Indigestion In Childrenaccording to TCM
Symptom families: Digestive Disturbances, Pediatric Disorders and Symptoms
Parent symptom: Indigestion
Sub-symptom(s): Chronic Indigestion In Children
What is Indigestion in Children?
Indigestion in children, often referred to as pediatric indigestion or food retention, is a common digestive complaint. It manifests as discomfort or pain in the upper abdomen, typically after eating. Symptoms may include bloating, nausea, belching, and sometimes vomiting.
Unlike in adults, children's digestive systems are still developing, making them more susceptible to indigestion. Chronic indigestion in children can impact their nutrition and overall well-being. This condition, while usually not serious, can cause considerable discomfort and distress to young patients.
How does TCM view Indigestion in Children?
Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) offers a unique perspective on indigestion in children, differing from Western medicine. TCM views this condition as a symptom of underlying imbalances within the body's energy systems, particularly involving the Spleen and Liver.
It emphasizes that symptoms in children can be caused by various patterns of disharmony, and identifying the correct pattern is crucial before commencing treatment. TCM considers the holistic health of the child, including dietary habits, emotional state, and overall Qi (vital energy) flow.
Causes of Indigestion in Children According to TCM
In TCM, indigestion in children is often attributed to specific imbalances or patterns. One such pattern is the weakness of the Spleen, which in TCM is crucial for digestion and assimilation of food. A weak Spleen can lead to symptoms like bloating, loose stools, and poor appetite.
Another common pattern is the Rebellious Liver Qi invading the Spleen, where the disrupted flow of Liver Qi affects the Spleen’s function, causing symptoms like abdominal pain and altered bowel habits. These patterns underscore the importance of a tailored approach in TCM to address the unique causes of indigestion in each child.
TCM Herbal Formulas for Indigestion In Children
TCM employs various herbal formulas to treat indigestion in children, based on the identified disharmony pattern. For instance, Tong Xie Yao Fang, which includes Atractylodes Rhizomes (Bai Zhu), is used to harmonize the Liver-Spleen relationship, particularly useful in cases of Rebellious Liver Qi.
This formula works to alleviate symptoms by restoring balance between these organs. TCM emphasizes the importance of selecting formulas and herbs that correspond to the child's specific pattern of imbalance, ensuring a personalized and effective treatment approach.
Explore below some TCM herbal formulas used to address indigestion in children, organized by formula type.
- By Formula Type
- Formulas that harmonize liver-Spleen
- Formulas that reduce food accumulation and transform stagnation
Formulas that harmonize Liver-Spleen
Indigestion in children can be treated by these formulas when there's an imbalance between the Liver and Spleen systems, often manifesting as digestive disturbances and emotional fluctuations.
One such formula is Tong Xie Yao Fang, with atractylodes rhizome as a key herb.
Formulas that reduce food accumulation and transform Stagnation
Indigestion in children can be treated by these formulas when it is due to the accumulation of undigested food and stagnation in the digestive system.
One such formula is Fei Er Wan, with quisqualis fruit as a key herb.
Acupoints for Indigestion In Children
TCM also incorporates acupuncture as a complementary treatment for indigestion in children. Specific acupoints like Sifeng EX-UE-10, located on the hands, are utilized for their effectiveness in tonifying the Spleen and reducing food stagnation.
This point is particularly beneficial in resolving Dampness, a common factor in pediatric digestive issues. The selection of acupoints in TCM is guided by the underlying pattern of disharmony, and their stimulation aims to enhance the body's natural healing processes and restore balance in the digestive system.
See more details below about Sifeng EX-UE-10, an acupoint used to address indigestion in children.
- By Meridian
- Extra Points: Upper Extremities (EX-UE)
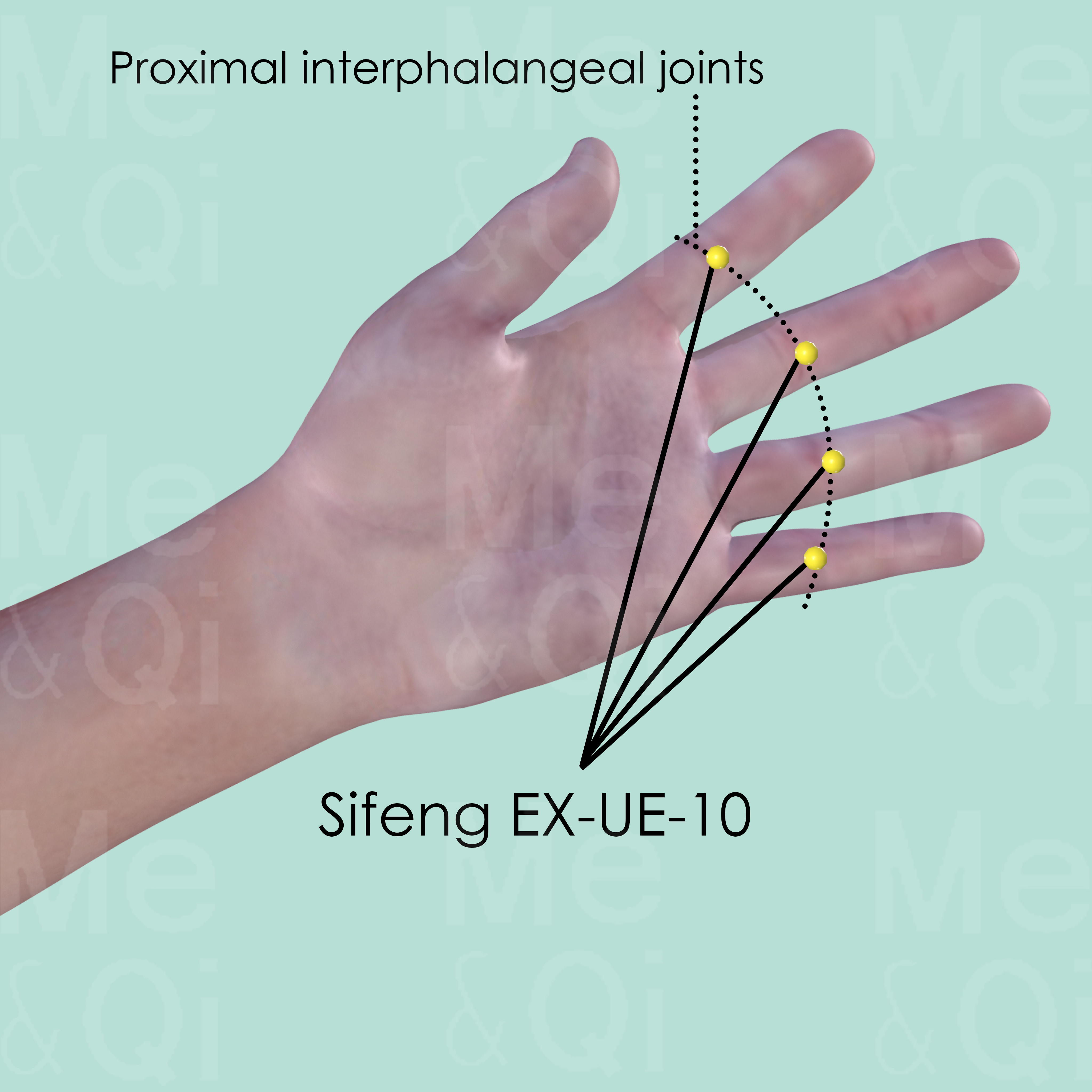
Sifeng EX-UE-10
This is a group of 4 points of each hand. On the palmar side of the 2nd to the 5th fingers, at the midpoint of the transverse creases of the proximal interphalangeal joints (PIP).
TCM Herbs for Indigestion In Children
Explore below some TCM herbs used to address indigestion in children, organized by herb category.
- By Herb Category
- Herbs that expel parasites
- Tonic herbs for qi deficiency
- Tonic herbs for blood deficiency
Herbs that expel parasites
Indigestion in children can be treated by these herbs if it arises from parasitic infections, utilizing their properties to eliminate parasites from the body.
One such herb is Quisqualis Fruits (Shi Jun Zi), a key herb in some formulas recommended for indigestion in children, like Fei Er Wan.
Other herbs of this category are listed in the table below.
"Herbs that expel parasites" recommended for indigestion in children
| Herb | Formulas they belong to (if applicable) |
|---|---|
| Quisqualis Fruits (Shi Jun Zi) | Fei Er Wan |
| Areca Nuts (Bing Lang) | Fei Er Wan |
Tonic herbs for Qi Deficiency
Indigestion in children can be treated by these herbs when stemming from a lack of vital energy or Qi, helping to boost energy and overall vitality.
One such herb is Atractylodes Rhizomes (Bai Zhu), a key herb in some formulas recommended for indigestion in children, like Tong Xie Yao Fang.
Tonic herbs for Blood Deficiency
Indigestion in children can be treated by these herbs in cases of blood deficiency, working to nourish and replenish the body's blood supply.
One such herb is White Peony Roots (Bai Shao), a key herb in some formulas recommended for indigestion in children, like Tong Xie Yao Fang.
