Shoulder Heavinessaccording to TCM
Symptom families: Joint Symptoms, Shoulder Issues
Parent symptom: Heavy Joint
Did you mean? Shoulder Swelling
What is Shoulder Heaviness?
Shoulder heaviness is a term used to describe a feeling of weight or burden in the shoulder area that can impede movement and cause discomfort. It is a sensation that can be constant or intermittent, often affecting one's ability to raise the arm or carry objects. The feeling of a heavy shoulder may not be associated with visible signs of inflammation or injury but can significantly affect daily activities and overall mobility. It can be a symptom of various conditions, ranging from muscular fatigue to neurological issues.
How does TCM view Shoulder Heaviness?
In the lens of Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), shoulder heaviness is often interpreted as a result of stagnation or obstruction within the body's meridians that run through the shoulder. TCM practitioners believe that a disruption in the flow of Qi, the body's vital energy, can lead to such a sensation.
Symptoms in TCM are not isolated problems but are indicative of a broader pattern of disharmony. To effectively alleviate the heaviness, it is crucial to identify and address the specific disharmony, whether it be due to an accumulation of Dampness, Qi stagnation, or Blood Deficiency.
Acupoints for Shoulder Heaviness
For the sensation of shoulder heaviness, TCM suggests several acupoints that can help alleviate the condition. One such point is Jianliao TB-14, located on the Triple Burner Channel. Stimulating this point is believed to remove obstructions from the channel, which may contribute to easing the heavy sensation in the shoulder.
The choice of acupoints in TCM is a thoughtful process that considers the individual's unique pattern of disharmony, aiming to restore the smooth flow of Qi and relieve discomfort.
See more details below about Jianliao TB-14, an acupoint used to address shoulder heaviness.
- By Meridian
- Triple Burner Channel
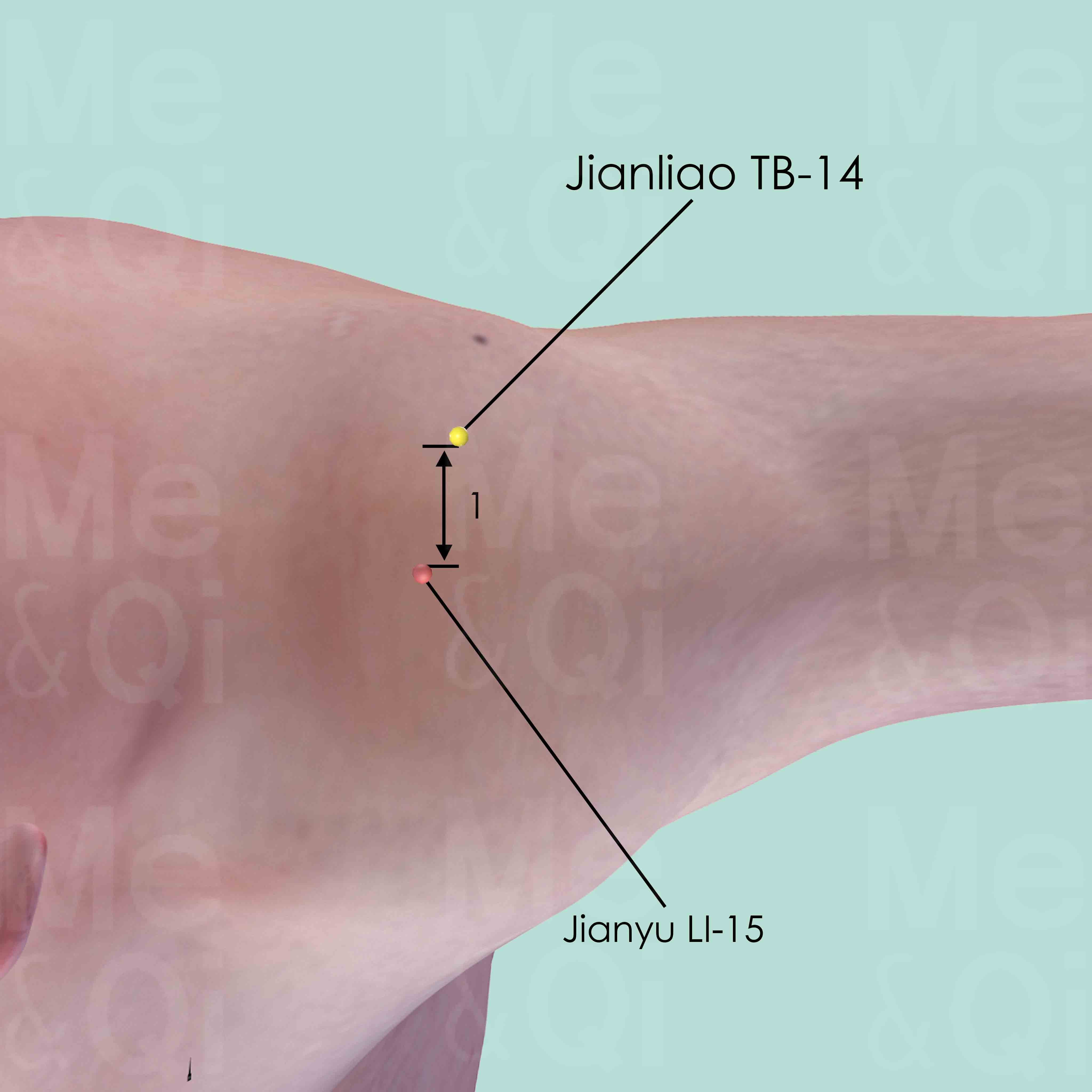
Jianliao TB-14
Posterior and inferior to the acromion, in the depression about 1 cun posterior to Jianyu LI-15.
