi throughout the body and alleviate pain. By targeting these acupoints, TCM practitioners aim to restore the balance of Yin and Yang in the body, thus improving joint mobility and reducing stiffness.
Explore below some acupoints used to address joint stiffness, organized by meridian.
- By Meridian
- Gall Bladder Channel
- Stomach Channel
- Large Intestine Channel
- Bladder Channel
- Extra Points: Lower Extremities (EX-LE)
- Heart Channel
- Extra Points: Back (EX-B)
- Spleen Channel
- Liver Channel
- Extra Points: Upper Extremities (EX-UE)
- Small Intestine Channel
- Triple Burner Channel
- Lung Channel
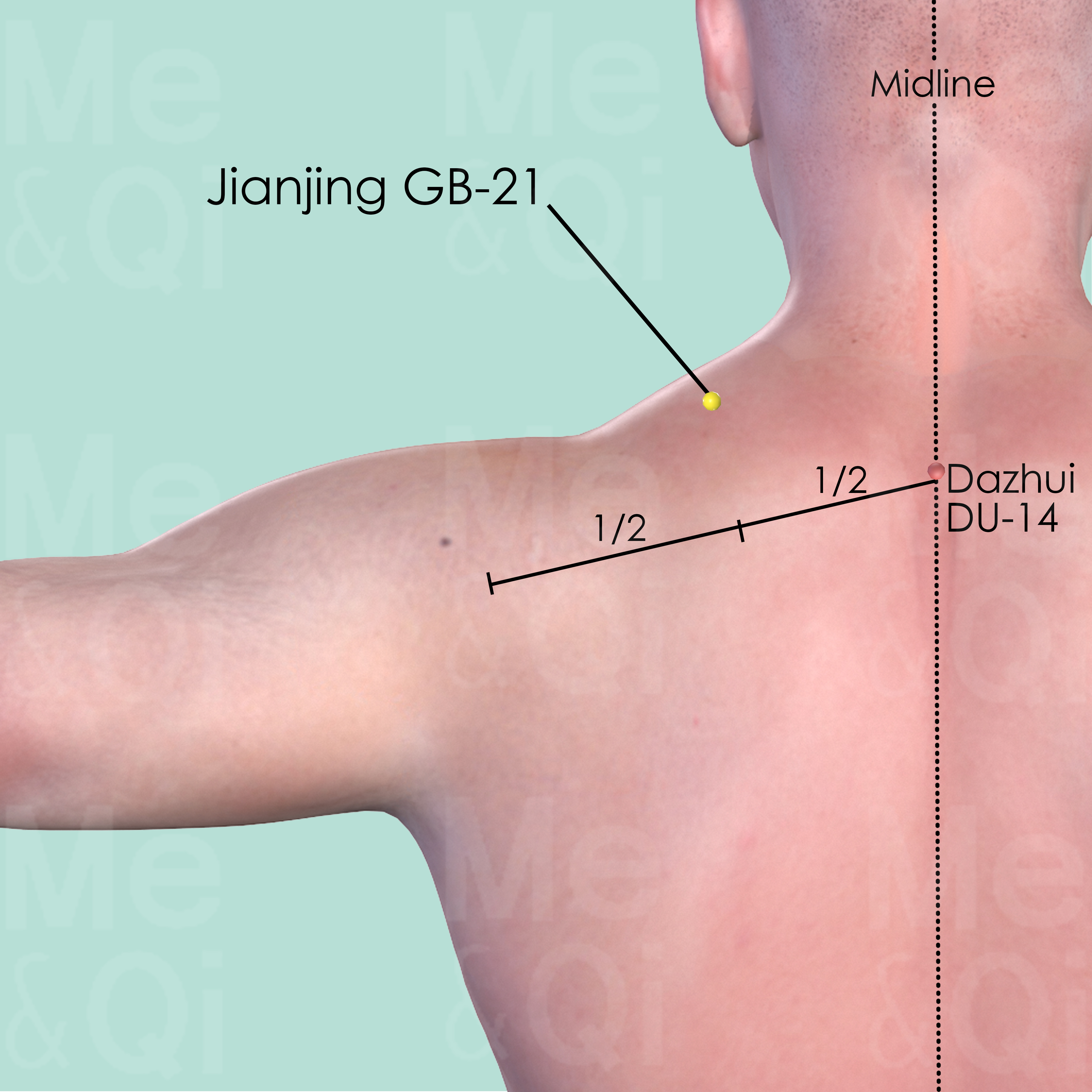
Jianjing GB-21
Midway between Dazhui DU-14 and the lateral extremity of the acromion, at the highest point of the shoulder.
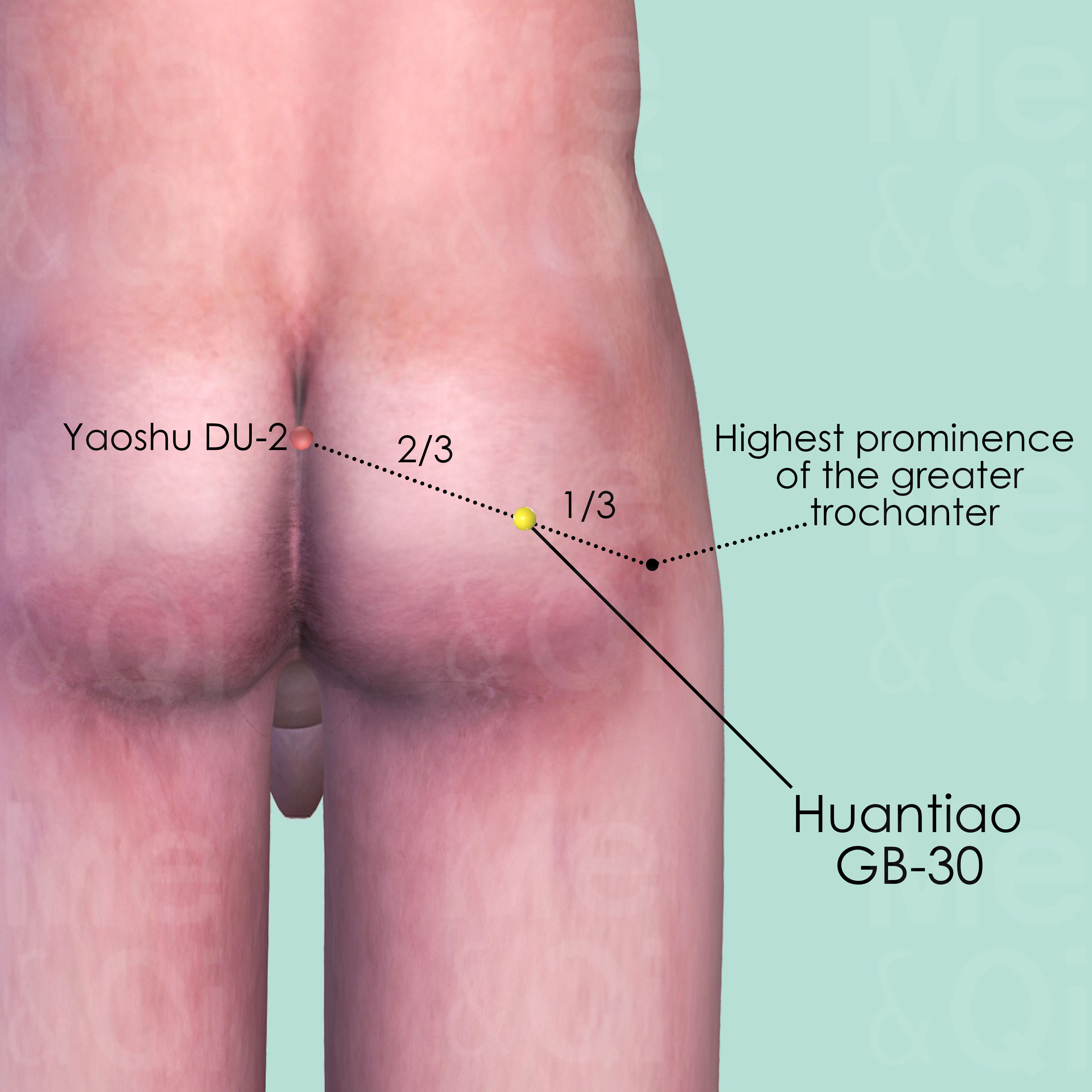
Huantiao GB-30
At the junction of the middle and lateral third of the distance between the great trochanter and Yaoshu DU-2 of the hiatus of the sacrum. When locating the point, put the patient in lateral recumbent position with the thigh flexed.
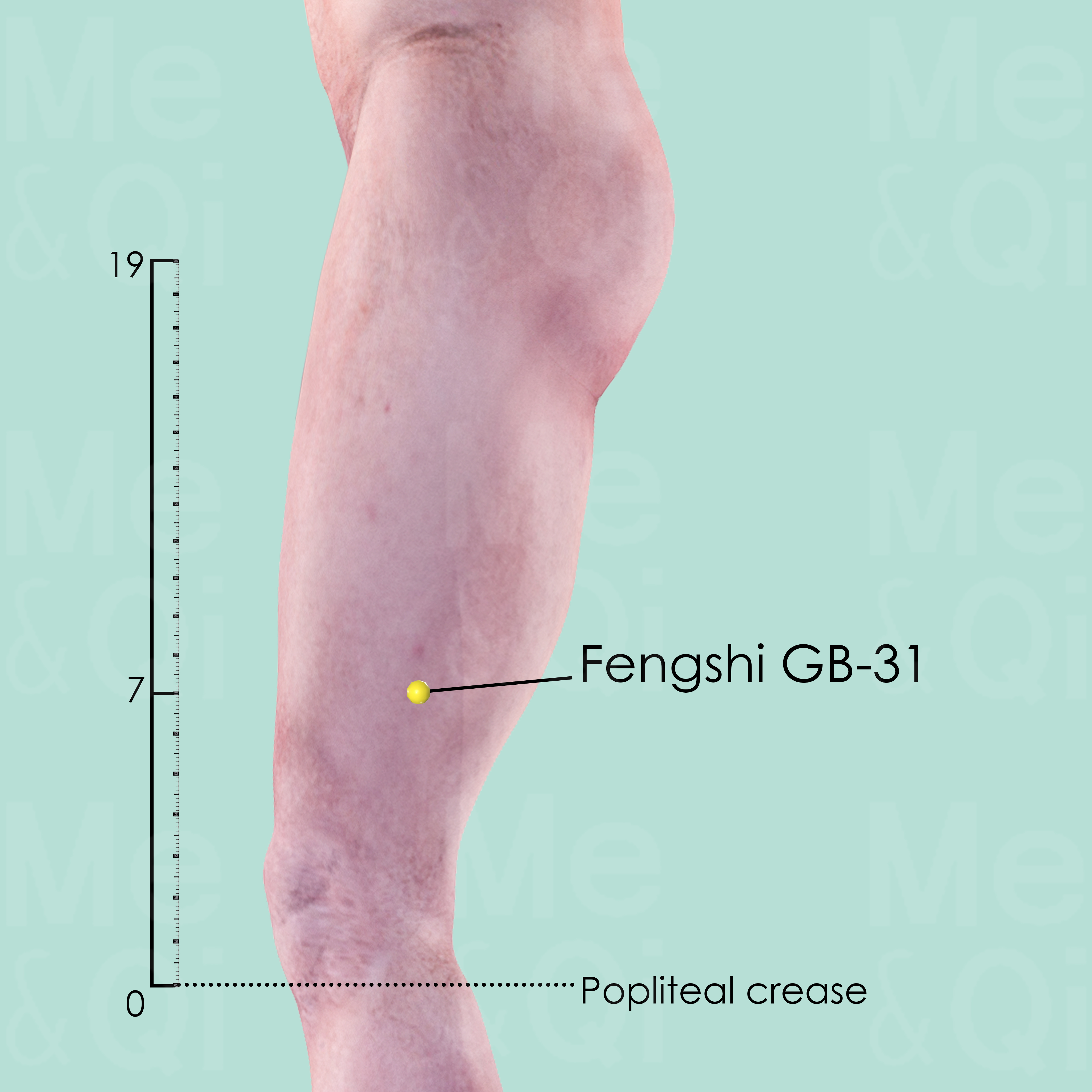
Fengshi GB-31
On the midline of the lateral aspect of the thigh, 7 cun above the transverse politeal crease.
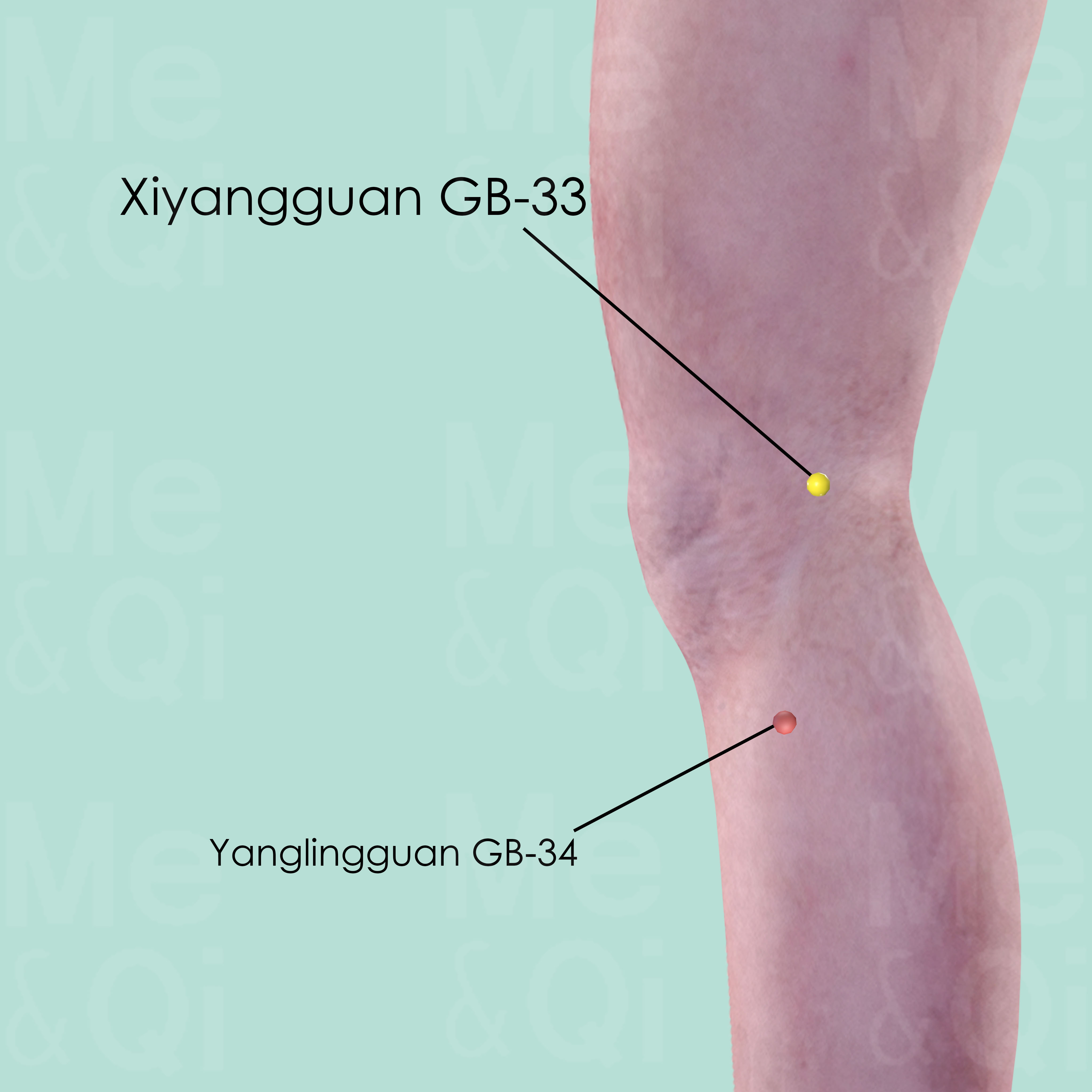
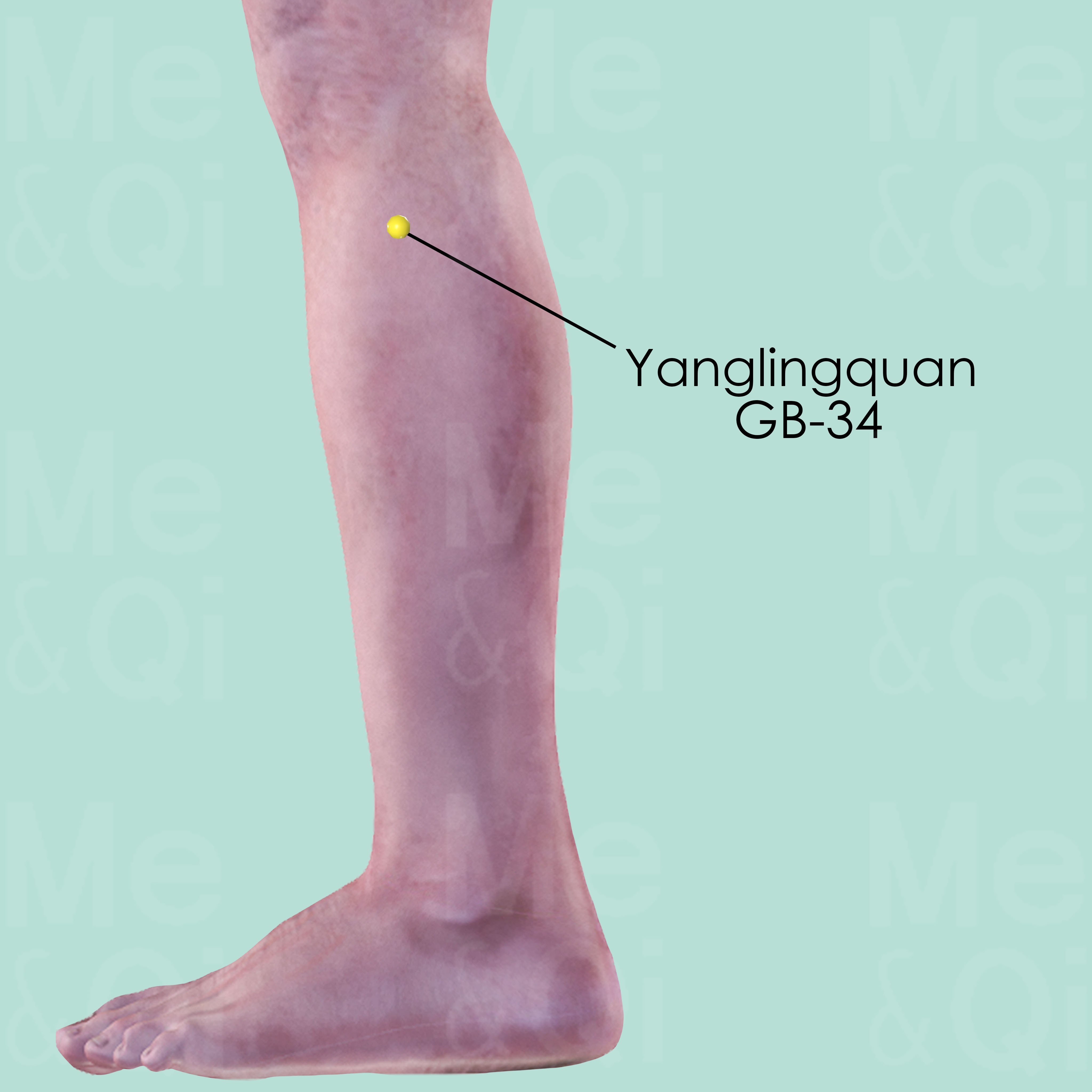
Xiyangguan GB-33
When the knee is flexed, Xiyangguan GB-33 is above Yanglingguan GB-34, in the depression between the shaft of the lateral epicondyle and the tendon of the biceps femoris muscle.
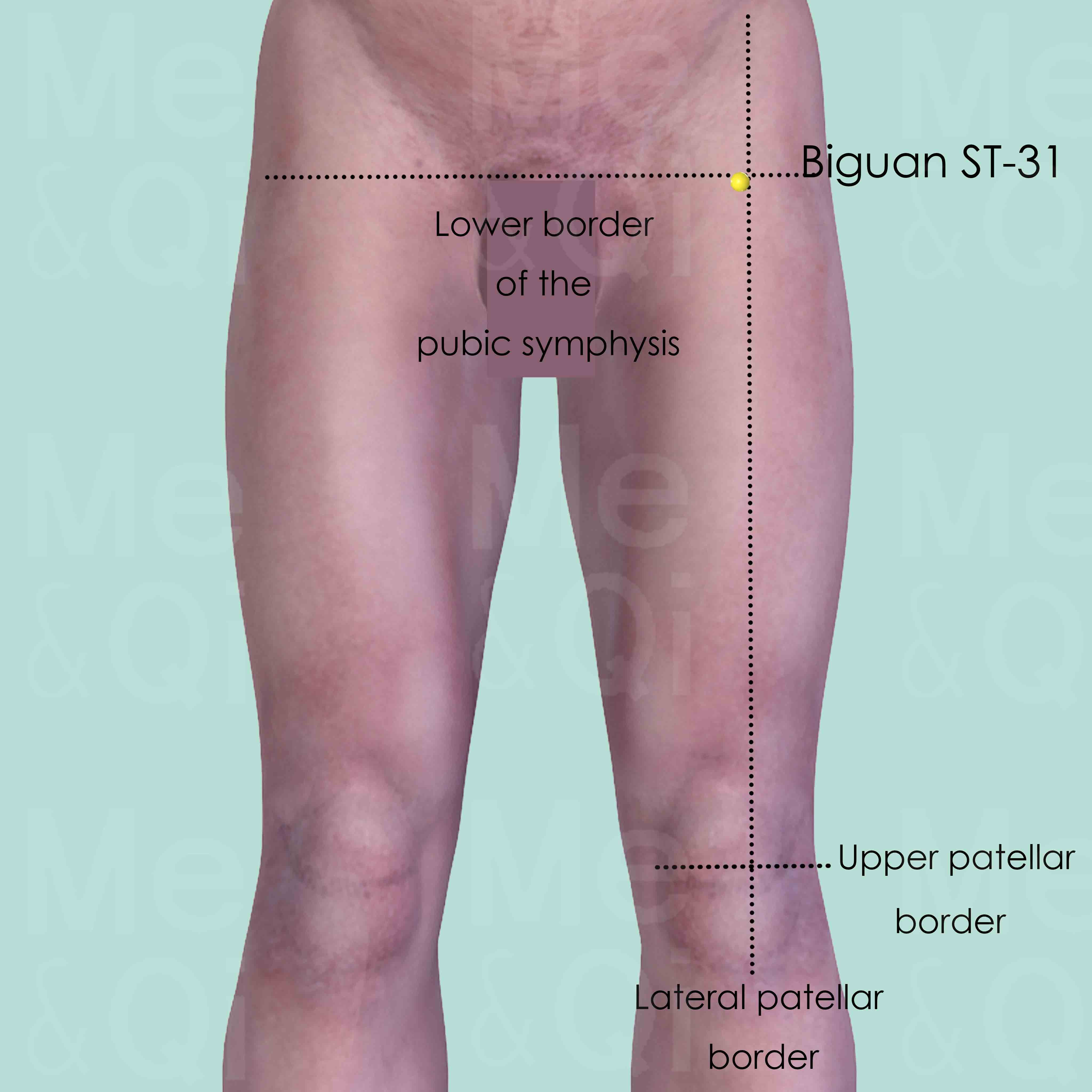
Biguan ST-31
Directly below the anterior superior iliac spine (ASIS), at the level of the lower border of the pubic symphysis, in the depression on the lateral side of sartorius muscle when the thigh is flex.
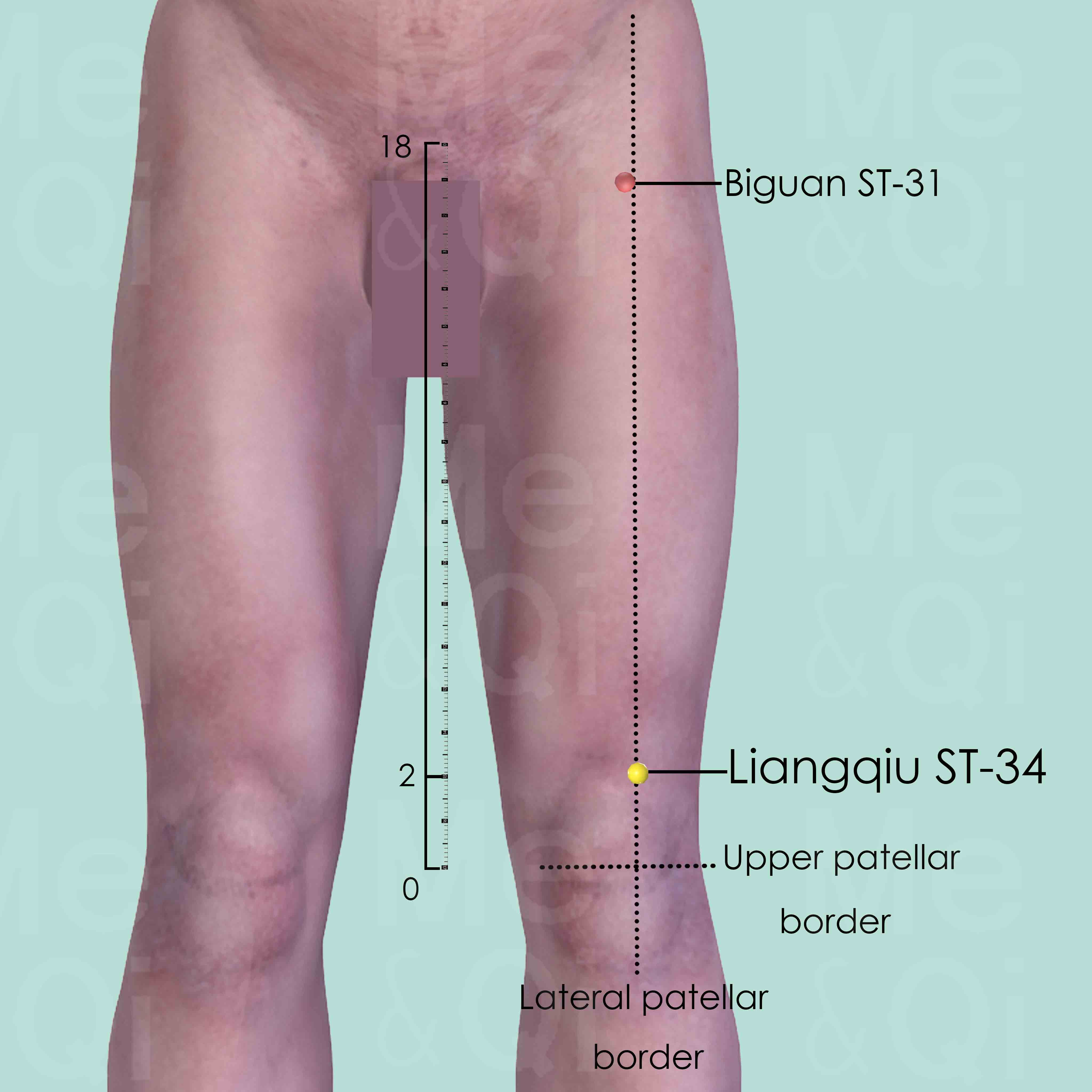
Liangqiu ST-34
2 cun above the upper-lateral border of the patella, on a line between the upper lateral patellar border and the anterior superior iliac spine (ASIS).
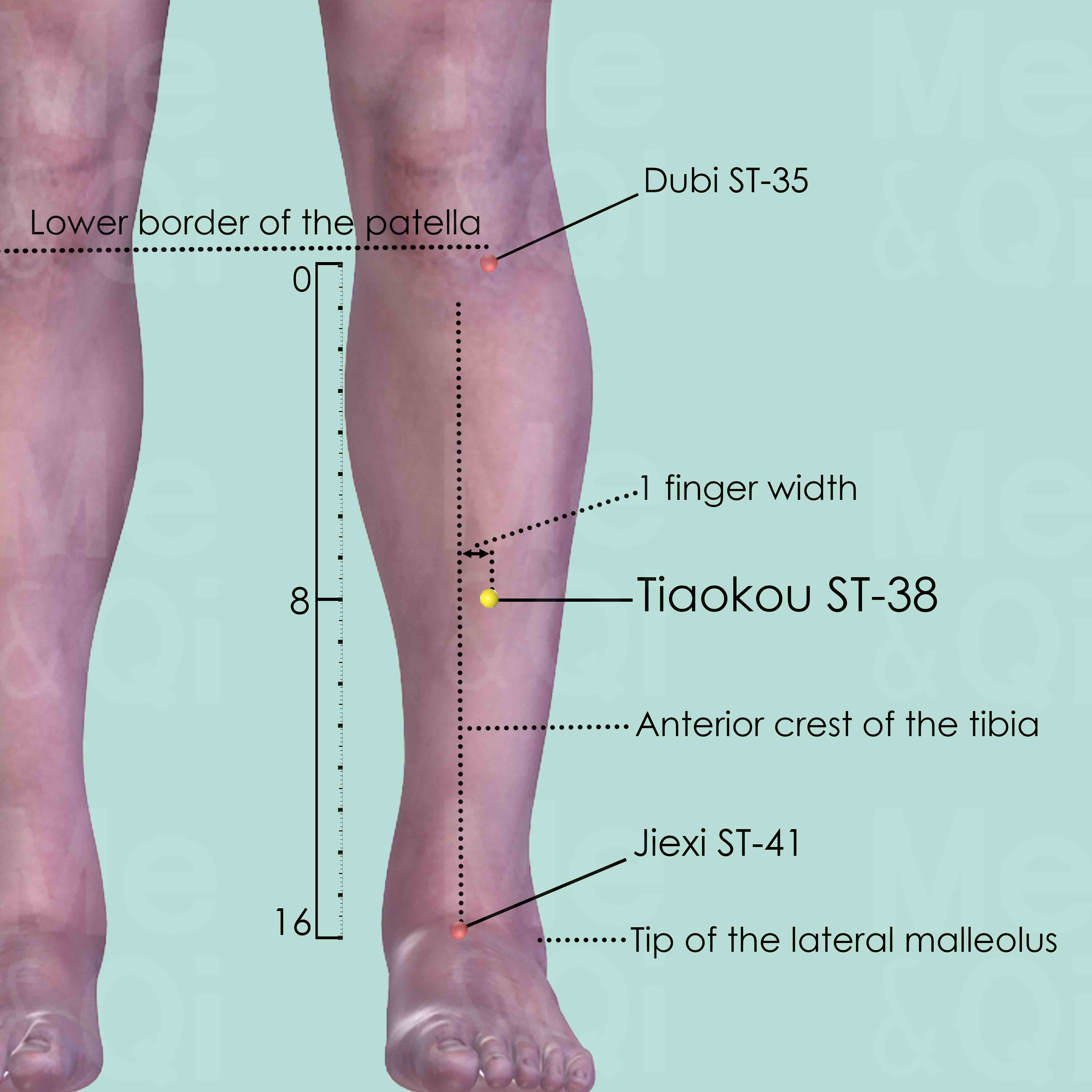
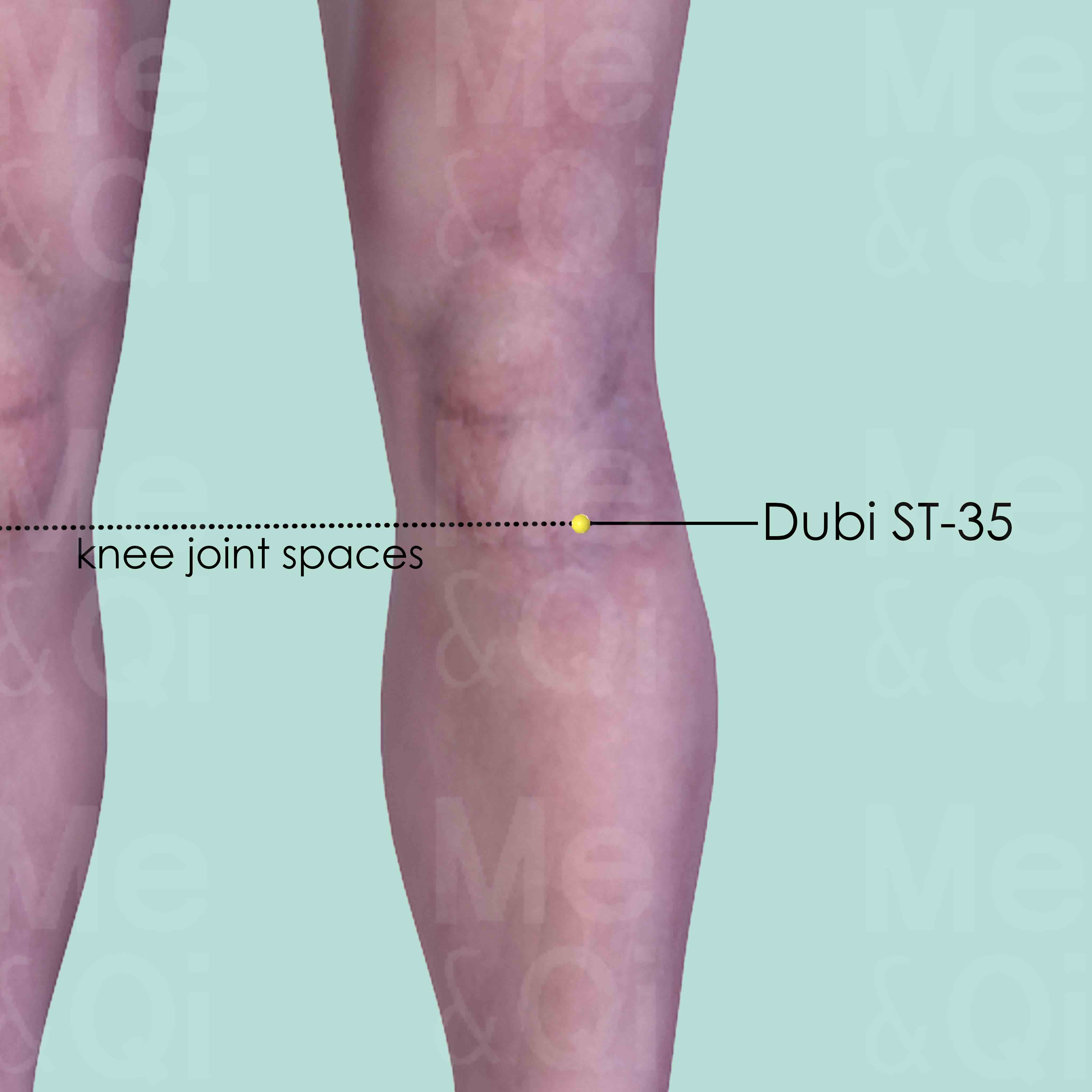
Tiaokou ST-38
8 cun below Dubi ST-35, midway between Dubi ST-35 and Jiexi ST-41, one middle finger-width from the anterior crest of the tibia.
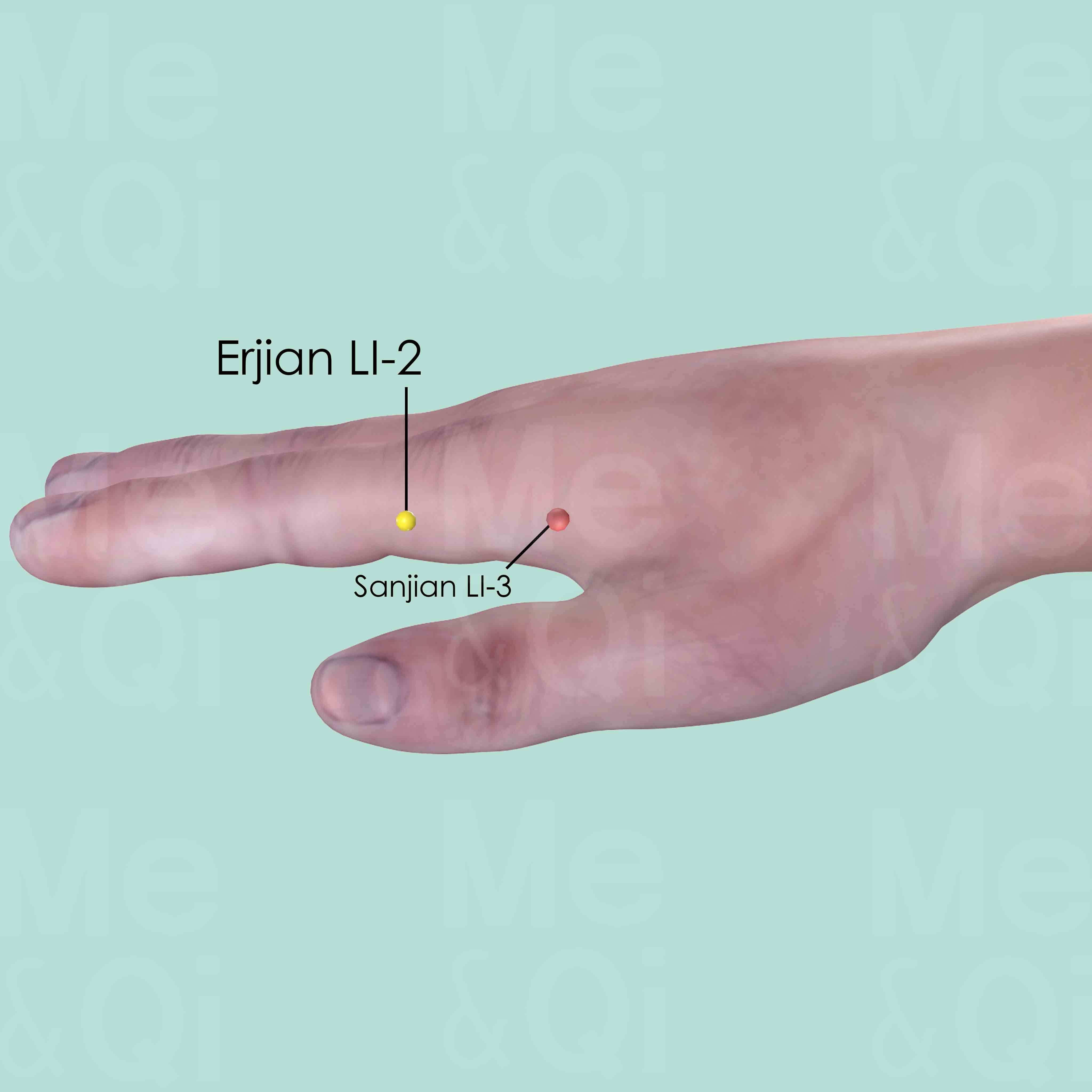
Erjian LI-2
On the radial side of the index finger, distal to the metacarpophalangeal joint, at the junction of the white and red skin.
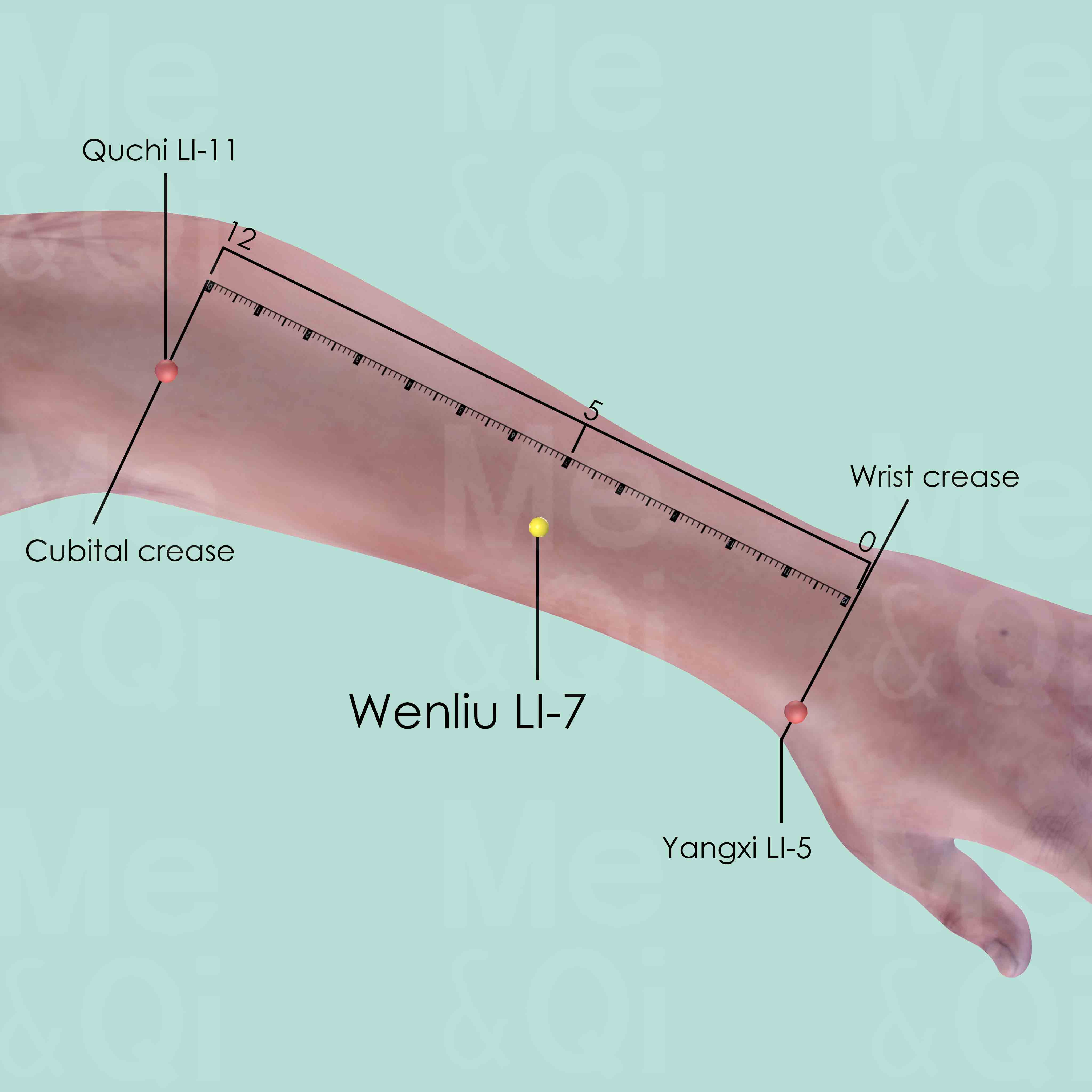
Wenliu LI-7
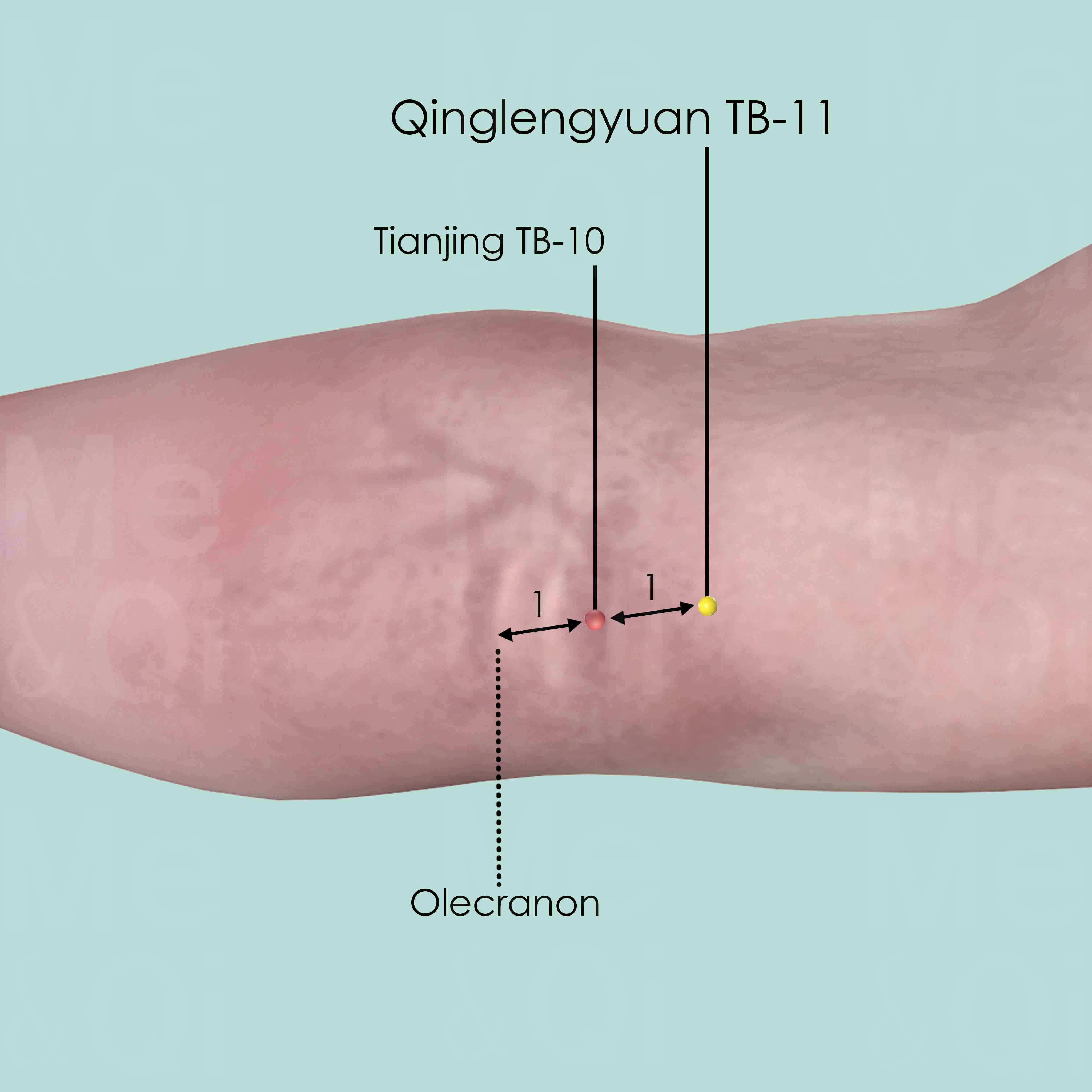
When a fist is made, with the ulnar side downward and elbow flexed, the point is 5 cun above Yangxi LI-5 at the wrist crease, 1 cun distal to the midpoint of the line joining Yangxi LI-5 and Quchi LI-11.
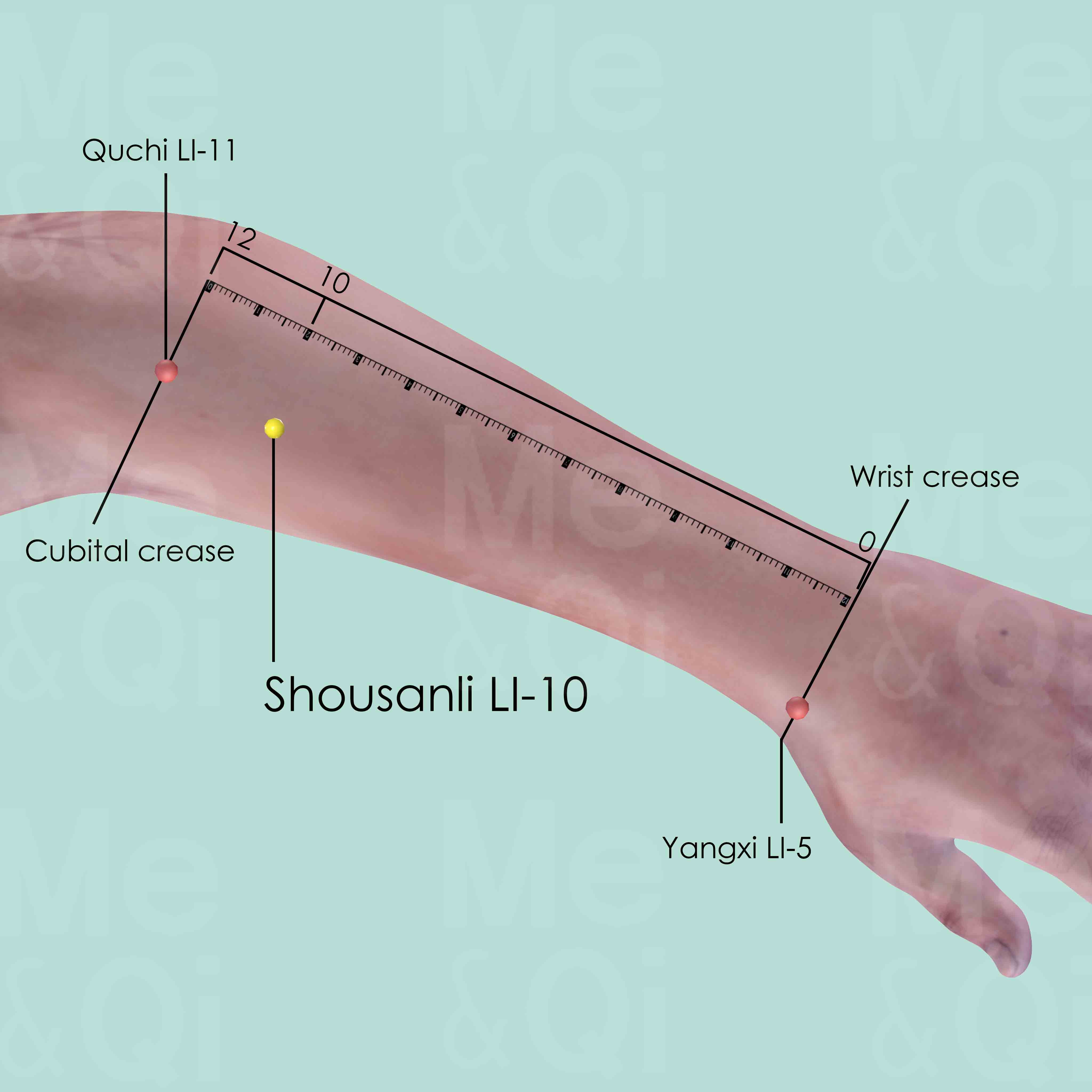
Shousanli LI-10
When a fist is made, with the ulnar side downward and elbow flexed, the point is 2 cun distal to Quchi LI-11 of the line joining Yangxi LI-5 and Quchi LI-11.
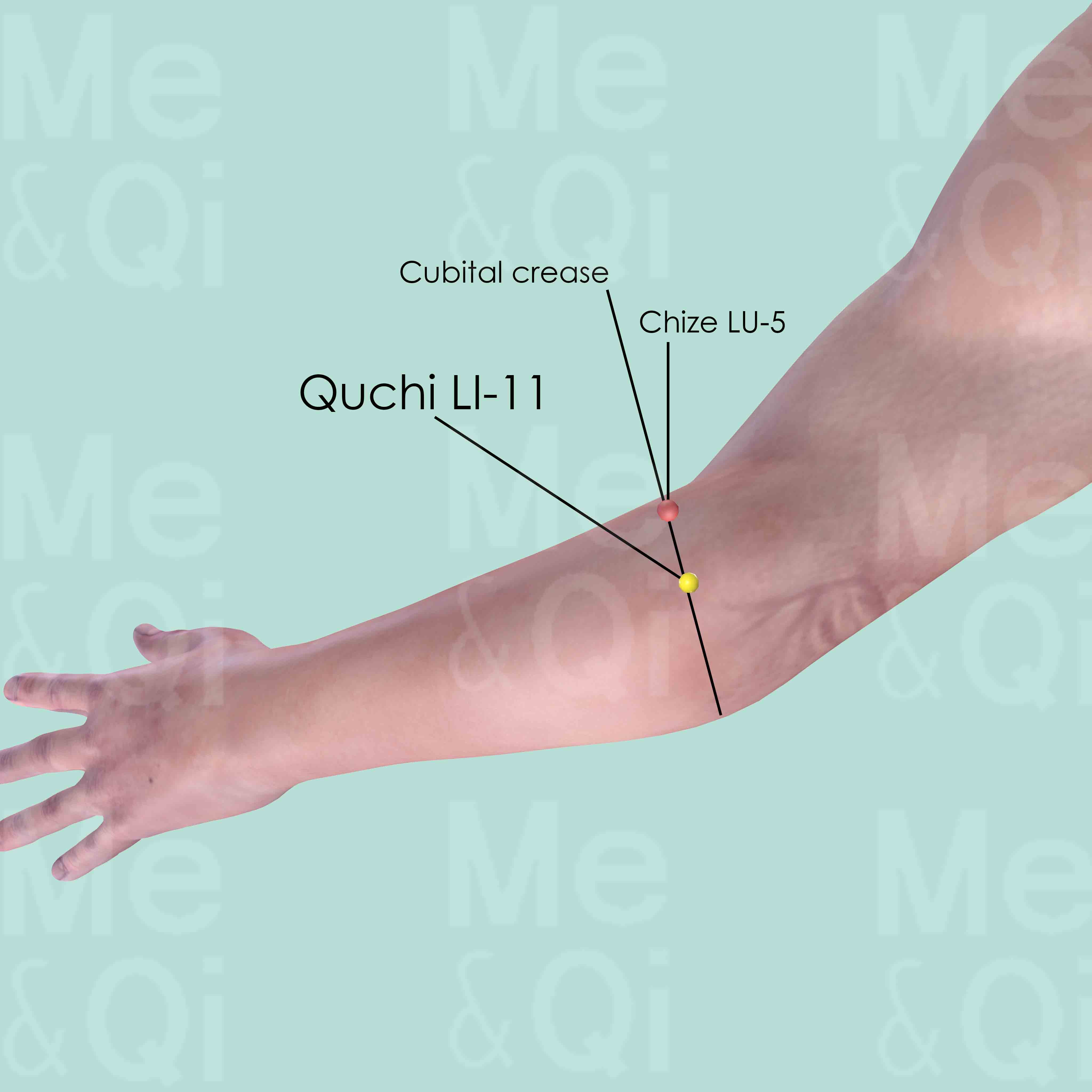
Quchi LI-11
When the elbow is flexed, Quchi LI-11 is in the depression at the lateral end of the cubital crease, midway between Chize LU-5 and the lateral epicondyle of the humerus.
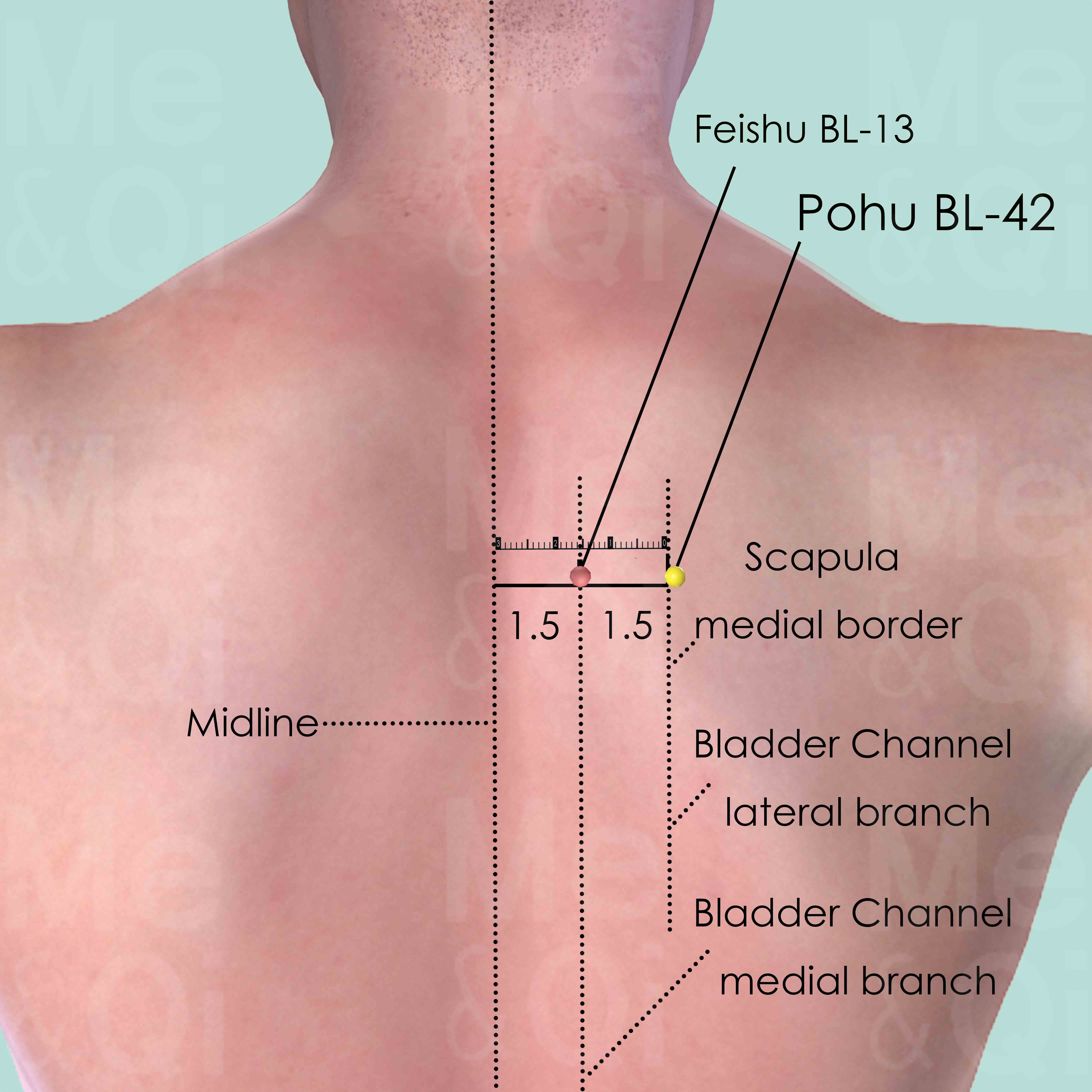
Pohu BL-42
3 cun (about 4 finger-breadths) lateral to the lower border of the spinous process of the 3rd thoracic vertebra (T3).
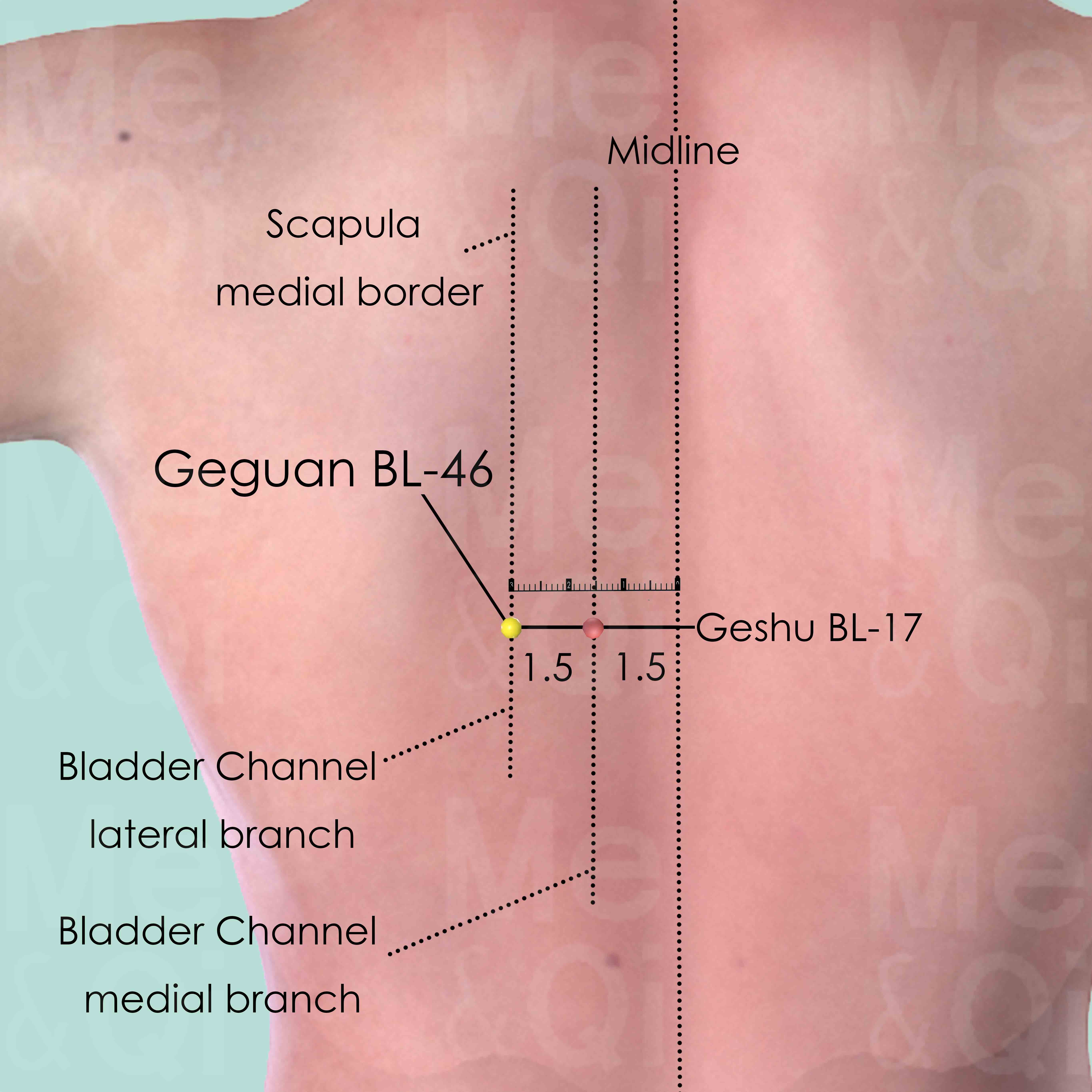
Geguan BL-46
3 cun (about 4 finger-breadths) lateral to the lower border of the spinous process of the 7th thoracic vertebra (T7).
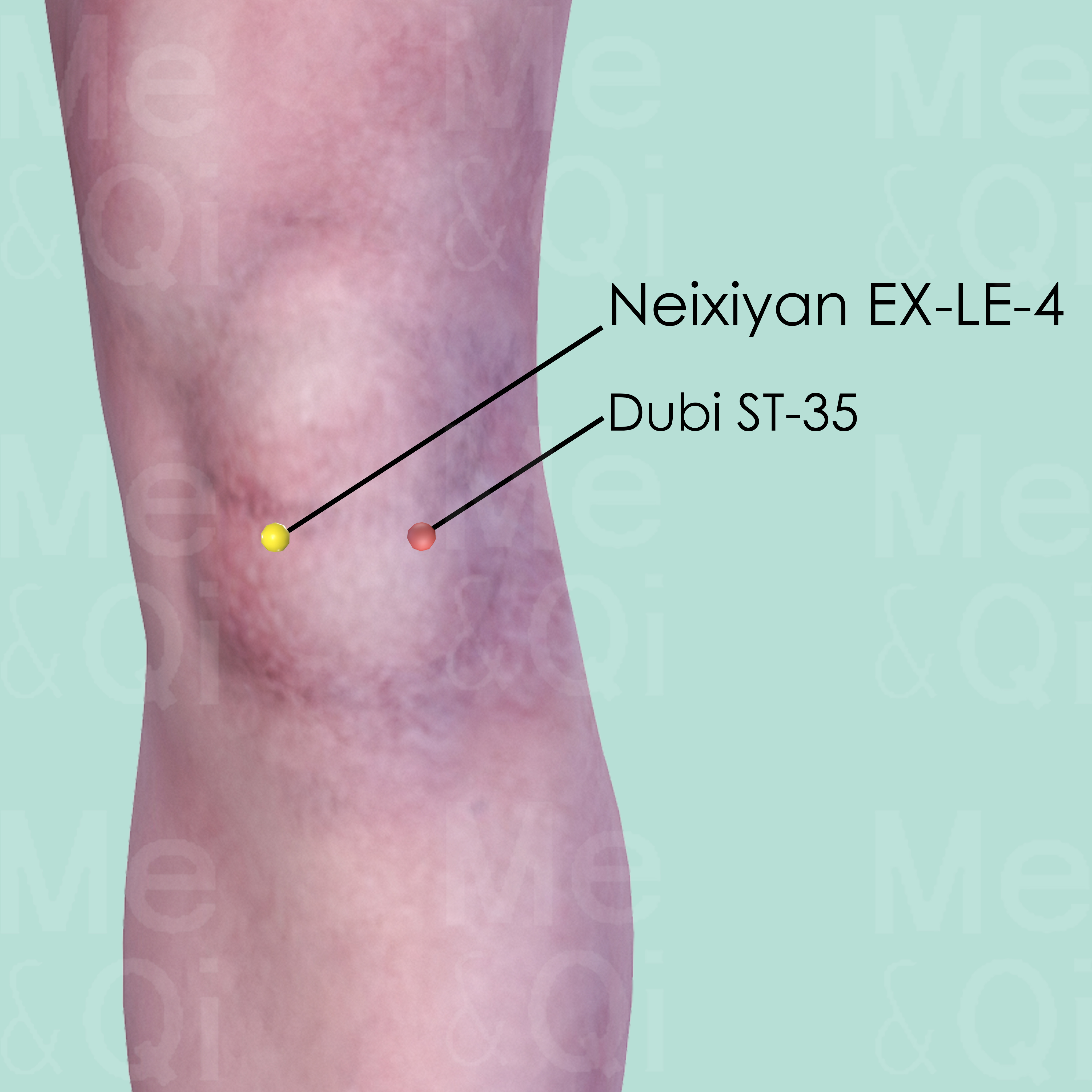
Neixiyan EX-LE-4
With the knee flexed, inferior to the patella, in a depression medial to the patellar ligament. Dubi ST-35 is at the same level, in a depression lateral to the patellar ligament. Both points form the Extra point of Xiyan EX-LE-5.
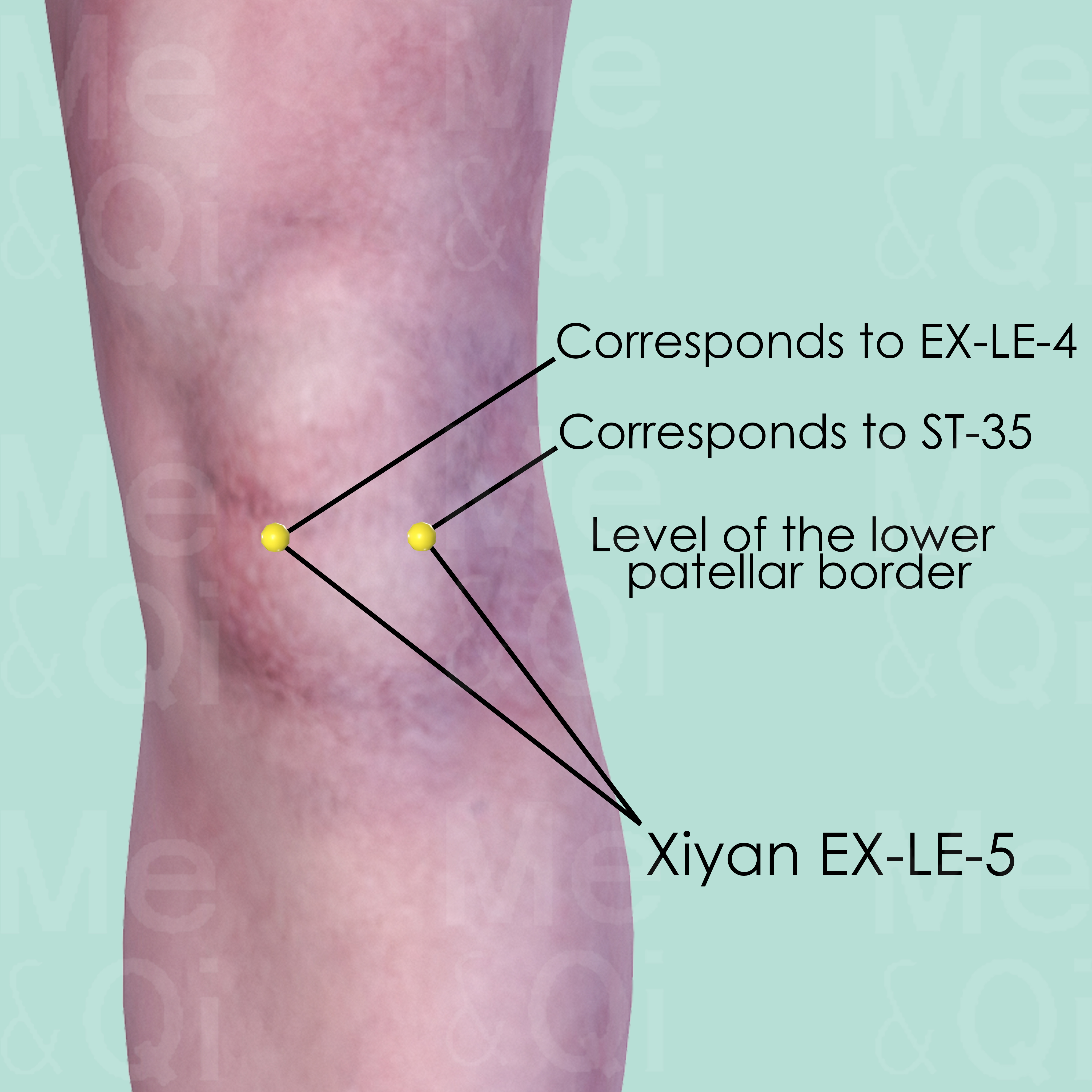
Xiyan EX-LE-5
This is a group of 2 points, composed of Dubi ST-35 and Neixiyan EX-LE-4. Both are located inferior to the patella, medial and lateral to the patellar ligament. Dubi ST-35 is the lateral one, while Neixiyan EX-LE-4 is the medial one.
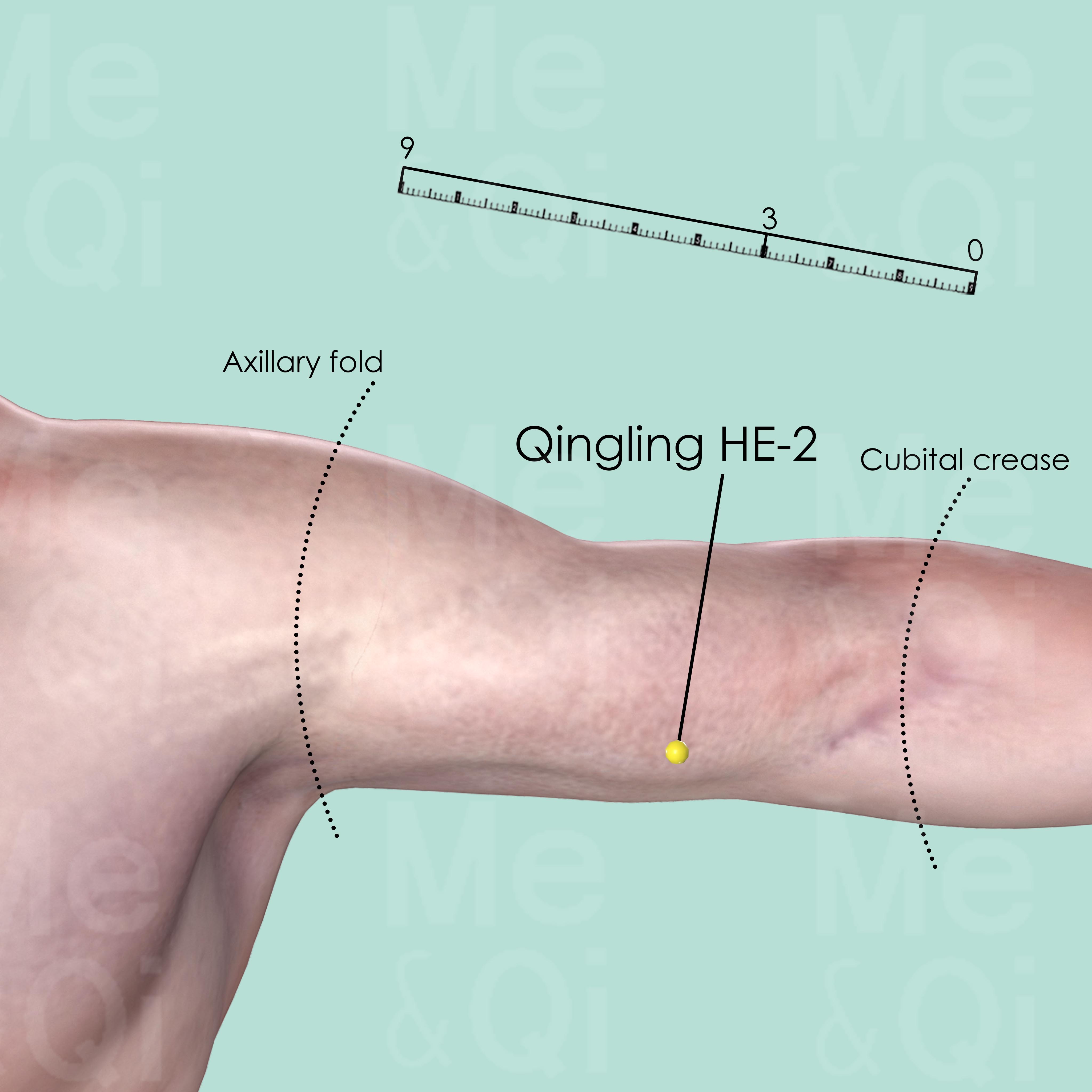
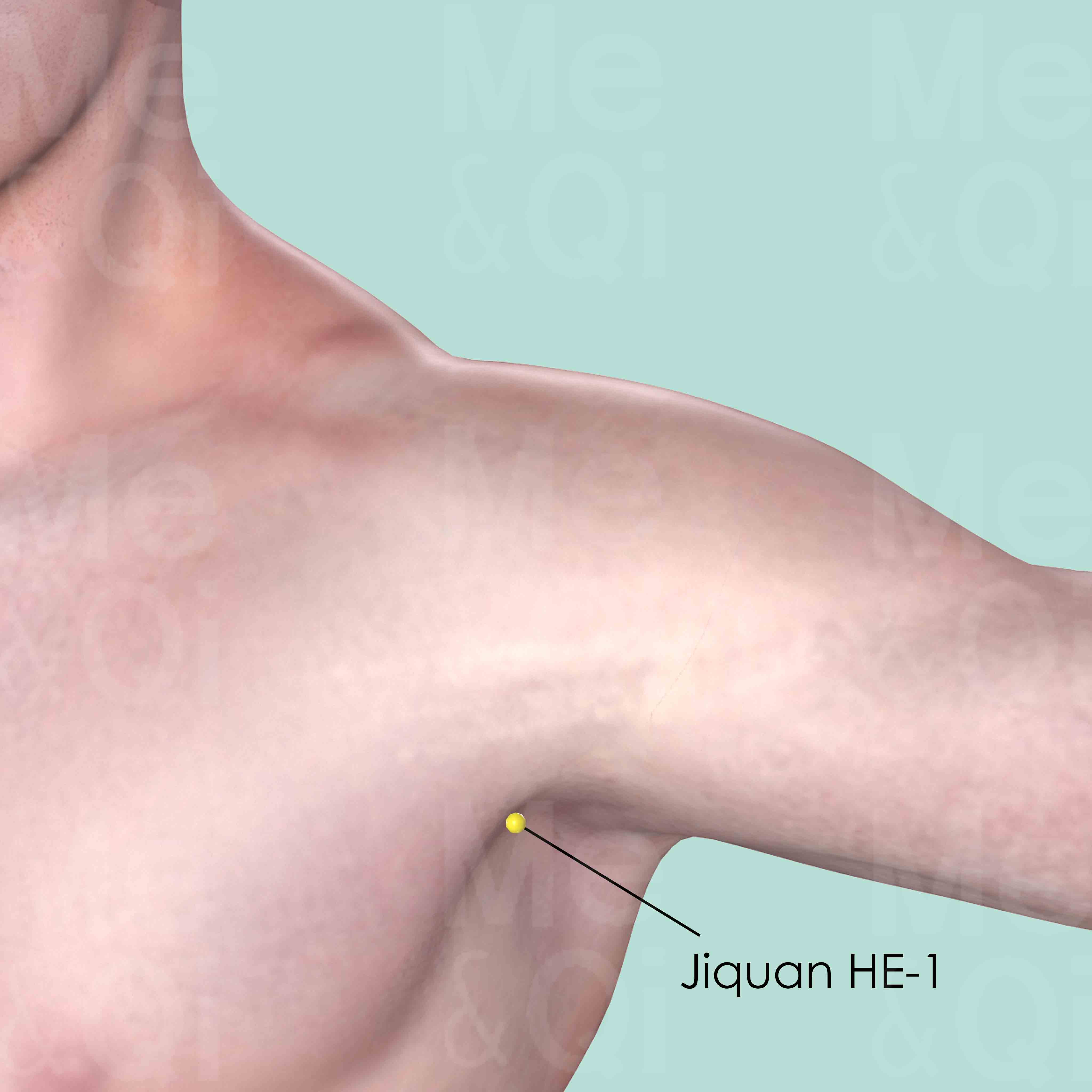
Qingling HE-2
3 cun above the medial end of the transverse cubital crease, in the depression medial to the biceps brachii muscle.
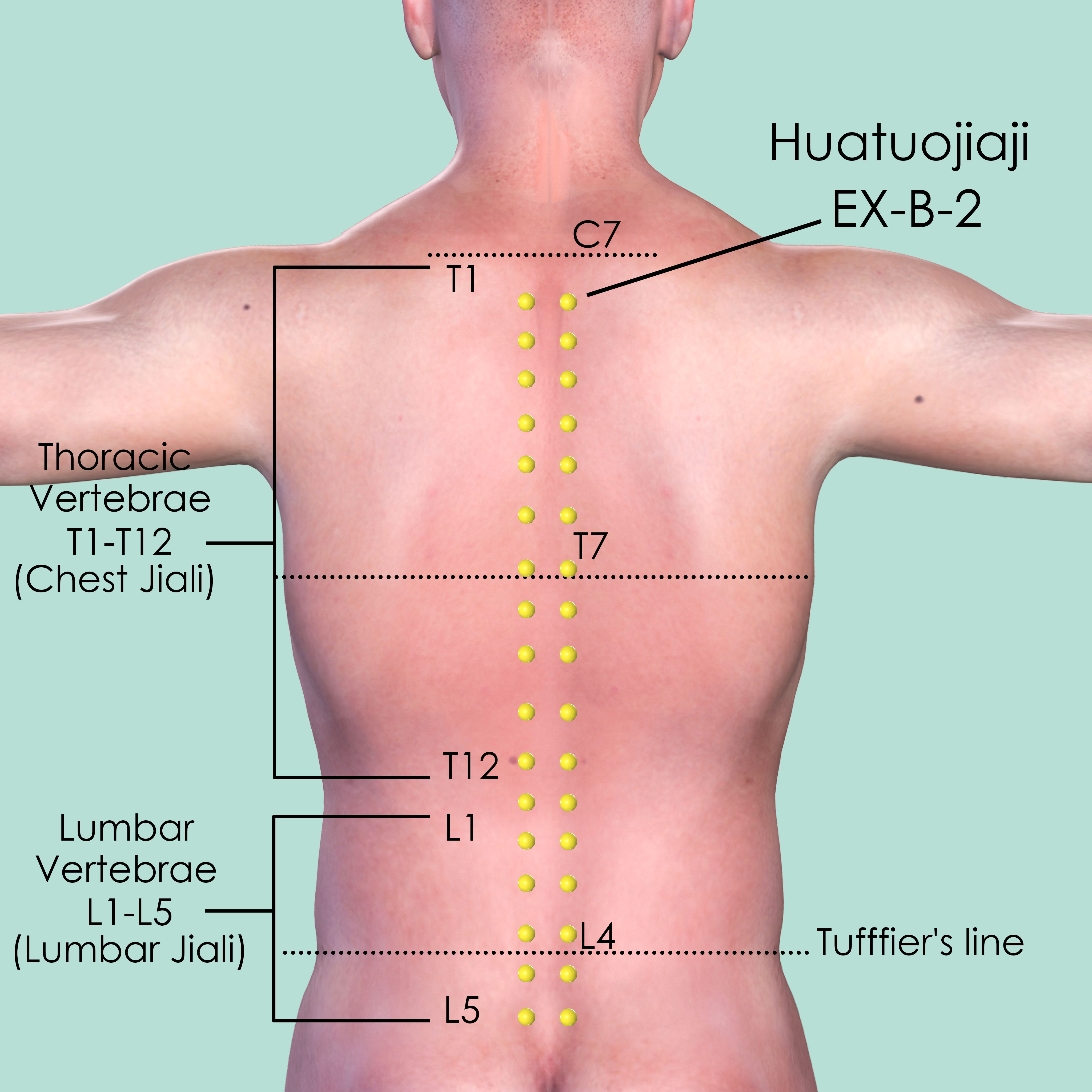
Huatuojiaji EX-B-2
This is a group of 17 point pairs. All of them are 0.5 cun lateral to the lower borders of the spinous processes of the 12 thoracic (Chest Jiali) and 5 lumbar vertebrae (Lumbar Jiali).
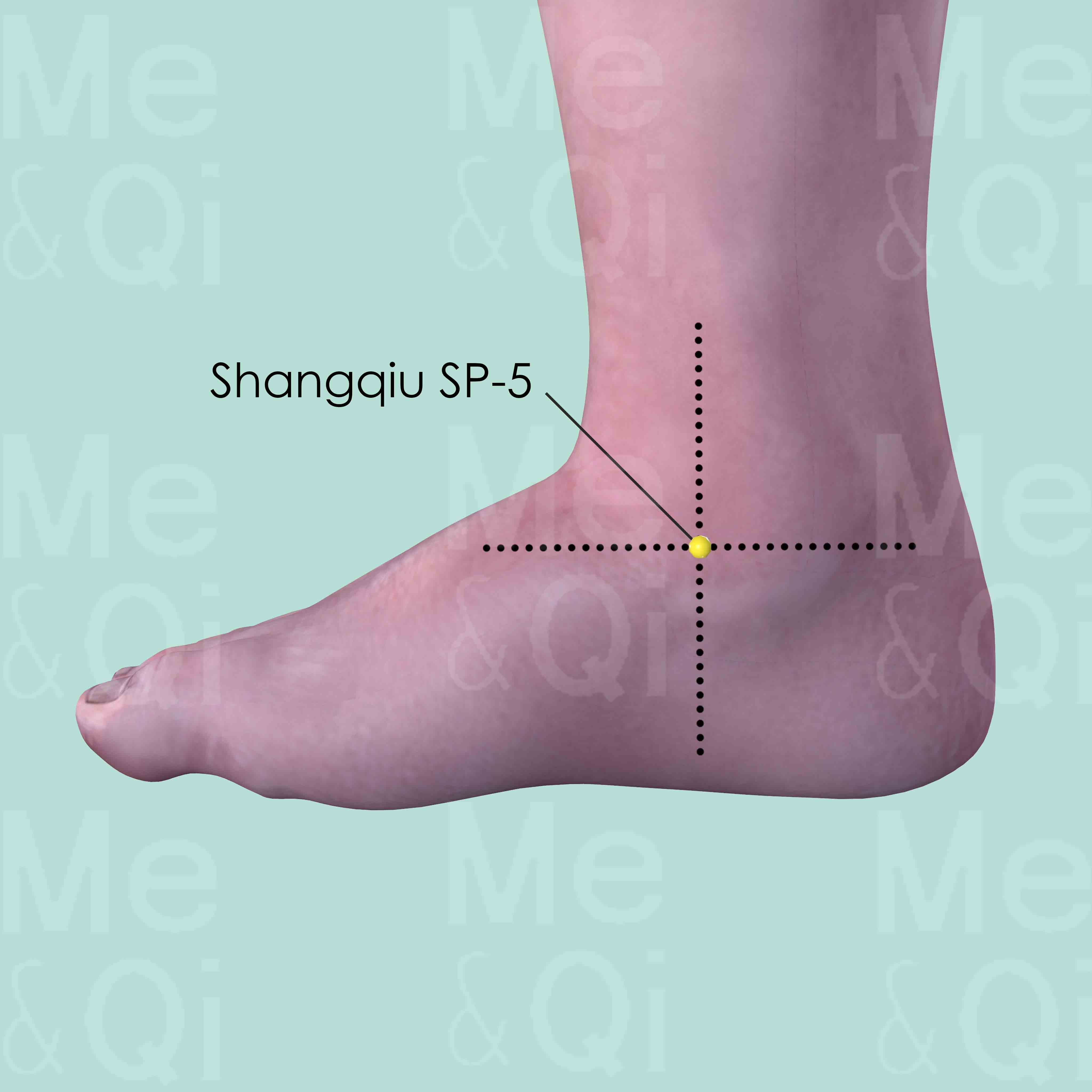
Shangqiu SP-5
In the depression distal and inferior to the medial malleolus, midway between the navicular bone tubercle and the tip of the medial malleolus.
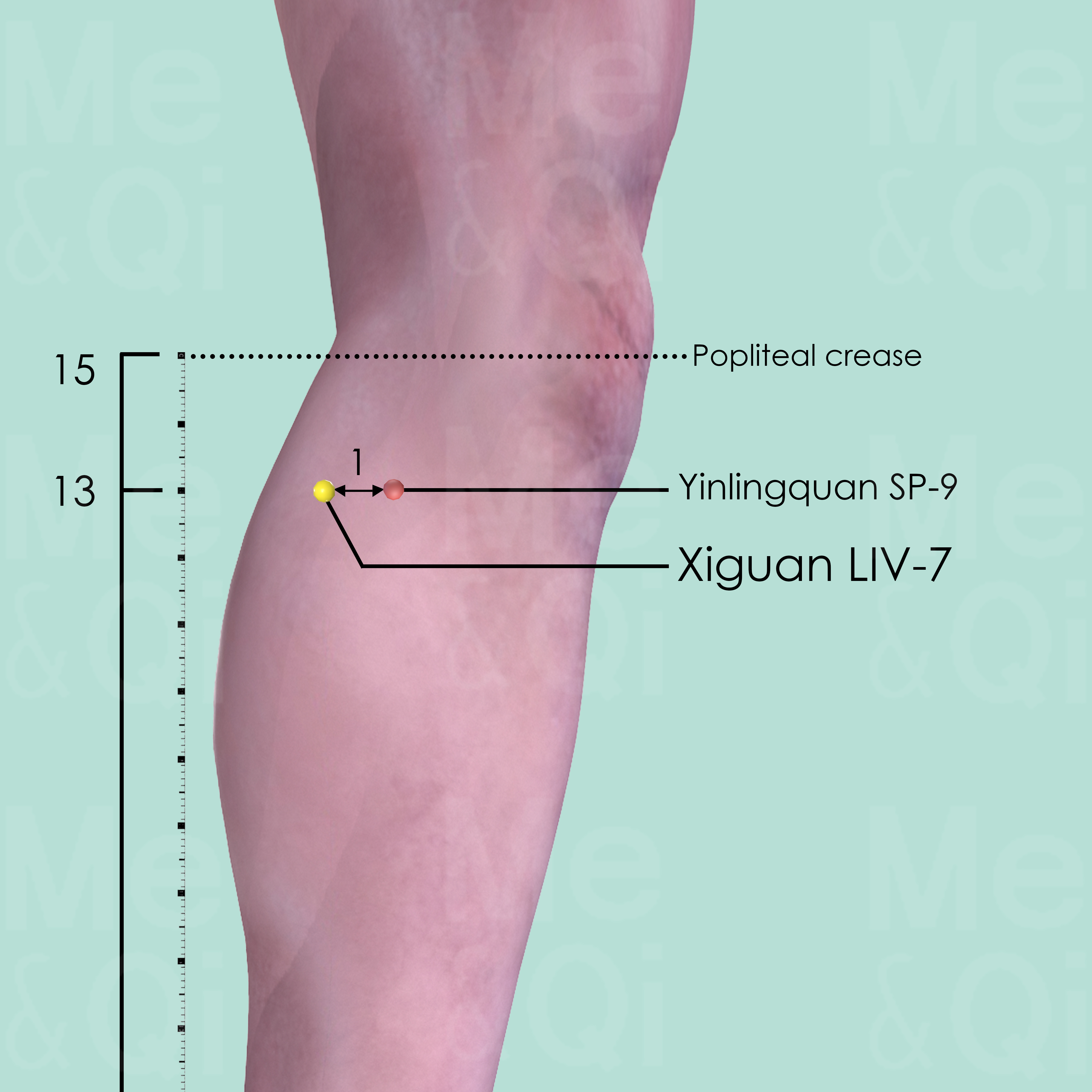
Xiguan LIV-7
Posterior and inferior to the medial condyle of the tibia, in the upper portion of the medial head of the gastrocnemius muscle, 1 cun posterior to Yinlingquan SP-9.
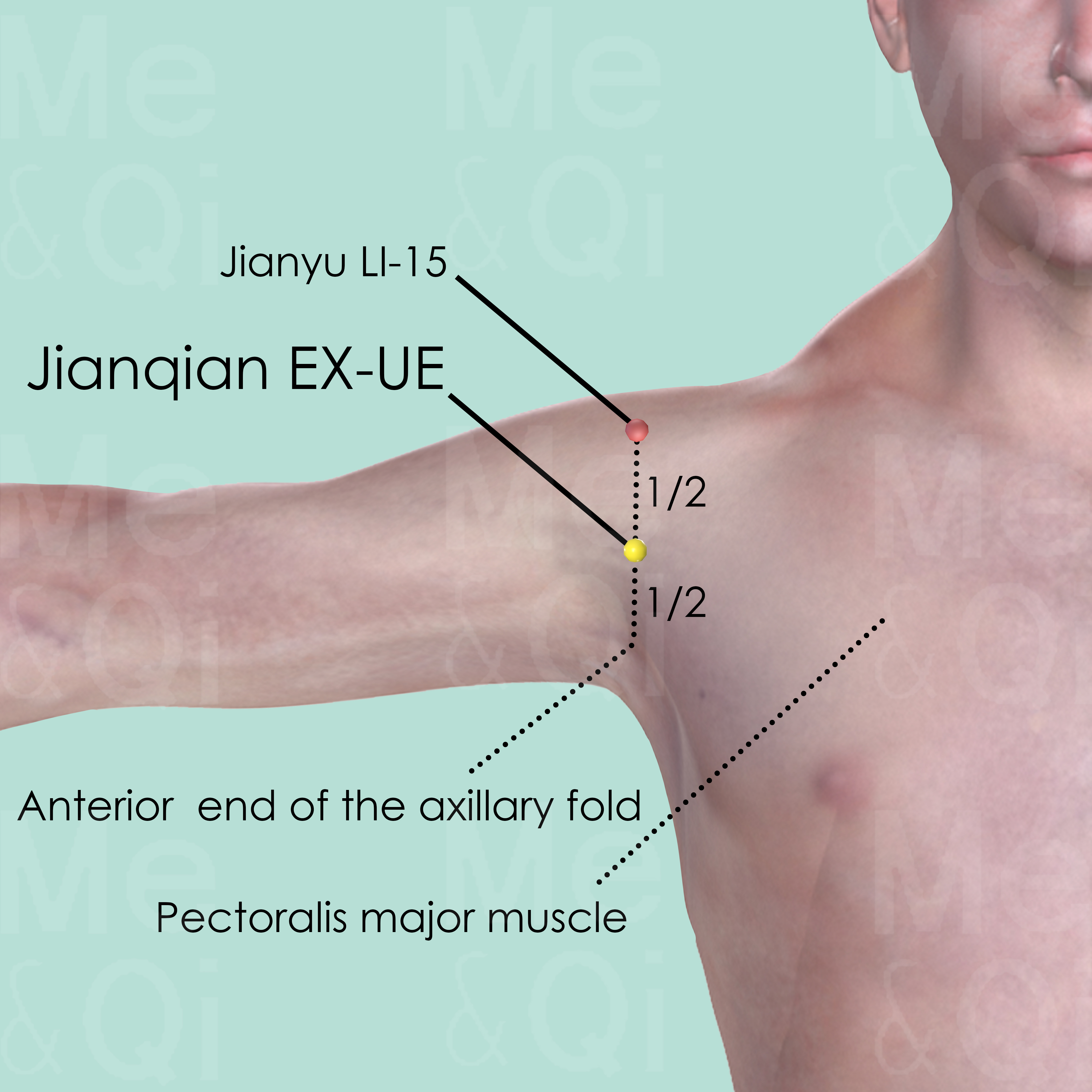
Jianqian EX-UE
On the midpoint of a line connecting the end of anterior axillary fold and Jianyu LI-15.
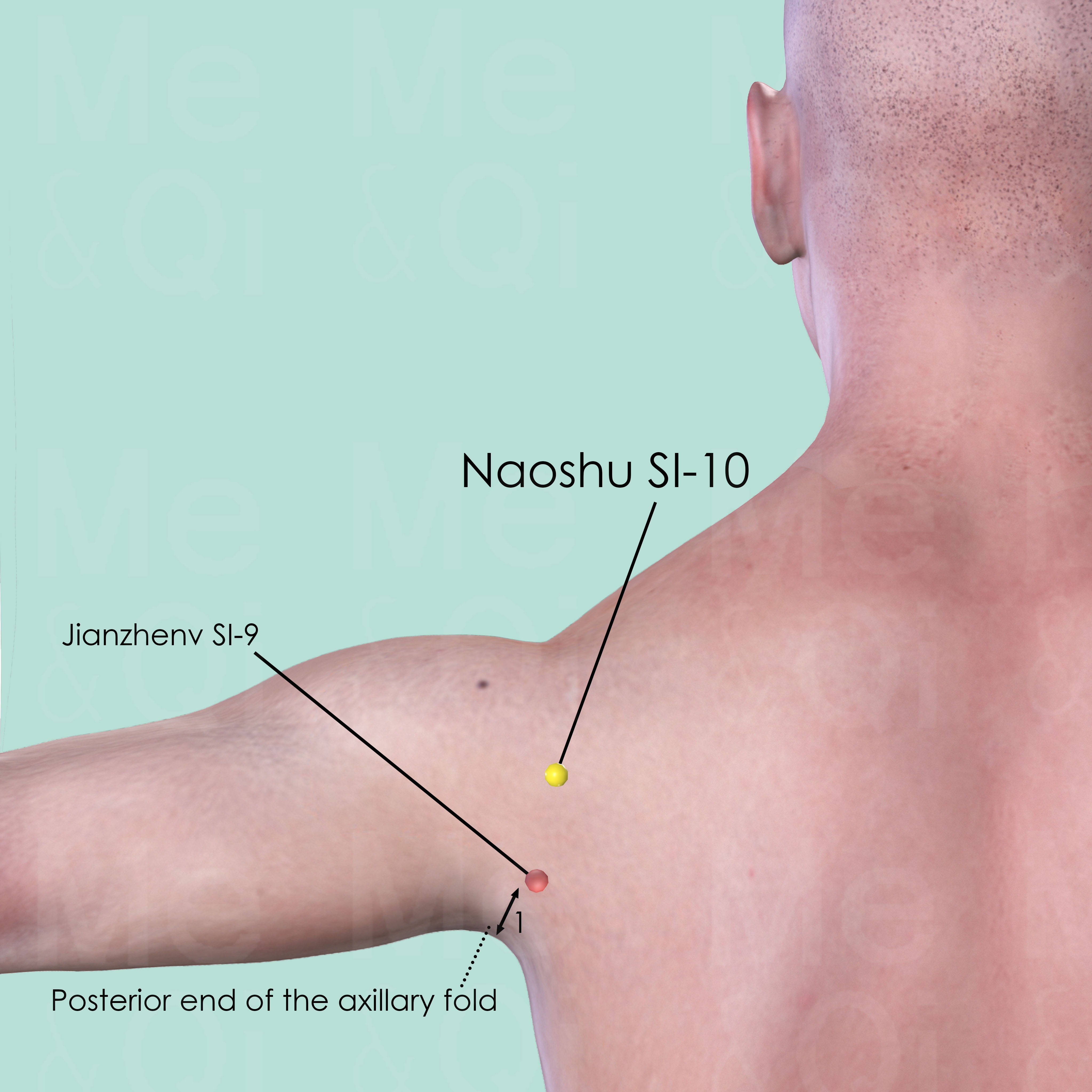
Naoshu SI-10
When the arm is adducted, Naoshu SI-10 is directly above JianZhen SI-9, in the depression inferior and lateral to the scapular spine.
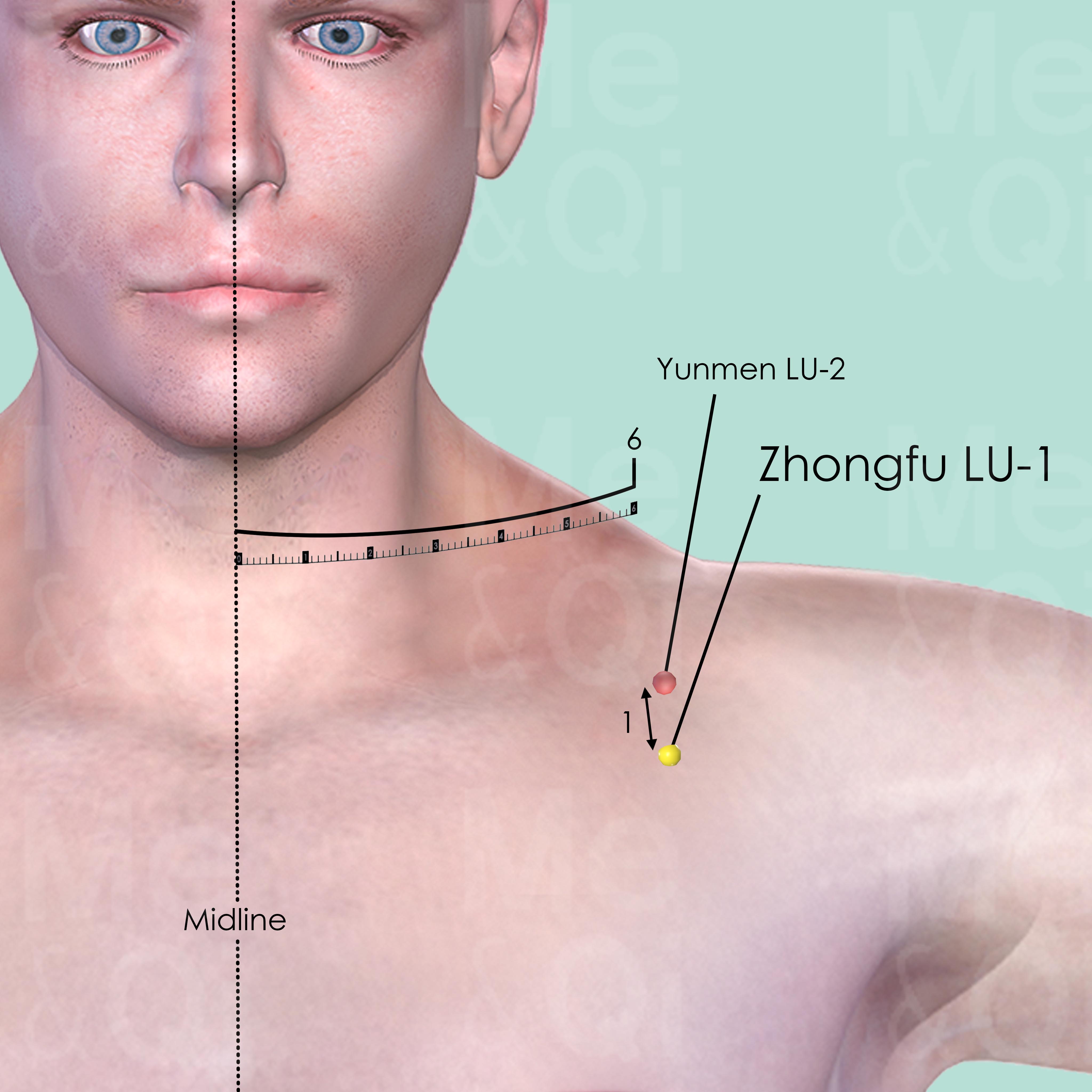
Zhongfu LU-1
On the lateral aspect of the chest, in the 1st intercostal space, 6 cun lateral to the midline, 1 cun inferior to Yunmen LU-2. Below the acromial extremity of the clavicle, slightly medial to the lower border of the coracoid process.